A question about how PaddlePaddle implements the L2 regularization.
Created by: lcy-seso
As far as I understand, after one forward-backward computation, when updating the learnable weights, the order is:
- Perform gradients clipping (if needed, including hard clipping, soft clipping, clipping by norm, and so on)
- Apply regularization (if needed). The regularization terms express our prior beliefs about the solution.
- Calculate the adaptive gradients according to different formula of the different optimization algorithms, such as Adagrad, Rmsprop, Adadelta, Adam, Adammax, and so on.
This is because the cost is usually made up of two parts:
- The error measure from a particular loss function.
- The penalty terms to avoid overfitting (the regularization term).
As a result, the gradient of the loss with respect to a learnable parameter is also made up of two parts: (1) the gradient from the loss function; (2) the loss from the regularization term.
When applying the adaptive gradient algorithms, we should sum up the gradients from the regularization term and the gradients from the loss function first.
In PaddlePaddle's codes, here I take the Adagrad for example, regularization is applied after performing the adaptive gradient algorithm, which affects algorithm like Adam when estimating the momentum.
https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle/blob/develop/paddle/math/TrainingAlgorithmOp.cu#L80
void adagradApply(BaseMatrix& value,
BaseMatrix& grad,
BaseMatrix& mom,
BaseMatrix& accum_buffer,
BaseMatrix& accum,
BaseMatrix& lr,
real epsilon,
real learningRate,
real momentum,
real decayRate) {
auto expr1 = accum.lazyAssign(accum + grad.square());
auto expr2 =
lr.lazyAssign((accum_buffer + accum + epsilon).sqrt().reciprocal());
auto expr3 = mom.lazyAssign(mom * momentum -
learningRate * lr * (grad + value * decayRate));
auto expr4 = value.lazyAssign(value + mom);
AssignEvaluate(expr1, expr2, expr3, expr4);
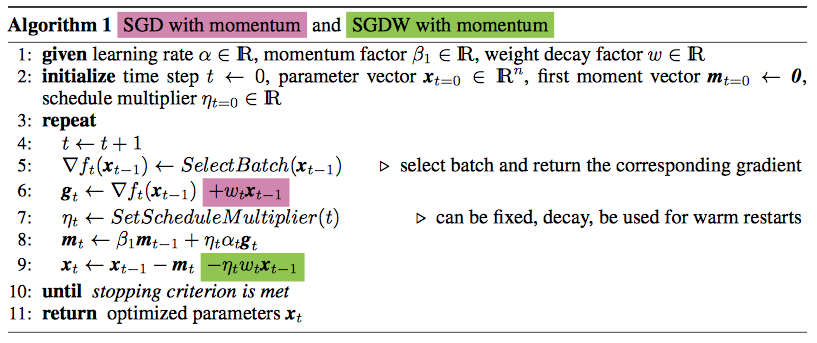
}A very interesting thing is, decoupling weight decay and the optimization steps are proposed by a recent paper: Fixing Weight Decay Regularization in Adam, and is claimed to have a better learning performance on CIFAR-10 and ImageNet32x32. The green color one is the way PaddlePaddle uses and the variant proposed by the paper.
@emailweixu I am very interested in (and curious about) the way PaddlePaddle applies the L2 regularization. I am not very sure whether my understanding about PaddlePaddle is right and why we implement the L2 regularization in this way before. Thank you for the help.