Merge branch 'develop' of https://github.com/cuicheng01/PaddleClas into develop
Showing
deploy/paddleserving/README.md
0 → 100644
deploy/paddleserving/README_CN.md
0 → 100644
deploy/paddleserving/__init__.py
0 → 100644
deploy/paddleserving/config.yml
0 → 100644
deploy/paddleserving/daisy.jpg
0 → 100644
38.8 KB
此差异已折叠。
8.8 KB
111.7 KB
deploy/paddleserving/utils.py
已删除
100644 → 0
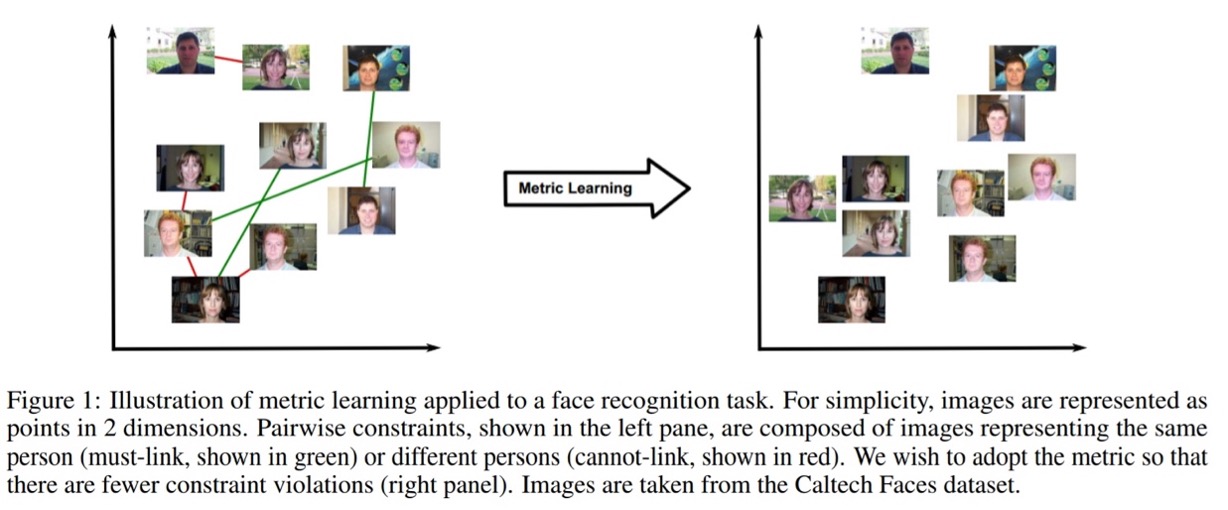
docs/images/ml_illustration.jpg
0 → 100644
118.8 KB
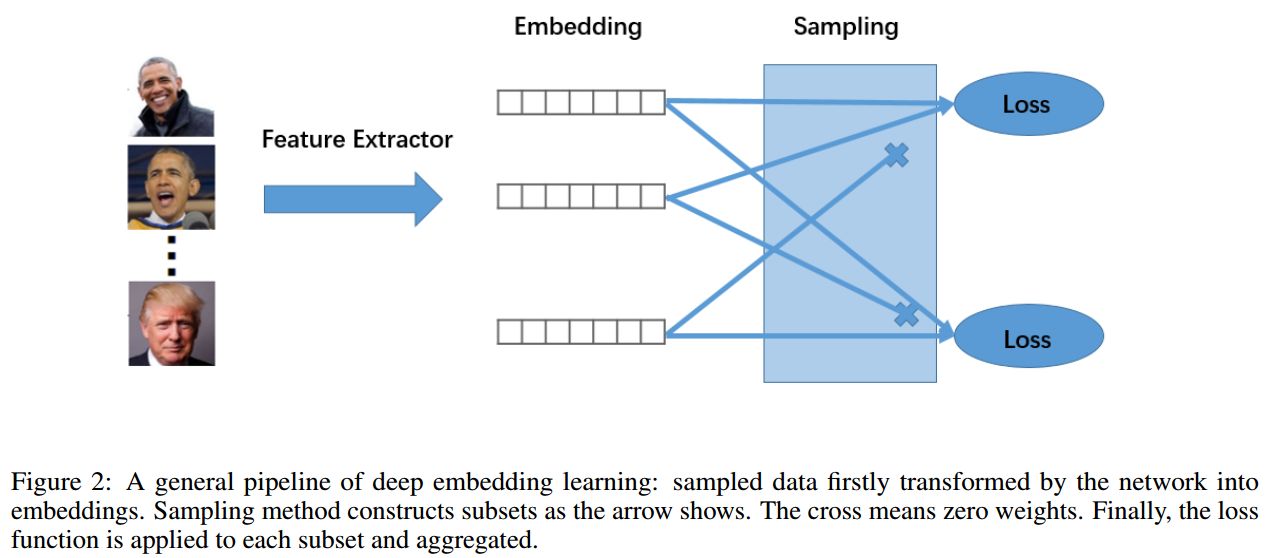
docs/images/ml_pipeline.jpg
0 → 100644
68.7 KB
| ... | @@ -8,4 +8,4 @@ visualdl >= 2.0.0b | ... | @@ -8,4 +8,4 @@ visualdl >= 2.0.0b |
| scipy | scipy | ||
| scikit-learn==0.23.2 | scikit-learn==0.23.2 | ||
| gast==0.3.3 | gast==0.3.3 | ||
| faiss-cpu==1.7.1 | faiss-cpu==1.7.1.post2 |
文件已移动
tests/config/cpp_config.txt
0 → 100755