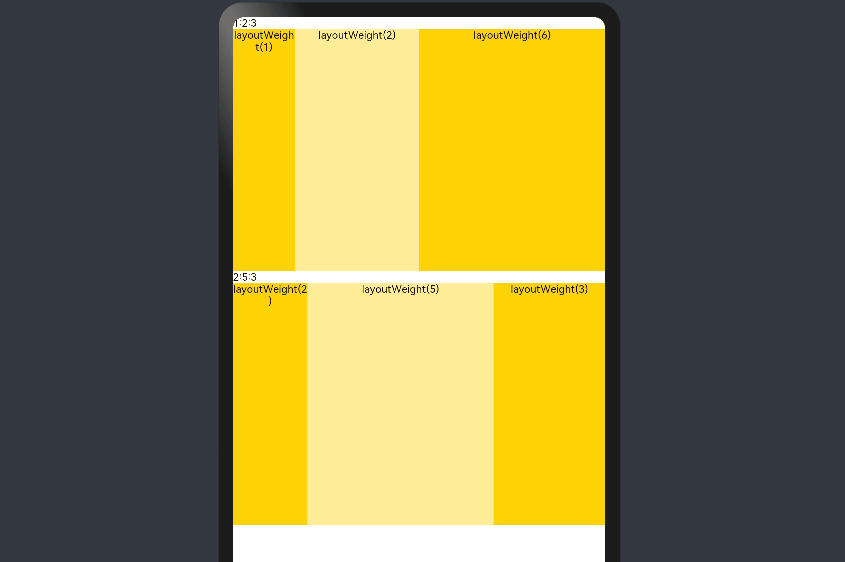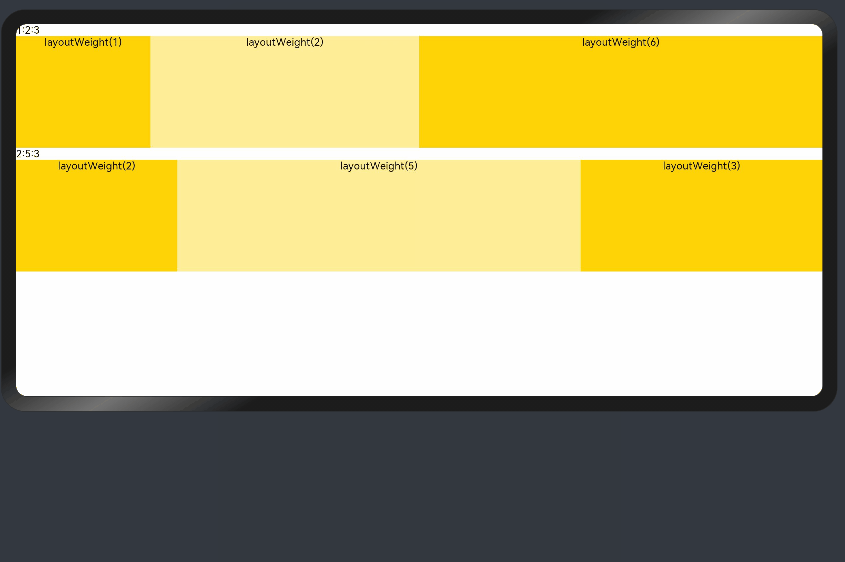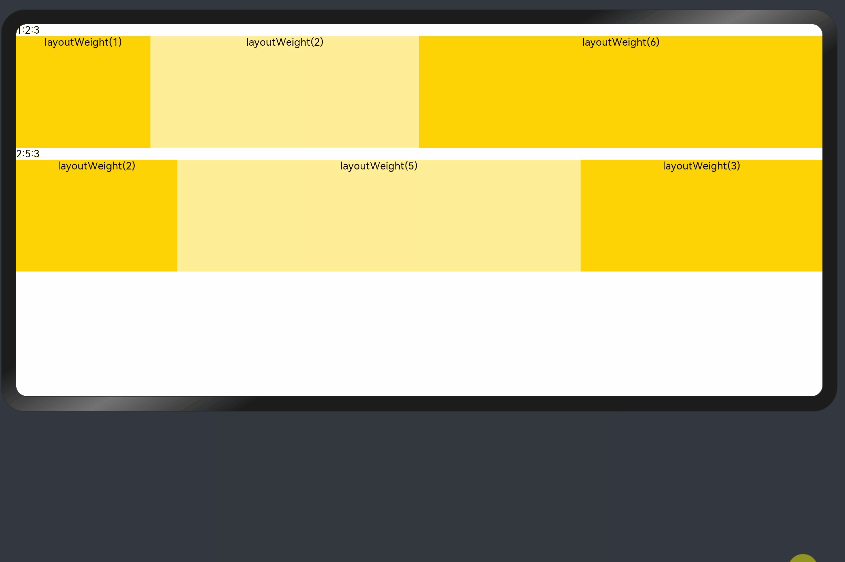
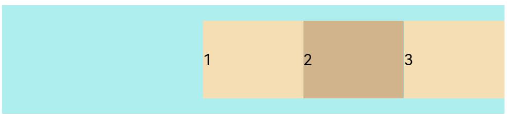
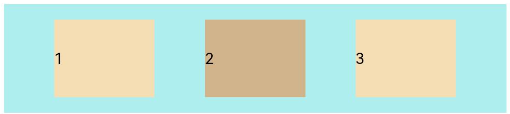
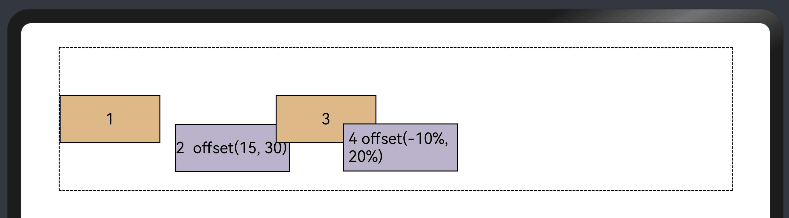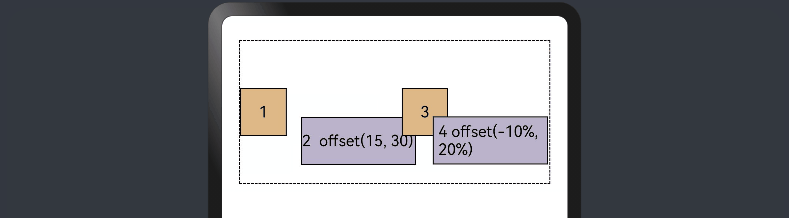
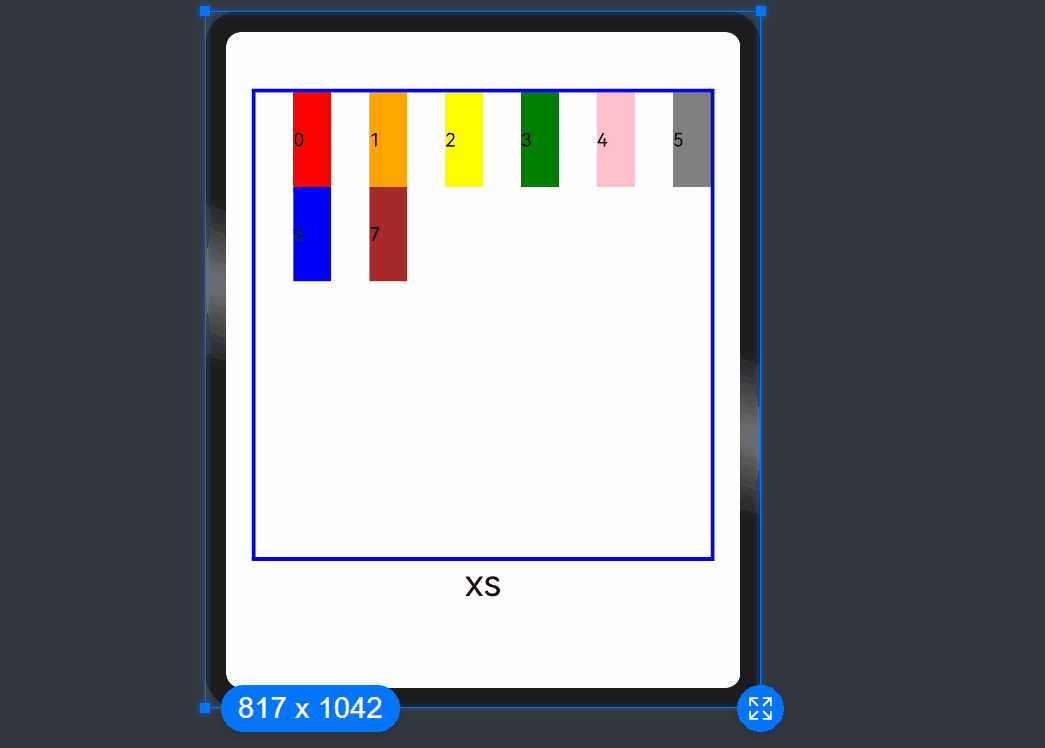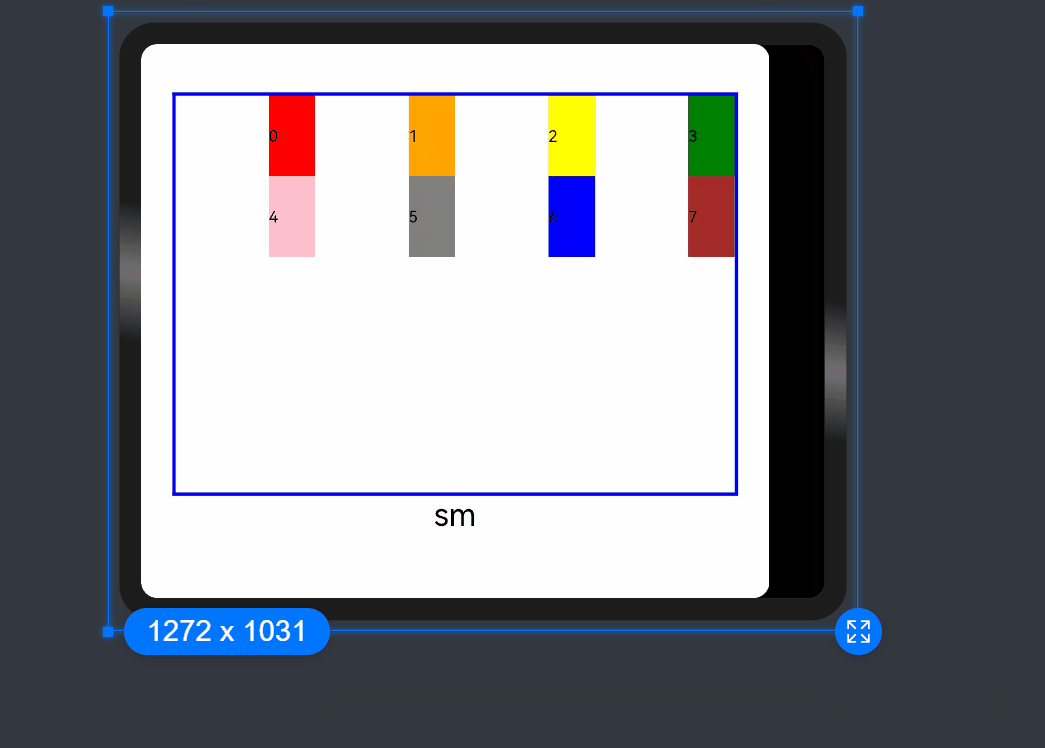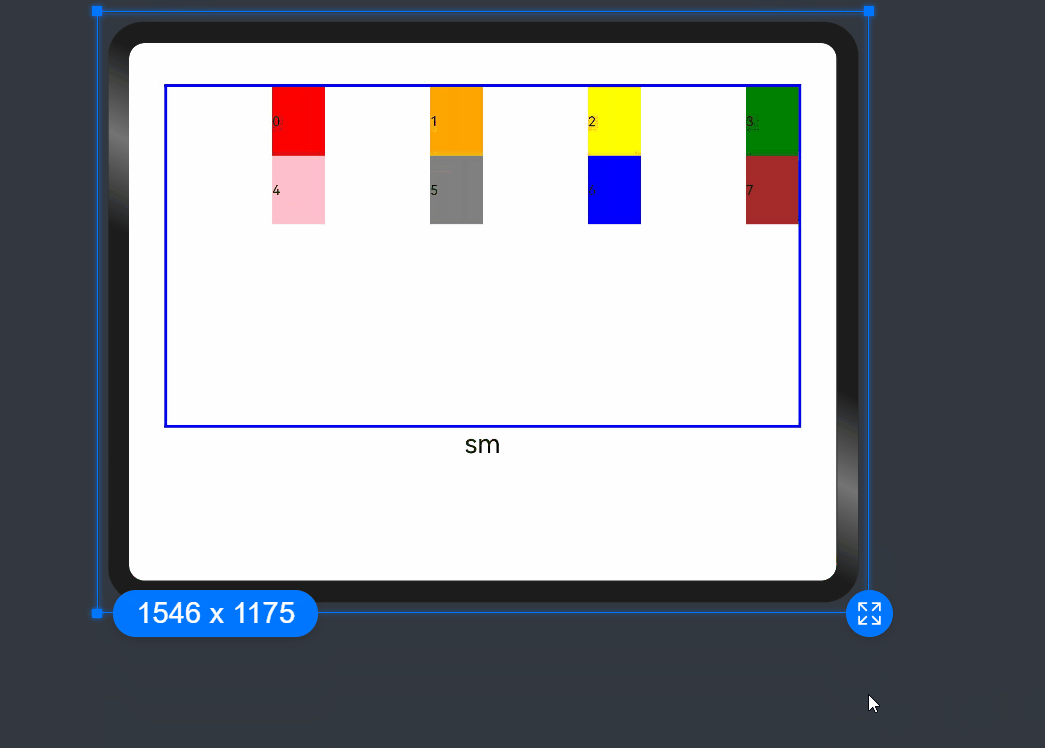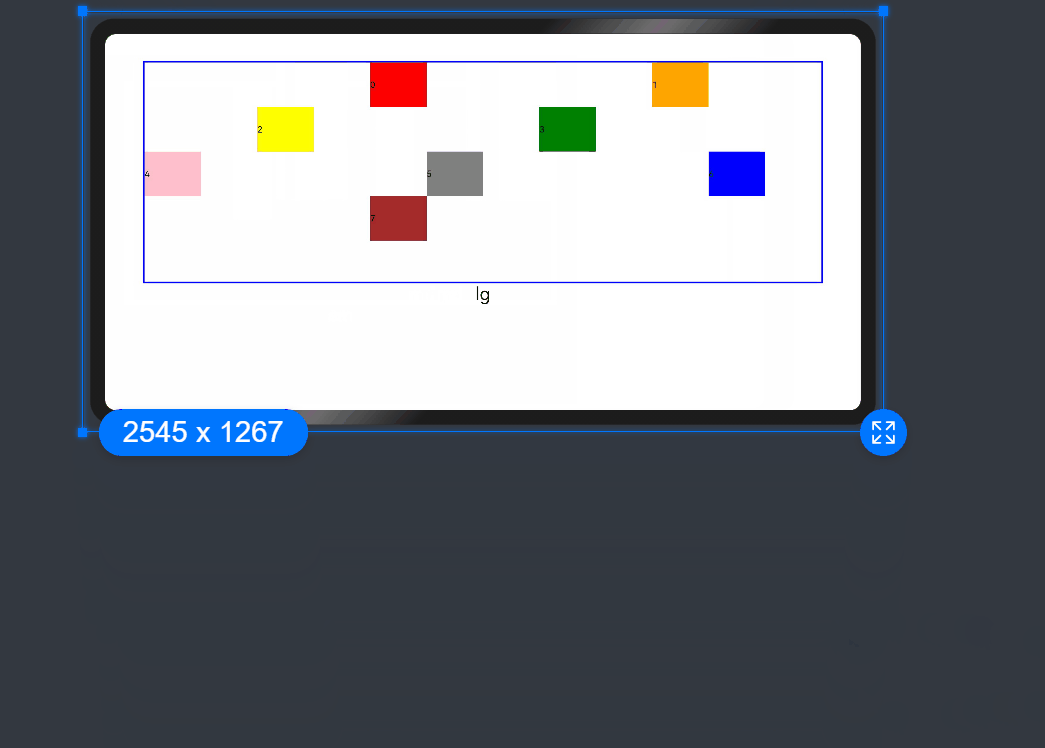
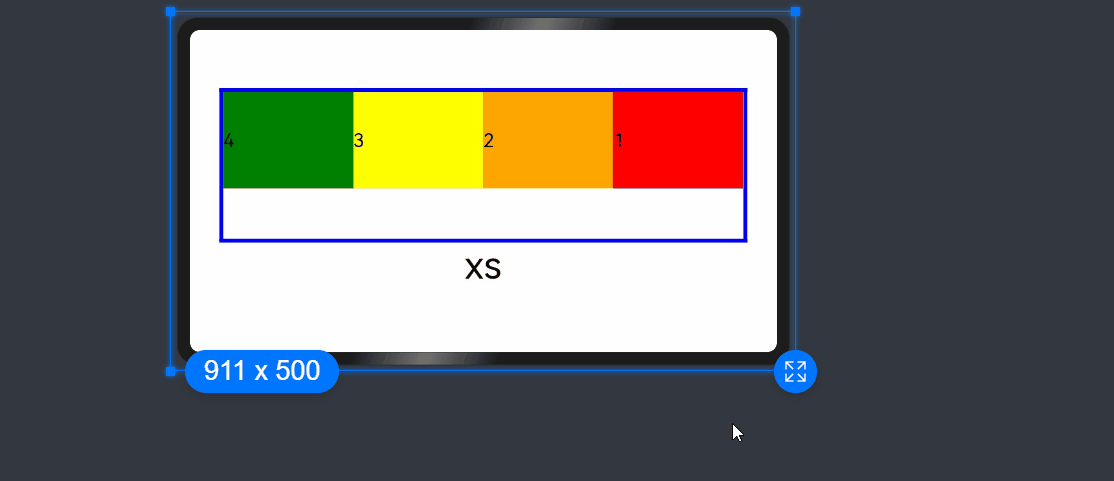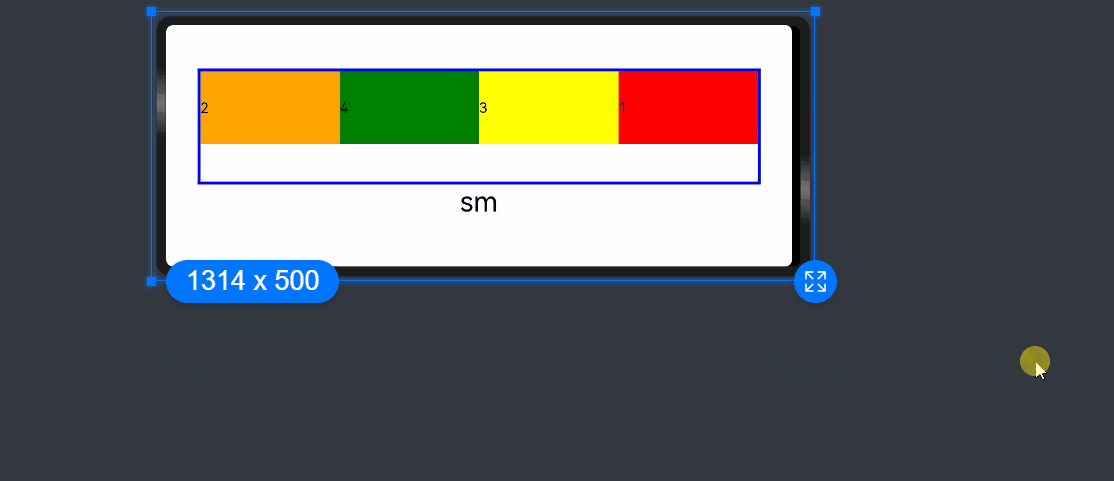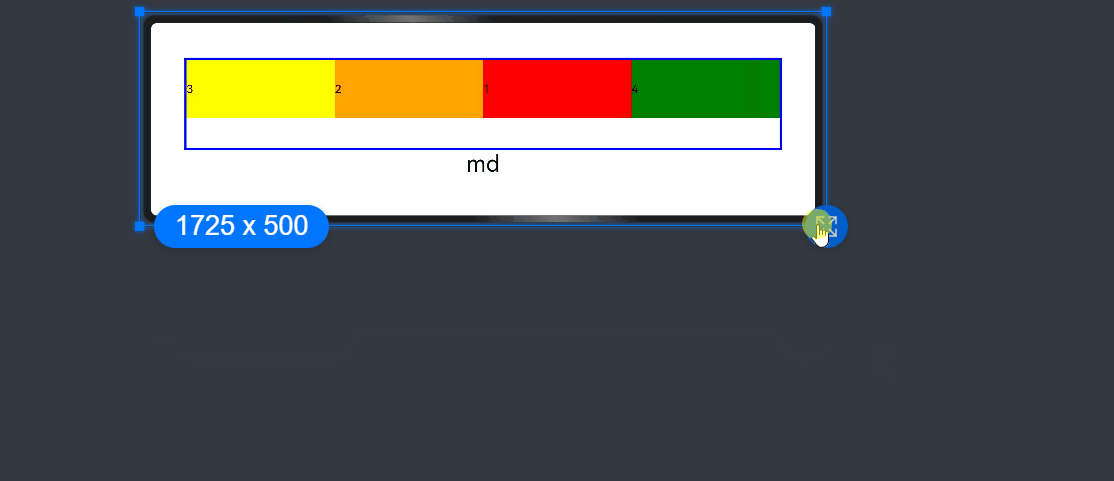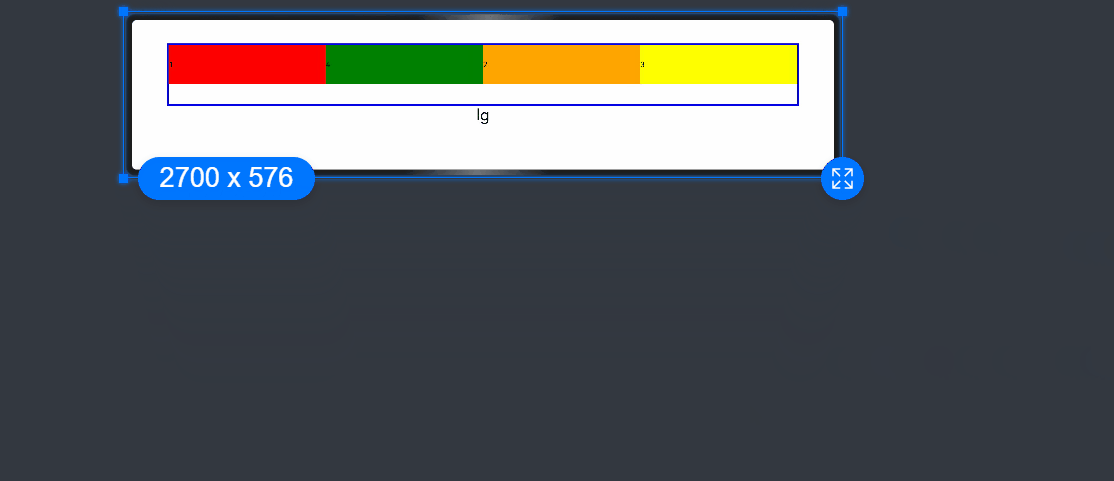
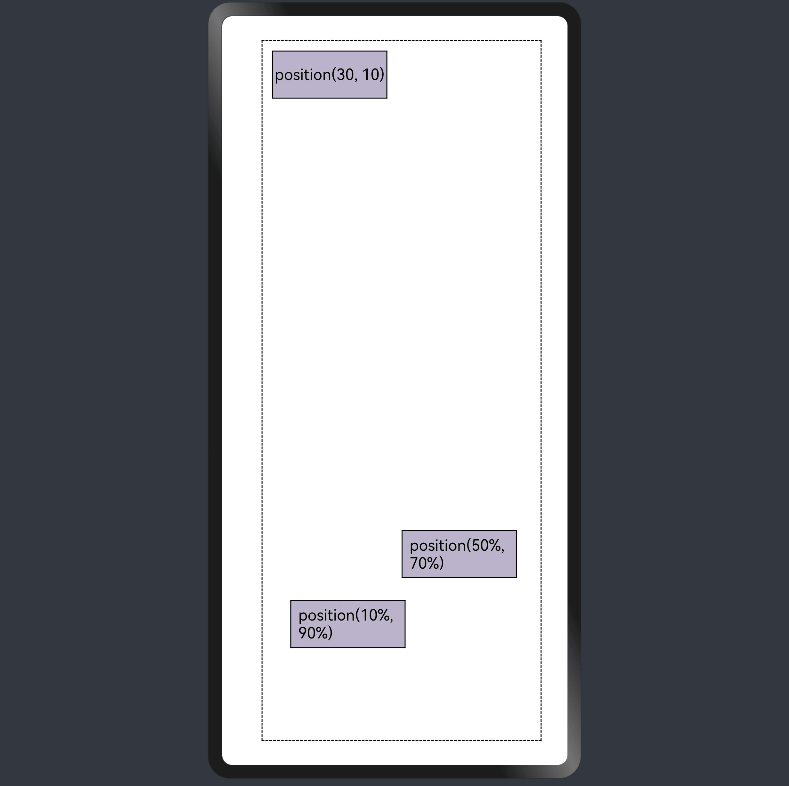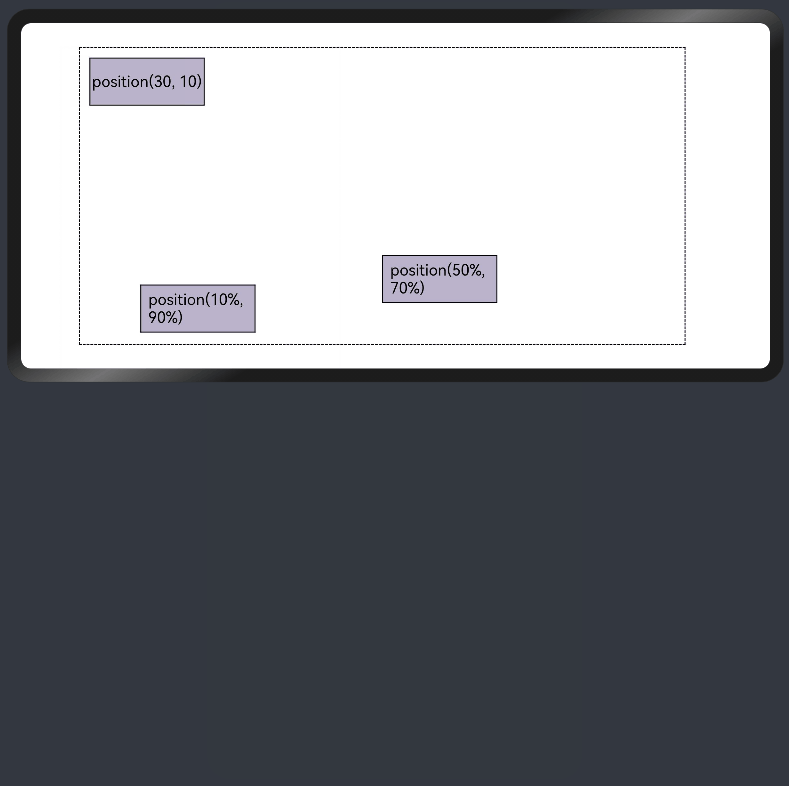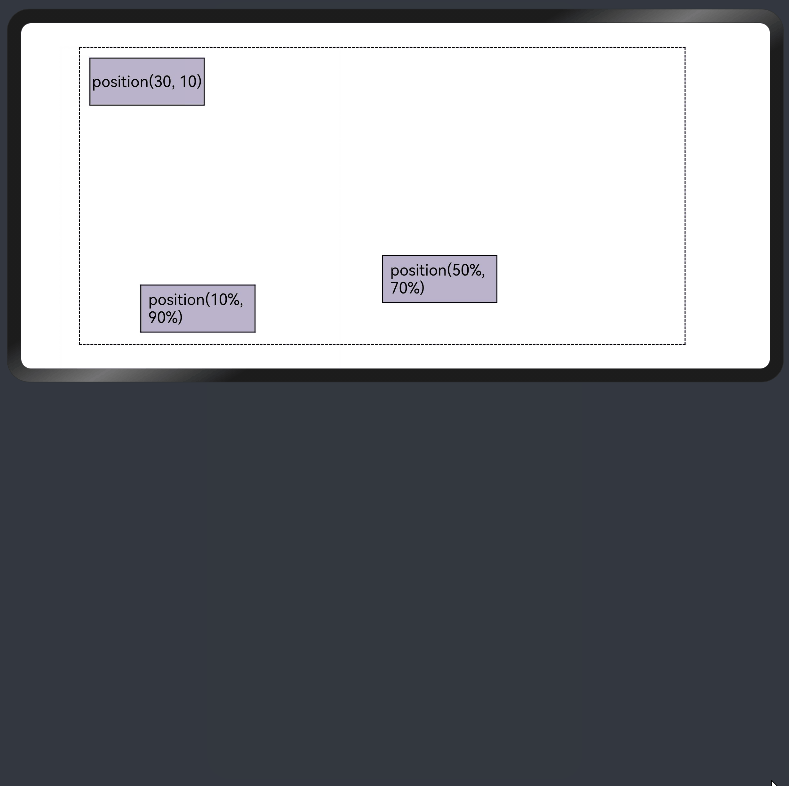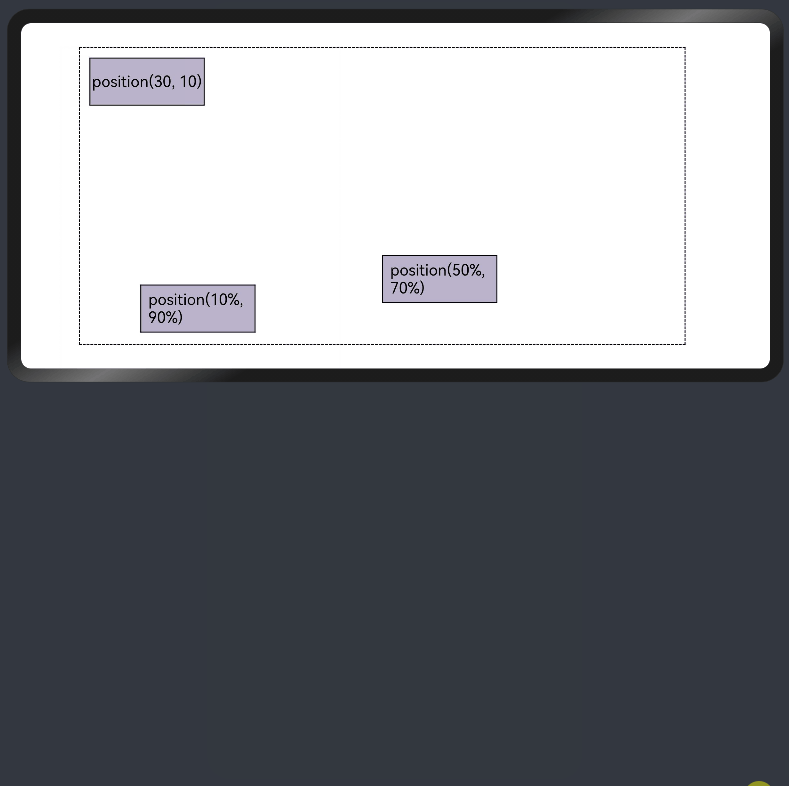
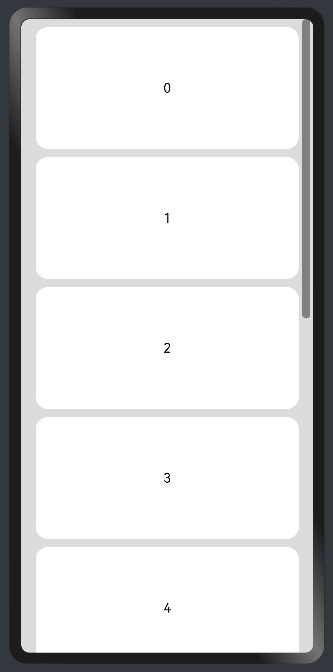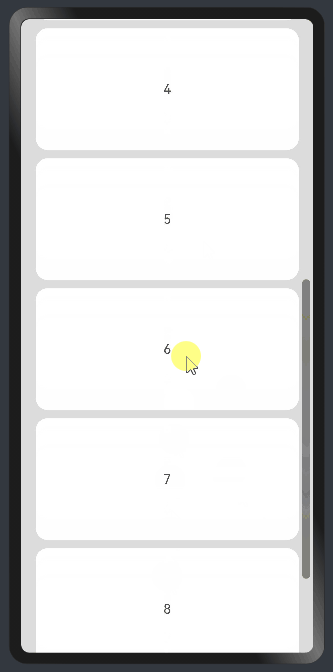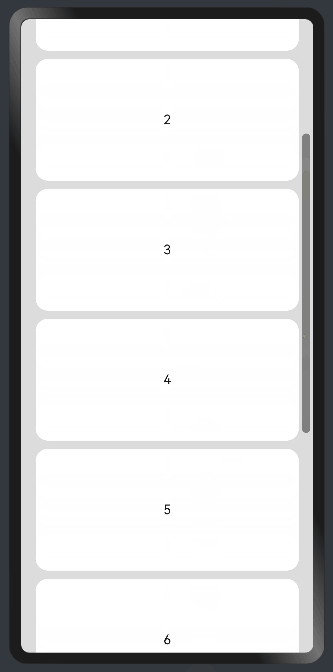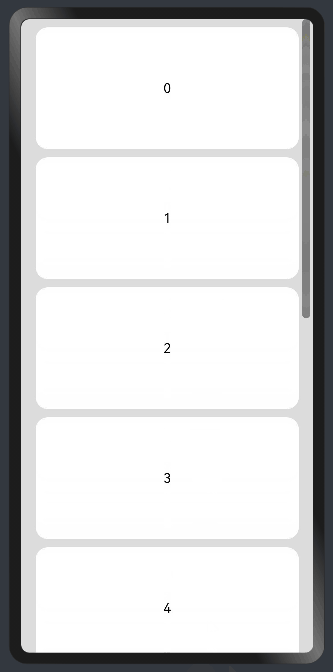
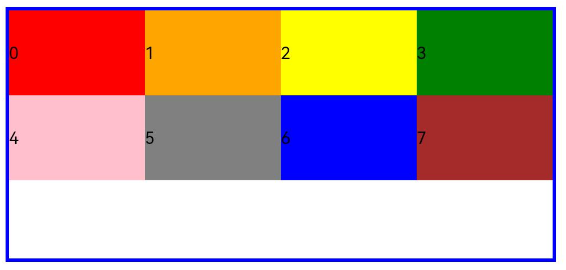
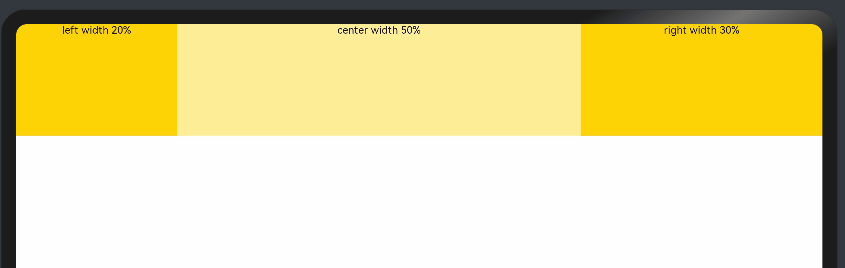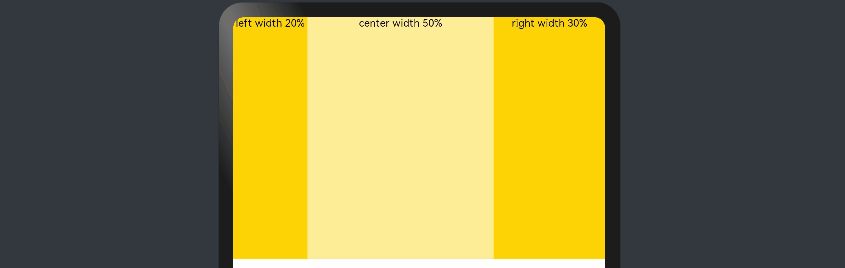
add layout
Signed-off-by: Nsienna1128 <lixiaoyan45@huawei.com>
Showing
16.3 KB
12.4 KB
3.1 MB
9.9 KB
9.6 KB
32.5 KB
79.6 KB
162.3 KB
32.9 KB
45.6 KB
8.7 KB
8.6 KB
8.8 KB
8.7 KB
9.4 KB
7.9 KB
12.4 KB
12.3 KB
6.9 KB
11.4 KB
14.1 KB
21.8 KB
23.4 KB
13.7 KB
29.8 KB
13.9 KB
12.6 KB
44.9 KB
2.0 MB
1.7 MB
6.7 KB
5.7 KB
7.8 KB
6.9 KB
6.0 KB
5.6 KB
30.5 KB
23.2 KB
1.8 MB
9.8 KB
941.8 KB
65.0 KB
16.1 KB
72.3 KB
151.1 KB
38.5 KB
382.5 KB
321.5 KB
15.9 KB
2.4 MB
26.1 KB
6.3 KB
6.6 KB
6.3 KB
6.4 KB
6.4 KB
6.2 KB
6.3 KB
6.7 KB
6.5 KB
6.3 KB
20.7 KB
20.8 KB