Skip to content
体验新版
项目
组织
正在加载...
登录
切换导航
打开侧边栏
PaddlePaddle
Paddle-Lite
提交
12667f27
P
Paddle-Lite
项目概览
PaddlePaddle
/
Paddle-Lite
通知
338
Star
4
Fork
1
代码
文件
提交
分支
Tags
贡献者
分支图
Diff
Issue
271
列表
看板
标记
里程碑
合并请求
78
Wiki
0
Wiki
分析
仓库
DevOps
项目成员
Pages
P
Paddle-Lite
项目概览
项目概览
详情
发布
仓库
仓库
文件
提交
分支
标签
贡献者
分支图
比较
Issue
271
Issue
271
列表
看板
标记
里程碑
合并请求
78
合并请求
78
Pages
分析
分析
仓库分析
DevOps
Wiki
0
Wiki
成员
成员
收起侧边栏
关闭侧边栏
动态
分支图
创建新Issue
提交
Issue看板
未验证
提交
12667f27
编写于
9月 21, 2020
作者:
Y
ysh329
提交者:
GitHub
9月 21, 2020
浏览文件
操作
浏览文件
下载
差异文件
Merge branch 'release/v2.6' into cherry-pick-precision-profiler-enhance
上级
e507e7b5
06cb6233
变更
30
隐藏空白更改
内联
并排
Showing
30 changed file
with
208 addition
and
219 deletion
+208
-219
docs/demo_guides/baidu_xpu.md
docs/demo_guides/baidu_xpu.md
+3
-60
docs/demo_guides/cuda.md
docs/demo_guides/cuda.md
+2
-0
docs/images/architecture.png
docs/images/architecture.png
+0
-0
docs/images/workflow.png
docs/images/workflow.png
+0
-0
docs/introduction/architecture.md
docs/introduction/architecture.md
+12
-10
docs/introduction/support_model_list.md
docs/introduction/support_model_list.md
+32
-28
docs/quick_start/tutorial.md
docs/quick_start/tutorial.md
+41
-28
lite/backends/x86/math/context_project.h
lite/backends/x86/math/context_project.h
+4
-4
lite/backends/x86/math/pooling.cc
lite/backends/x86/math/pooling.cc
+40
-40
lite/backends/x86/math/sequence_padding.h
lite/backends/x86/math/sequence_padding.h
+1
-1
lite/backends/x86/parallel.h
lite/backends/x86/parallel.h
+3
-3
lite/core/mir/memory_optimize_pass.cc
lite/core/mir/memory_optimize_pass.cc
+1
-1
lite/core/mir/static_kernel_pick_pass.h
lite/core/mir/static_kernel_pick_pass.h
+1
-1
lite/core/mir/subgraph/subgraph_detector.cc
lite/core/mir/subgraph/subgraph_detector.cc
+32
-0
lite/kernels/apu/bridges/softmax_op.cc
lite/kernels/apu/bridges/softmax_op.cc
+1
-1
lite/kernels/host/crf_decoding_compute.h
lite/kernels/host/crf_decoding_compute.h
+2
-2
lite/kernels/host/multiclass_nms_compute.cc
lite/kernels/host/multiclass_nms_compute.cc
+4
-4
lite/kernels/host/print_compute.cc
lite/kernels/host/print_compute.cc
+1
-1
lite/kernels/host/retinanet_detection_output_compute.cc
lite/kernels/host/retinanet_detection_output_compute.cc
+8
-8
lite/kernels/x86/elementwise_op_function.h
lite/kernels/x86/elementwise_op_function.h
+1
-1
lite/kernels/x86/sequence_arithmetic_compute.h
lite/kernels/x86/sequence_arithmetic_compute.h
+3
-3
lite/kernels/x86/sequence_conv_compute.h
lite/kernels/x86/sequence_conv_compute.h
+2
-2
lite/kernels/x86/slice_compute.h
lite/kernels/x86/slice_compute.h
+4
-4
lite/model_parser/model_parser.cc
lite/model_parser/model_parser.cc
+2
-2
lite/operators/conv_op.cc
lite/operators/conv_op.cc
+1
-1
lite/operators/elementwise_ops.cc
lite/operators/elementwise_ops.cc
+1
-1
lite/operators/pool_op.h
lite/operators/pool_op.h
+2
-2
lite/operators/slice_op.cc
lite/operators/slice_op.cc
+3
-3
lite/tools/build_windows.bat
lite/tools/build_windows.bat
+1
-1
lite/utils/string.h
lite/utils/string.h
+0
-7
未找到文件。
docs/demo_guides/baidu_xpu.md
浏览文件 @
12667f27
...
...
@@ -16,69 +16,12 @@ Paddle Lite已支持百度XPU在x86和arm服务器(例如飞腾 FT-2000+/64)
### 已支持的Paddle模型
-
[
ResNet50
](
https://paddlelite-demo.bj.bcebos.com/models/resnet50_fp32_224_fluid.tar.gz
)
-
[
BERT
](
https://paddlelite-demo.bj.bcebos.com/models/bert_fp32_fluid.tar.gz
)
-
[
ERNIE
](
https://paddlelite-demo.bj.bcebos.com/models/ernie_fp32_fluid.tar.gz
)
-
YOLOv3
-
Mask R-CNN
-
Faster R-CNN
-
UNet
-
SENet
-
SSD
-
[
开源模型支持列表
](
../introduction/support_model_list
)
-
百度内部业务模型(由于涉密,不方便透露具体细节)
### 已支持(或部分支持)的Paddle算子(Kernel接入方式)
-
scale
-
relu
-
tanh
-
sigmoid
-
stack
-
matmul
-
pool2d
-
slice
-
lookup_table
-
elementwise_add
-
elementwise_sub
-
cast
-
batch_norm
-
mul
-
layer_norm
-
softmax
-
conv2d
-
io_copy
-
io_copy_once
-
__xpu__fc
-
__xpu__multi_encoder
-
__xpu__resnet50
-
__xpu__embedding_with_eltwise_add
### 已支持(或部分支持)的Paddle算子(子图/XTCL接入方式)
-
relu
-
tanh
-
conv2d
-
depthwise_conv2d
-
elementwise_add
-
pool2d
-
softmax
-
mul
-
batch_norm
-
stack
-
gather
-
scale
-
lookup_table
-
slice
-
transpose
-
transpose2
-
reshape
-
reshape2
-
layer_norm
-
gelu
-
dropout
-
matmul
-
cast
-
yolo_box
-
[
算子支持列表
](
../introduction/support_operation_list
)
## 参考示例演示
...
...
@@ -233,7 +176,7 @@ $ ./lite/tools/build.sh --arm_os=armlinux --arm_abi=armv8 --arm_lang=gcc --build
```
-
将编译生成的build.lite.x86/inference_lite_lib/cxx/include替换PaddleLite-linux-demo/libs/PaddleLite/amd64/include目录;
-
将编译生成的build.lite.x86/inference_lite_lib/cxx/
include/
lib/libpaddle_full_api_shared.so替换PaddleLite-linux-demo/libs/PaddleLite/amd64/lib/libpaddle_full_api_shared.so文件;
-
将编译生成的build.lite.x86/inference_lite_lib/cxx/lib/libpaddle_full_api_shared.so替换PaddleLite-linux-demo/libs/PaddleLite/amd64/lib/libpaddle_full_api_shared.so文件;
-
将编译生成的build.lite.armlinux.armv8.gcc/inference_lite_lib.armlinux.armv8.xpu/cxx/include替换PaddleLite-linux-demo/libs/PaddleLite/arm64/include目录;
-
将编译生成的build.lite.armlinux.armv8.gcc/inference_lite_lib.armlinux.armv8.xpu/cxx/lib/libpaddle_full_api_shared.so替换PaddleLite-linux-demo/libs/PaddleLite/arm64/lib/libpaddle_full_api_shared.so文件。
...
...
docs/demo_guides/cuda.md
浏览文件 @
12667f27
# PaddleLite使用CUDA预测部署
**注意**
: Lite CUDA仅作为Nvidia GPU加速库,支持模型有限,如有需要请使用
[
PaddleInference
](
https://paddle-inference.readthedocs.io/en/latest
)
。
Lite支持在x86_64,arm64架构上(如:TX2)进行CUDA的编译运行。
## 编译
...
...
docs/images/architecture.png
查看替换文件 @
e507e7b5
浏览文件 @
12667f27
149.8 KB
|
W:
|
H:
227.6 KB
|
W:
|
H:
2-up
Swipe
Onion skin
docs/images/workflow.png
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
12667f27
210.4 KB
docs/introduction/architecture.md
浏览文件 @
12667f27
...
...
@@ -5,23 +5,25 @@ Mobile 在这次升级为 Lite 架构, 侧重多硬件、高性能的支持,
-
引入 Type system,强化多硬件、量化方法、data layout 的混合调度能力
-
硬件细节隔离,通过不同编译开关,对支持的任何硬件可以自由插拔
-
引入 MIR(Machine IR) 的概念,强化带执行环境下的优化支持
-
优化期和执行期严格隔离,保证预测时
轻量和高效率
-
图优化模块和执行引擎实现了良好的解耦拆分,保证预测执行阶段的
轻量和高效率
架构图如下

<p
align=
"center"
><img
width=
"500"
src=
"https://raw.githubusercontent.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle-Lite/release/v2.6/docs/images/architecture.png"
/></p>
##
编译期和执行期严格
隔离设计
##
模型优化阶段和预测执行阶段的
隔离设计
-
compile time 优化完毕可以将优化信息存储到模型中;execution time 载入并执行
-
两套 API 及对应的预测lib,满足不同场景
-
`CxxPredictor`
打包了
`Compile Time`
和
`Execution Time`
,可以 runtime 在具体硬件上做分析和优化,得到最优效果
-
`MobilePredictor`
只打包
`Execution Time`
,保持部署和执行的轻量
-
Analysis Phase为模型优化阶段,输入为Paddle的推理模型,通过Lite的模型加速和优化策略对计算图进行相关的优化分析,包含算子融合,计算裁剪,存储优化,量化精度转换、存储优化、Kernel优选等多类图优化手段。优化后的模型更轻量级,在相应的硬件上运行时耗费资源更少,并且执行速度也更快。
-
Execution Phase为预测执行阶段,输入为优化后的Lite模型,仅做模型加载和预测执行两步操作,支持极致的轻量级部署,无任何第三方依赖。
## `Execution Time` 轻量级设计和实现
Lite设计了两套 API 及对应的预测库,满足不同场景需求:
-
`CxxPredictor`
同时包含
`Analysis Phase`
和
`Execution Phase`
,支持一站式的预测任务,同时支持模型进行分析优化与预测执行任务,适用于对预测库大小不敏感的硬件场景。
-
`MobilePredictor`
只包含
`Execution Phase`
,保持预测部署和执行的轻量级和高性能,支持从内存或者文件中加载优化后的模型,并进行预测执行。
-
每个 batch 实际执行只包含两个步骤执行
-
`Op.InferShape`
## Execution Phase轻量级设计和实现
-
在预测执行阶段,每个 batch 实际执行只包含两个步骤执行
-
`OpLite.InferShape`
基于输入推断得到输出的维度
-
`Kernel.Run`
,Kernel 相关参数均使用指针提前确定,后续无查找或传参消耗
-
设计目标,执行时,只有 kernel 计算本身消耗
-
轻量级
`Op`
及
`Kernel`
设计,避免框架额外消耗
...
...
docs/introduction/support_model_list.md
浏览文件 @
12667f27
# 支持模型
目前已严格验证2
4
个模型的精度和性能,对视觉类模型做到了较为充分的支持,覆盖分类、检测和定位,包含了特色的OCR模型的支持,并在不断丰富中。
目前已严格验证2
8
个模型的精度和性能,对视觉类模型做到了较为充分的支持,覆盖分类、检测和定位,包含了特色的OCR模型的支持,并在不断丰富中。
| 类别 | 类别细分 | 模型 | 支持Int8 | 支持平台 |
|-|-|:-:|:-:|-:|
| CV | 分类 | mobilenetv1 | Y | ARM,X86,NPU,RKNPU,APU |
| CV | 分类 | mobilenetv2 | Y | ARM,X86,NPU |
| CV | 分类 | resnet18 | Y | ARM,NPU |
| CV | 分类 | resnet50 | Y | ARM,X86,NPU,XPU |
| CV | 分类 | mnasnet | | ARM,NPU |
| CV | 分类 | efficientnet | | ARM |
| CV | 分类 | squeezenetv1.1 | | ARM,NPU |
| CV | 分类 | ShufflenetV2 | Y | ARM |
| CV | 分类 | shufflenet | Y | ARM |
| CV | 分类 | inceptionv4 | Y | ARM,X86,NPU |
| CV | 分类 | vgg16 | Y | ARM |
| CV | 分类 | googlenet | Y | ARM,X86 |
| CV | 检测 | mobilenet_ssd | Y | ARM,NPU
*
|
| CV | 检测 | mobilenet_yolov3 | Y | ARM,NPU
*
|
| CV | 检测 | Faster RCNN | | ARM |
| CV | 检测 | Mask RCNN | | ARM |
| CV | 分割 | Deeplabv3 | Y | ARM |
| CV | 分割 | unet | | ARM |
| CV | 人脸 | facedetection | | ARM |
| CV | 人脸 | facebox | | ARM |
| CV | 人脸 | blazeface | Y | ARM |
| CV | 人脸 | mtcnn | | ARM |
| CV | OCR | ocr_attention | | ARM |
| NLP | 机器翻译 | transformer | | ARM,NPU
*
|
| 类别 | 类别细分 | 模型 | 支持平台 |
|-|-|:-|:-|
| CV | 分类 | mobilenetv1 | ARM,X86,NPU,RKNPU,APU |
| CV | 分类 | mobilenetv2 | ARM,X86,NPU |
| CV | 分类 | resnet18 | ARM,NPU |
| CV | 分类 | resnet50 | ARM,X86,NPU,XPU |
| CV | 分类 | mnasnet | ARM,NPU |
| CV | 分类 | efficientnet | ARM |
| CV | 分类 | squeezenetv1.1 | ARM,NPU |
| CV | 分类 | ShufflenetV2 | ARM |
| CV | 分类 | shufflenet | ARM |
| CV | 分类 | inceptionv4 | ARM,X86,NPU |
| CV | 分类 | vgg16 | ARM |
| CV | 分类 | vgg19 | XPU|
| CV | 分类 | googlenet | ARM,X86 |
| CV | 检测 | mobilenet_ssd | ARM,NPU
*
|
| CV | 检测 | mobilenet_yolov3 | ARM,NPU
*
|
| CV | 检测 | Faster RCNN | ARM |
| CV | 检测 | Mask RCNN | ARM |
| CV | 分割 | Deeplabv3 | ARM |
| CV | 分割 | unet | ARM |
| CV | 人脸 | facedetection | ARM |
| CV | 人脸 | facebox | ARM |
| CV | 人脸 | blazeface | ARM |
| CV | 人脸 | mtcnn | ARM |
| CV | OCR | ocr_attention | ARM |
| CV | GAN | CycleGAN | NPU |
| NLP | 机器翻译 | transformer | ARM,NPU
*
|
| NLP | 机器翻译 | BERT | XPU |
| NLP | 语义表示 | ERNIE | XPU |
>
**注意:** NPU* 代表ARM+NPU异构计算
**注意:**
NPU
*
代表ARM+NPU异构计算
docs/quick_start/tutorial.md
浏览文件 @
12667f27
...
...
@@ -2,51 +2,64 @@
Lite是一种轻量级、灵活性强、易于扩展的高性能的深度学习预测框架,它可以支持诸如ARM、OpenCL、NPU等等多种终端,同时拥有强大的图优化及预测加速能力。如果您希望将Lite框架集成到自己的项目中,那么只需要如下几步简单操作即可。
## 一. 准备模型
Lite框架目前支持的模型结构为
[
PaddlePaddle
](
https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle
)
深度学习框架产出的模型格式。因此,在您开始使用 Lite 框架前您需要准备一个由PaddlePaddle框架保存的模型。
如果您手中的模型是由诸如Caffe2、Tensorflow等框架产出的,那么我们推荐您使用
[
X2Paddle
](
https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/X2Paddle
)
工具进行模型格式转换。
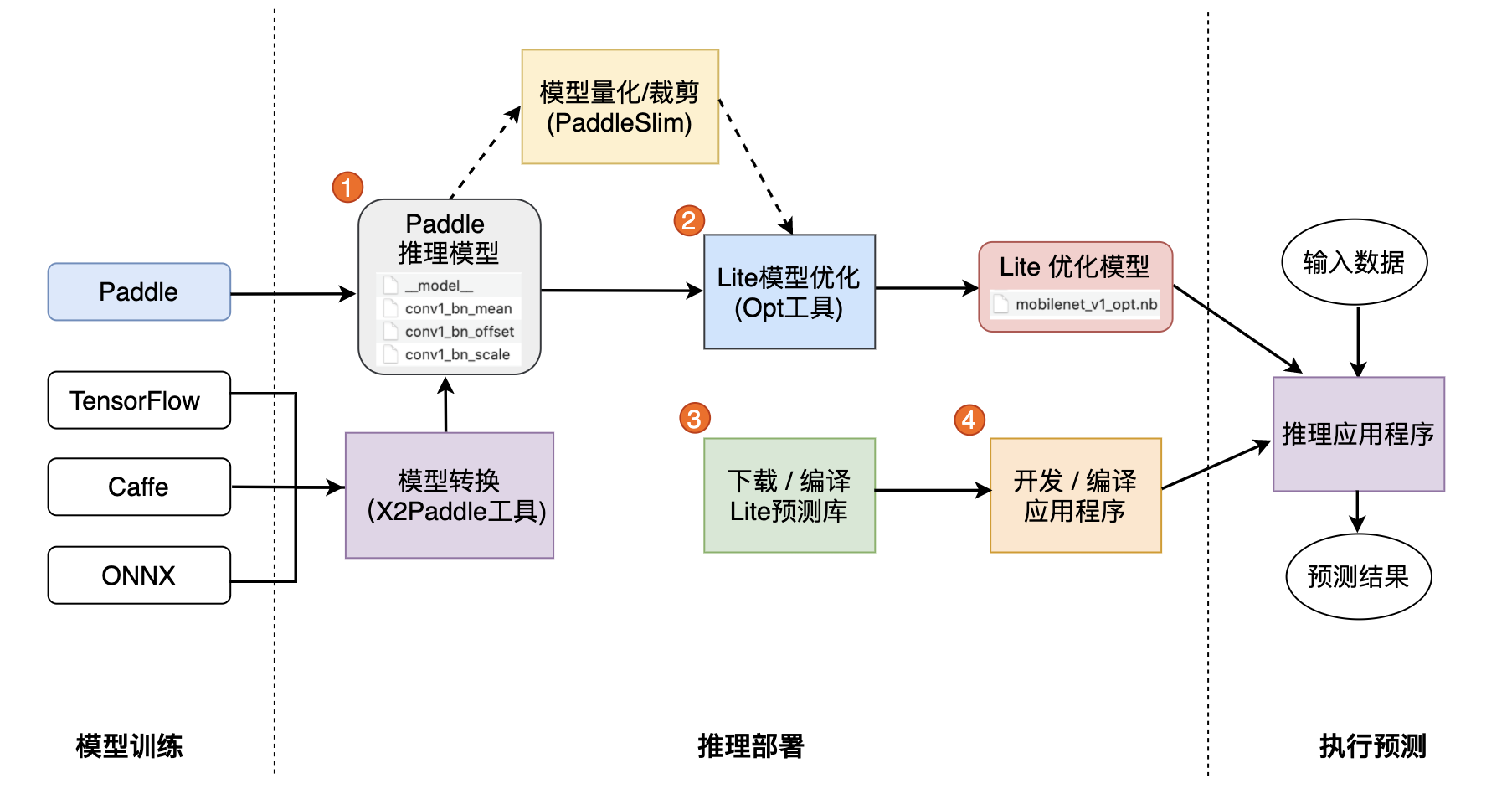
## 二. 模型优化
**一. 准备模型**
Lite框架拥有强大的加速、优化策略及实现,其中包含诸如量化、子图融合、Kernel优选等等优化手段,为了方便您使用这些优化策略,我们提供了
[
opt
](
../user_guides/model_optimize_tool
)
帮助您轻松进行模型优化。优化后的模型更轻量级,耗费资源更少,并且执行速度也更快。
Paddle Lite框架直接支持模型结构为
[
PaddlePaddle
](
https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle
)
深度学习框架产出的模型格式。目前PaddlePaddle用于推理的模型是通过
[
save_inference_model
](
https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/documentation/docs/zh/api_cn/io_cn/save_inference_model_cn.html#save-inference-model
)
这个API保存下来的。
如果您手中的模型是由诸如Caffe、Tensorflow、PyTorch等框架产出的,那么您可以使用
[
X2Paddle
](
https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/X2Paddle
)
工具将模型转换为PadddlePaddle格式。
opt的详细介绍,请您参考
[
模型优化方法
](
../user_guides/model_optimize_tool
)
。
**二. 模型优化**
下载opt工具后执行以下代码:
Paddle Lite框架拥有优秀的加速、优化策略及实现,包含量化、子图融合、Kernel优选等优化手段。优化后的模型更轻量级,耗费资源更少,并且执行速度也更快。
这些优化通过Paddle Lite提供的opt工具实现。opt工具还可以统计并打印出模型中的算子信息,并判断不同硬件平台下Paddle Lite的支持情况。您获取PaddlePaddle格式的模型之后,一般需要通该opt工具做模型优化。opt工具的下载和使用,请参考
[
模型优化方法
](
../user_guides/model_optimize_tool.html
)
。
```
shell
$
./opt
\
--model_dir
=
<model_param_dir>
\
--model_file
=
<model_path>
\
--param_file
=
<param_path>
\
--optimize_out_type
=(
protobuf|naive_buffer
)
\
--optimize_out
=
<output_optimize_model_dir>
\
--valid_targets
=(
arm|opencl|x86
)
```
**注意**
: 为了减少第三方库的依赖、提高Lite预测框架的通用性,在移动端使用Lite API您需要准备Naive Buffer存储格式的模型。
其中,optimize_out为您希望的优化模型的输出路径。optimize_out_type则可以指定输出模型的序列化方式,其目前支持Protobuf与Naive Buffer两种方式,其中Naive Buffer是一种更轻量级的序列化/反序列化实现。如果你需要使用Lite在mobile端进行预测,那么您需要设置optimize_out_type=naive_buffer。
**三. 下载或编译**
## 三. 使用Lite框架执行预测
Paddle Lite提供了Android/iOS/X86平台的官方Release预测库下载,我们优先推荐您直接下载
[
Paddle Lite预编译库
](
../quick_start/release_lib.html
)
。
您也可以根据目标平台选择对应的
[
源码编译方法
](
../source_compile/compile_env
)
。Paddle Lite 提供了源码编译脚本,位于
`lite/tools/`
文件夹下,只需要
[
准备环境
](
../source_compile/compile_env
)
和
[
调用编译脚本
](
../source_compile/compile_env
)
两个步骤即可一键编译得到目标平台的Paddle Lite预测库。
在上一节中,我们已经通过
`opt`
获取到了优化后的模型,使用优化模型进行预测也十分的简单。为了方便您的使用,Lite进行了良好的API设计,隐藏了大量您不需要投入时间研究的细节。您只需要简单的五步即可使用Lite在移动端完成预测(以C++ API进行说明):
**四. 开发应用程序**
Paddle Lite提供了C++、Java、Python三种API,只需简单五步即可完成预测(以C++ API为例):
1.
声明MobileConfig。在config中可以设置
**从文件加载模型**
也可以设置
**从memory加载模型**
。从文件加载模型需要声明模型文件路径,如
`config.set_model_from_file(FLAGS_model_file)`
;从memory加载模型方法现只支持加载优化后模型的naive buffer,实现方法为:
`void set_model_from_buffer(model_buffer) `
1.
声明
`MobileConfig`
,设置第二步优化后的模型文件路径,或选择从内存中加载模型
2.
创建
`Predictor`
,调用
`CreatePaddlePredictor`
接口,一行代码即可完成引擎初始化
3.
准备输入,通过
`predictor->GetInput(i)`
获取输入变量,并为其指定输入大小和输入值
4.
执行预测,只需要运行
`predictor->Run()`
一行代码,即可使用Lite框架完成预测执行
5.
获得输出,使用
`predictor->GetOutput(i)`
获取输出变量,并通过
`data<T>`
取得输出值
2.
创建Predictor。Predictor即为Lite框架的预测引擎,为了方便您的使用我们提供了
`CreatePaddlePredictor`
接口,你只需要简单的执行一行代码即可完成预测引擎的初始化,
`std::shared_ptr<PaddlePredictor> predictor = CreatePaddlePredictor(config)`
。
3.
准备输入。执行predictor->GetInput(0)您将会获得输入的第0个field,同样的,如果您的模型有多个输入,那您可以执行
`predictor->GetInput(i)`
来获取相应的输入变量。得到输入变量后您可以使用Resize方法指定其具体大小,并填入输入值。
4.
执行预测。您只需要执行
`predictor->Run()`
即可使用Lite框架完成预测。
5.
获取输出。与输入类似,您可以使用
`predictor->GetOutput(i)`
来获得输出的第i个变量。您可以通过其shape()方法获取输出变量的维度,通过
`data<T>()`
模板方法获取其输出值。
Paddle Lite提供了C++、Java、Python三种API的完整使用示例和开发说明文档,您可以参考示例中的说明快速了解使用方法,并集成到您自己的项目中去。
-
[
C++完整示例
](
cpp_demo.html
)
-
[
Java完整示例
](
java_demo.html
)
-
[
Python完整示例
](
python_demo.html
)
针对不同的硬件平台,Paddle Lite提供了各个平台的完整示例:
-
[
Android示例
](
../demo_guides/android_app_demo.html
)
-
[
iOS示例
](
../demo_guides/ios_app_demo.html
)
-
[
ARMLinux示例
](
../demo_guides/linux_arm_demo.html
)
-
[
X86示例
](
../demo_guides/x86.html
)
-
[
CUDA示例
](
../demo_guides/cuda.html
)
-
[
OpenCL示例
](
../demo_guides/opencl.html
)
-
[
FPGA示例
](
../demo_guides/fpga.html
)
-
[
华为NPU示例
](
../demo_guides/huawei_kirin_npu.html
)
-
[
百度XPU示例
](
../demo_guides/baidu_xpu.html
)
-
[
瑞芯微NPU示例
](
../demo_guides/rockchip_npu.html
)
-
[
联发科APU示例
](
../demo_guides/mediatek_apu.html
)
## 四. Lite API
您也可以下载以下基于Paddle-Lite开发的预测APK程序,安装到Andriod平台上,先睹为快:
为了方便您的使用,我们提供了C++、Java、Python三种API,并且提供了相应的api的完整使用示例:
[
C++完整示例
](
cpp_demo
)
、
[
Java完整示例
](
java_demo
)
、
[
Python完整示例
](
python_demo
)
,您可以参考示例中的说明快速了解C++/Java/Python的API使用方法,并集成到您自己的项目中去。需要说明的是,为了减少第三方库的依赖、提高Lite预测框架的通用性,在移动端使用Lite API您需要准备Naive Buffer存储格式的模型,具体方法可参考第2节
`模型优化`
。
-
[
图像分类
](
https://paddlelite-demo.bj.bcebos.com/apps/android/mobilenet_classification_demo.apk
)
-
[
目标检测
](
https://paddlelite-demo.bj.bcebos.com/apps/android/yolo_detection_demo.apk
)
-
[
口罩检测
](
https://paddlelite-demo.bj.bcebos.com/apps/android/mask_detection_demo.apk
)
-
[
人脸关键点
](
https://paddlelite-demo.bj.bcebos.com/apps/android/face_keypoints_detection_demo.apk
)
-
[
人像分割
](
https://paddlelite-demo.bj.bcebos.com/apps/android/human_segmentation_demo.apk
)
##
五.
测试工具
##
更多
测试工具
为了使您更好的了解并使用Lite框架,我们向有进一步使用需求的用户开放了
[
Debug工具
](
../user_guides/debug
)
和
[
Profile工具
](
../user_guides/debug
)
。Lite Model Debug Tool可以用来查找Lite框架与PaddlePaddle框架在执行预测时模型中的对应变量值是否有差异,进一步快速定位问题Op,方便复现与排查问题。Profile Monitor Tool可以帮助您了解每个Op的执行时间消耗,其会自动统计Op执行的次数,最长、最短、平均执行时间等等信息,为性能调优做一个基础参考。您可以通过
[
相关专题
](
../user_guides/debug
)
了解更多内容。
lite/backends/x86/math/context_project.h
浏览文件 @
12667f27
...
...
@@ -161,7 +161,7 @@ class ContextProjectFunctor {
sequence_width
});
if
(
up_pad
>
0
)
{
// add up pad
int
padding_rows
=
std
::
min
(
int
padding_rows
=
(
std
::
min
)
(
up_pad
,
static_cast
<
int
>
(
lod_level_0
[
i
+
1
]
-
lod_level_0
[
i
]));
for
(
int
k
=
0
;
k
<
padding_rows
;
++
k
)
{
...
...
@@ -180,10 +180,10 @@ class ContextProjectFunctor {
}
if
(
down_pad
>
0
)
{
// add down pad
int
down_pad_begin_row
=
std
::
max
(
0
,
(
sequence_height
-
context_start
-
context_length
)
+
1
)
+
(
std
::
max
)(
0
,
(
sequence_height
-
context_start
-
context_length
)
+
1
)
+
1
;
int
padding_begin
=
std
::
max
(
0
,
context_start
-
sequence_height
);
int
padding_begin
=
(
std
::
max
)
(
0
,
context_start
-
sequence_height
);
int
padding_size
=
sequence_height
-
context_start
>=
context_length
?
1
...
...
lite/backends/x86/math/pooling.cc
浏览文件 @
12667f27
...
...
@@ -67,8 +67,8 @@ class Pool2dFunctor<lite::TargetType::kX86, PoolProcess, T> {
hend
=
AdaptEndIndex
(
ph
,
input_height
,
output_height
);
}
else
{
hstart
=
ph
*
stride_height
-
padding_height
;
hend
=
std
::
min
(
hstart
+
ksize_height
,
input_height
);
hstart
=
std
::
max
(
hstart
,
0
);
hend
=
(
std
::
min
)
(
hstart
+
ksize_height
,
input_height
);
hstart
=
(
std
::
max
)
(
hstart
,
0
);
}
for
(
int
pw
=
0
;
pw
<
output_width
;
++
pw
)
{
if
(
adaptive
)
{
...
...
@@ -76,8 +76,8 @@ class Pool2dFunctor<lite::TargetType::kX86, PoolProcess, T> {
wend
=
AdaptEndIndex
(
pw
,
input_width
,
output_width
);
}
else
{
wstart
=
pw
*
stride_width
-
padding_width
;
wend
=
std
::
min
(
wstart
+
ksize_width
,
input_width
);
wstart
=
std
::
max
(
wstart
,
0
);
wend
=
(
std
::
min
)
(
wstart
+
ksize_width
,
input_width
);
wstart
=
(
std
::
max
)
(
wstart
,
0
);
}
T
ele
=
pool_process
.
initial
();
...
...
@@ -150,8 +150,8 @@ class Pool2dGradFunctor<lite::TargetType::kX86, PoolProcess, T> {
hend
=
AdaptEndIndex
(
ph
,
input_height
,
output_height
);
}
else
{
hstart
=
ph
*
stride_height
-
padding_height
;
hend
=
std
::
min
(
hstart
+
ksize_height
,
input_height
);
hstart
=
std
::
max
(
hstart
,
0
);
hend
=
(
std
::
min
)
(
hstart
+
ksize_height
,
input_height
);
hstart
=
(
std
::
max
)
(
hstart
,
0
);
}
for
(
int
pw
=
0
;
pw
<
output_width
;
++
pw
)
{
if
(
adaptive
)
{
...
...
@@ -159,8 +159,8 @@ class Pool2dGradFunctor<lite::TargetType::kX86, PoolProcess, T> {
wend
=
AdaptEndIndex
(
pw
,
input_width
,
output_width
);
}
else
{
wstart
=
pw
*
stride_width
-
padding_width
;
wend
=
std
::
min
(
wstart
+
ksize_width
,
input_width
);
wstart
=
std
::
max
(
wstart
,
0
);
wend
=
(
std
::
min
)
(
wstart
+
ksize_width
,
input_width
);
wstart
=
(
std
::
max
)
(
wstart
,
0
);
}
int
pool_size
=
(
exclusive
||
adaptive
)
?
(
hend
-
hstart
)
*
(
wend
-
wstart
)
...
...
@@ -228,12 +228,12 @@ class MaxPool2dGradFunctor<lite::TargetType::kX86, T> {
for
(
int
c
=
0
;
c
<
output_channels
;
++
c
)
{
for
(
int
ph
=
0
;
ph
<
output_height
;
++
ph
)
{
int
hstart
=
ph
*
stride_height
-
padding_height
;
int
hend
=
std
::
min
(
hstart
+
ksize_height
,
input_height
);
hstart
=
std
::
max
(
hstart
,
0
);
int
hend
=
(
std
::
min
)
(
hstart
+
ksize_height
,
input_height
);
hstart
=
(
std
::
max
)
(
hstart
,
0
);
for
(
int
pw
=
0
;
pw
<
output_width
;
++
pw
)
{
int
wstart
=
pw
*
stride_width
-
padding_width
;
int
wend
=
std
::
min
(
wstart
+
ksize_width
,
input_width
);
wstart
=
std
::
max
(
wstart
,
0
);
int
wend
=
(
std
::
min
)
(
wstart
+
ksize_width
,
input_width
);
wstart
=
(
std
::
max
)
(
wstart
,
0
);
bool
stop
=
false
;
for
(
int
h
=
hstart
;
h
<
hend
&&
!
stop
;
++
h
)
{
...
...
@@ -337,8 +337,8 @@ class Pool3dFunctor<lite::TargetType::kX86, PoolProcess, T> {
dend
=
AdaptEndIndex
(
pd
,
input_depth
,
output_depth
);
}
else
{
dstart
=
pd
*
stride_depth
-
padding_depth
;
dend
=
std
::
min
(
dstart
+
ksize_depth
,
input_depth
);
dstart
=
std
::
max
(
dstart
,
0
);
dend
=
(
std
::
min
)
(
dstart
+
ksize_depth
,
input_depth
);
dstart
=
(
std
::
max
)
(
dstart
,
0
);
}
for
(
int
ph
=
0
;
ph
<
output_height
;
++
ph
)
{
if
(
adaptive
)
{
...
...
@@ -346,8 +346,8 @@ class Pool3dFunctor<lite::TargetType::kX86, PoolProcess, T> {
hend
=
AdaptEndIndex
(
ph
,
input_height
,
output_height
);
}
else
{
hstart
=
ph
*
stride_height
-
padding_height
;
hend
=
std
::
min
(
hstart
+
ksize_height
,
input_height
);
hstart
=
std
::
max
(
hstart
,
0
);
hend
=
(
std
::
min
)
(
hstart
+
ksize_height
,
input_height
);
hstart
=
(
std
::
max
)
(
hstart
,
0
);
}
for
(
int
pw
=
0
;
pw
<
output_width
;
++
pw
)
{
if
(
adaptive
)
{
...
...
@@ -355,8 +355,8 @@ class Pool3dFunctor<lite::TargetType::kX86, PoolProcess, T> {
wend
=
AdaptEndIndex
(
pw
,
input_width
,
output_width
);
}
else
{
wstart
=
pw
*
stride_width
-
padding_width
;
wend
=
std
::
min
(
wstart
+
ksize_width
,
input_width
);
wstart
=
std
::
max
(
wstart
,
0
);
wend
=
(
std
::
min
)
(
wstart
+
ksize_width
,
input_width
);
wstart
=
(
std
::
max
)
(
wstart
,
0
);
}
int
output_idx
=
(
pd
*
output_height
+
ph
)
*
output_width
+
pw
;
T
ele
=
pool_process
.
initial
();
...
...
@@ -441,8 +441,8 @@ class Pool3dGradFunctor<lite::TargetType::kX86, PoolProcess, T> {
dend
=
AdaptEndIndex
(
pd
,
input_depth
,
output_depth
);
}
else
{
dstart
=
pd
*
stride_depth
-
padding_depth
;
dend
=
std
::
min
(
dstart
+
ksize_depth
,
input_depth
);
dstart
=
std
::
max
(
dstart
,
0
);
dend
=
(
std
::
min
)
(
dstart
+
ksize_depth
,
input_depth
);
dstart
=
(
std
::
max
)
(
dstart
,
0
);
}
for
(
int
ph
=
0
;
ph
<
output_height
;
++
ph
)
{
if
(
adaptive
)
{
...
...
@@ -450,8 +450,8 @@ class Pool3dGradFunctor<lite::TargetType::kX86, PoolProcess, T> {
hend
=
AdaptEndIndex
(
ph
,
input_height
,
output_height
);
}
else
{
hstart
=
ph
*
stride_height
-
padding_height
;
hend
=
std
::
min
(
hstart
+
ksize_height
,
input_height
);
hstart
=
std
::
max
(
hstart
,
0
);
hend
=
(
std
::
min
)
(
hstart
+
ksize_height
,
input_height
);
hstart
=
(
std
::
max
)
(
hstart
,
0
);
}
for
(
int
pw
=
0
;
pw
<
output_width
;
++
pw
)
{
if
(
adaptive
)
{
...
...
@@ -459,8 +459,8 @@ class Pool3dGradFunctor<lite::TargetType::kX86, PoolProcess, T> {
wend
=
AdaptEndIndex
(
pw
,
input_width
,
output_width
);
}
else
{
wstart
=
pw
*
stride_width
-
padding_width
;
wend
=
std
::
min
(
wstart
+
ksize_width
,
input_width
);
wstart
=
std
::
max
(
wstart
,
0
);
wend
=
(
std
::
min
)
(
wstart
+
ksize_width
,
input_width
);
wstart
=
(
std
::
max
)
(
wstart
,
0
);
}
int
pool_size
=
...
...
@@ -540,16 +540,16 @@ class MaxPool3dGradFunctor<lite::TargetType::kX86, T> {
for
(
int
c
=
0
;
c
<
output_channels
;
++
c
)
{
for
(
int
pd
=
0
;
pd
<
output_depth
;
++
pd
)
{
int
dstart
=
pd
*
stride_depth
-
padding_depth
;
int
dend
=
std
::
min
(
dstart
+
ksize_depth
,
input_depth
);
dstart
=
std
::
max
(
dstart
,
0
);
int
dend
=
(
std
::
min
)
(
dstart
+
ksize_depth
,
input_depth
);
dstart
=
(
std
::
max
)
(
dstart
,
0
);
for
(
int
ph
=
0
;
ph
<
output_height
;
++
ph
)
{
int
hstart
=
ph
*
stride_height
-
padding_height
;
int
hend
=
std
::
min
(
hstart
+
ksize_height
,
input_height
);
hstart
=
std
::
max
(
hstart
,
0
);
int
hend
=
(
std
::
min
)
(
hstart
+
ksize_height
,
input_height
);
hstart
=
(
std
::
max
)
(
hstart
,
0
);
for
(
int
pw
=
0
;
pw
<
output_width
;
++
pw
)
{
int
wstart
=
pw
*
stride_width
-
padding_width
;
int
wend
=
std
::
min
(
wstart
+
ksize_width
,
input_width
);
wstart
=
std
::
max
(
wstart
,
0
);
int
wend
=
(
std
::
min
)
(
wstart
+
ksize_width
,
input_width
);
wstart
=
(
std
::
max
)
(
wstart
,
0
);
bool
stop
=
false
;
for
(
int
d
=
dstart
;
d
<
dend
&&
!
stop
;
++
d
)
{
for
(
int
h
=
hstart
;
h
<
hend
&&
!
stop
;
++
h
)
{
...
...
@@ -651,8 +651,8 @@ class MaxPool2dWithIndexFunctor<lite::TargetType::kX86, T1, T2> {
hend
=
AdaptEndIndex
(
ph
,
input_height
,
output_height
);
}
else
{
hstart
=
ph
*
stride_height
-
padding_height
;
hend
=
std
::
min
(
hstart
+
ksize_height
,
input_height
);
hstart
=
std
::
max
(
hstart
,
0
);
hend
=
(
std
::
min
)
(
hstart
+
ksize_height
,
input_height
);
hstart
=
(
std
::
max
)
(
hstart
,
0
);
}
for
(
int
pw
=
0
;
pw
<
output_width
;
++
pw
)
{
if
(
adaptive
)
{
...
...
@@ -660,8 +660,8 @@ class MaxPool2dWithIndexFunctor<lite::TargetType::kX86, T1, T2> {
wend
=
AdaptEndIndex
(
pw
,
input_width
,
output_width
);
}
else
{
wstart
=
pw
*
stride_width
-
padding_width
;
wend
=
std
::
min
(
wstart
+
ksize_width
,
input_width
);
wstart
=
std
::
max
(
wstart
,
0
);
wend
=
(
std
::
min
)
(
wstart
+
ksize_width
,
input_width
);
wstart
=
(
std
::
max
)
(
wstart
,
0
);
}
T1
ele
=
static_cast
<
T1
>
(
-
FLT_MAX
);
...
...
@@ -794,8 +794,8 @@ class MaxPool3dWithIndexFunctor<lite::TargetType::kX86, T1, T2> {
dend
=
AdaptEndIndex
(
pd
,
input_depth
,
output_depth
);
}
else
{
dstart
=
pd
*
stride_depth
-
padding_depth
;
dend
=
std
::
min
(
dstart
+
ksize_depth
,
input_depth
);
dstart
=
std
::
max
(
dstart
,
0
);
dend
=
(
std
::
min
)
(
dstart
+
ksize_depth
,
input_depth
);
dstart
=
(
std
::
max
)
(
dstart
,
0
);
}
for
(
int
ph
=
0
;
ph
<
output_height
;
++
ph
)
{
if
(
adaptive
)
{
...
...
@@ -803,8 +803,8 @@ class MaxPool3dWithIndexFunctor<lite::TargetType::kX86, T1, T2> {
hend
=
AdaptEndIndex
(
ph
,
input_height
,
output_height
);
}
else
{
hstart
=
ph
*
stride_height
-
padding_height
;
hend
=
std
::
min
(
hstart
+
ksize_height
,
input_height
);
hstart
=
std
::
max
(
hstart
,
0
);
hend
=
(
std
::
min
)
(
hstart
+
ksize_height
,
input_height
);
hstart
=
(
std
::
max
)
(
hstart
,
0
);
}
for
(
int
pw
=
0
;
pw
<
output_width
;
++
pw
)
{
if
(
adaptive
)
{
...
...
@@ -812,8 +812,8 @@ class MaxPool3dWithIndexFunctor<lite::TargetType::kX86, T1, T2> {
wend
=
AdaptEndIndex
(
pw
,
input_width
,
output_width
);
}
else
{
wstart
=
pw
*
stride_width
-
padding_width
;
wend
=
std
::
min
(
wstart
+
ksize_width
,
input_width
);
wstart
=
std
::
max
(
wstart
,
0
);
wend
=
(
std
::
min
)
(
wstart
+
ksize_width
,
input_width
);
wstart
=
(
std
::
max
)
(
wstart
,
0
);
}
int
output_idx
=
(
pd
*
output_height
+
ph
)
*
output_width
+
pw
;
...
...
lite/backends/x86/math/sequence_padding.h
浏览文件 @
12667f27
...
...
@@ -35,7 +35,7 @@ inline static uint64_t MaximumSequenceLength(
uint64_t
seq_num
=
seq_offset
.
size
()
-
1
;
uint64_t
max_seq_len
=
0
;
for
(
size_t
i
=
0
;
i
<
seq_num
;
++
i
)
{
max_seq_len
=
std
::
max
(
max_seq_len
,
seq_offset
[
i
+
1
]
-
seq_offset
[
i
]);
max_seq_len
=
(
std
::
max
)
(
max_seq_len
,
seq_offset
[
i
+
1
]
-
seq_offset
[
i
]);
}
return
max_seq_len
;
}
...
...
lite/backends/x86/parallel.h
浏览文件 @
12667f27
...
...
@@ -26,7 +26,7 @@ namespace x86 {
static
void
SetNumThreads
(
int
num_threads
)
{
#ifdef PADDLE_WITH_MKLML
int
real_num_threads
=
std
::
max
(
num_threads
,
1
);
int
real_num_threads
=
(
std
::
max
)
(
num_threads
,
1
);
x86
::
MKL_Set_Num_Threads
(
real_num_threads
);
omp_set_num_threads
(
real_num_threads
);
#endif
...
...
@@ -52,14 +52,14 @@ static inline void RunParallelFor(const int64_t begin,
}
#ifdef PADDLE_WITH_MKLML
int64_t
num_threads
=
std
::
min
(
GetMaxThreads
(),
end
-
begin
);
int64_t
num_threads
=
(
std
::
min
)
(
GetMaxThreads
(),
end
-
begin
);
if
(
num_threads
>
1
)
{
#pragma omp parallel num_threads(num_threads)
{
int64_t
tid
=
omp_get_thread_num
();
int64_t
chunk_size
=
(
end
-
begin
+
num_threads
-
1
)
/
num_threads
;
int64_t
begin_tid
=
begin
+
tid
*
chunk_size
;
f
(
begin_tid
,
std
::
min
(
end
,
chunk_size
+
begin_tid
));
f
(
begin_tid
,
(
std
::
min
)
(
end
,
chunk_size
+
begin_tid
));
}
return
;
}
...
...
lite/core/mir/memory_optimize_pass.cc
浏览文件 @
12667f27
...
...
@@ -151,7 +151,7 @@ void MemoryOptimizePass::CollectLifeCycleByDevice(
int
cur_life
=
(
*
lifecycles
)[
TargetToStr
(
target_type
)][
var_name
].
second
;
(
*
lifecycles
)[
TargetToStr
(
target_type
)][
var_name
].
second
=
std
::
max
(
max_lifecycle_
,
cur_life
);
(
std
::
max
)
(
max_lifecycle_
,
cur_life
);
}
}
++
max_lifecycle_
;
...
...
lite/core/mir/static_kernel_pick_pass.h
浏览文件 @
12667f27
...
...
@@ -62,7 +62,7 @@ class StaticKernelPickPass : public mir::StmtPass {
float
final_score
{
-
1.
};
Place
winner_place
{
places
[
0
]};
const
int
kMax
=
std
::
numeric_limits
<
core
::
KernelPickFactor
::
value_type
>::
max
();
(
std
::
numeric_limits
<
core
::
KernelPickFactor
::
value_type
>::
max
)
();
size_t
place_size
=
places
.
size
();
// NOTE: We compare kernel's place with place in valid_places to select the
...
...
lite/core/mir/subgraph/subgraph_detector.cc
浏览文件 @
12667f27
...
...
@@ -463,6 +463,38 @@ void SubgraphFuser::InsertNewNode(SSAGraph *graph,
idata_var_names
);
subgraph_op_desc
.
SetAttr
<
std
::
vector
<
std
::
string
>>
(
"output_data_names"
,
odata_var_names
);
// Set input/output scale values of input/output var nodes for
// type_precision_cast_pass.
std
::
vector
<
float
>
input_data_scales
;
std
::
vector
<
float
>
output_data_scales
;
for
(
auto
&
var_node
:
idata_var_nodes
)
{
auto
any_op_node
=
var_node
->
outlinks
.
front
();
CHECK
(
any_op_node
->
IsStmt
());
auto
&
any_inst
=
any_op_node
->
AsStmt
();
if
(
any_inst
.
op_info
()
->
HasAttr
(
"input_scale"
))
{
input_data_scales
.
push_back
(
any_inst
.
op_info
()
->
GetAttr
<
float
>
(
"input_scale"
));
}
}
for
(
auto
&
var_node
:
odata_var_nodes
)
{
auto
any_op_node
=
var_node
->
inlinks
.
front
();
CHECK
(
any_op_node
->
IsStmt
());
auto
&
any_inst
=
any_op_node
->
AsStmt
();
if
(
any_inst
.
op_info
()
->
HasAttr
(
"output_scale"
))
{
output_data_scales
.
push_back
(
any_inst
.
op_info
()
->
GetAttr
<
float
>
(
"output_scale"
));
}
}
if
(
input_data_scales
.
size
()
>
0
)
{
subgraph_op_desc
.
SetAttr
<
std
::
vector
<
float
>>
(
"input_data_scales"
,
input_data_scales
);
}
if
(
output_data_scales
.
size
()
>
0
)
{
subgraph_op_desc
.
SetAttr
<
std
::
vector
<
float
>>
(
"output_data_scales"
,
output_data_scales
);
}
// Set all of the inputs and outputs to the target subgraph op
// To prevent vars are removed in RuntimeProgram::UpdateVarsOfProgram()
std
::
vector
<
std
::
string
>
input_var_names
;
...
...
lite/kernels/apu/bridges/softmax_op.cc
浏览文件 @
12667f27
...
...
@@ -104,7 +104,7 @@ int SoftmaxConverter(void* ctx, OpLite* op, KernelBase* kernel) {
// Add out operand
NeuronOperandType
outType
;
outType
.
type
=
NEURON_TENSOR_QUANT8_ASYMM
;
outType
.
scale
=
out_scale
/
127
;
outType
.
scale
=
out_scale
;
outType
.
zeroPoint
=
128
;
outType
.
dimensionCount
=
x_dims
.
size
();
outType
.
dimensions
=
&
dims_x
[
0
];
...
...
lite/kernels/host/crf_decoding_compute.h
浏览文件 @
12667f27
...
...
@@ -52,7 +52,7 @@ void Decode(const Tensor& emission_weights,
for
(
int
k
=
1
;
k
<
seq_len
;
++
k
)
{
for
(
int
i
=
0
;
i
<
tag_num
;
++
i
)
{
T
max_score
=
-
std
::
numeric_limits
<
T
>::
max
();
T
max_score
=
-
(
std
::
numeric_limits
<
T
>::
max
)
();
int
max_j
=
0
;
for
(
size_t
j
=
0
;
j
<
tag_num
;
++
j
)
{
T
score
=
alpha_value
[(
k
-
1
)
*
tag_num
+
j
]
+
...
...
@@ -67,7 +67,7 @@ void Decode(const Tensor& emission_weights,
}
}
T
max_score
=
-
std
::
numeric_limits
<
T
>::
max
();
T
max_score
=
-
(
std
::
numeric_limits
<
T
>::
max
)
();
int
max_i
=
0
;
for
(
size_t
i
=
0
;
i
<
tag_num
;
++
i
)
{
T
score
=
alpha_value
[(
seq_len
-
1
)
*
tag_num
+
i
]
+
w
[
tag_num
+
i
];
...
...
lite/kernels/host/multiclass_nms_compute.cc
浏览文件 @
12667f27
...
...
@@ -72,10 +72,10 @@ static T JaccardOverlap(const T* box1, const T* box2, const bool normalized) {
box2
[
3
]
<
box1
[
1
])
{
return
static_cast
<
T
>
(
0.
);
}
else
{
const
T
inter_xmin
=
std
::
max
(
box1
[
0
],
box2
[
0
]);
const
T
inter_ymin
=
std
::
max
(
box1
[
1
],
box2
[
1
]);
const
T
inter_xmax
=
std
::
min
(
box1
[
2
],
box2
[
2
]);
const
T
inter_ymax
=
std
::
min
(
box1
[
3
],
box2
[
3
]);
const
T
inter_xmin
=
(
std
::
max
)
(
box1
[
0
],
box2
[
0
]);
const
T
inter_ymin
=
(
std
::
max
)
(
box1
[
1
],
box2
[
1
]);
const
T
inter_xmax
=
(
std
::
min
)
(
box1
[
2
],
box2
[
2
]);
const
T
inter_ymax
=
(
std
::
min
)
(
box1
[
3
],
box2
[
3
]);
T
norm
=
normalized
?
static_cast
<
T
>
(
0.
)
:
static_cast
<
T
>
(
1.
);
T
inter_w
=
inter_xmax
-
inter_xmin
+
norm
;
T
inter_h
=
inter_ymax
-
inter_ymin
+
norm
;
...
...
lite/kernels/host/print_compute.cc
浏览文件 @
12667f27
...
...
@@ -128,7 +128,7 @@ class TensorFormatter {
void
FormatData
(
const
Tensor
&
print_tensor
,
std
::
stringstream
&
log_stream
)
{
int64_t
print_size
=
summarize_
==
-
1
?
print_tensor
.
numel
()
:
std
::
min
(
summarize_
,
print_tensor
.
numel
());
:
(
std
::
min
)
(
summarize_
,
print_tensor
.
numel
());
const
T
*
data
=
print_tensor
.
data
<
T
>
();
// Always kHost, so unnessary to
// copy the data from device
log_stream
<<
" - data: ["
;
...
...
lite/kernels/host/retinanet_detection_output_compute.cc
浏览文件 @
12667f27
...
...
@@ -83,10 +83,10 @@ static inline T JaccardOverlap(const std::vector<T>& box1,
box2
[
3
]
<
box1
[
1
])
{
return
static_cast
<
T
>
(
0.
);
}
else
{
const
T
inter_xmin
=
std
::
max
(
box1
[
0
],
box2
[
0
]);
const
T
inter_ymin
=
std
::
max
(
box1
[
1
],
box2
[
1
]);
const
T
inter_xmax
=
std
::
min
(
box1
[
2
],
box2
[
2
]);
const
T
inter_ymax
=
std
::
min
(
box1
[
3
],
box2
[
3
]);
const
T
inter_xmin
=
(
std
::
max
)
(
box1
[
0
],
box2
[
0
]);
const
T
inter_ymin
=
(
std
::
max
)
(
box1
[
1
],
box2
[
1
]);
const
T
inter_xmax
=
(
std
::
min
)
(
box1
[
2
],
box2
[
2
]);
const
T
inter_ymax
=
(
std
::
min
)
(
box1
[
3
],
box2
[
3
]);
T
norm
=
normalized
?
static_cast
<
T
>
(
0.
)
:
static_cast
<
T
>
(
1.
);
T
inter_w
=
inter_xmax
-
inter_xmin
+
norm
;
T
inter_h
=
inter_ymax
-
inter_ymin
+
norm
;
...
...
@@ -183,10 +183,10 @@ void DeltaScoreToPrediction(
pred_box_xmax
=
pred_box_xmax
/
im_scale
;
pred_box_ymax
=
pred_box_ymax
/
im_scale
;
pred_box_xmin
=
std
::
max
(
std
::
min
(
pred_box_xmin
,
im_width
-
1
),
zero
);
pred_box_ymin
=
std
::
max
(
std
::
min
(
pred_box_ymin
,
im_height
-
1
),
zero
);
pred_box_xmax
=
std
::
max
(
std
::
min
(
pred_box_xmax
,
im_width
-
1
),
zero
);
pred_box_ymax
=
std
::
max
(
std
::
min
(
pred_box_ymax
,
im_height
-
1
),
zero
);
pred_box_xmin
=
(
std
::
max
)((
std
::
min
)
(
pred_box_xmin
,
im_width
-
1
),
zero
);
pred_box_ymin
=
(
std
::
max
)((
std
::
min
)
(
pred_box_ymin
,
im_height
-
1
),
zero
);
pred_box_xmax
=
(
std
::
max
)((
std
::
min
)
(
pred_box_xmax
,
im_width
-
1
),
zero
);
pred_box_ymax
=
(
std
::
max
)((
std
::
min
)
(
pred_box_ymax
,
im_height
-
1
),
zero
);
std
::
vector
<
T
>
one_pred
;
one_pred
.
push_back
(
pred_box_xmin
);
...
...
lite/kernels/x86/elementwise_op_function.h
浏览文件 @
12667f27
...
...
@@ -74,7 +74,7 @@ inline void get_mid_dims(const lite::DDim &x_dims,
for
(
size_t
j
=
0
;
j
<
i
;
++
j
)
{
(
*
pre
)
*=
y_dims
[
j
];
}
*
n
=
std
::
max
(
x_dims
[
i
+
axis
],
y_dims
[
i
]);
*
n
=
(
std
::
max
)
(
x_dims
[
i
+
axis
],
y_dims
[
i
]);
*
mid_flag
=
1
;
mid
=
i
;
break
;
...
...
lite/kernels/x86/sequence_arithmetic_compute.h
浏览文件 @
12667f27
...
...
@@ -55,7 +55,7 @@ class SequenceArithmeticCompute
auto
input_x
=
x_data
+
x_seq_offset
[
i
]
*
inner_size
;
auto
input_y
=
y_data
+
y_seq_offset
[
i
]
*
inner_size
;
auto
t_out
=
out_data
+
x_seq_offset
[
i
]
*
inner_size
;
int
len
=
std
::
min
(
len_x
,
len_y
);
int
len
=
(
std
::
min
)
(
len_x
,
len_y
);
for
(
int
j
=
0
;
j
<
len
;
j
++
)
{
t_out
[
j
]
=
input_x
[
j
]
+
input_y
[
j
];
}
...
...
@@ -73,7 +73,7 @@ class SequenceArithmeticCompute
auto
input_x
=
x_data
+
x_seq_offset
[
i
]
*
inner_size
;
auto
input_y
=
y_data
+
y_seq_offset
[
i
]
*
inner_size
;
auto
t_out
=
out_data
+
x_seq_offset
[
i
]
*
inner_size
;
int
len
=
std
::
min
(
len_x
,
len_y
);
int
len
=
(
std
::
min
)
(
len_x
,
len_y
);
for
(
int
j
=
0
;
j
<
len
;
j
++
)
{
t_out
[
j
]
=
input_x
[
j
]
-
input_y
[
j
];
}
...
...
@@ -91,7 +91,7 @@ class SequenceArithmeticCompute
auto
input_x
=
x_data
+
x_seq_offset
[
i
]
*
inner_size
;
auto
input_y
=
y_data
+
y_seq_offset
[
i
]
*
inner_size
;
auto
t_out
=
out_data
+
x_seq_offset
[
i
]
*
inner_size
;
int
len
=
std
::
min
(
len_x
,
len_y
);
int
len
=
(
std
::
min
)
(
len_x
,
len_y
);
for
(
int
j
=
0
;
j
<
len
;
j
++
)
{
t_out
[
j
]
=
input_x
[
j
]
*
input_y
[
j
];
}
...
...
lite/kernels/x86/sequence_conv_compute.h
浏览文件 @
12667f27
...
...
@@ -49,8 +49,8 @@ class SequenceConvCompute : public KernelLite<TARGET(kX86), PRECISION(kFloat)> {
bool
padding_trainable
=
false
;
const
Tensor
*
padding_data
=
nullptr
;
int
up_pad
=
std
::
max
(
0
,
-
context_start
);
int
down_pad
=
std
::
max
(
0
,
context_start
+
context_length
-
1
);
int
up_pad
=
(
std
::
max
)
(
0
,
-
context_start
);
int
down_pad
=
(
std
::
max
)
(
0
,
context_start
+
context_length
-
1
);
auto
sequence_width
=
static_cast
<
int64_t
>
(
in
->
dims
()[
1
]);
std
::
vector
<
int64_t
>
col_shape
{
in
->
dims
()[
0
],
...
...
lite/kernels/x86/slice_compute.h
浏览文件 @
12667f27
...
...
@@ -102,9 +102,9 @@ void slice_compute(const lite::Tensor* in,
start
=
starts
[
i
]
<
0
?
(
starts
[
i
]
+
dim_value
)
:
starts
[
i
];
end
=
ends
[
i
]
<
0
?
(
ends
[
i
]
+
dim_value
)
:
ends
[
i
];
start
=
std
::
max
(
start
,
0
);
end
=
std
::
max
(
end
,
0
);
end
=
std
::
min
(
end
,
dim_value
);
start
=
(
std
::
max
)
(
start
,
0
);
end
=
(
std
::
max
)
(
end
,
0
);
end
=
(
std
::
min
)
(
end
,
dim_value
);
CHECK_GT
(
end
,
start
)
<<
"end should greater than start"
;
out_dims
[
axes
[
i
]]
=
end
-
start
;
}
...
...
@@ -172,7 +172,7 @@ void slice_compute(const lite::Tensor* in,
if
(
start
<
0
)
{
start
=
(
start
+
in_dims
[
axes
[
i
]]);
}
start
=
std
::
max
(
start
,
0
);
start
=
(
std
::
max
)
(
start
,
0
);
offsets
[
axes
[
i
]]
=
start
;
}
auto
in_t
=
...
...
lite/model_parser/model_parser.cc
浏览文件 @
12667f27
...
...
@@ -390,7 +390,7 @@ void TensorToStream(std::ostream &os, const lite::Tensor &tensor) {
}
{
// the 3rd field, tensor data
uint64_t
size
=
tensor
.
memory_size
();
CHECK_LT
(
size
,
std
::
numeric_limits
<
std
::
streamsize
>::
max
())
CHECK_LT
(
size
,
(
std
::
numeric_limits
<
std
::
streamsize
>::
max
)
())
<<
"Index overflow when writing tensor"
;
#ifdef LITE_WITH_CUDA
...
...
@@ -460,7 +460,7 @@ void SetParamInfoNaive(naive_buffer::ParamDesc *param_desc,
}
desc
.
SetDim
(
tensor
.
dims
().
Vectorize
());
uint64_t
size
=
tensor
.
memory_size
();
CHECK_LT
(
size
,
std
::
numeric_limits
<
std
::
streamsize
>::
max
())
CHECK_LT
(
size
,
(
std
::
numeric_limits
<
std
::
streamsize
>::
max
)
())
<<
"Index overflow when writing tensor"
;
#ifdef LITE_WITH_CUDA
...
...
lite/operators/conv_op.cc
浏览文件 @
12667f27
...
...
@@ -62,7 +62,7 @@ void UpdatePaddingAndDilation(std::vector<int>* paddings,
if
(
padding_algorithm
==
"SAME"
)
{
for
(
size_t
i
=
0
;
i
<
strides
.
size
();
++
i
)
{
int
out_size
=
(
data_dims
[
i
+
2
]
+
strides
[
i
]
-
1
)
/
strides
[
i
];
int
pad_sum
=
std
::
max
(
int
pad_sum
=
(
std
::
max
)
(
(
out_size
-
1
)
*
strides
[
i
]
+
ksize
[
i
+
2
]
-
data_dims
[
i
+
2
],
(
int64_t
)
0
);
int
pad_0
=
pad_sum
/
2
;
...
...
lite/operators/elementwise_ops.cc
浏览文件 @
12667f27
...
...
@@ -75,7 +75,7 @@ bool ElementwiseOp::InferShapeImpl() const {
if
(
x_dims_array
[
i
]
==
-
1
||
y_dims_array
[
i
]
==
-
1
)
{
out_dims_array
[
i
]
=
-
1
;
}
else
{
out_dims_array
[
i
]
=
std
::
max
(
x_dims_array
[
i
],
y_dims_array
[
i
]);
out_dims_array
[
i
]
=
(
std
::
max
)
(
x_dims_array
[
i
],
y_dims_array
[
i
]);
}
}
param_
.
Out
->
Resize
(
DDim
(
out_dims_array
));
...
...
lite/operators/pool_op.h
浏览文件 @
12667f27
...
...
@@ -128,8 +128,8 @@ inline void UpdatePadding(std::vector<int> *paddings,
for
(
size_t
i
=
0
;
i
<
strides
.
size
();
++
i
)
{
int
out_size
=
(
data_dims
[
i
+
2
]
+
strides
[
i
]
-
1
)
/
strides
[
i
];
int
pad_sum
=
std
::
max
((
out_size
-
1
)
*
strides
[
i
]
+
ksize
[
i
]
-
data_dims
[
i
+
2
],
(
int64_t
)
0
);
(
std
::
max
)
((
out_size
-
1
)
*
strides
[
i
]
+
ksize
[
i
]
-
data_dims
[
i
+
2
],
(
int64_t
)
0
);
int
pad_0
=
pad_sum
/
2
;
int
pad_1
=
pad_sum
-
pad_0
;
*
(
paddings
->
begin
()
+
i
*
2
)
=
pad_0
;
...
...
lite/operators/slice_op.cc
浏览文件 @
12667f27
...
...
@@ -51,9 +51,9 @@ bool SliceOp::InferShapeImpl() const {
if
(
dim_value
>
0
)
{
start
=
starts
[
i
]
<
0
?
(
starts
[
i
]
+
dim_value
)
:
starts
[
i
];
end
=
ends
[
i
]
<
0
?
(
ends
[
i
]
+
dim_value
)
:
ends
[
i
];
start
=
std
::
max
(
start
,
0
);
end
=
std
::
max
(
end
,
0
);
end
=
std
::
min
(
end
,
dim_value
);
start
=
(
std
::
max
)
(
start
,
0
);
end
=
(
std
::
max
)
(
end
,
0
);
end
=
(
std
::
min
)
(
end
,
dim_value
);
out_dims
[
axes
[
i
]]
=
end
-
start
;
}
}
...
...
lite/tools/build_windows.bat
浏览文件 @
12667f27
...
...
@@ -70,7 +70,7 @@ cd "%build_directory%"
call
"
%vcvarsall_dir%
"
amd64
msbuild
/m /p
:Configuration
=
Release
lite
\publish_inference.vcxproj
>
mylog
.txt
2
>&
1
msbuild
/m /p
:Configuration
=
Release
lite
\publish_inference.vcxproj
goto
:eof
:prepare
_thirdparty
...
...
lite/utils/string.h
浏览文件 @
12667f27
...
...
@@ -60,13 +60,6 @@ static std::string to_string(const T& v) {
return
ss
.
str
();
}
static
std
::
string
to_string
(
int
index
)
{
const
int
BUFFER_LENGTH
=
15
;
char
buffer
[
BUFFER_LENGTH
];
snprintf
(
buffer
,
sizeof
(
buffer
),
"%d"
,
index
);
return
std
::
string
(
buffer
);
}
template
<
typename
T
=
std
::
string
>
static
T
parse_string
(
const
std
::
string
&
v
)
{
return
v
;
...
...
编辑
预览
Markdown
is supported
0%
请重试
或
添加新附件
.
添加附件
取消
You are about to add
0
people
to the discussion. Proceed with caution.
先完成此消息的编辑!
取消
想要评论请
注册
或
登录