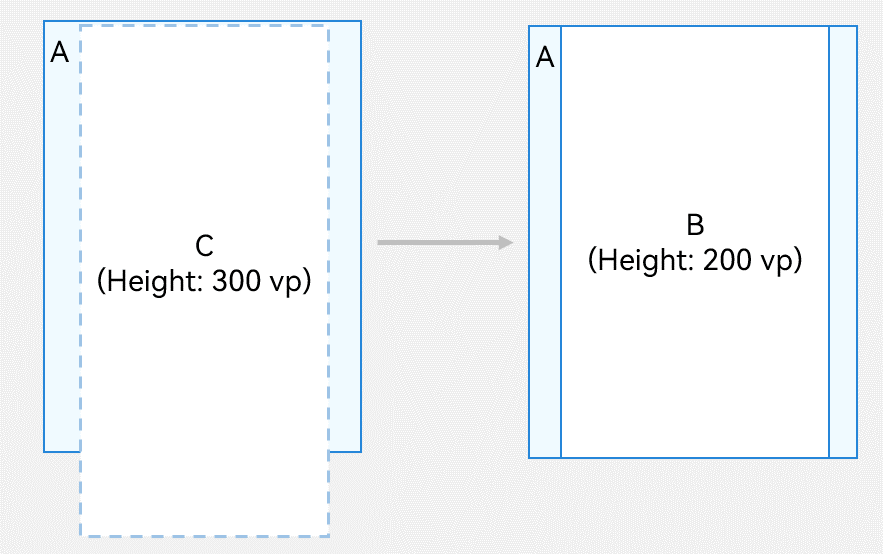
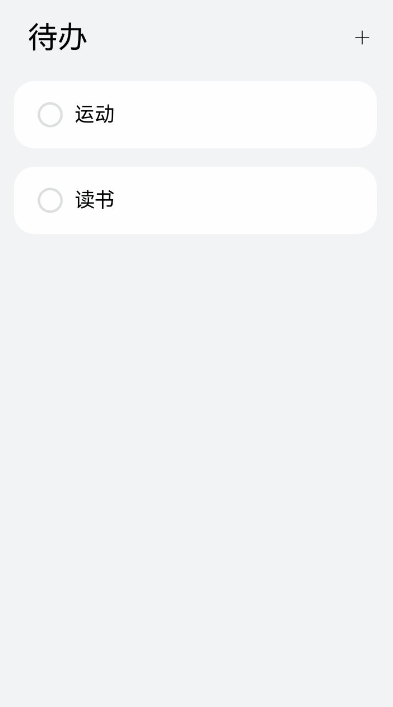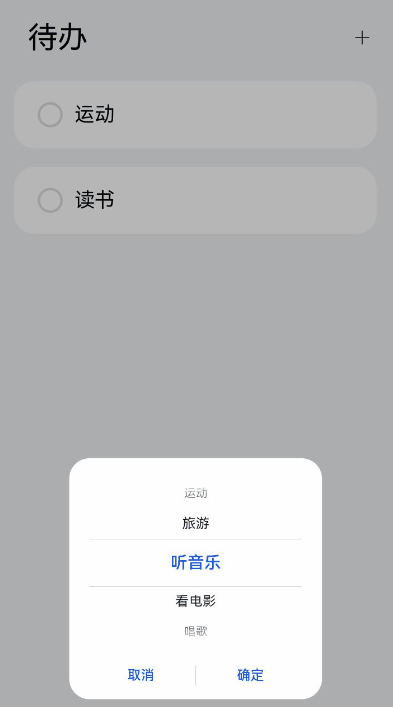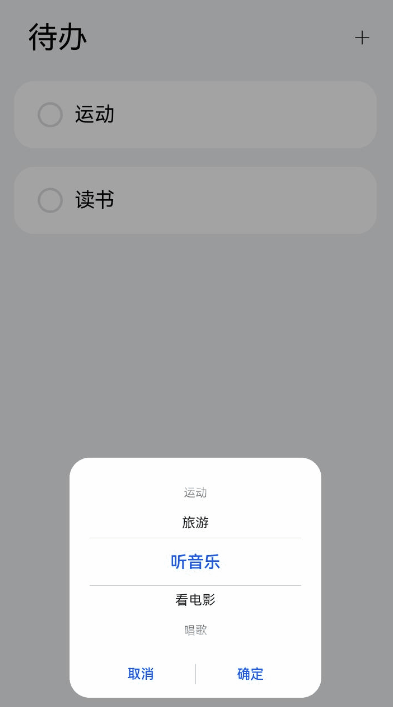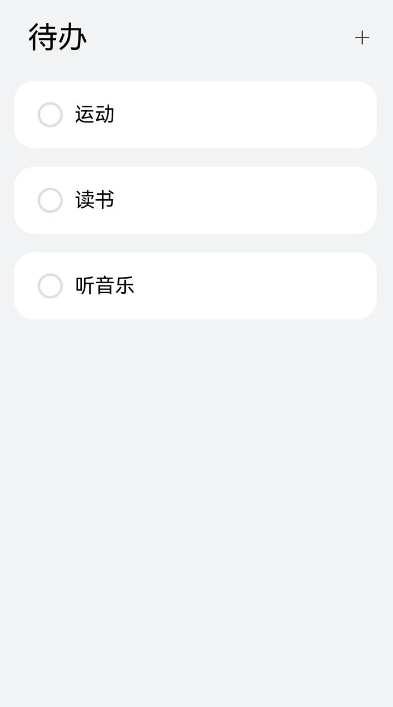
!18240 翻译完成 17277+17318:ui文件夹更新
Merge pull request !18240 from ester.zhou/TR-17277
Showing
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
3.1 KB
4.9 KB
5.5 KB
312.4 KB
12.3 KB
32.3 KB
14.6 KB
75.2 KB
21.6 KB
18.2 KB
32.2 KB
13.3 KB
77.6 KB
42.1 KB
981.6 KB
87.3 KB
11.7 KB
17.9 KB
490.3 KB
382.5 KB
61.3 KB
65.0 KB
321.5 KB
17.2 KB
69.8 KB
12.4 KB
20.5 KB
20.3 KB
19.6 KB
12.8 KB
2.1 KB
4.5 KB
115.4 KB
57.1 KB