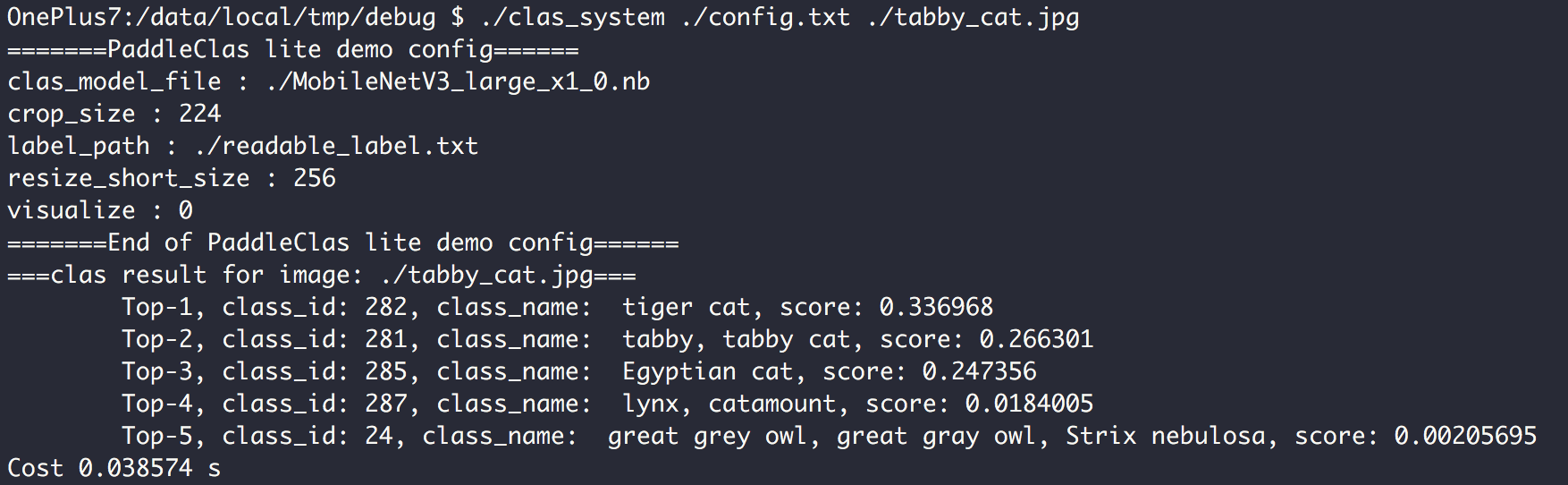
Merge pull request #303 from littletomatodonkey/sta/add_lite_demo
Add lite demo
Showing
deploy/lite/Makefile
0 → 100644
deploy/lite/config.txt
0 → 100644
142.7 KB
deploy/lite/imgs/tabby_cat.jpg
0 → 100644
24.3 KB
deploy/lite/prepare.sh
0 → 100644
deploy/lite/readme.md
0 → 100644