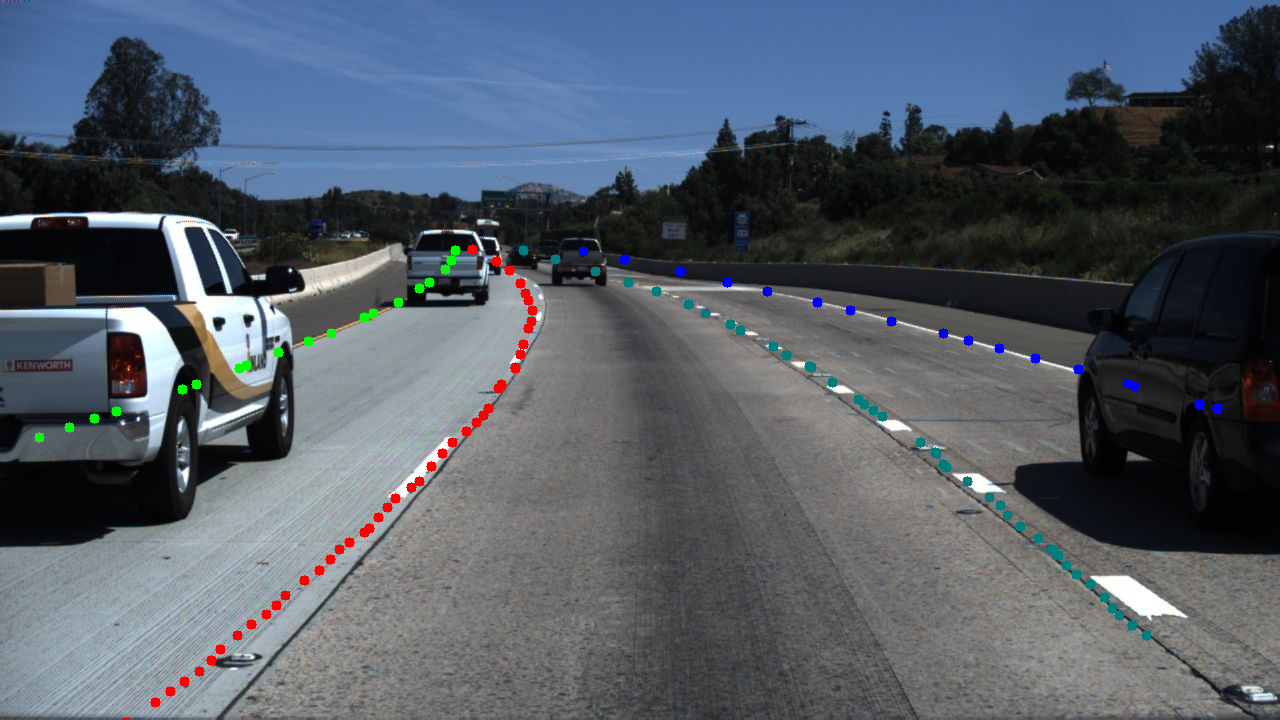
add LaneNet
Showing
contrib/LaneNet/README.md
0 → 100644
contrib/LaneNet/data_aug.py
0 → 100644
contrib/LaneNet/eval.py
0 → 100644
2.2 KB
3.2 KB
1.1 MB
contrib/LaneNet/loss.py
0 → 100644
contrib/LaneNet/reader.py
0 → 100644
此差异已折叠。
contrib/LaneNet/solver.py
0 → 100644
contrib/LaneNet/train.py
0 → 100644
contrib/LaneNet/utils/__init__.py
0 → 100644
contrib/LaneNet/utils/collect.py
0 → 100644
contrib/LaneNet/utils/config.py
0 → 100644
contrib/LaneNet/utils/timer.py
0 → 100644
此差异已折叠。
contrib/LaneNet/vis.py
0 → 100644