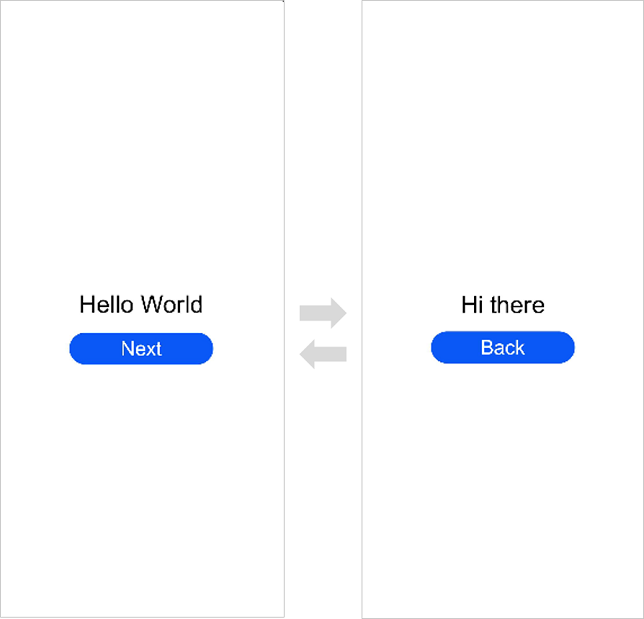
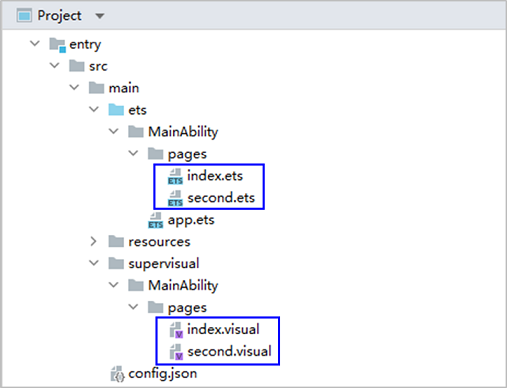
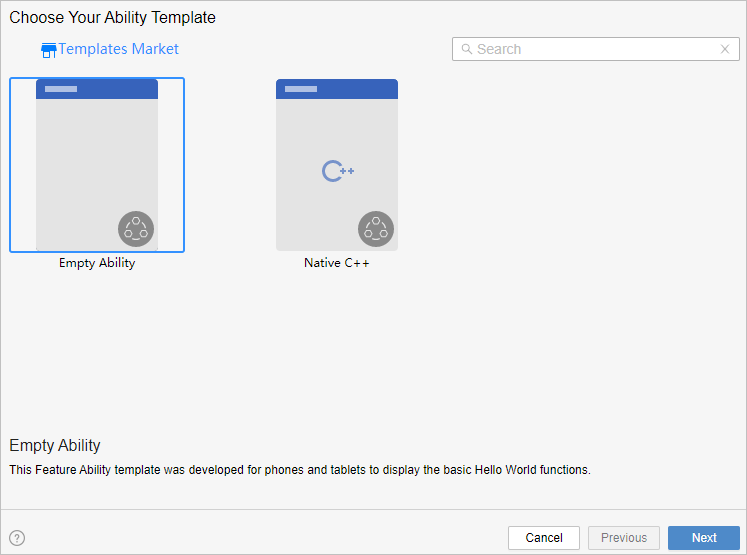
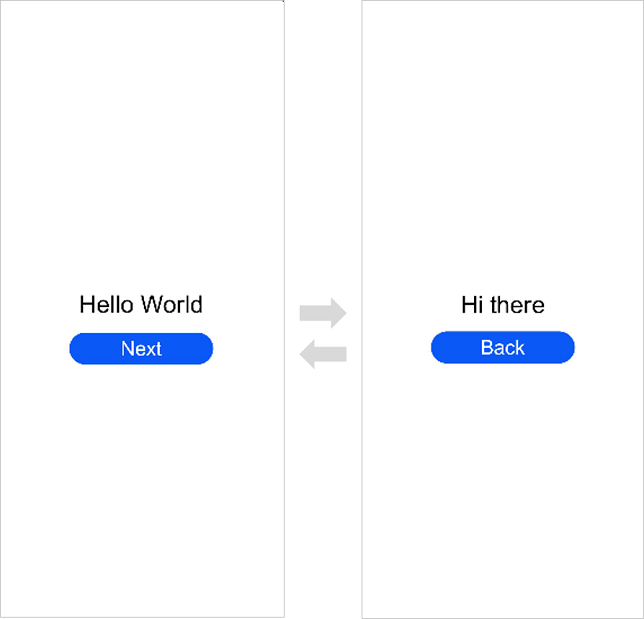
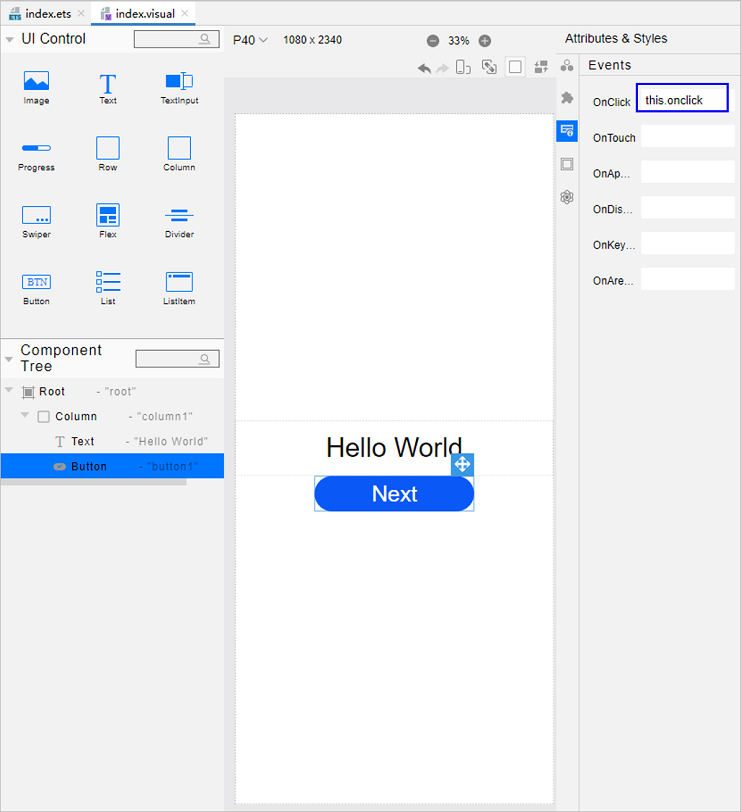
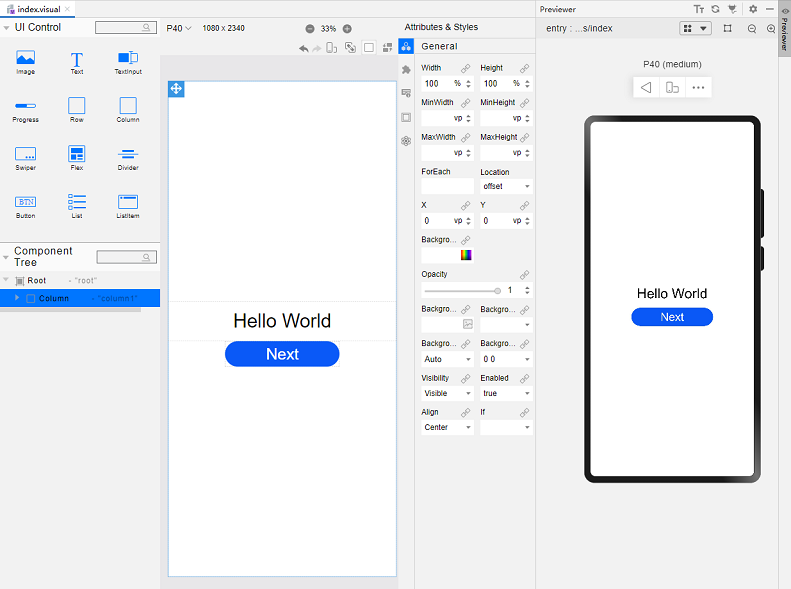
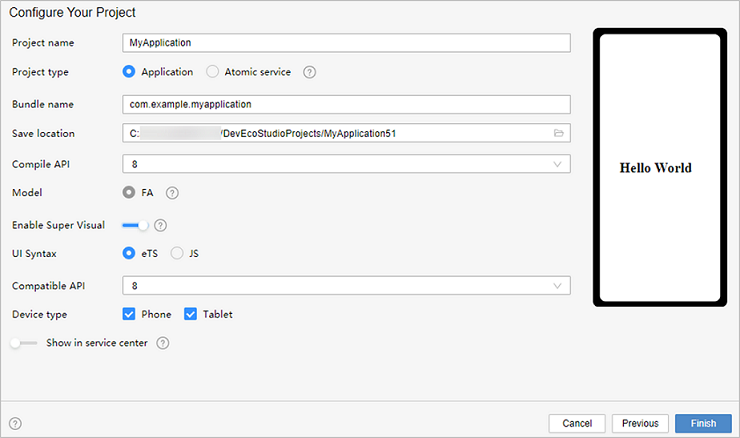
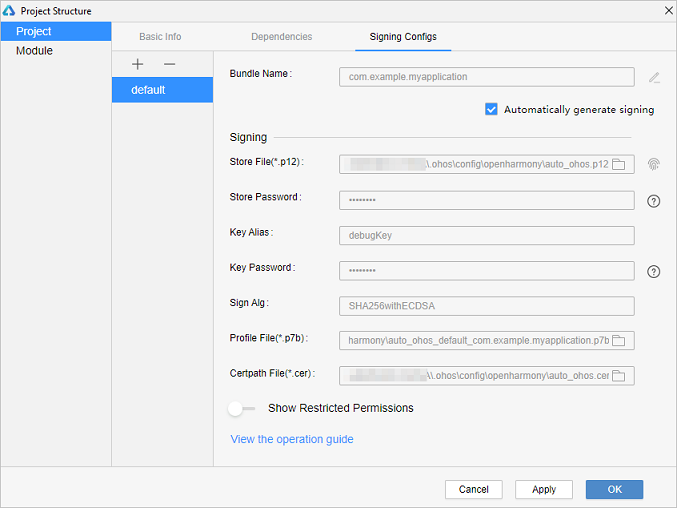
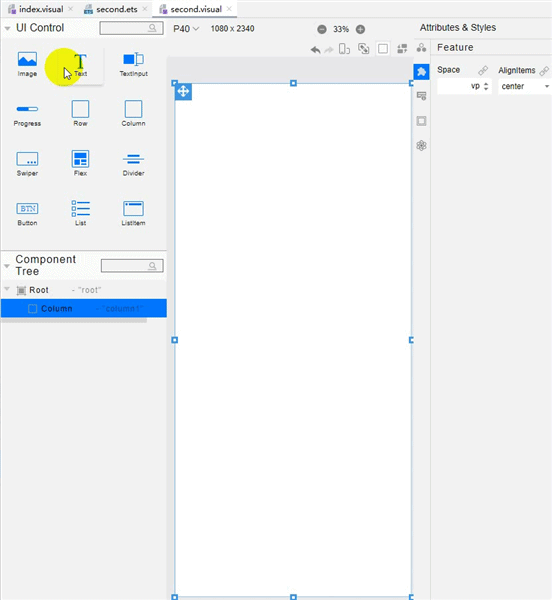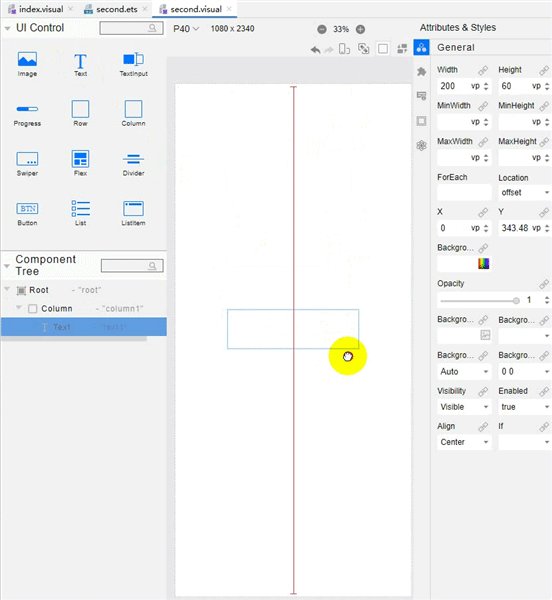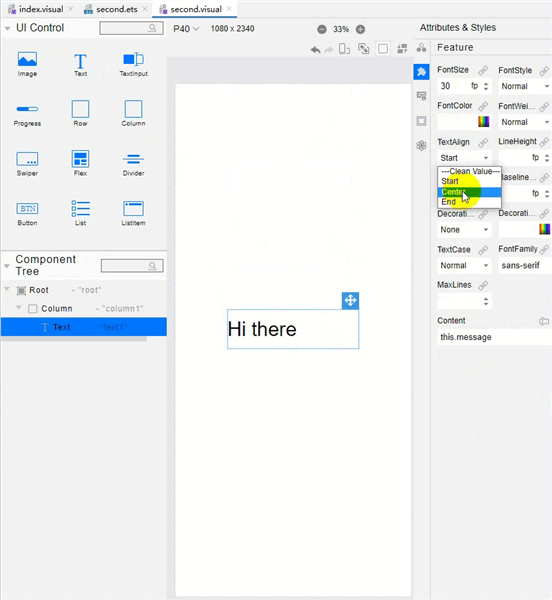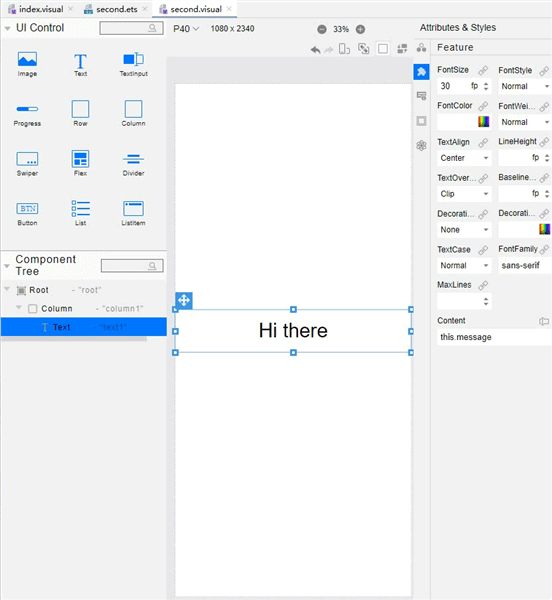
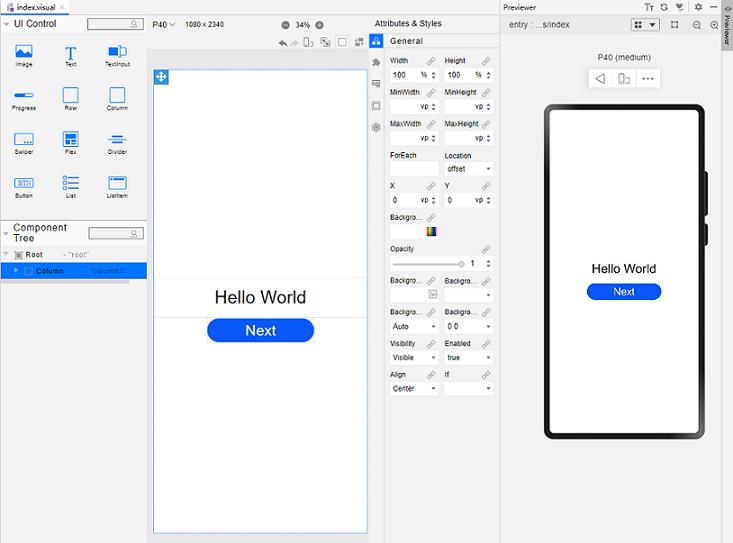
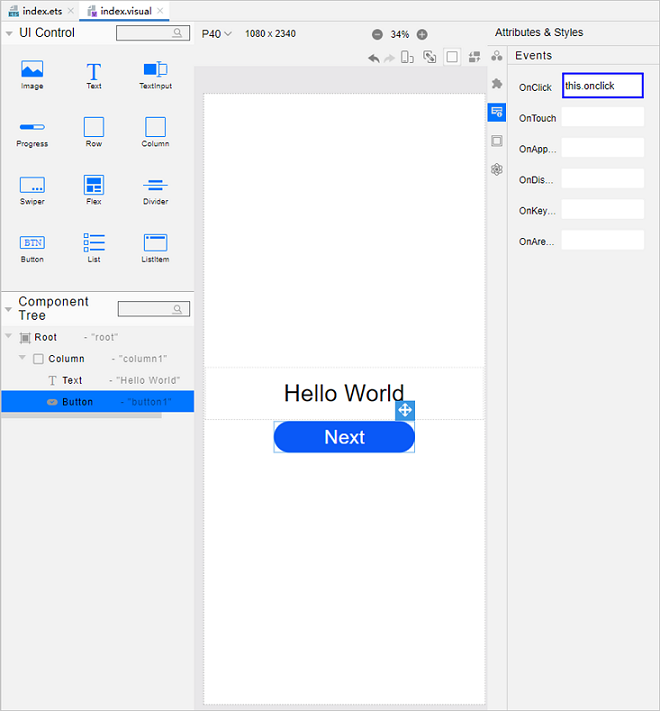
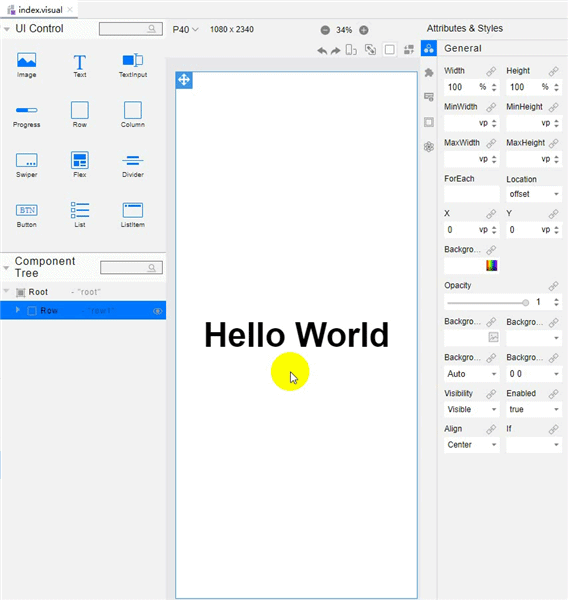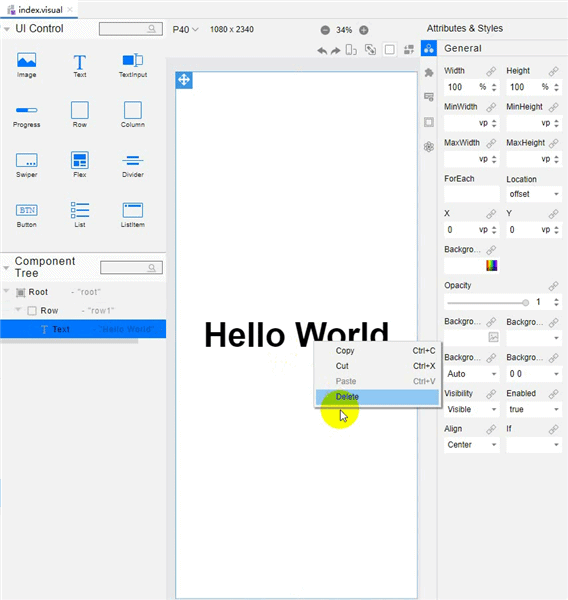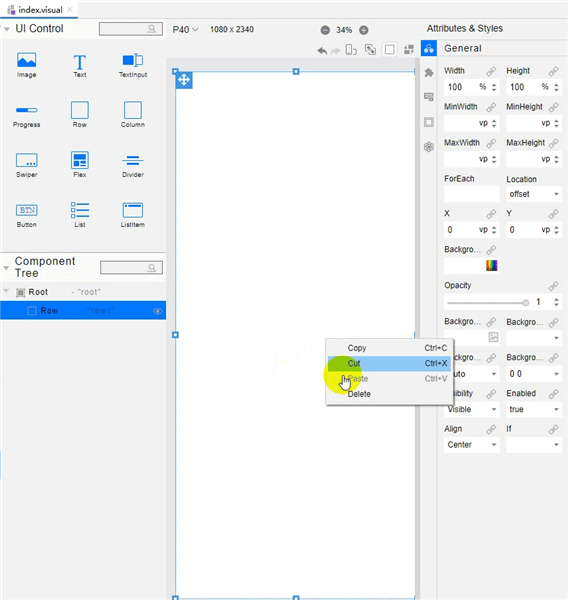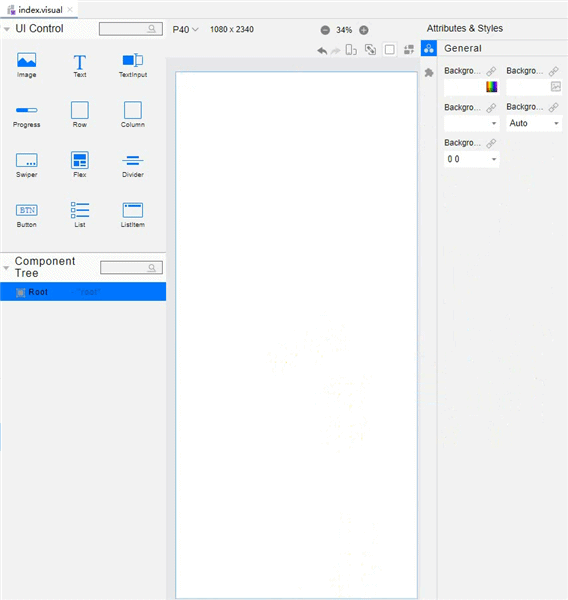
!3251 快速入门新增eTS低代码开发章节+英文术语同步:无需翻译
Merge pull request !3251 from 葛亚芳/OpenHarmony-3.1-Release
Showing
277 字节
2.4 MB
287 字节
21.2 KB
400 字节
42.4 KB
287 字节
18.2 KB
277 字节
21.2 KB
7.2 MB
7.2 MB
112.3 KB
100.0 KB
4.2 MB
400 字节
400 字节
481 字节
75.7 KB
277 字节
400 字节
79.1 KB
37.6 KB
400 字节
228 字节
8.6 MB
5.7 MB
113.2 KB
en/glossary.md
0 → 100644
277 字节
120.9 KB
101.7 KB
2.4 MB
9.8 MB
287 字节
21.2 KB
400 字节
44.7 KB
287 字节
47.4 KB
8.1 MB
277 字节
21.2 KB
4.2 MB
400 字节
93.7 KB
400 字节
8.9 MB
481 字节
81.2 KB
277 字节
400 字节
93.4 KB
45.1 KB
400 字节
因为 它太大了无法显示 image diff 。你可以改为 查看blob。
228 字节