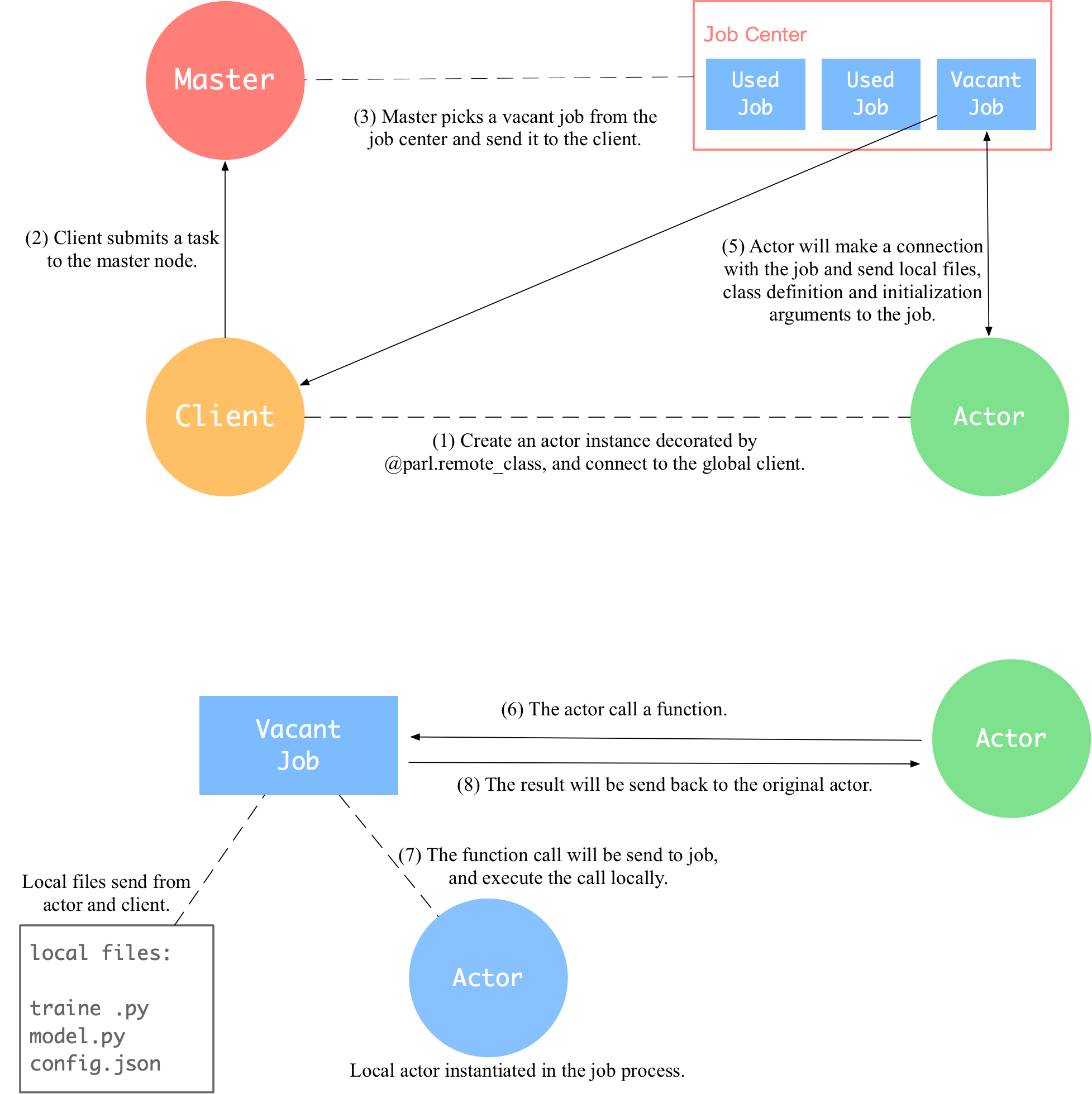
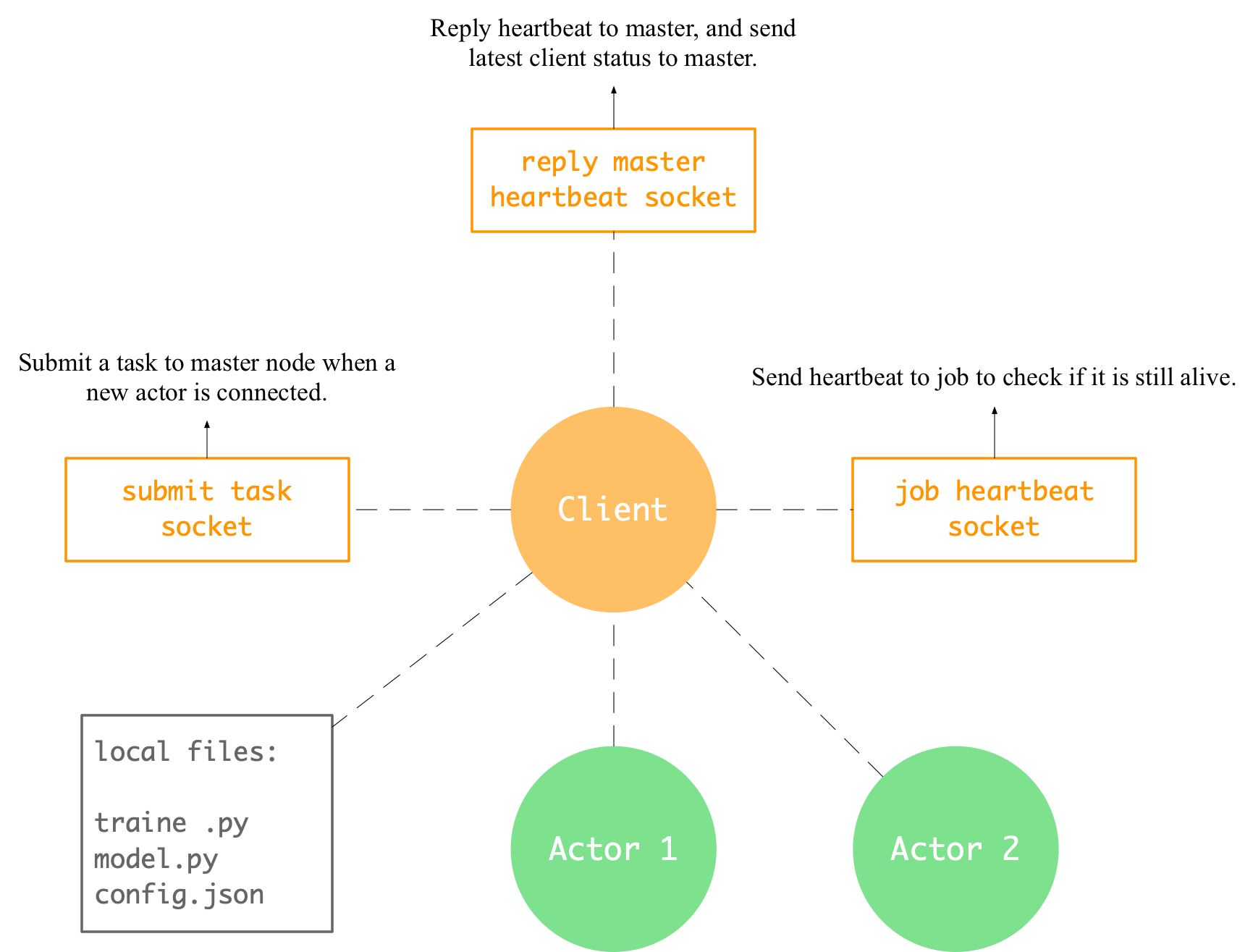
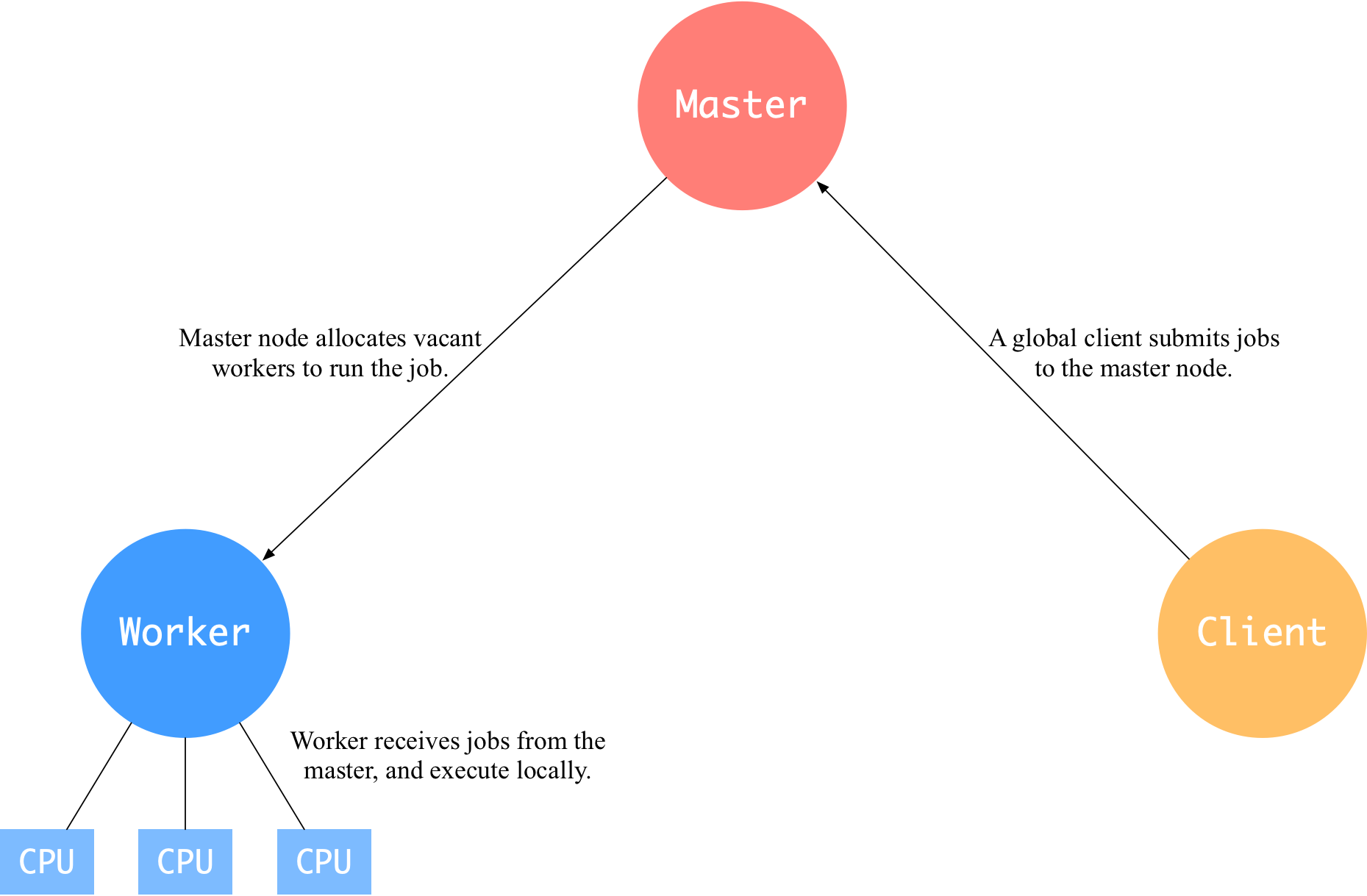
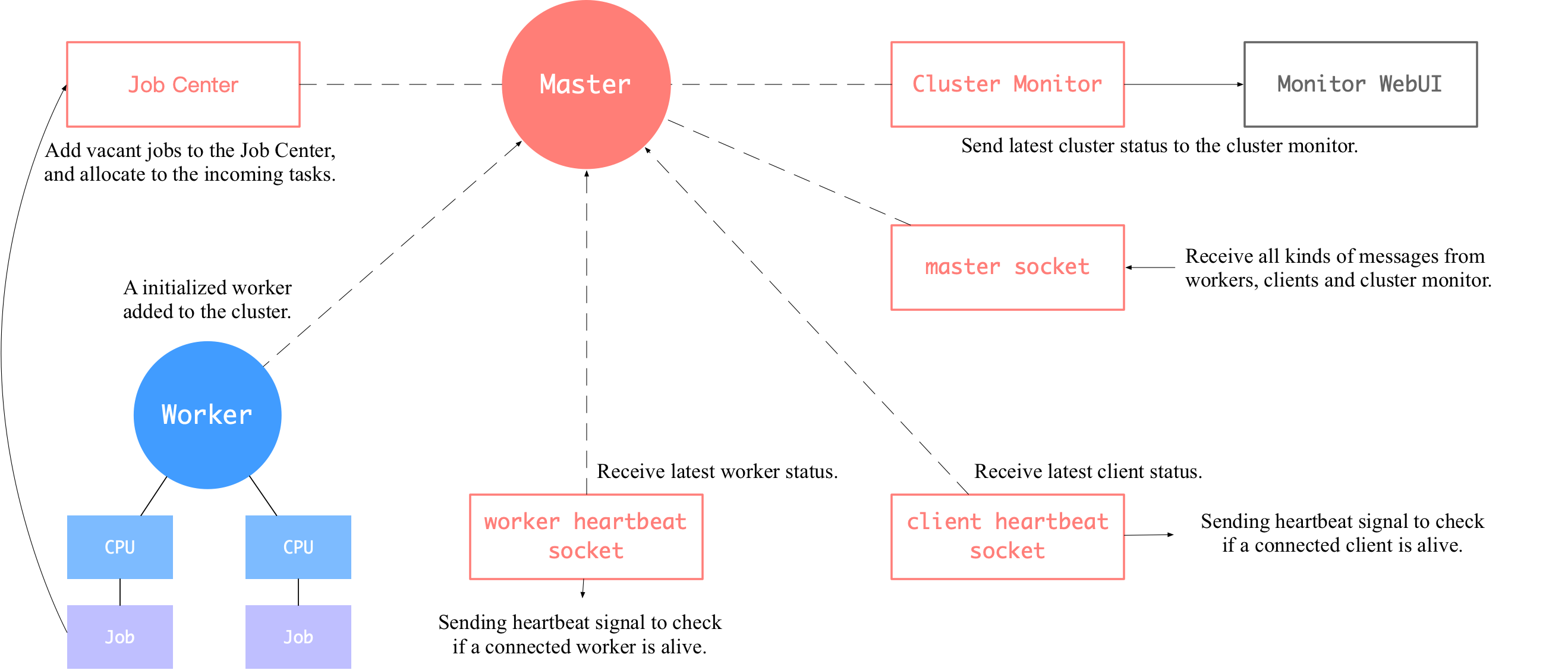
Add cluster docs
Showing
docs/images/parl.graffle
0 → 100644
文件已添加
docs/parallel_training/Actor.png
0 → 100644
263.2 KB
docs/parallel_training/client.png
0 → 100644
131.5 KB
117.8 KB
docs/parallel_training/master.png
0 → 100644
196.9 KB
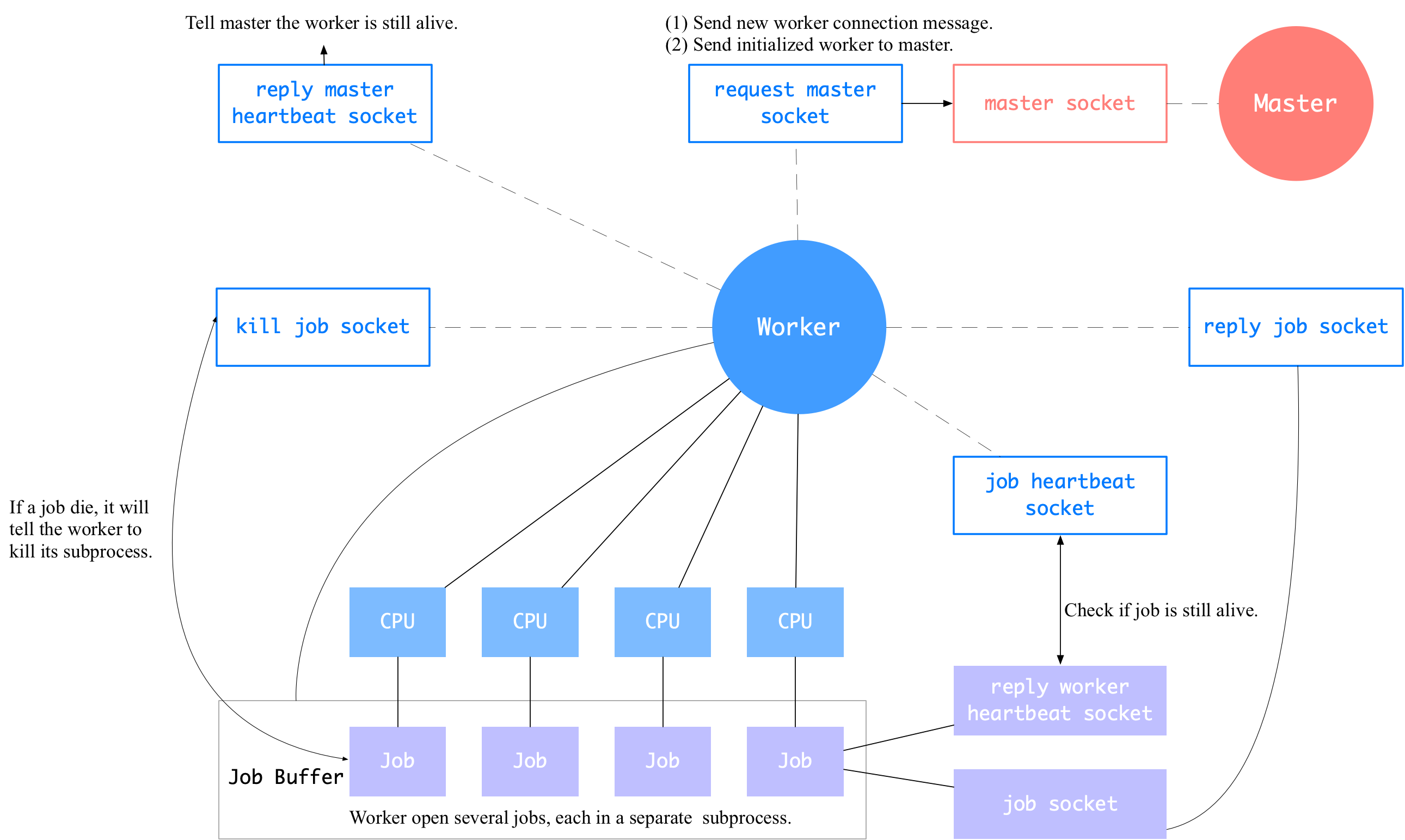
docs/parallel_training/worker.png
0 → 100644
236.2 KB