Merge branch 'master' of https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleClas into add_efficientnet
Showing
.travis/precommit.sh
0 → 100644
configs/CSPNet/CSPResNet50.yaml
0 → 100644
configs/ResNet/ResNet50_fp16.yml
0 → 100644
134.6 KB
140.8 KB
136.6 KB
438.0 KB
181.7 KB
194.3 KB
180.0 KB
126.4 KB
139.0 KB
129.3 KB
129.1 KB
129.5 KB
132.2 KB
185.7 KB
197.9 KB
189.0 KB
244.9 KB
244.1 KB
244.3 KB
88.5 KB
57.3 KB
54.4 KB
57.1 KB
83.9 KB
105.3 KB
88.6 KB
54.3 KB
56.2 KB
58.1 KB
81.6 KB
80.8 KB
49.3 KB
50.6 KB
53.7 KB
53.9 KB
54.5 KB
58.2 KB
78.3 KB
80.5 KB
82.9 KB
105.1 KB
106.0 KB
107.6 KB
150.7 KB
140.5 KB
141.0 KB
57.8 KB
88.5 KB
55.8 KB
55.5 KB
85.5 KB
106.0 KB
文件已移动
356.5 KB
| W: | H:
| W: | H:


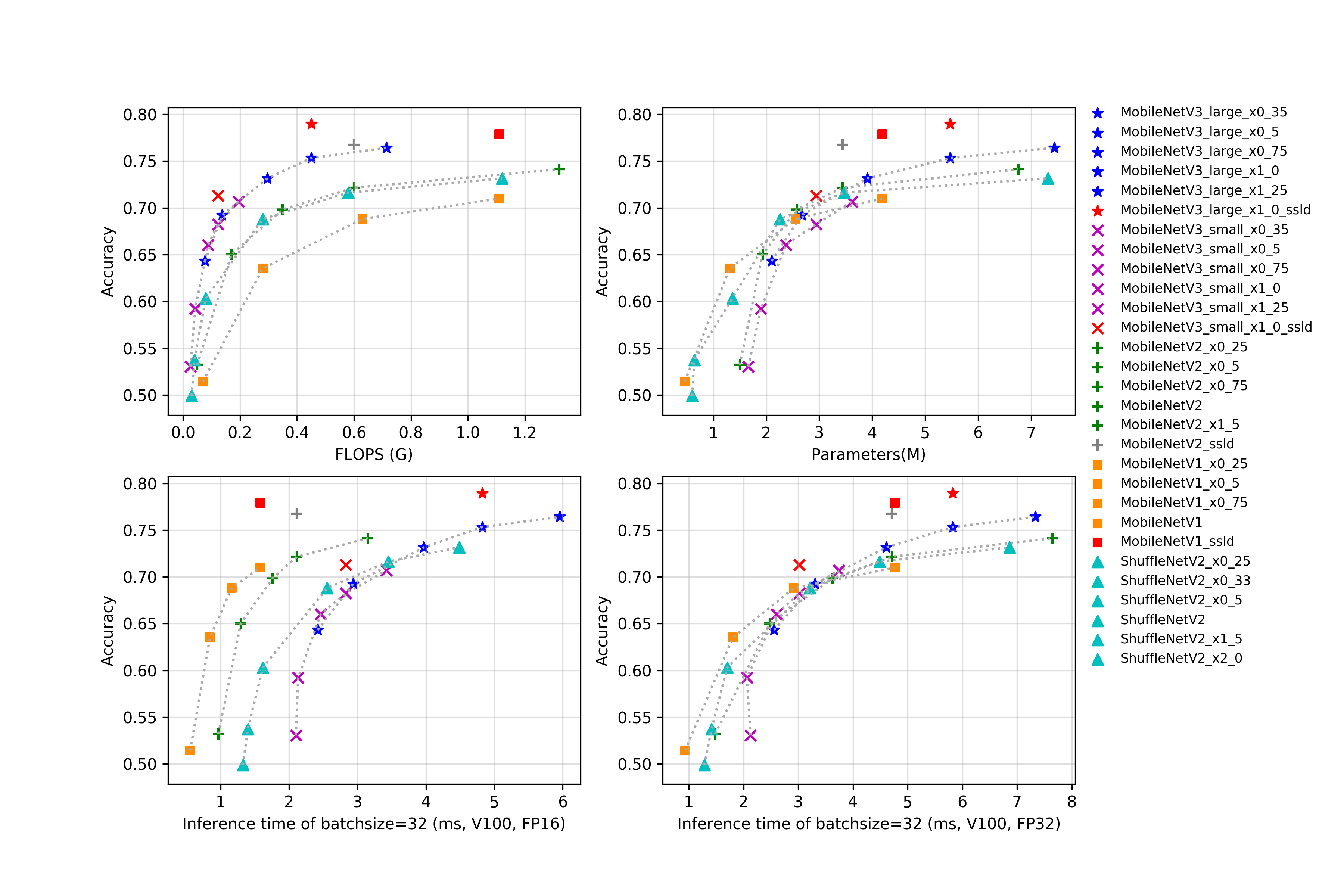
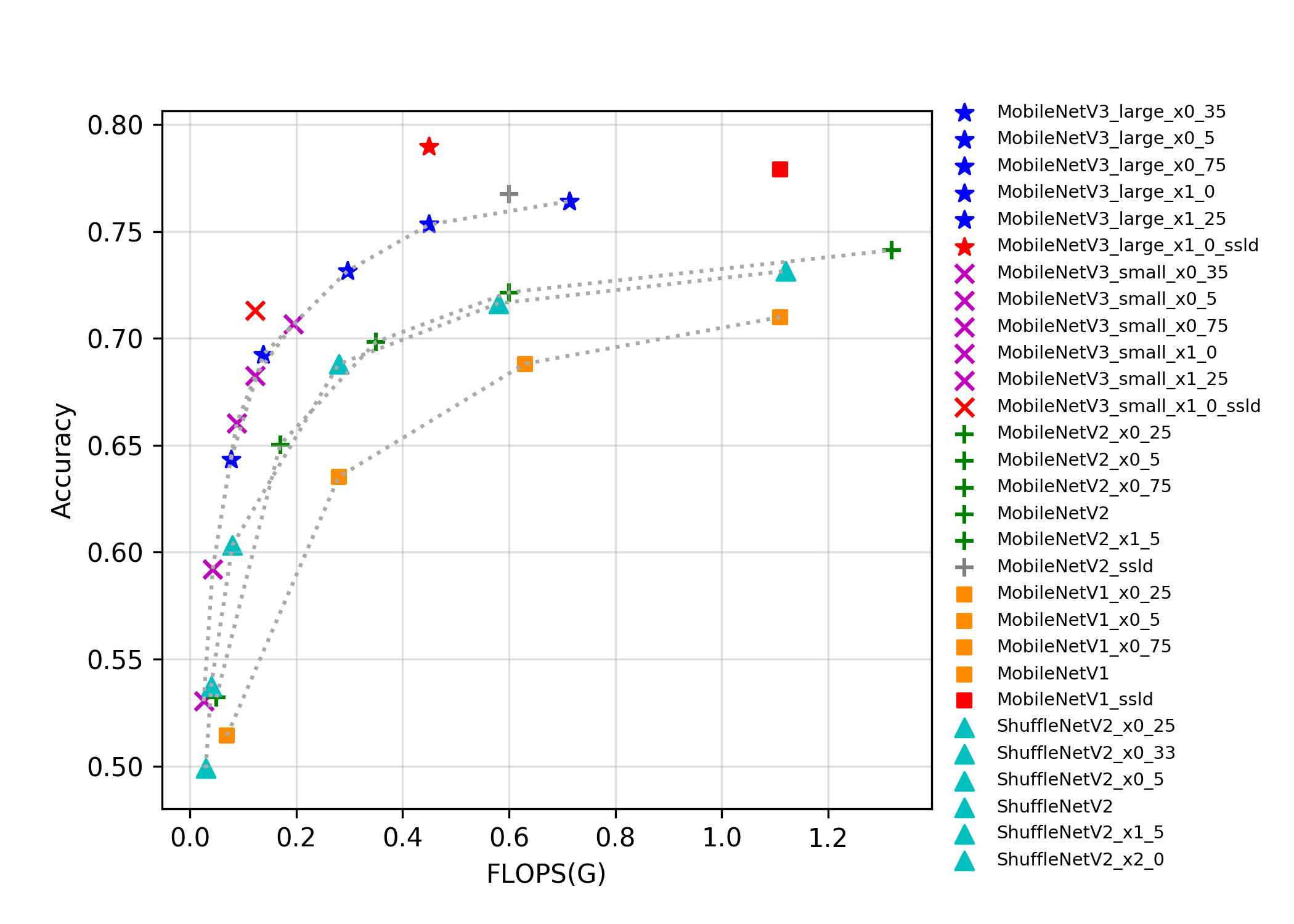
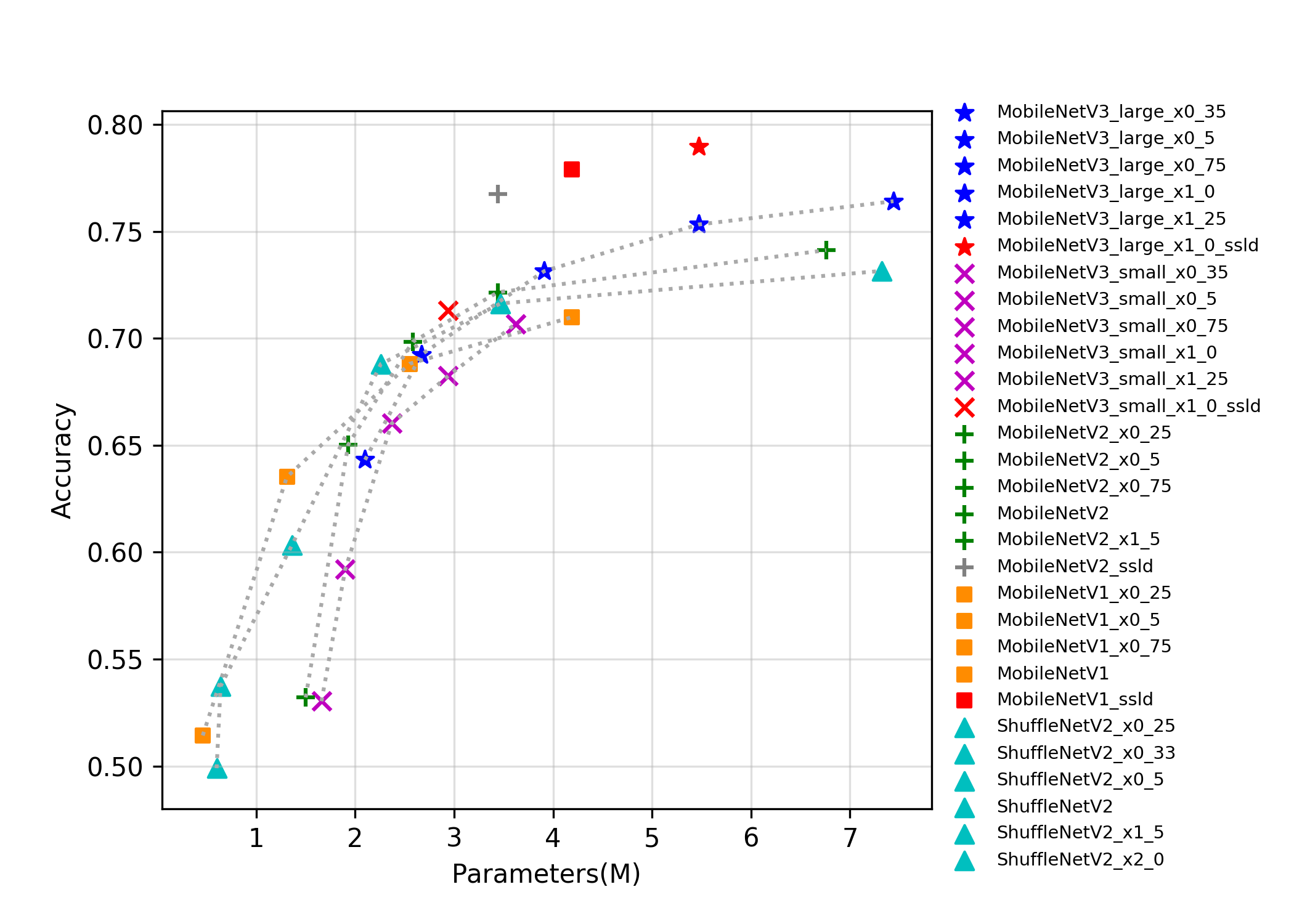
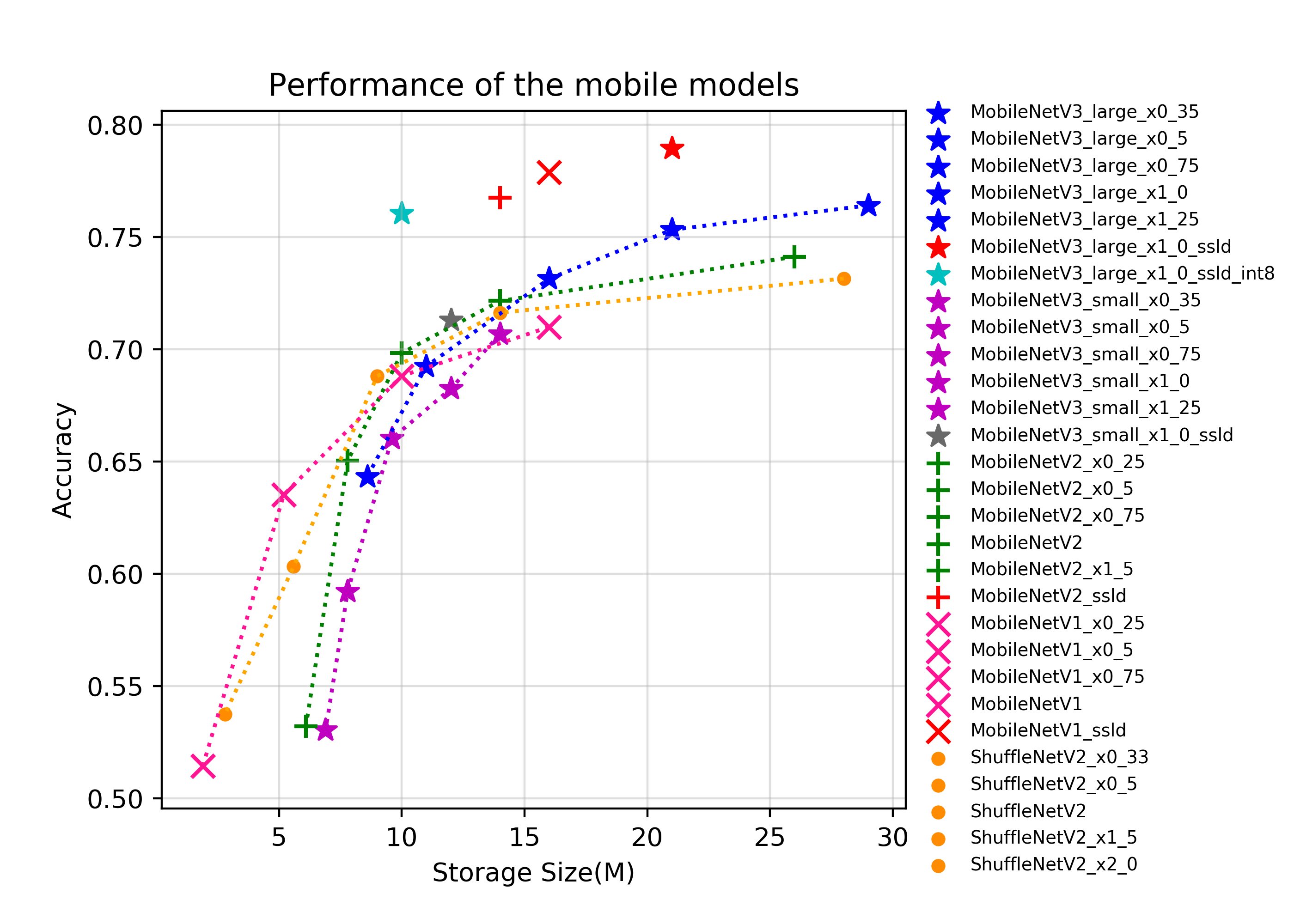
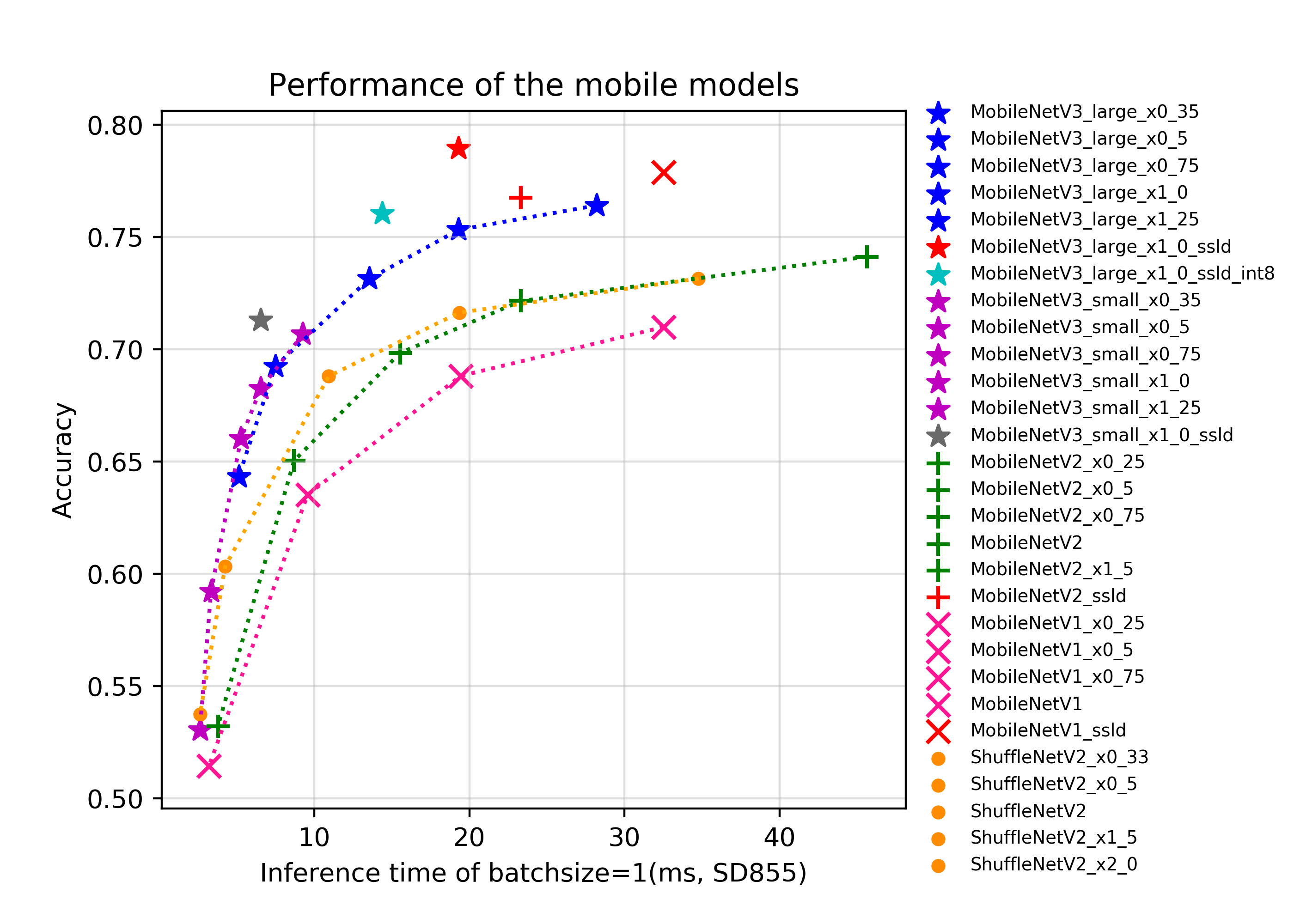
docs/images/models/mobile_arm_top1.png
100755 → 100644
| W: | H:
| W: | H:


219.3 KB
590.3 KB
312.2 KB
313.7 KB
tools/export_serving_model.py
0 → 100644
tools/lite/benchmark.sh
0 → 100644
tools/serving/utils.py
0 → 100644