Merge pull request #171 from 123malin/readme
word2vec readme
Showing
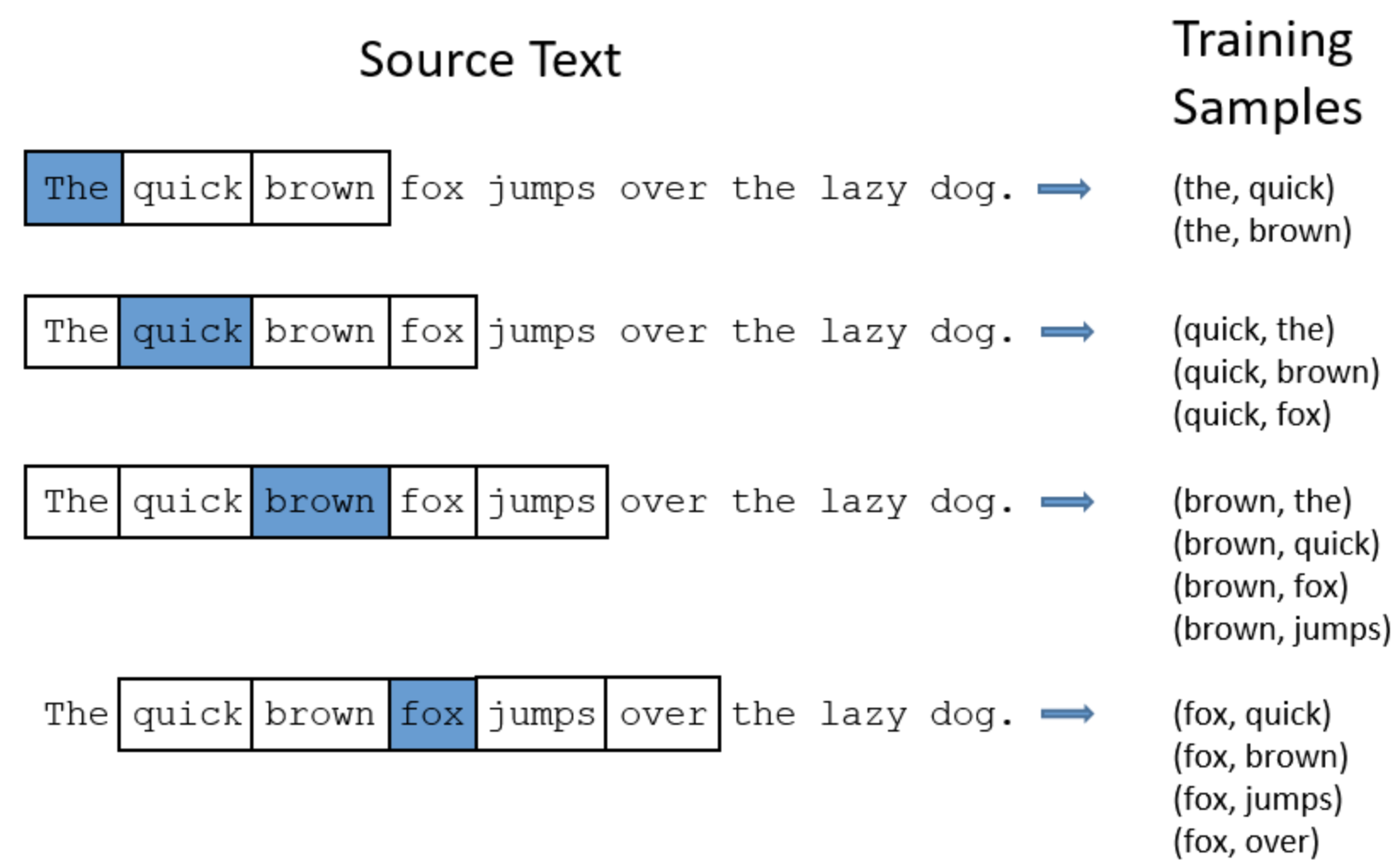
doc/imgs/w2v_train.png
0 → 100644
223.3 KB
models/recall/word2vec/README.md
0 → 100644
models/recall/word2vec/infer.py
0 → 100644
models/recall/word2vec/utils.py
0 → 100644