add industrial code and doc (#5493)
* add industrial code and doc
Showing
tutorials/README.md
0 → 100644
112.4 KB
195.9 KB
42.1 KB
20.5 KB
257.7 KB
127.5 KB
* add industrial code and doc

112.4 KB

195.9 KB

42.1 KB

20.5 KB
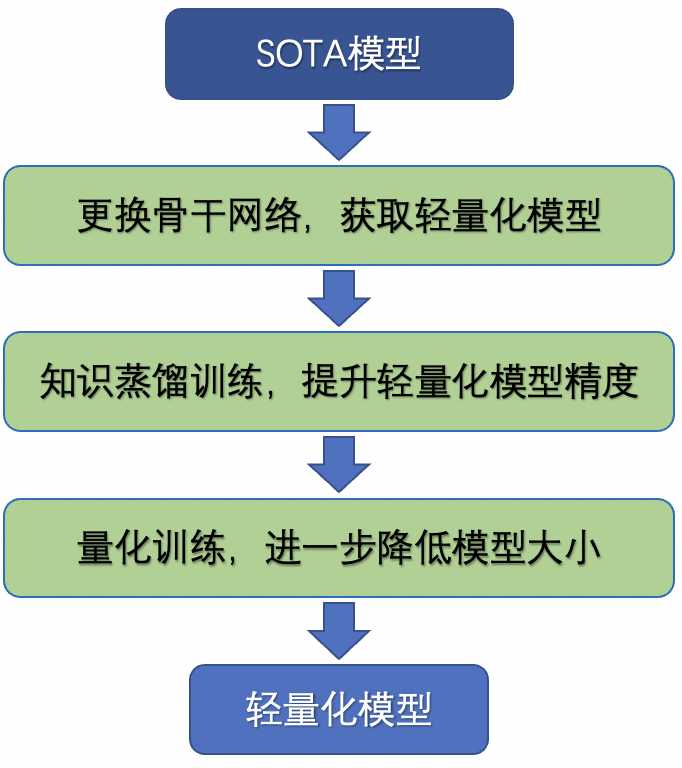
257.7 KB
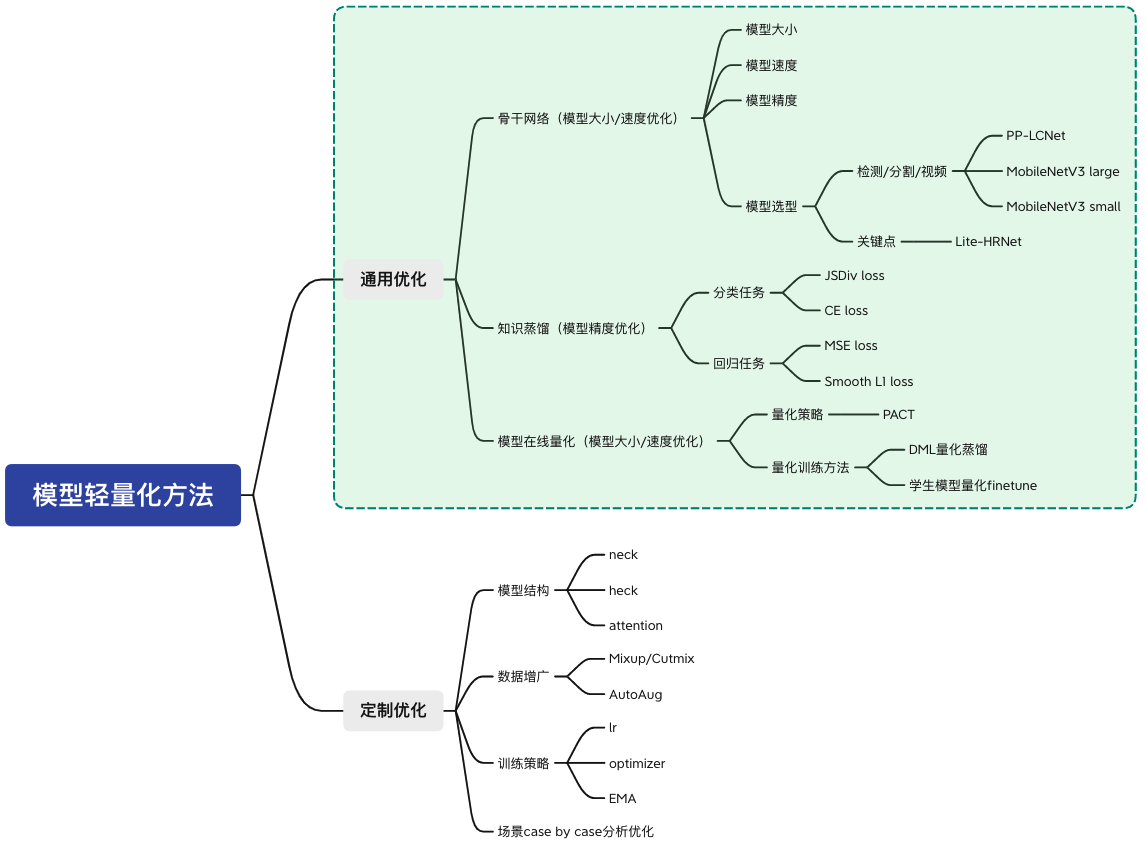
127.5 KB
