optimize docs for mkdocs
Showing
docs/cnstd_cnocr.md
0 → 100644
docs/contact.md
0 → 100644
docs/demo.md
0 → 100644
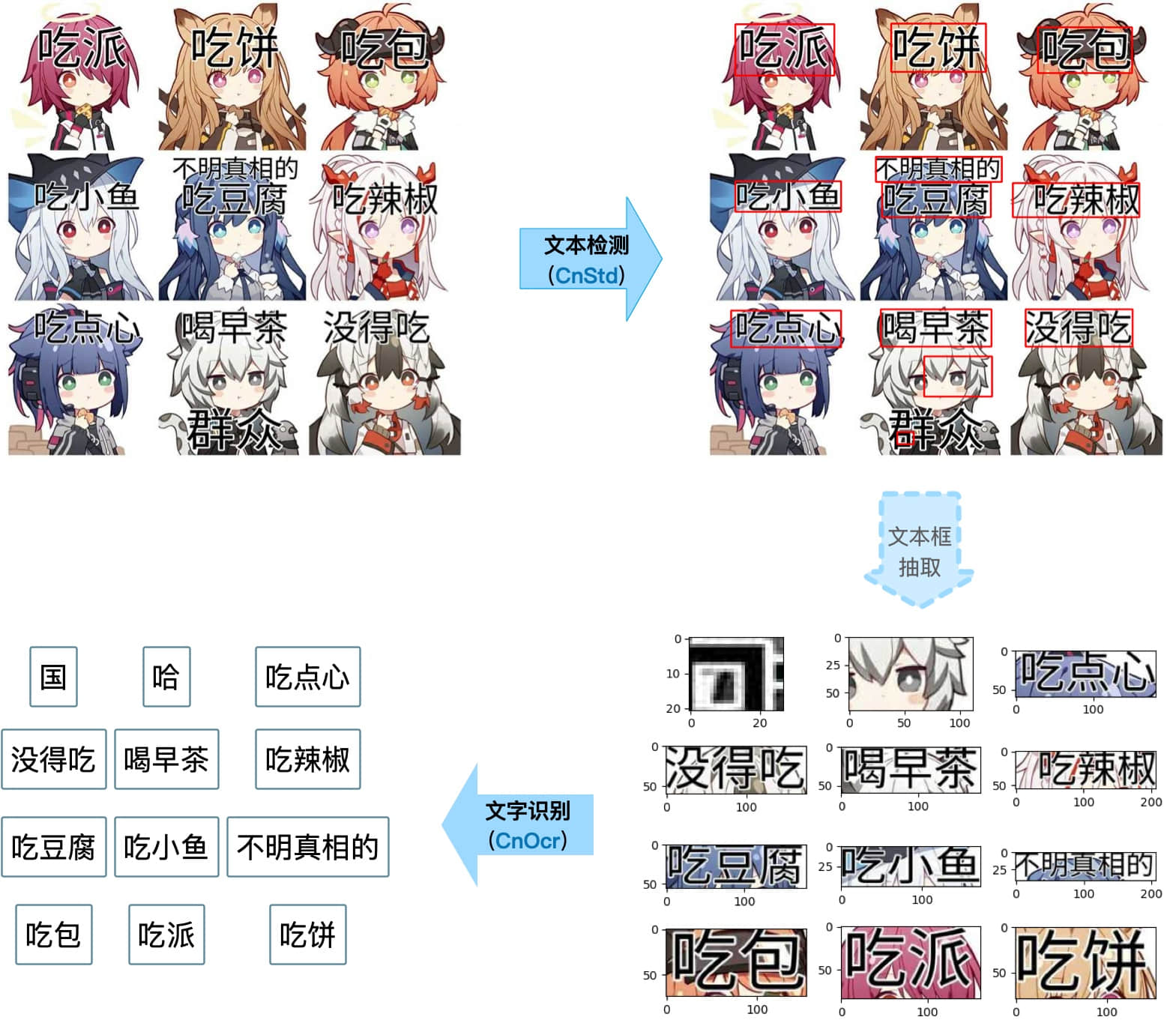
docs/figs/std-ocr.jpg
0 → 100644
237.0 KB
docs/install.md
0 → 100644
docs/models.md
0 → 100644
docs/std_ocr.md
0 → 100644
docs/train.md
0 → 100644
docs/usage.md
0 → 100644