add base train infer python (#5372)
* add base train infer python * fix jeston doc
Showing
63.0 KB
115.4 KB
120.2 KB
82.2 KB
446.4 KB
45.9 KB
95.5 KB
73.8 KB
233.0 KB
195.7 KB
170.3 KB
391.0 KB
74.0 KB
137.6 KB
* add base train infer python * fix jeston doc
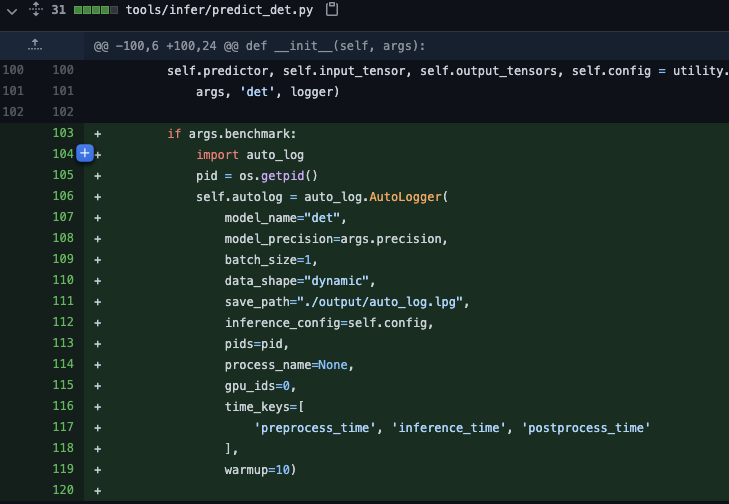
63.0 KB
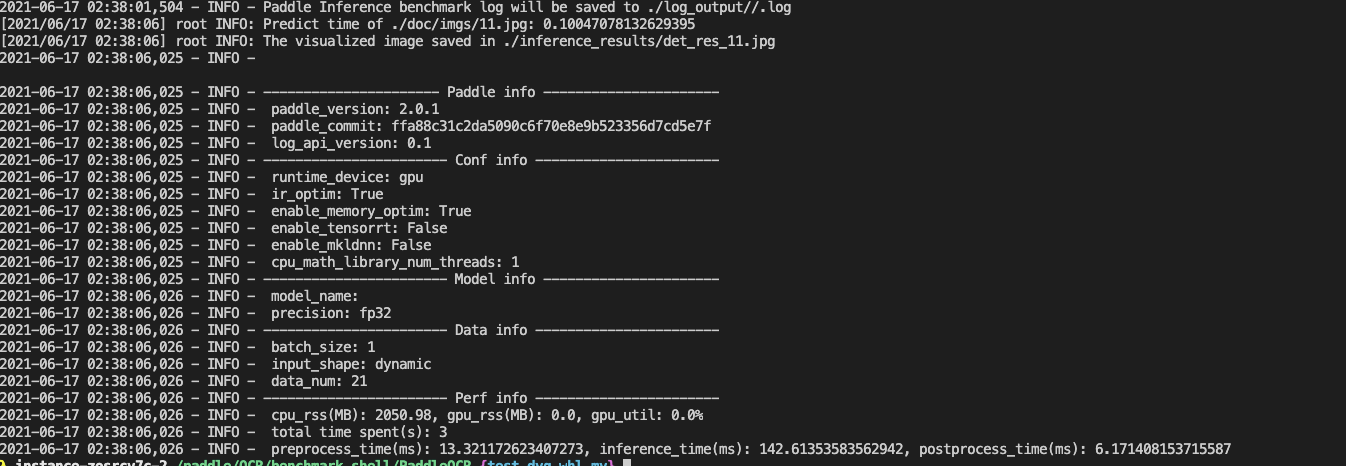
115.4 KB
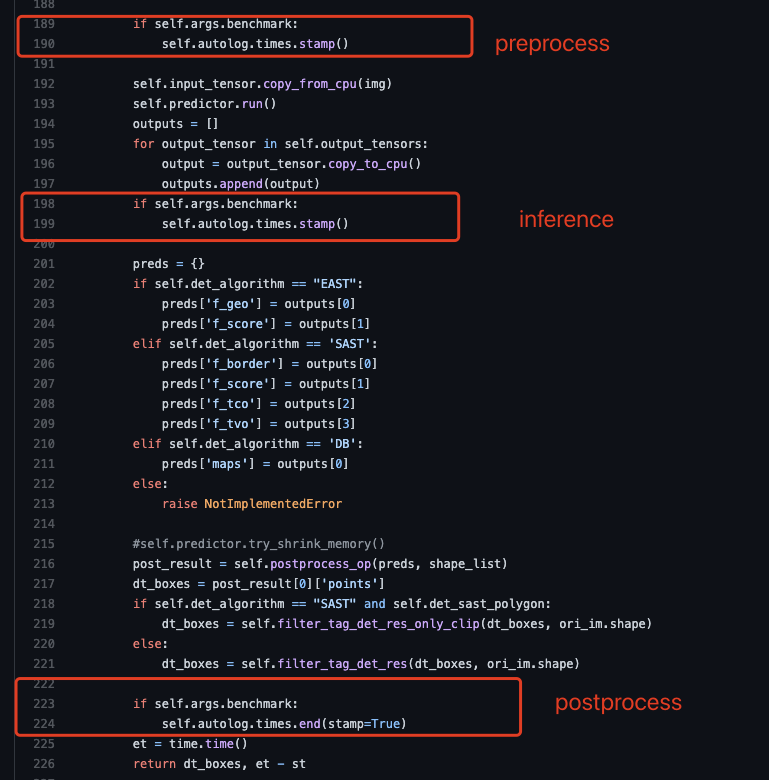
120.2 KB
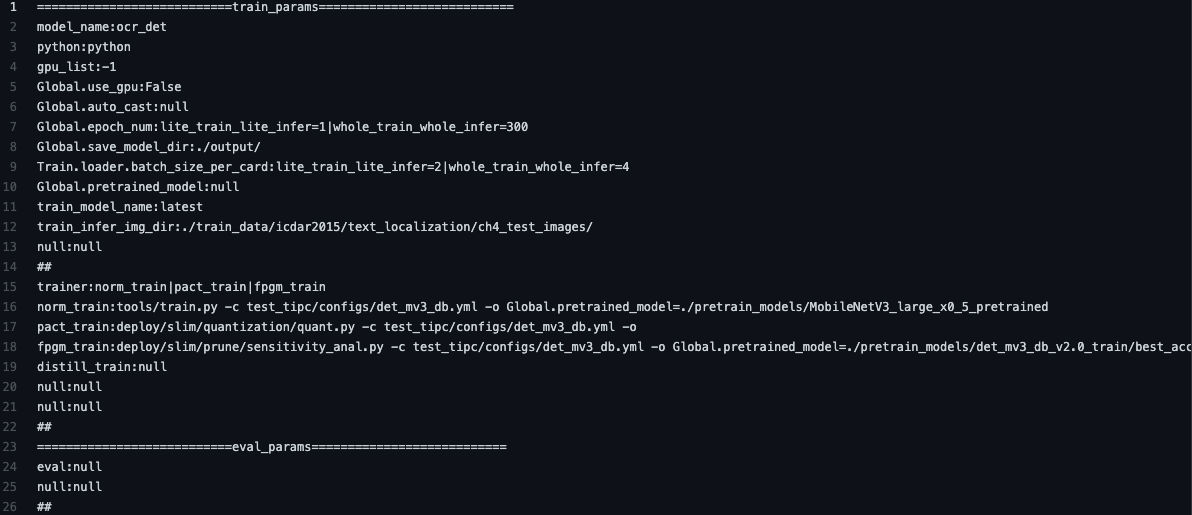
82.2 KB
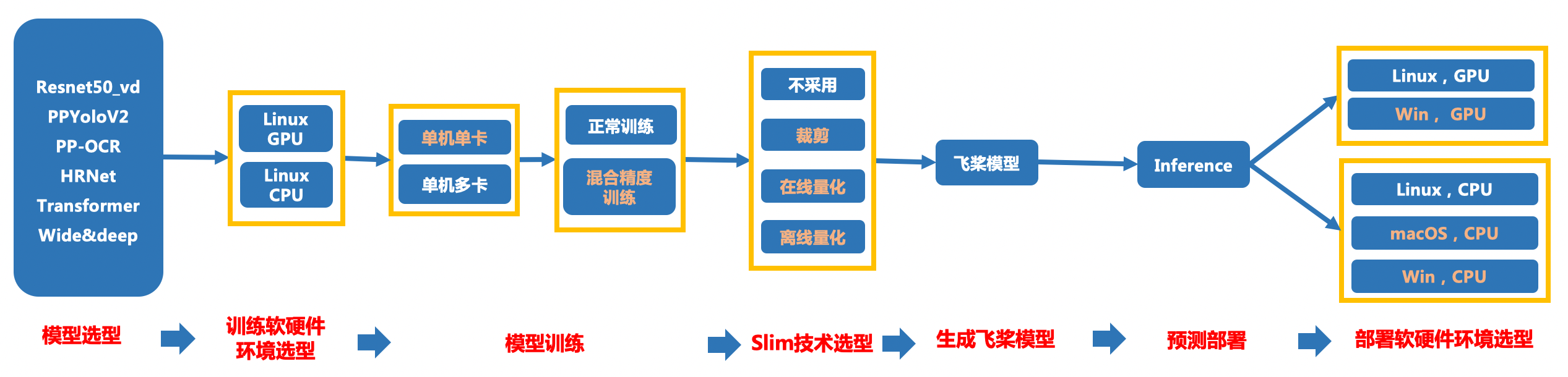
446.4 KB

45.9 KB
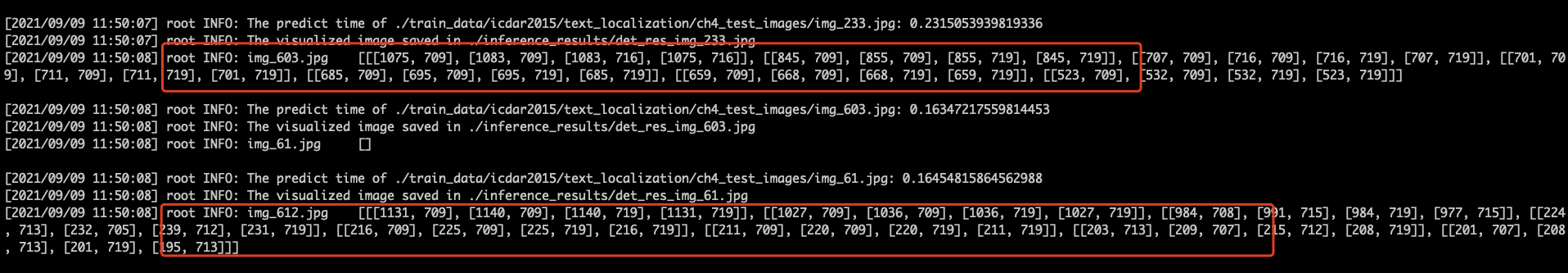
95.5 KB
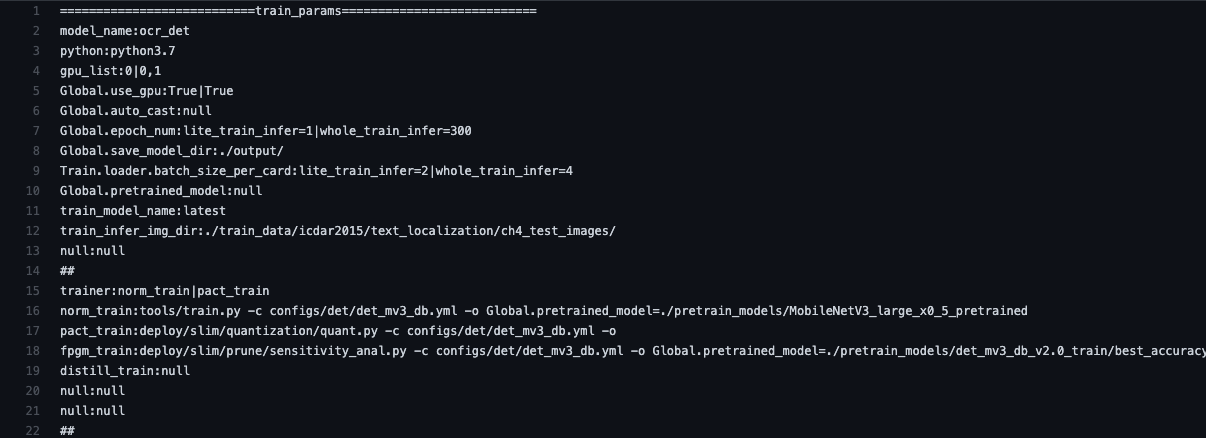
73.8 KB
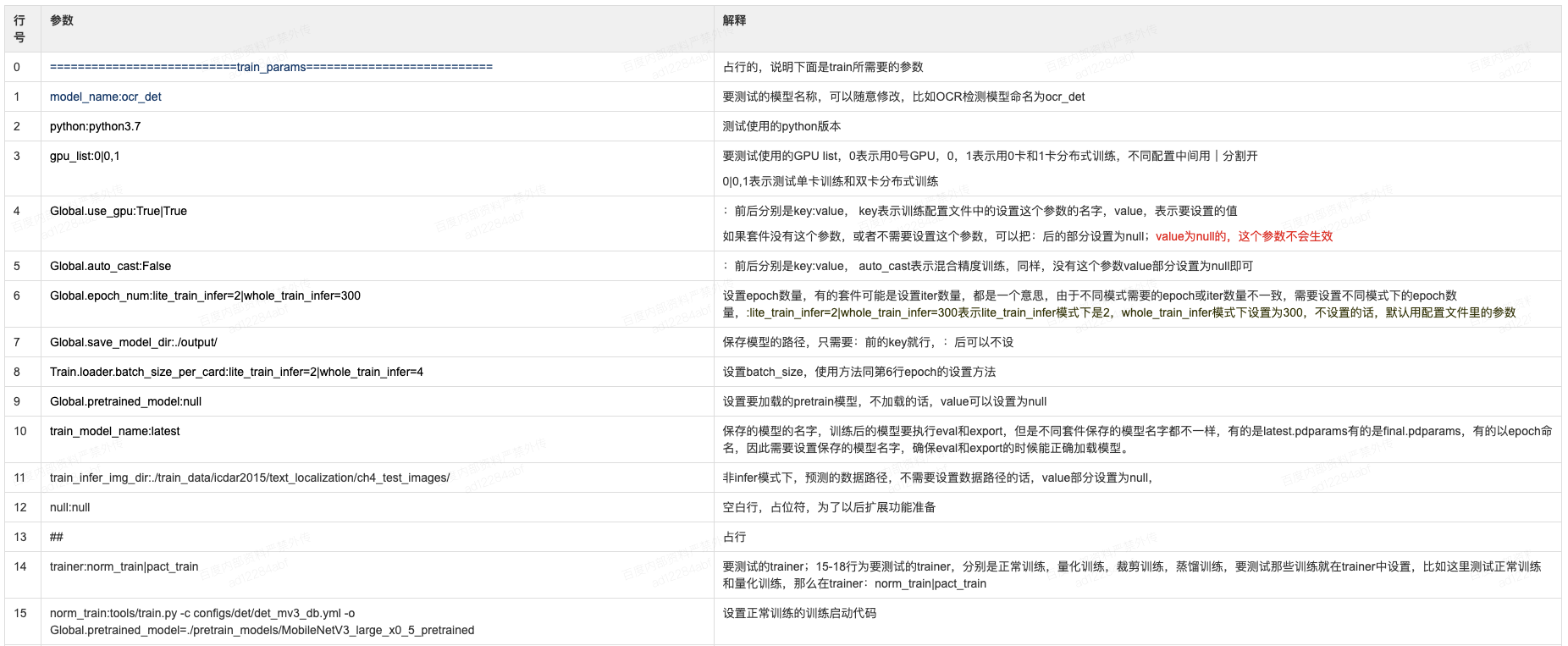
233.0 KB

195.7 KB
170.3 KB
391.0 KB
74.0 KB

137.6 KB
