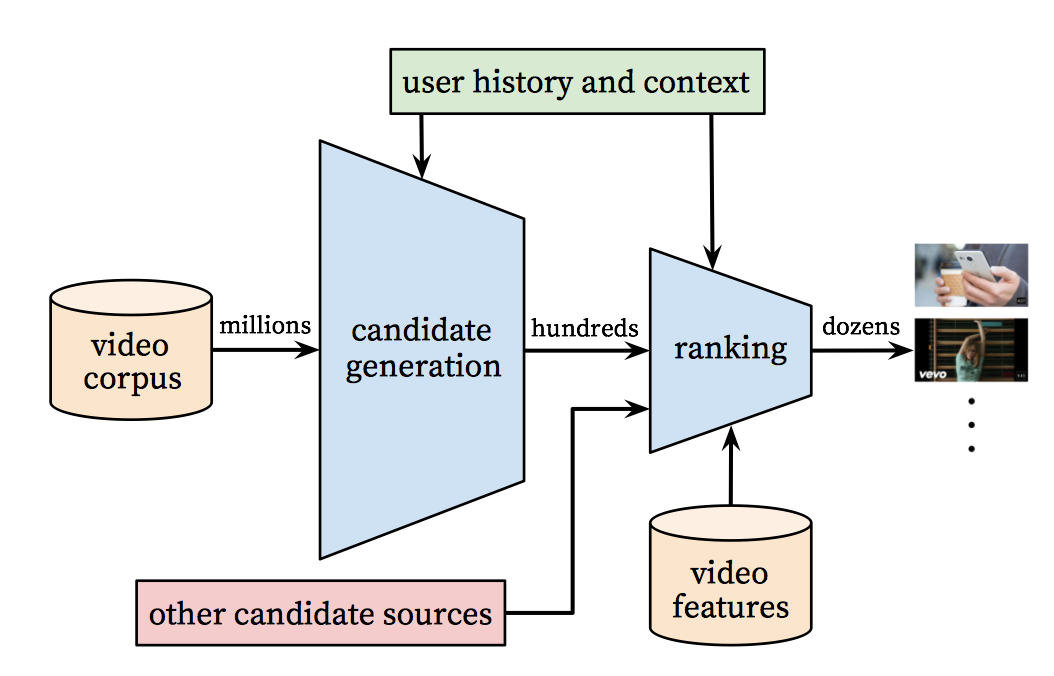
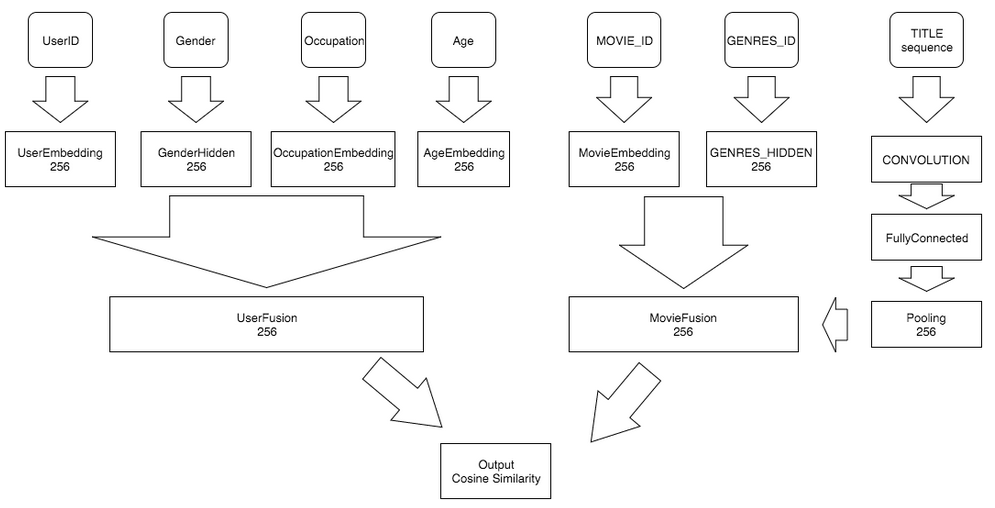
initial complete recommender_system
Showing
recommender_system/data/split.py
0 → 100644
recommender_system/evaluate.py
0 → 100755
292.5 KB
323.9 KB
180.6 KB
164.8 KB
100.6 KB
130.9 KB
81.2 KB
recommender_system/prediction.py
0 → 100755
recommender_system/preprocess.sh
0 → 100755
recommender_system/train.sh
0 → 100755