MCTS¶
Overview¶
Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) is a search method that combines the precision of tree search with the generality of random sampling. MCTS is used to find optimal decisions in a given domain by building a search tree according to explorations.
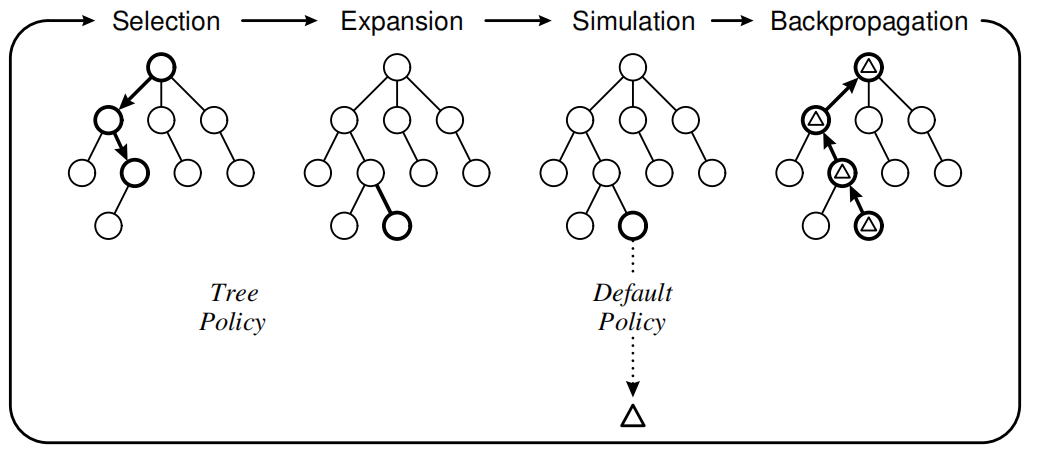
MCTS contains 4 phases in one iteration, the selection phase, the expansion phase, the simulation phase, and the backpropagation phase.
MCTS mainly contains two policies, the tree policy, and the default policy.
The tree policy determines which node to select and expand. The tree policy attempts to balance considerations of exploration and exploitation using bandit-based algorithms such as the Upper Confidence Tree(UCT) algorithm or “temperature”.
The default policy is the policy used in the simulation, which runs from the selected node and the search tree updated according to the result. The simplest case of default policy is to make uniform random moves.
Quick Facts¶
MCTS can combine with model-free and model-free RL algorithm.
Usually, MCTS use bandit based algorithm such as Upper Confidence Bounds for Trees(UCT) to balance exploration and exploitation.
MCTS can combine with deep neural network, to predict value of certain state or learn the policy of MCTS. The policy network can be used as default policy in the simulation phase of MCTS, and the value network can be used as the value estimation of tree policy in MCTS.
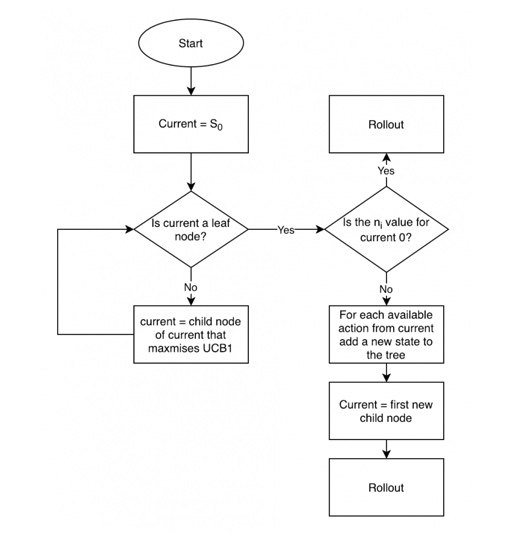
Pseudo-code¶

Extensions¶
MCTS can be combined with:
neural networks
By combining with deep neural networks, the MCTS can improve the tree policy and the default policy. The neural network can be used to predict the value of certain states or learn the policy performed by MCTS. Using the value predicted by the neural network, the tree policy of MCTS can explore and exploit more efficiently. Using the policy learned, the MCTS simulation will gain better performance compared to simply make uniform random moves.
Google Brain’s AlphaGo combined the MCTS algorithm and the deep neural network, makes dramatic performance improvement.
bandit algorithms
The bandit algorithm mostly used in MCTS is the UCT algorithm.
\(U C T=\bar{X}_{j}+2 C_{p} \sqrt{\frac{2 \ln n}{n_{j}}}\)
There are certain variation of UCT algorithm, such as PUCT which used in AlphaGo.
\(U(s, a)=c_{\text {puct }} P(s, a) \frac{\sqrt{\sum_{b} N(s, b)}}{1+N(s, a)}\)
where \(N(s, a)\) is the visit count state and action, and \(c_{puct}\) is a constant determining the level of exploration.
model-based RL algorithms
MCTS gained huge success in environments where a perfect simulator is available, but in real-world problems, the dynamics governing the environment are often complex and unknown. By combining MCTS with a learned model, Google Brain presented Muzero, which achieves superhuman performance in a range of challenging and visually complex domains, without any knowledge of their underlying dynamics. The MuZero algorithm learns an iterable model that produces predictions relevant to planning: the action-selection policy, the value function and the reward.
Implementations¶
The default config is defined as follows:
TBD
The network interface MCTS used is defined as follows:
TBD
References¶
(Fig1) Maciej Świechowski, Konrad Godlewski, Bartosz Sawicki, Jacek Mańdziuk: “Monte Carlo Tree Search: A Review of Recent Modifications and Applications”, 2021; [http://arxiv.org/abs/2103.04931 arXiv:2103.04931].