Skip to content
体验新版
项目
组织
正在加载...
登录
切换导航
打开侧边栏
PaddlePaddle
Paddle-Lite
提交
6fcad721
P
Paddle-Lite
项目概览
PaddlePaddle
/
Paddle-Lite
通知
338
Star
4
Fork
1
代码
文件
提交
分支
Tags
贡献者
分支图
Diff
Issue
271
列表
看板
标记
里程碑
合并请求
78
Wiki
0
Wiki
分析
仓库
DevOps
项目成员
Pages
P
Paddle-Lite
项目概览
项目概览
详情
发布
仓库
仓库
文件
提交
分支
标签
贡献者
分支图
比较
Issue
271
Issue
271
列表
看板
标记
里程碑
合并请求
78
合并请求
78
Pages
分析
分析
仓库分析
DevOps
Wiki
0
Wiki
成员
成员
收起侧边栏
关闭侧边栏
动态
分支图
创建新Issue
提交
Issue看板
未验证
提交
6fcad721
编写于
2月 24, 2020
作者:
H
huzhiqiang
提交者:
GitHub
2月 24, 2020
浏览文件
操作
浏览文件
下载
电子邮件补丁
差异文件
[doc]modify cpp_demo doc (#2984)
上级
16b8f9de
变更
2
隐藏空白更改
内联
并排
Showing
2 changed file
with
169 addition
and
246 deletion
+169
-246
docs/user_guides/cpp_demo.md
docs/user_guides/cpp_demo.md
+161
-238
docs/user_guides/tutorial.md
docs/user_guides/tutorial.md
+8
-8
未找到文件。
docs/user_guides/cpp_demo.md
浏览文件 @
6fcad721
# C++ Demo
##
编译
##
1. 下载最新版本预测库
首先按照
[
PaddleLite 源码编译
](
../installation/source_compile
)
准备交叉编译环境,之后拉取最新
[
PaddleLite release发布版代码
](
https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle-Lite
)
。下面以Android-ARMv8架构为例,介绍编译过程,并最终在手机上跑通MobilNetv1模型
。
预测库下载界面位于
[
Paddle-Lite官方预编译库
](
../installation/release_lib
)
,可根据需求选择合适版本
。
进入 Paddle-Lite 目录,运行以下命令编译代码(
**需加编译选项`--build_extra=ON`确保完整编译**
)
:
以
**Android-ARMv8架构**
为例,可以下载以下版本
:
|ARM Version|build_extra|arm_stl|target|下载|
|:-------:|:-----:|:-----:|:-----:|:-------:|
|armv8|OFF|c++_static|tiny_publish|
[
release/v2.3
](
https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle-Lite/releases/download/v2.3.0/inference_lite_lib.android.armv8.gcc.c++_static.tiny_publish.tar.gz
)
|
**解压后内容如下图所示:**

## 2. 转化模型
PaddlePaddle的原生模型需要经过
[
opt
](
)工具转化为Paddle-Lite可以支持的naive_buffer格式。
以
`mobilenet_v1`
模型为例:
(1)下载
[
mobilenet_v1模型
](
http://paddle-inference-dist.bj.bcebos.com/mobilenet_v1.tar.gz
)
后解压:
```
shell
wget http://paddle-inference-dist.bj.bcebos.com/mobilenet_v1.tar.gz
tar
zxf mobilenet_v1.tar.gz
```
./lite/tools/build.sh \
--arm_os=android \
--arm_abi=armv8 \
--arm_lang=gcc \
--android_stl=c++_static \
--build_extra=ON \
full_publish
**如下图所示:**

(2)下载
[
opt工具
](
https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle-Lite/releases/download/v2.3.0/opt
)
。放入同一文件夹,终端输入命令转化模型:
```
shell
wget https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle-Lite/releases/download/v2.3.0/opt
chmod
+x opt
./opt
--model_dir
=
./mobilenet_v1
--optimize_out_type
=
naive_buffer
--optimize_out
=
./mobilenet_v1_opt
```
编译完成后
`./build.lite.android.armv8.gcc/inference_lite_lib.android.armv8/`
文件夹下包含:
**结果如下图所示:**

-
cxx
-
include (头文件文件夹)
-
lib (库文件文件夹)
-
libpaddle_api_full_bundled.a
-
libpaddle_api_light_bundled.a
-
libpaddle_light_api_shared.so
-
libpaddle_full_api_shared.so
-
demo
-
cxx (C++ demo)
-
mobile_light (light api demo)
-
mobile_full (full api demo)
-
mobile_detection (detection model api demo)
-
mobile_classify (classify model api demo)
-
Makefile.def
-
include
-
third_party (第三方库文件夹)
-
gflags
## 3. 编写预测程序
## 准备执行环境
准备好预测库和模型,我们便可以编写程序来执行预测。我们提供涵盖图像分类、目标检测等多种应用场景的C++示例demo可供参考,位于
`inference_lite_lib.android.armv8/demo/cxx`
。
执行环境有两种:使用安卓手机;若没安卓手机,也可在安卓模拟器中执行
。
以mobile net_v1预测为例:
`mobile_light`
为mobilenet_v1预测示例,可以直接调用
。
### 环境一:使用安卓手机
**示例如下图所示:**
将手机连上电脑,在手机上打开选项 -> 开启-开发者模式 -> 开启-USB调试模式。确保
`adb devices`
能够看到相应的设备。

### 环境二:使用安卓模拟器
运行下面命令,分别创建安卓armv8、armv7架构的模拟器。若需在真机测试,将模拟器换成相应架构的真机环境即可。
## 4. 编译
预测程序需要编译为Android可执行文件。
以mobilenet_v1模型为例,C++示例位于
`inference_lite_lib.android.armv8/demo/mobile_light`
```
shell
cd
inference_lite_lib.android.armv8/demo/mobile_light
```
*android-armv8*
adb kill-server
adb devices | grep emulator | cut -f1 | while read line; do adb -s $line emu kill; done
echo n | avdmanager create avd -f -n paddle-armv8 -k "system-images;android-24;google_apis;arm64-v8a"
echo -ne '\n' | ${ANDROID_HOME}/emulator/emulator -avd paddle-armv8 -noaudio -no-window -gpu off -port 5554 &
sleep 1m
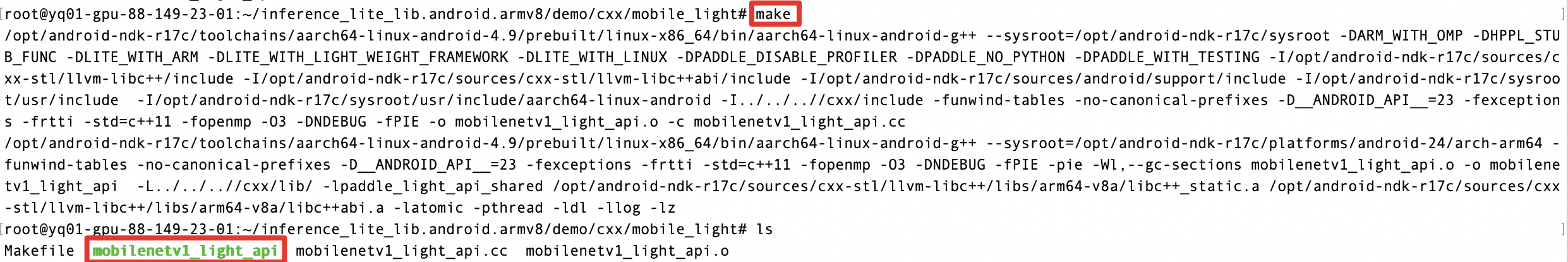
编译demo
```
shell
make
```
**结果如下图所示:**
## 5. 执行预测
通过adb工具将可执行文件推送到手机上执行预测
(1)保证电脑已经安装adb工具,手机以"USB调试"、"文件传输模式"连接到电脑。
```
shell
adb deveices
#查看adb设备是否已被识别
```
*android-armv7*
adb kill-server
adb devices | grep emulator | cut -f1 | while read line; do adb -s $line emu kill; done
echo n | avdmanager create avd -f -n paddle-armv7 -k "system-images;android-24;google_apis;armeabi-v7a"
echo -ne '\n' | ${ANDROID_HOME}/emulator/emulator -avd paddle-armv7 -noaudio -no-window -gpu off -port 5554 &
sleep 1m
**连接如下图所示:**

(2)准备预测库、模型和预测文件
1、将模型、动态库和预测文件放入同一文件夹:

**注意**
:动态预测库文件位于:
`inference_lite_lib.android.armv8/cxx/liblibpaddle_light_api_shared.so`
2、文件推送到手机:
```
shell
chmod
+x mobilenetv1_light_api
adb push mobilenet_v1_opt.nb /data/local/tmp
adb push libpaddle_light_api_shared.so /data/local/tmp
adb push mobilenetv1_light_api /data/local/tmp
```
**效果如下图所示:**
## 下载模型并运行示例

(3)执行预测
```
shell
adb shell
'cd /data/local/tmp && export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$LD_LIBRARY_PATH:/data/local/tmp && mobilenetv1_light_api ./mobilenet_v1_opt.nb'
```
cd inference_lite_lib.android.armv8/demo/cxx/mobile_full
wget http://paddle-inference-dist.bj.bcebos.com/mobilenet_v1.tar.gz
tar zxvf mobilenet_v1.tar.gz
**结果如下图所示:**
make
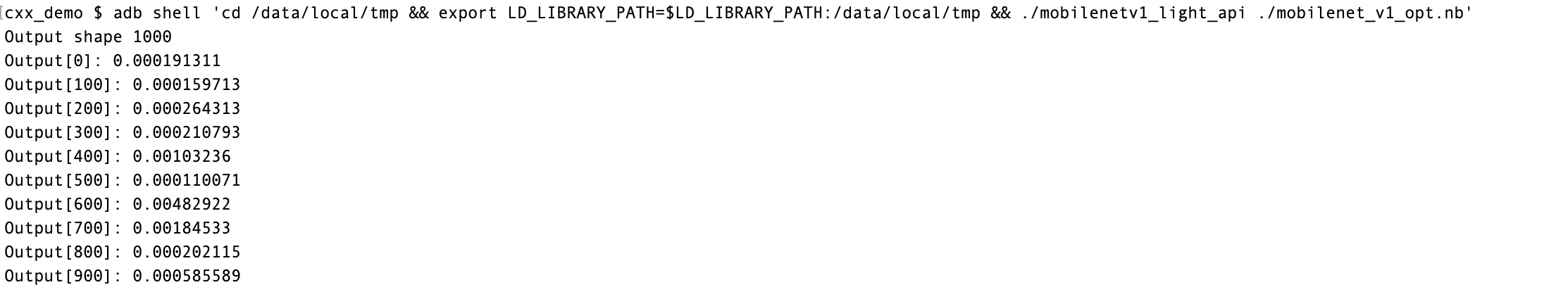
上图的
`Output`
为mobilenet_v1模型在全1输入时,得到的预测输出。至此,Paddle-Lite的C++ demo执行完毕。
## 注:如何在代码中使用 API
C++代码调用Paddle-Lite执行预测库仅需以下五步:
adb push mobilenet_v1 /data/local/tmp/
adb push mobilenetv1_full_api /data/local/tmp/
adb shell chmod +x /data/local/tmp/mobilenetv1_full_api
adb shell "/data/local/tmp/mobilenetv1_full_api --model_dir=/data/local/tmp/mobilenet_v1 --optimized_model_dir=/data/local/tmp/mobilenet_v1.opt"
(1)引用头文件和命名空间
```
c++
#include "paddle_api.h"
using
namespace
paddle
::
lite_api
;
```
注:我们也提供了轻量级 API 的 demo、图像分类demo和目标检测demo,支持图像输入;
(2)指定模型文件,创建Predictor
### Light API Demo
```
C++
// 1. Set MobileConfig, model_file_path is
// the path to model model file.
MobileConfig config;
config.set_model_from_file(model_file_path);
// 2. Create PaddlePredictor by MobileConfig
std::shared_ptr<PaddlePredictor> predictor =
CreatePaddlePredictor<MobileConfig>(config);
```
(3)设置模型输入 (下面以全一输入为例)
```
c++
std
::
unique_ptr
<
Tensor
>
input_tensor
(
std
::
move
(
predictor
->
GetInput
(
0
)));
input_tensor
->
Resize
({
1
,
3
,
224
,
224
});
auto
*
data
=
input_tensor
->
mutable_data
<
float
>
();
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
ShapeProduction
(
input_tensor
->
shape
());
++
i
)
{
data
[
i
]
=
1
;
}
```
(4)执行预测
```
c++
predictor
->
Run
();
```
(5)获得预测结果
```
c++
std
::
unique_ptr
<
const
Tensor
>
output_tensor
(
std
::
move
(
predictor
->
GetOutput
(
0
)));
// 转化为数据
auto
output_data
=
output_tensor
<
float
>
();
```
## 其他cxx_demo的编译与预期结果
### Light API Demo
```
shell
cd
../mobile_light
make
adb push mobilenetv1_light_api /data/local/tmp/
...
...
@@ -96,7 +195,7 @@ adb shell "/data/local/tmp/mobilenetv1_light_api --model_dir=/data/local/tmp/mob
### 图像分类 Demo
```
```
shell
cd
../mobile_classify
wget http://paddle-inference-dist.bj.bcebos.com/mobilenet_v1.tar.gz
tar
zxvf mobilenet_v1.tar.gz
...
...
@@ -111,7 +210,7 @@ adb shell "export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/data/local/tmp/:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH && /data/loc
### 目标检测 Demo
```
```
shell
cd
../mobile_detection
wget https://paddle-inference-dist.bj.bcebos.com/mobilenetv1-ssd.tar.gz
tar
zxvf mobilenetv1-ssd.tar.gz
...
...
@@ -124,13 +223,11 @@ adb shell "export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/data/local/tmp/:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH && /data/loc
adb pull /data/local/tmp/test_detection_result.jpg ./
```
## Demo 程序运行结果
### light API Demo 运行结果
运行成功后 ,将在控制台输出预测结果的前10个类别的预测概率:
```
```
shell
Output dim: 1000
Output[0]: 0.000191
Output[100]: 0.000160
...
...
@@ -148,7 +245,7 @@ Output[900]: 0.000586
运行成功后 ,将在控制台输出预测结果的前5个类别的类型索引、名字和预测概率:
```
```
shell
parameter: model_dir, image_path and label_file are necessary
parameter: topk, input_width, input_height, are optional
i: 0, index: 285, name: Egyptian
cat
, score: 0.482870
...
...
@@ -162,182 +259,8 @@ i: 4, index: 722, name: ping-pong ball, score: 0.000508
运行成功后 ,将在控制台输出检测目标的类型、预测概率和坐标:
```
```
shell
running result:
detection image size: 935, 1241, detect object: person, score: 0.996098, location:
x
=
187,
y
=
43,
width
=
540,
height
=
592
detection image size: 935, 1241, detect object: person, score: 0.935293, location:
x
=
123,
y
=
639,
width
=
579,
height
=
597
```
## 如何在代码中使用 API
在C++中使用PaddleLite API非常简单,不需要添加太多额外代码,具体步骤如下:
-
加入头文件引用
```
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include "paddle_api.h"
#include "paddle_use_kernels.h"
#include "paddle_use_ops.h"
#include "paddle_use_passes.h"
```
-
通过MobileConfig设置:模型文件位置(model_dir)、线程数(thread)和能耗模式( power mode )。输入数据(input),从 MobileConfig 创建 PaddlePredictor 并执行预测。 (注:Lite还支持从memory直接加载模型,可以通过MobileConfig::set_model_buffer方法实现)
代码示例:
```
// 1. Create MobileConfig
MobileConfig config;
// 2. Load model
config.set_model_dir("path to your model directory"); // model dir
/*load model: Lite supports loading model from file or from memory (naive buffer from optimized model)
//Method One: Load model from memory:
void set_model_buffer(const char* model_buffer,
size_t model_buffer_size,
const char* param_buffer,
size_t param_buffer_size)
//Method Two: Load model from file:
void set_model_dir(const std::string& model_dir) */
// 3. Set MobileConfig (or you can skip this step to use default value):
config.set_power_mode(LITE_POWER_HIGH); // power mode
/*power modes: Lite supports the following power modes
LITE_POWER_HIGH
LITE_POWER_LOW
LITE_POWER_FULL
LITE_POWER_NO_BIND
LITE_POWER_RAND_HIGH
LITE_POWER_RAND_LOW */
config.set_threads("num of threads"); // threads
// 4. Create PaddlePredictor by MobileConfig
std::shared_ptr<PaddlePredictor> predictor =
CreatePaddlePredictor<MobileConfig>(config);
// 5. Prepare input data
std::unique_ptr<Tensor> input_tensor(std::move(predictor->GetInput(0)));
input_tensor->Resize({1, 3, 224, 224});
auto *data = input_tensor -> mutable_data<float>();
for (int i = 0; i < ShapeProduction(input_tensor->shape()); ++i) {
data[i] = 1;
}
// 6. Run predictor
predictor->Run();
// 7. Get output
std::unique_ptr<const Tensor> output_tensor(std::move(predictor->GetOutput(0)));
```
## CxxConfig案例: OCR_model的运行
1.
OCR 模型文件:
-
我们提供Pb格式的
[
ocr_attention_mode
](
https://paddle-inference-dist.cdn.bcebos.com/ocr_attention.tar.gz
)
l下载
-
也可以从
[
Paddle/model项目
](
https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/models/tree/develop/PaddleCV/ocr_recognition
)
中训练出模型
2.
示例代码:
```
#include "paddle_api.h" // NOLINT
#include "paddle_use_passes.h" // NOLINT
#include <gflags/gflags.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <vector>
using namespace paddle::lite_api; // NOLINT
DEFINE_string(model_dir, "", "Model dir path.");
DEFINE_bool(prefer_int8_kernel, false, "Prefer to run model with int8 kernels");
int64_t ShapeProduction(const shape_t &shape) {
int64_t res = 1;
for (auto i : shape)
res *= i;
return res;
}
void RunModel() {
// 1. Set CxxConfig
CxxConfig config;
config.set_model_dir(FLAGS_model_dir);
std::vector<Place> valid_places({Place{TARGET(kARM), PRECISION(kFloat)}});
if (FLAGS_prefer_int8_kernel) {
valid_places.insert(valid_places.begin(),
Place{TARGET(kARM), PRECISION(kInt8)});
}
config.set_valid_places(valid_places);
// 2. Create PaddlePredictor by CxxConfig
std::shared_ptr<PaddlePredictor> predictor =
CreatePaddlePredictor<CxxConfig>(config);
// 3. Prepare input data
// input 0
std::unique_ptr<Tensor> input_tensor(std::move(predictor->GetInput(0)));
input_tensor->Resize(shape_t({1, 1, 48, 512}));
auto *data = input_tensor->mutable_data<float>();
for (int i = 0; i < ShapeProduction(input_tensor->shape()); ++i) {
data[i] = 1;
}
// input1
std::unique_ptr<Tensor> init_ids(std::move(predictor->GetInput(1)));
init_ids->Resize(shape_t({1, 1}));
auto *data_ids = init_ids->mutable_data<float>();
for (int i = 0; i < ShapeProduction(init_ids->shape()); ++i) {
data_ids[i] = 0;
}
lod_t lod_i;
lod_i.push_back({0, 1});
lod_i.push_back({0, 1});
init_ids->SetLoD(lod_i);
// input2
std::unique_ptr<Tensor> init_scores(std::move(predictor->GetInput(2)));
init_scores->Resize(shape_t({1, 1}));
auto *data_scores = init_scores->mutable_data<float>();
for (int i = 0; i < ShapeProduction(init_scores->shape()); ++i) {
data_scores[i] = 0;
}
lod_t lod_s;
lod_s.push_back({0, 1});
lod_s.push_back({0, 1});
init_scores->SetLoD(lod_s);
// 4. Run predictor
predictor->Run();
// 5. Get output
std::unique_ptr<const Tensor> output_tensor(
std::move(predictor->GetOutput(0)));
for (int i = 0; i < ShapeProduction(output_tensor->shape()); i++) {
printf("Output[%d]: %f\n", i, output_tensor->data<float>()[i]);
}
}
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
google::ParseCommandLineFlags(&argc, &argv, true);
RunModel();
return 0;
}
```
3.
运行方法:
参考以上代码编译出可执行文件
`OCR_DEMO`
,模型文件夹为
`ocr_attention`
。手机以USB调试、文件传输模式连接电脑。
```
简单编译出`OCR_DEMO`的方法:用以上示例代码替换编译结果中`build.lite.android.armv8.gcc/inference_lite_lib.android.armv8/demo/cxx/mobile_full/mobilenetv1_full_api.cc`文件的内容,终端进入该路径(`demo/cxx/mobile_full/`),终端中执行`make && mv mobilenetv1_full_api OCR_DEMO`即编译出了OCR模型的可执行文件`OCR_DEMO`
```
在终端中输入以下命令执行OCR model测试:
```
#OCR_DEMO为编译出的可执行文件名称;ocr_attention为ocr_attention模型的文件夹名称;libpaddle_full_api_shared.so是编译出的动态库文件,位于`build.lite.android.armv8.gcc/inference_lite_lib.android.armv8/cxx/lib`
adb push OCR_DEMO /data/local/tmp
adb push ocr_attention /data/local/tmp
adb push libpaddle_full_api_shared.so /data/local/tmp/
adb shell 'export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/data/local/tmp/:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH && cd /data/local/tmp && ./OCR_DEMO --model_dir=./OCR_DEMO'
```
4.
运行结果
<img
src=
'https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/45189361/64398400-46531580-d097-11e9-9f1c-5aba1dfbc24f.png'
align=
'left'
width=
"150"
height=
"200"
/>
docs/user_guides/tutorial.md
浏览文件 @
6fcad721
...
...
@@ -9,16 +9,16 @@ Lite框架目前支持的模型结构为[PaddlePaddle](https://github.com/Paddle
## 二. 模型优化
Lite框架拥有强大的加速、优化策略及实现,其中包含诸如量化、子图融合、Kernel优选等等优化手段,为了方便您使用这些优化策略,我们提供了
[
Model Optimize Tool
](
model_optimize_tool
)
帮助您轻松进行模型优化。优化后的模型更轻量级,耗费资源更少,并且执行速度也更快。
Lite框架拥有强大的加速、优化策略及实现,其中包含诸如量化、子图融合、Kernel优选等等优化手段,为了方便您使用这些优化策略,我们提供了
[
opt
](
model_optimize_tool
)
帮助您轻松进行模型优化。优化后的模型更轻量级,耗费资源更少,并且执行速度也更快。
Model Optimize Tool
的详细介绍,请您参考
[
模型优化方法
](
model_optimize_tool
)
。
opt
的详细介绍,请您参考
[
模型优化方法
](
model_optimize_tool
)
。
使用
Model Optimize Tool
,您只需编译后在开发机上执行以下代码:
使用
opt
,您只需编译后在开发机上执行以下代码:
```
shell
$
cd
<PaddleLite_base_path>
$
cd
build.
model_optimize_tool
/lite/api/
$
./
model_optimize_tool
\
$
cd
build.
opt
/lite/api/
$
./
opt
\
--model_dir
=
<model_param_dir>
\
--model_file
=
<model_path>
\
--param_file
=
<param_path>
\
...
...
@@ -32,11 +32,11 @@ $ ./model_optimize_tool \
## 三. 使用Lite框架执行预测
在上一节中,我们已经通过
Model Optimize Tool
获取到了优化后的模型,使用优化模型进行预测也十分的简单。为了方便您的使用,Lite进行了良好的API设计,隐藏了大量您不需要投入时间研究的细节。您只需要简单的五步即可使用Lite在移动端完成预测(以C++ API进行说明):
在上一节中,我们已经通过
`opt`
获取到了优化后的模型,使用优化模型进行预测也十分的简单。为了方便您的使用,Lite进行了良好的API设计,隐藏了大量您不需要投入时间研究的细节。您只需要简单的五步即可使用Lite在移动端完成预测(以C++ API进行说明):
1.
声明MobileConfig。在config中可以设置
**从文件加载模型**
也可以设置
**从memory加载模型**
。从文件加载模型需要声明模型文件路径,如
`config.set_model_
dir(FLAGS_model_dir
)`
;从memory加载模型方法现只支持加载优化后模型的naive buffer,实现方法为:
`void set_model_
buffer(model_buffer,model_buffer_size,param_buffer,param_buffer_size
) `
1.
声明MobileConfig。在config中可以设置
**从文件加载模型**
也可以设置
**从memory加载模型**
。从文件加载模型需要声明模型文件路径,如
`config.set_model_
from_file(FLAGS_model_file
)`
;从memory加载模型方法现只支持加载优化后模型的naive buffer,实现方法为:
`void set_model_
from_buffer(model_buffer
) `
2.
创建Predictor。Predictor即为Lite框架的预测引擎,为了方便您的使用我们提供了
`CreatePaddlePredictor`
接口,你只需要简单的执行一行代码即可完成预测引擎的初始化,
`std::shared_ptr<PaddlePredictor> predictor = CreatePaddlePredictor(config)`
。
3.
准备输入。执行predictor->GetInput(0)您将会获得输入的第0个field,同样的,如果您的模型有多个输入,那您可以执行
`predictor->GetInput(i)`
来获取相应的输入变量。得到输入变量后您可以使用Resize方法指定其具体大小,并填入输入值。
...
...
编辑
预览
Markdown
is supported
0%
请重试
或
添加新附件
.
添加附件
取消
You are about to add
0
people
to the discussion. Proceed with caution.
先完成此消息的编辑!
取消
想要评论请
注册
或
登录