Merge branch 'develop' of https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle into update-api-reference-1
Showing
cmake/external/anakin.cmake
0 → 100644
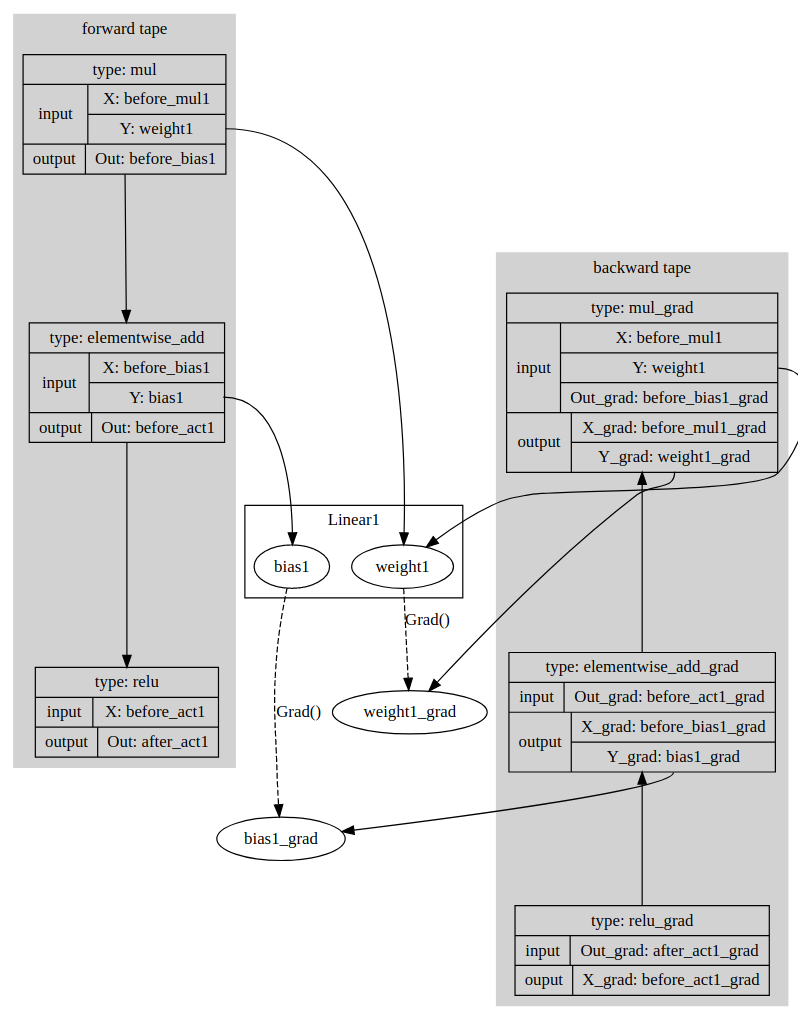
paddle/contrib/tape/README.md
0 → 100644
94.4 KB
paddle/contrib/tape/function.h
0 → 100644
paddle/contrib/tape/tape.cc
0 → 100644
paddle/contrib/tape/tape.h
0 → 100644
paddle/contrib/tape/test_tape.cc
0 → 100644
paddle/contrib/tape/variable.cc
0 → 100644
paddle/contrib/tape/variable.h
0 → 100644