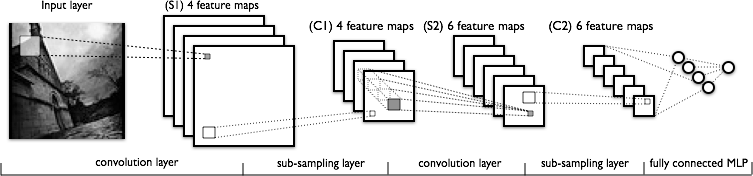
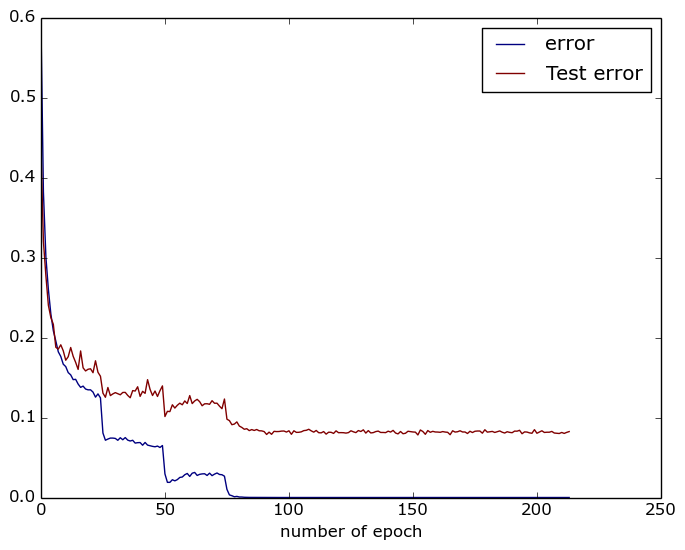
image classification tutorial
Showing
image_classification/.gitignore
0 → 100644
455.6 KB
108.0 KB
51.4 KB
48.7 KB
30.3 KB
109.5 KB
image_classification/predict.sh
0 → 100755
image_classification/train.sh
0 → 100755