Merge pull request #13 from PaddlePaddle/develop
00
Showing
docs/appendix/slim_model_zoo.md
0 → 100644
| W: | H:
| W: | H:
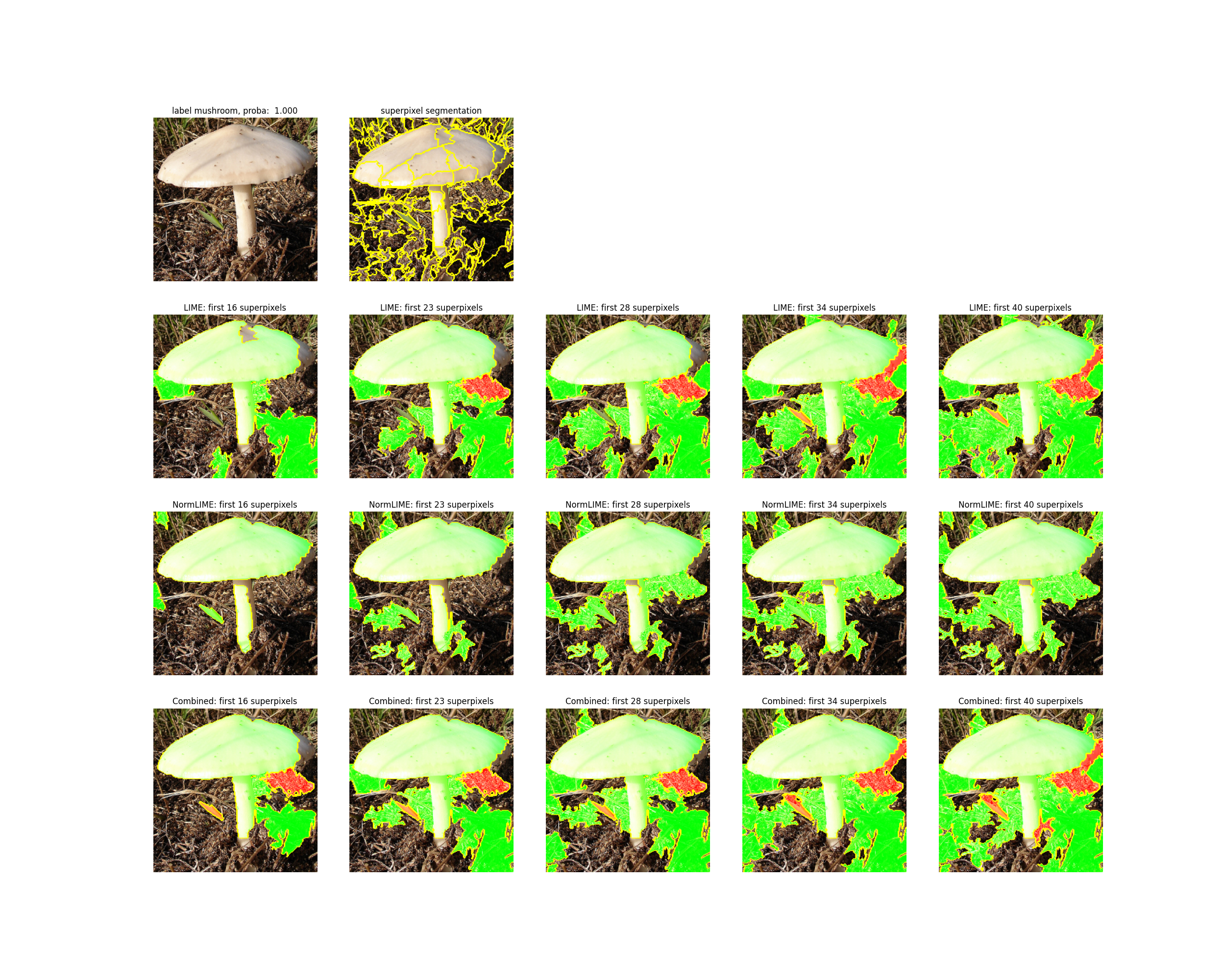



| W: | H:
| W: | H:


docs/tuning_strategy/index.rst
0 → 100644
| W: | H:
| W: | H:


| W: | H:
| W: | H:


| W: | H:
| W: | H:


83.3 KB
397.9 KB
new_tutorials/train/README.md
已删除
100644 → 0
paddlex/cv/models/fast_scnn.py
0 → 100644
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。