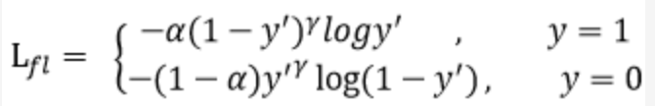“7c10f0bb007a6ed164b73e2fb4a5b88303e986ac”上不存在“source/libs/catalog/git@gitcode.net:taosdata/tdengine.git”
update enhanced ctc loss (#4256)
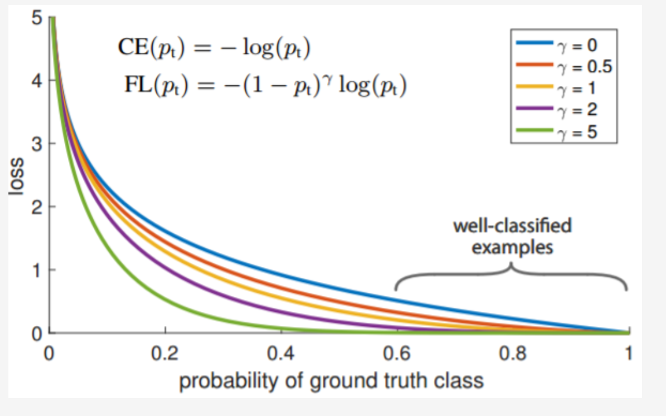
* fix Focal-ctc bug * add enhanced_ctc_loss.md
Showing
doc/doc_ch/enhanced_ctc_loss.md
0 → 100644
doc/doc_ch/equation_a_ctc.png
0 → 100644
10.2 KB
doc/doc_ch/equation_c_ctc.png
0 → 100644
10.6 KB
doc/doc_ch/equation_ctcloss.png
0 → 100644
9.3 KB
doc/doc_ch/equation_focal_ctc.png
0 → 100644
14.5 KB
doc/doc_ch/focal_loss_formula.png
0 → 100644
23.3 KB
doc/doc_ch/focal_loss_image.png
0 → 100644
124.7 KB
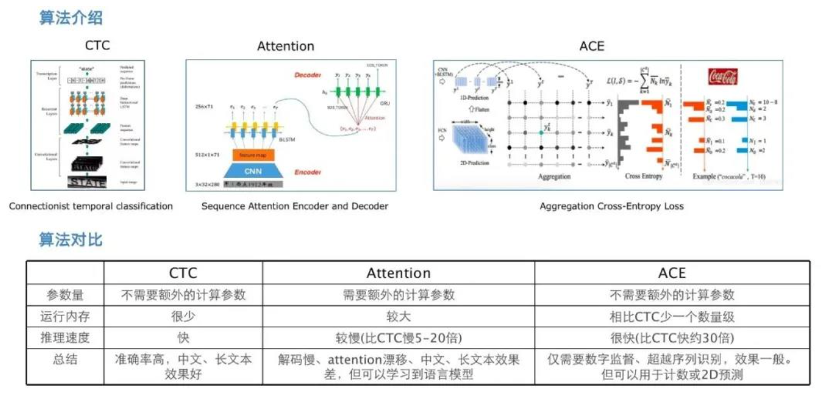
doc/doc_ch/rec_algo_compare.png
0 → 100644
223.6 KB
tools/export_center.py
0 → 100644