add application-test folder (10924)
Signed-off-by: Nesterzhou <ester.zhou@huawei.com>
Showing
514.3 KB
69.6 KB
66.4 KB
58.7 KB
54.5 KB
45.5 KB
26.6 KB
28.0 KB
24.7 KB
Signed-off-by: Nesterzhou <ester.zhou@huawei.com>
514.3 KB
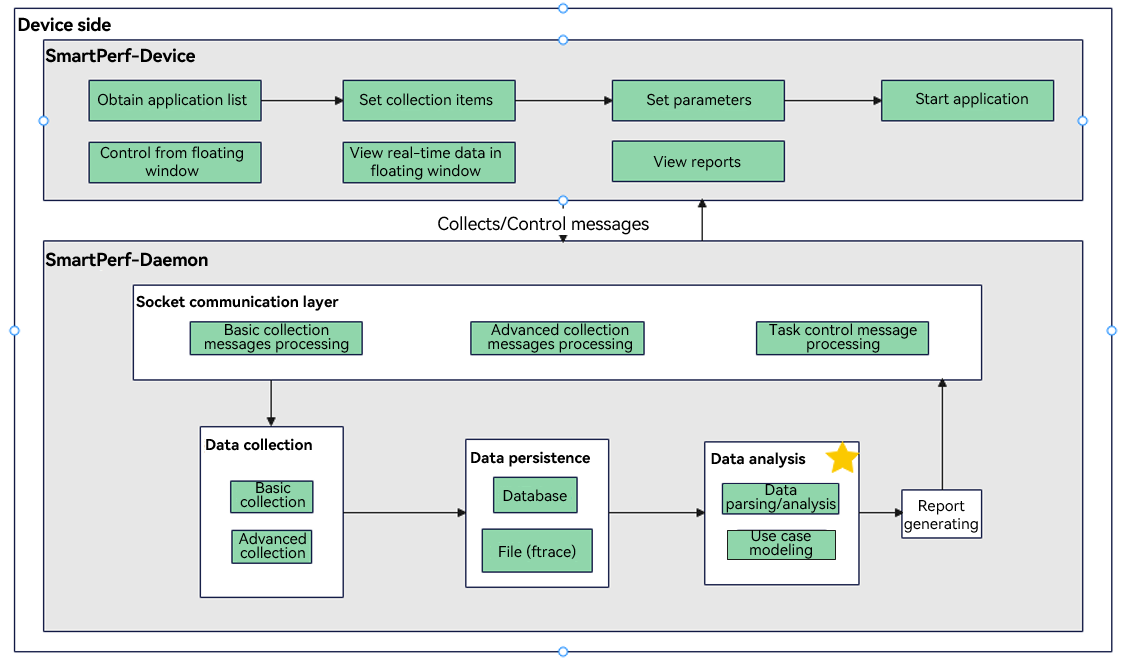
69.6 KB
66.4 KB
58.7 KB
54.5 KB
45.5 KB
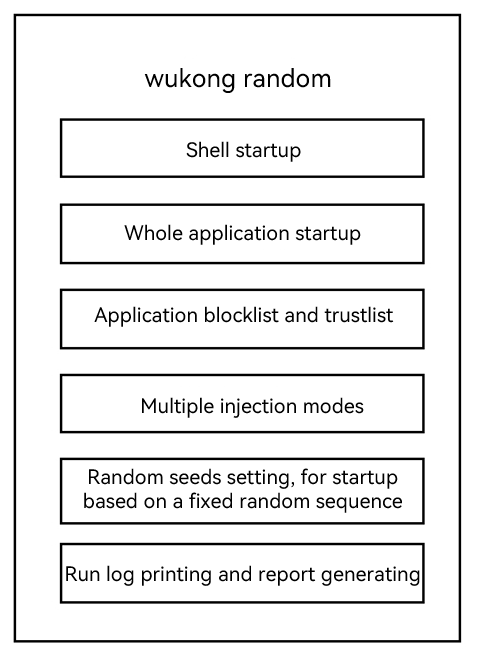
26.6 KB
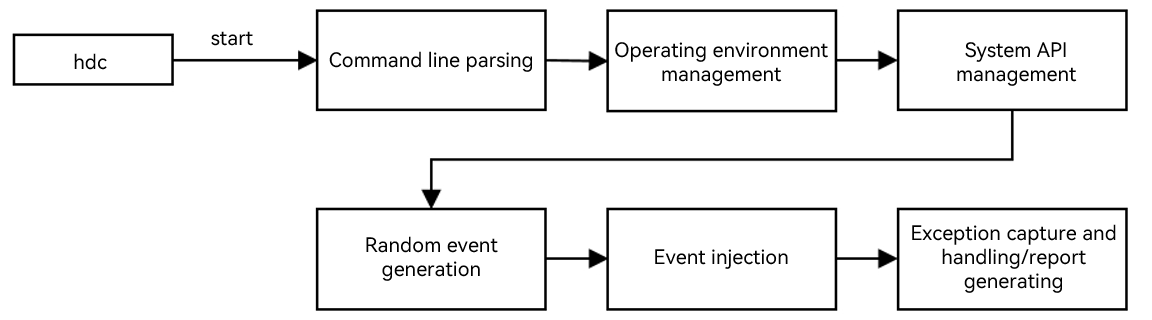
28.0 KB
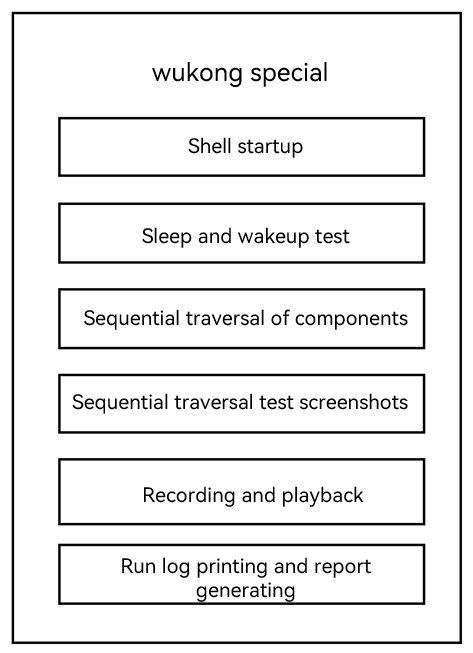
24.7 KB
