新增op和Tensor实现耗时对比
Created by: zhengzhe97
一个功能,分别使用新增python op和Tensor实现,耗时相差较大
python op实现
def crop(masks, boxes):
"""
"Crop" predicted masks by zeroing out everything not in the predicted bbox.
Vectorized by Chong (thanks Chong).
Args:
- masks should be a size [h, w, n] tensor of masks
- boxes should be a size [n, 4] tensor of bbox coords in relative point form
"""
start_time = time.time()
padding = 1
masks = np.array(masks)
boxes = np.array(boxes)
h, w, n = np.shape(masks)
x1, x2 = sanitize_coordinates(boxes[:, 0], boxes[:, 2], w, padding, cast=False)
y1, y2 = sanitize_coordinates(boxes[:, 1], boxes[:, 3], h, padding, cast=False)
rows = np.broadcast_to(np.reshape(np.arange(w, dtype=x1.dtype),(1, -1, 1)),(h, w, n))
cols = np.broadcast_to(np.reshape(np.arange(h, dtype=x1.dtype),(-1, 1, 1)),(h, w, n))
# print('rows',np.sum(rows))
masks_left = rows >= np.reshape(x1, (1, 1, -1))
masks_right = rows < np.reshape(x2, (1, 1, -1))
masks_up = cols >= np.reshape(y1, (1, 1, -1))
masks_down = cols < np.reshape(y2, (1, 1, -1))
crop_mask = masks_left * masks_right * masks_up * masks_down
# print('crop_mask:',np.sum(crop_mask))
end_time = time.time()
# print('time1',end_time - start_time)
return crop_mask.astype('float32')
def sanitize_coordinates(_x1, _x2, img_size:int, padding:int=0, cast:bool=True):
"""
Sanitizes the input coordinates so that x1 < x2, x1 != x2, x1 >= 0, and x2 <= image_size.
Also converts from relative to absolute coordinates and casts the results to long tensors.
If cast is false, the result won't be cast to longs.
Warning: this does things in-place behind the scenes so copy if necessary.
"""
_x1 = _x1 * img_size
_x2 = _x2 * img_size
if cast:
_x1 = _x1.astype('int32')
_x2 = _x2.astype('int32')
x1 = numpyminmax(_x1, _x2, False)
x2 = numpyminmax(_x1, _x2)
x1 = np.clip(x1-padding, a_min=0, a_max=1000000)
x2 = np.clip(x2+padding, a_min=-1000000, a_max=img_size)
return x1, x2 Tensor实现:
def crop_tensor(masks, boxes):
# fluid.layers.py_func(func=start_time, x=fluid.layers.shape(masks) ,out=None)
padding = 1
s = fluid.layers.shape(masks)
h = fluid.layers.cast(s[0], 'float32')
w = fluid.layers.cast(s[1], 'float32')
n = fluid.layers.cast(s[2], 'float32')
x1, x2 = sanitize_coordinates_tensor(boxes[:, 0], boxes[:, 2], w, padding, cast=False)
y1, y2 = sanitize_coordinates_tensor(boxes[:, 1], boxes[:, 3], h, padding, cast=False)
rows = fluid.layers.expand_as(fluid.layers.reshape(fluid.layers.range(0, w, 1, 'float32'), shape=(1, -1, 1)), target_tensor=masks)
cols = fluid.layers.expand_as(fluid.layers.reshape(fluid.layers.range(0, h, 1, 'float32'), shape=(-1, 1, 1)), target_tensor=masks)
# fluid.layers.py_func(func=debug_sum, x=rows ,out=None)
masks_left = rows >= fluid.layers.reshape(x1, shape=(1,1,-1))
masks_right = rows < fluid.layers.reshape(x2, shape=(1,1,-1))
masks_up = cols >= fluid.layers.reshape(y1, shape=(1,1,-1))
masks_down = cols < fluid.layers.reshape(y2, shape=(1,1,-1))
masks_left = fluid.layers.cast(masks_left, 'float32')
masks_right = fluid.layers.cast(masks_right, 'float32')
masks_up = fluid.layers.cast(masks_up, 'float32')
masks_down = fluid.layers.cast(masks_down, 'float32')
crop_mask = masks_left * masks_right * masks_up * masks_down
# fluid.layers.py_func(func=end_time, x=fluid.layers.shape(masks) ,out=None)
crop_mask.stop_gradient = True
# fluid.layers.py_func(func=debug_sum, x=crop_mask ,out=None)
return masks * crop_mask
def sanitize_coordinates_tensor(_x1, _x2, img_size, padding:int=0, cast:bool=True):
_x1 = fluid.layers.elementwise_mul(fluid.layers.cast(_x1, 'float32'), img_size)
_x2 = fluid.layers.elementwise_mul(fluid.layers.cast(_x2, 'float32'), img_size)
if cast:
_x1 = fluid.layers.cast(_x1, 'int32')
_x2 = fluid.layers.cast(_x2, 'int32')
x1 = fluid.layers.elementwise_min(_x1, _x2)
x2 = fluid.layers.elementwise_max(_x1, _x2)
x1 = fluid.layers.clip(x=x1-padding, min=0, max=10000)
x2 = fluid.layers.clip(x=x2+padding, min=-10000, max=144)
return x1, x2对于python op,直接使用time.clock(),计算前后时差
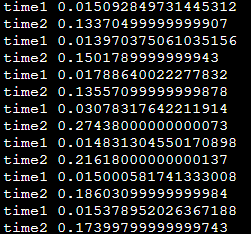
发现基于Tensor的实现慢了好多,想知道是什么原因

