Merge remote-tracking branch 'origin/dygraph' into dygraph
Showing
applications/多模态表单识别.md
0 → 100644
configs/rec/rec_svtrnet.yml
0 → 100644
deploy/README.md
0 → 100644
deploy/README_ch.md
0 → 100644
791.1 KB
352.4 KB
deploy/lite/readme_ch.md
0 → 100644
deploy/lite/readme_en.md
已删除
100644 → 0
deploy/paddle2onnx/readme_ch.md
0 → 100644
deploy/paddlejs/README.md
0 → 100644
deploy/paddlejs/README_ch.md
0 → 100644
deploy/paddlejs/paddlejs_demo.gif
0 → 100644
553.7 KB
492.9 KB
doc/PPOCR.pdf
已删除
100644 → 0
文件已删除
594.4 KB
628.5 KB
162.7 KB
120.4 KB
9.1 KB
27.5 KB
doc/datasets/table_tal_demo/1.jpg
0 → 100644
232.7 KB
doc/datasets/table_tal_demo/2.jpg
0 → 100644
232.7 KB
613.0 KB
224.1 KB
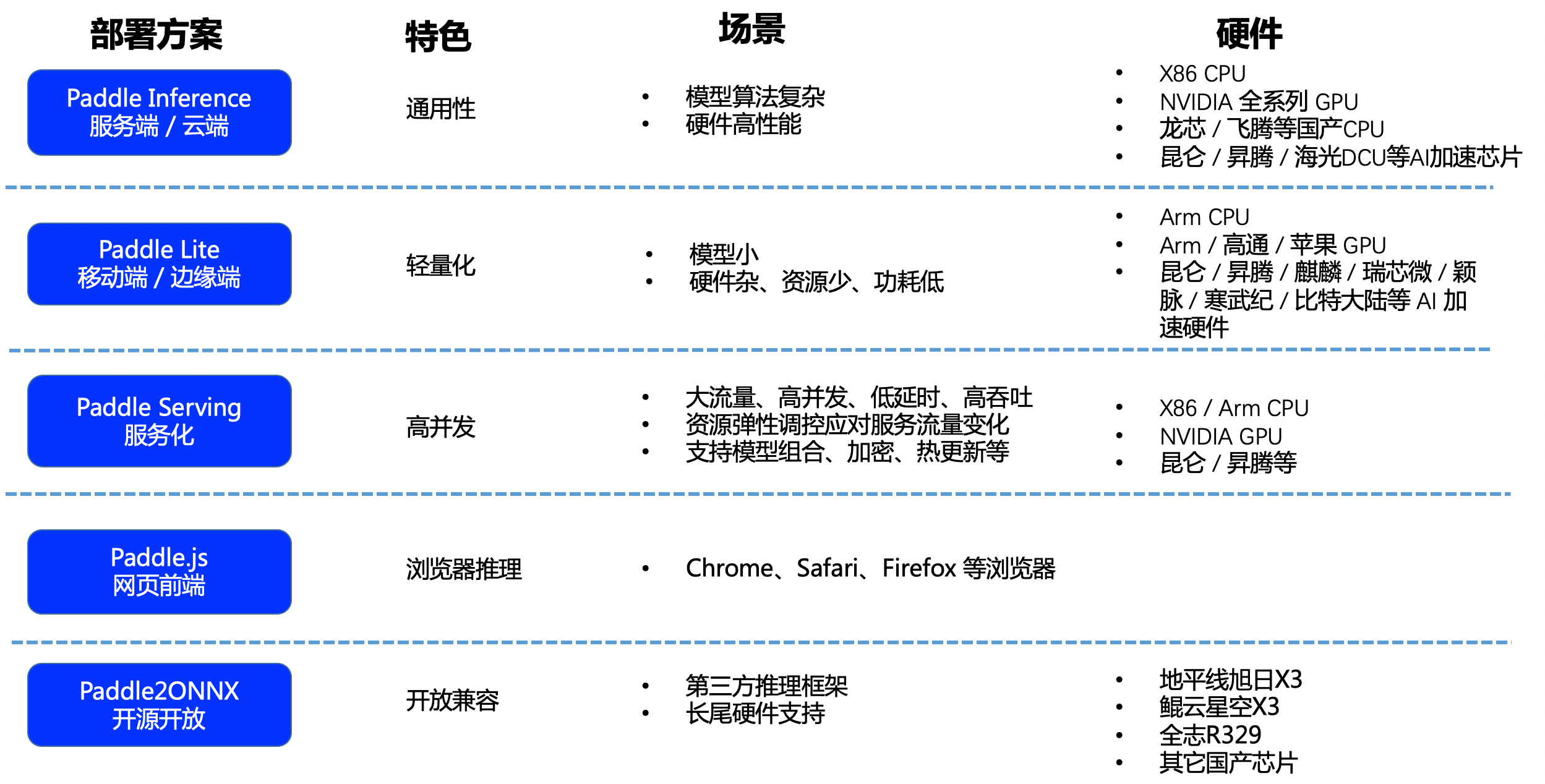
doc/deployment.png
0 → 100644
992.0 KB
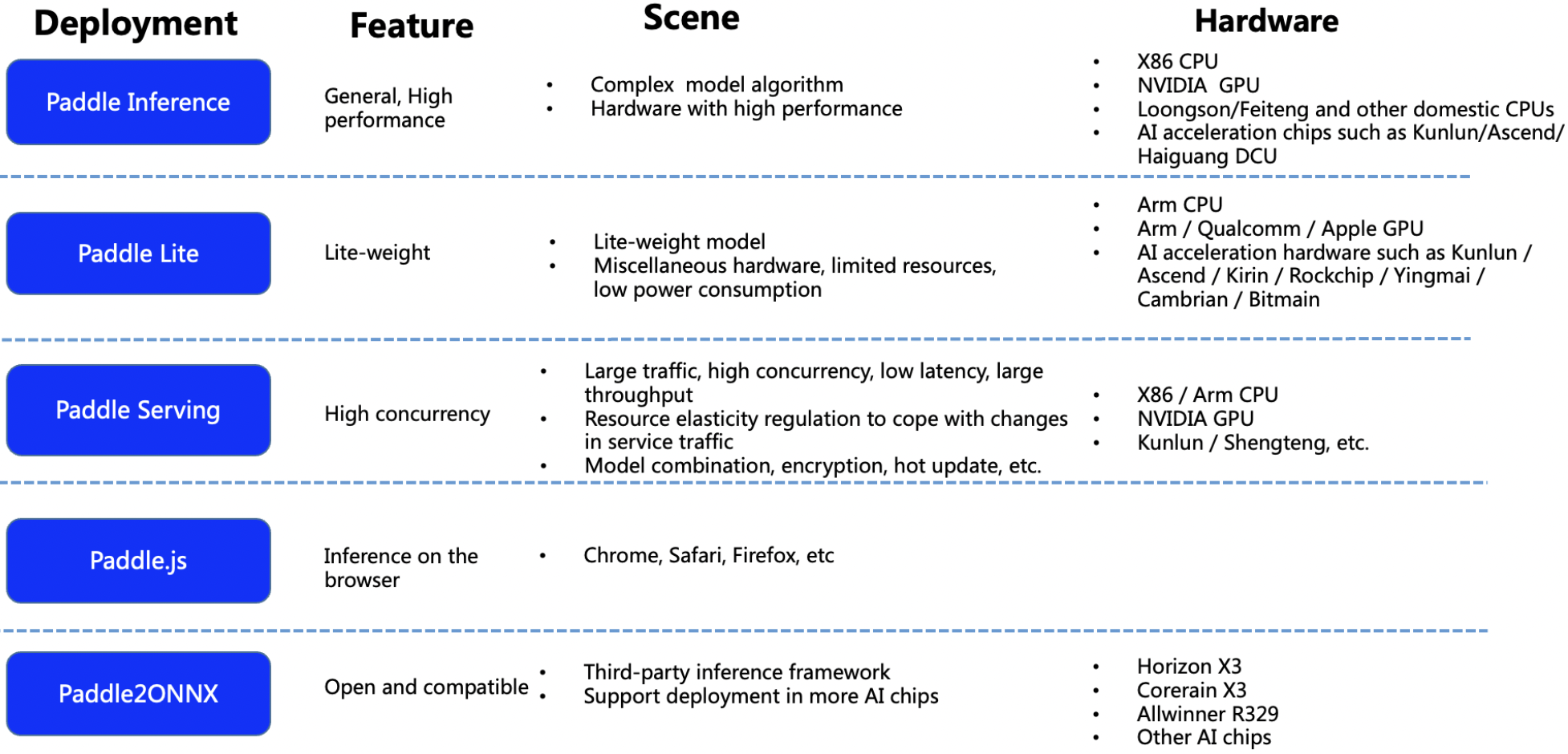
doc/deployment_en.png
0 → 100644
650.2 KB
doc/doc_ch/algorithm.md
0 → 100644
doc/doc_ch/algorithm_det_db.md
0 → 100644
doc/doc_ch/algorithm_rec_sar.md
0 → 100644
doc/doc_ch/algorithm_rec_srn.md
0 → 100644
doc/doc_ch/android_demo.md
已删除
100644 → 0
doc/doc_ch/application.md
0 → 100644
doc/doc_ch/ocr_book.md
0 → 100644
doc/doc_ch/ppocr_introduction.md
0 → 100644
doc/doc_en/algorithm_det_db_en.md
0 → 100644
doc/doc_en/algorithm_en.md
0 → 100644
doc/doc_en/android_demo_en.md
已删除
100644 → 0
doc/doc_en/ocr_book_en.md
0 → 100644
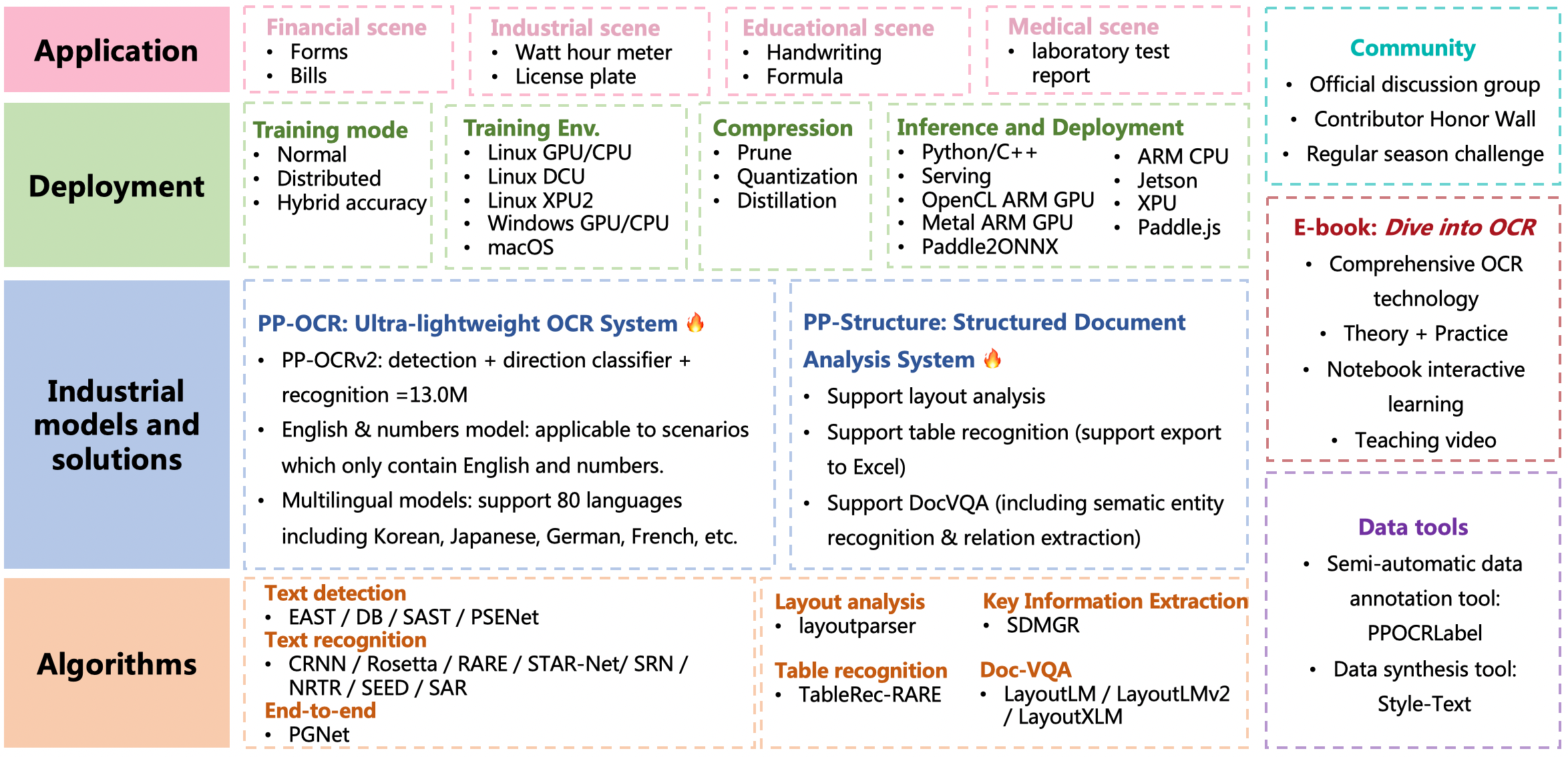
doc/features.png
0 → 100644
1.1 MB
doc/features_en.png
0 → 100644
1.2 MB
133.7 KB
329.9 KB
330.4 KB
332.1 KB
doc/ocr-android-easyedge.png
已删除
100644 → 0
291.8 KB
doc/overview.png
已删除
100644 → 0
142.8 KB
ppocr/data/imaug/ssl_img_aug.py
0 → 100644
ppocr/losses/rec_multi_loss.py
0 → 100644
ppstructure/docs/inference.md
0 → 100644
ppstructure/docs/inference_en.md
0 → 100644
ppstructure/docs/quickstart_en.md
0 → 100644
文件已移动
文件已移动
文件已移动
文件已移动
文件已移动
文件已移动