1
上级
Showing
.github/pull_request_template.md
0 → 100644
LICENSE
0 → 100644
此差异已折叠。
README.md
0 → 100644
README_OLD.md
0 → 100644
此差异已折叠。
RELEASE_NOTES.md
0 → 100644
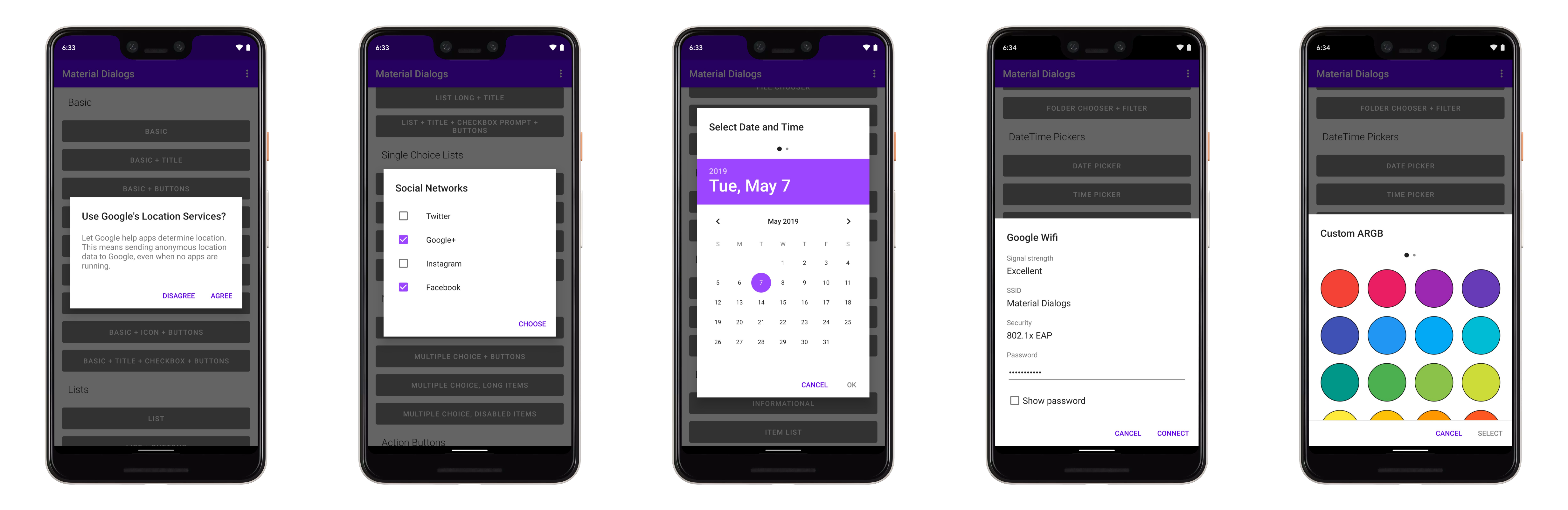
art/basic.png
0 → 100644
423.4 KB
art/basic_list.png
0 → 100644
359.7 KB
art/basic_with_buttons.png
0 → 100644
430.0 KB
art/bottomsheet_customview.png
0 → 100644
390.4 KB
art/bottomsheet_peekheight.gif
0 → 100644
564.6 KB
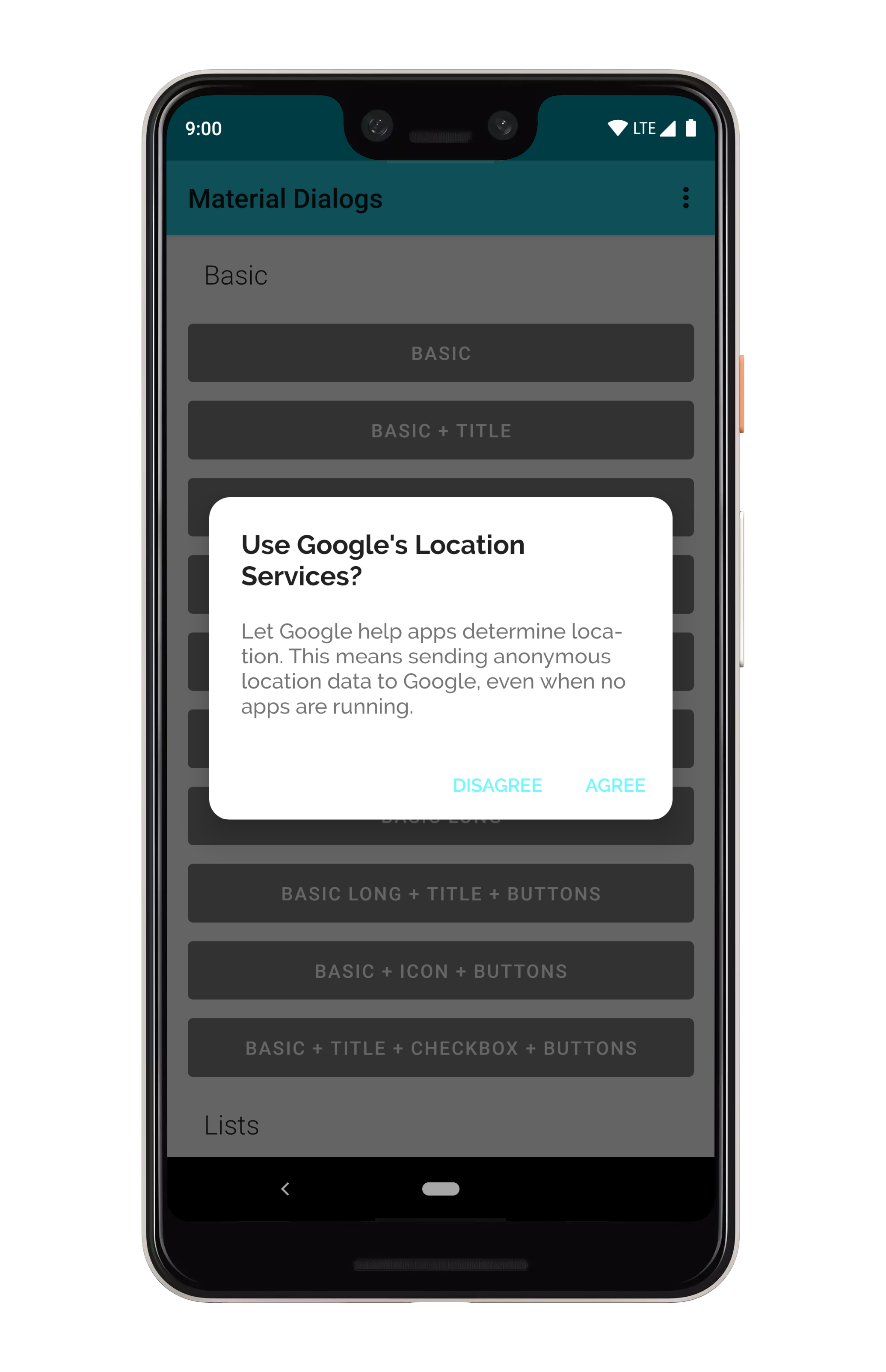
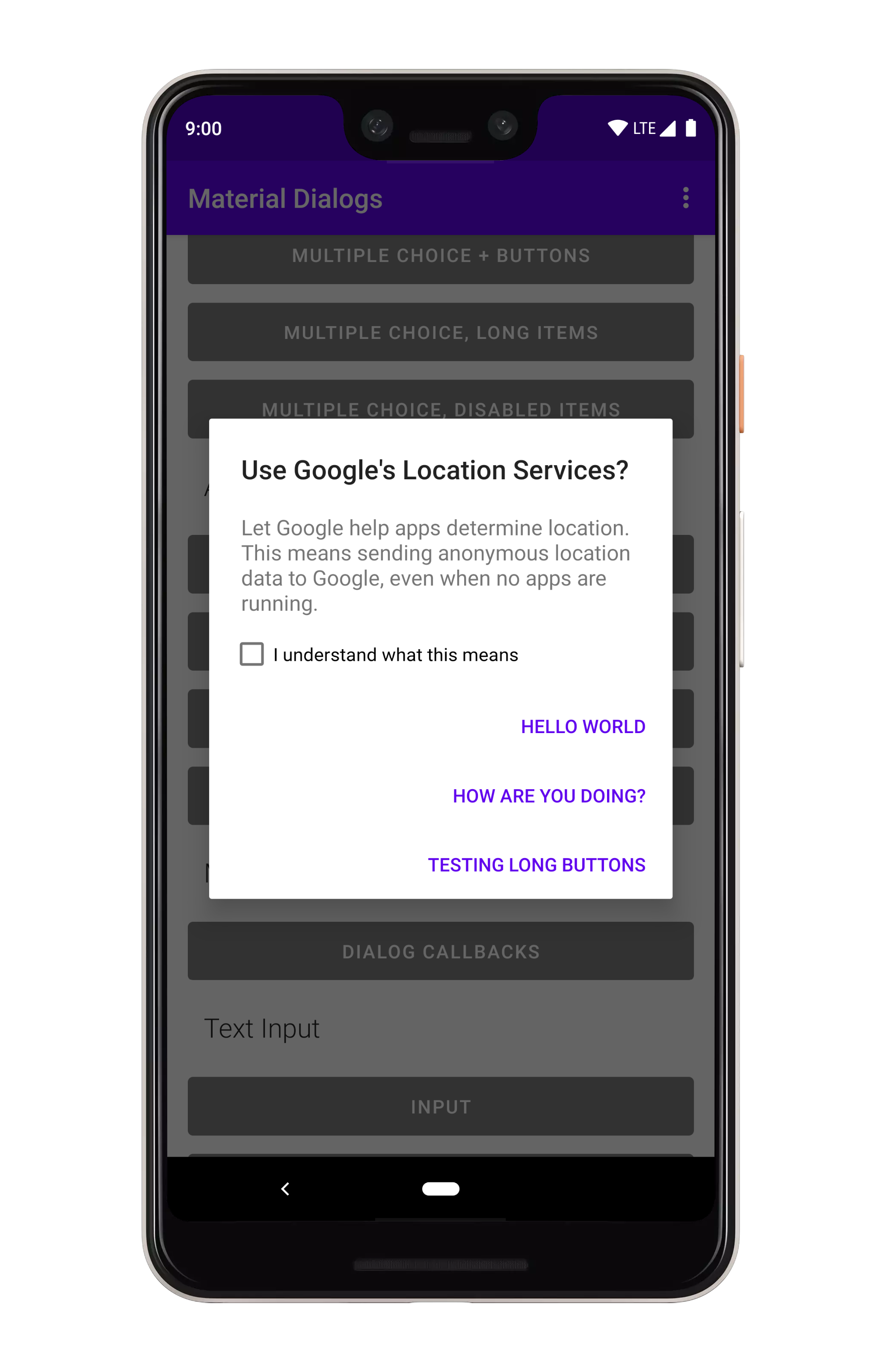
art/checkbox_prompt.png
0 → 100644
435.6 KB
art/color_chooser.png
0 → 100644
524.5 KB
art/color_chooser_sub.png
0 → 100644
455.9 KB
art/custom_argb.png
0 → 100644
349.7 KB
art/custom_view.png
0 → 100644
398.2 KB
art/customtheme.png
0 → 100644
434.8 KB
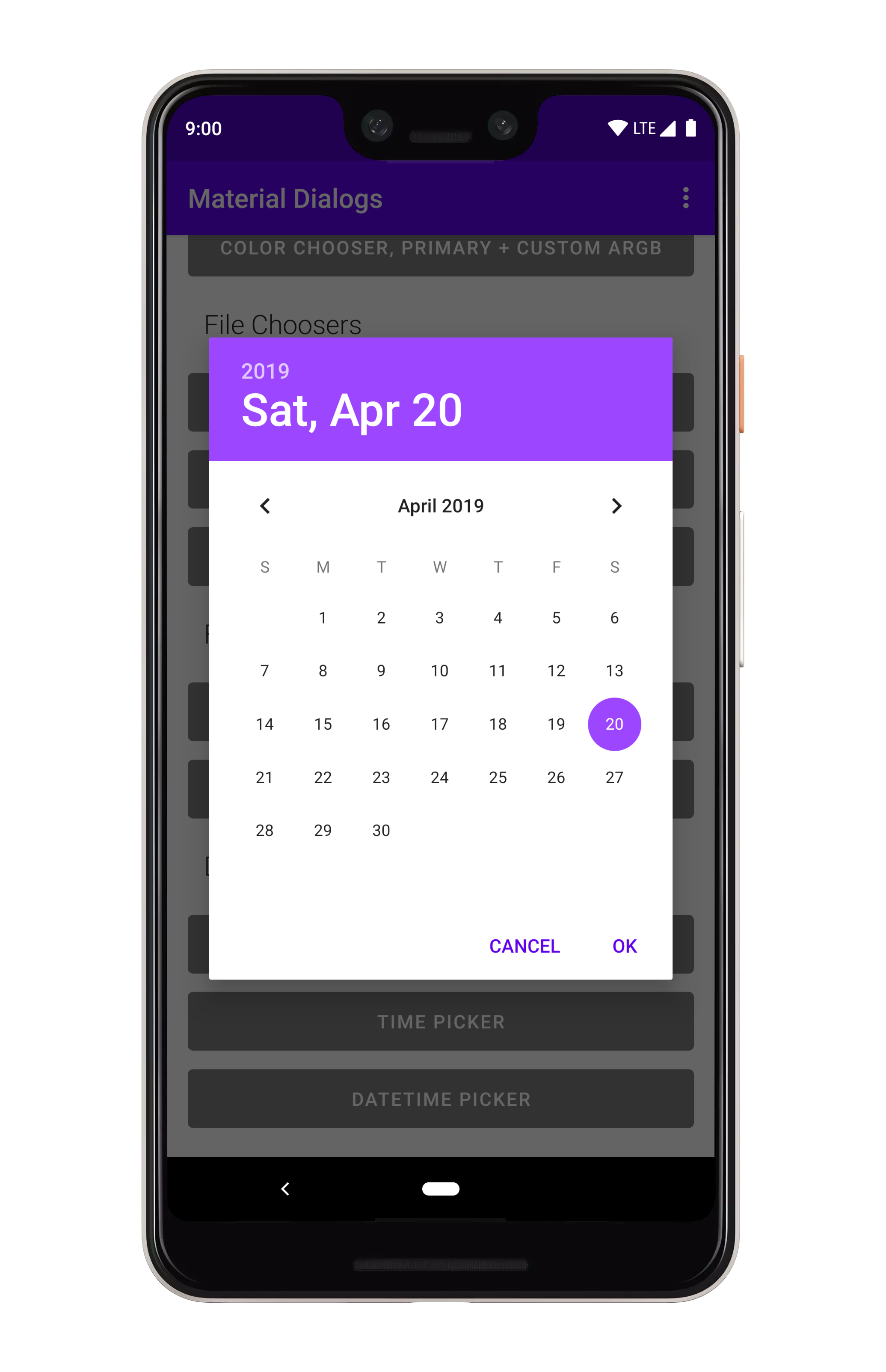
art/datepicker.png
0 → 100644
379.5 KB
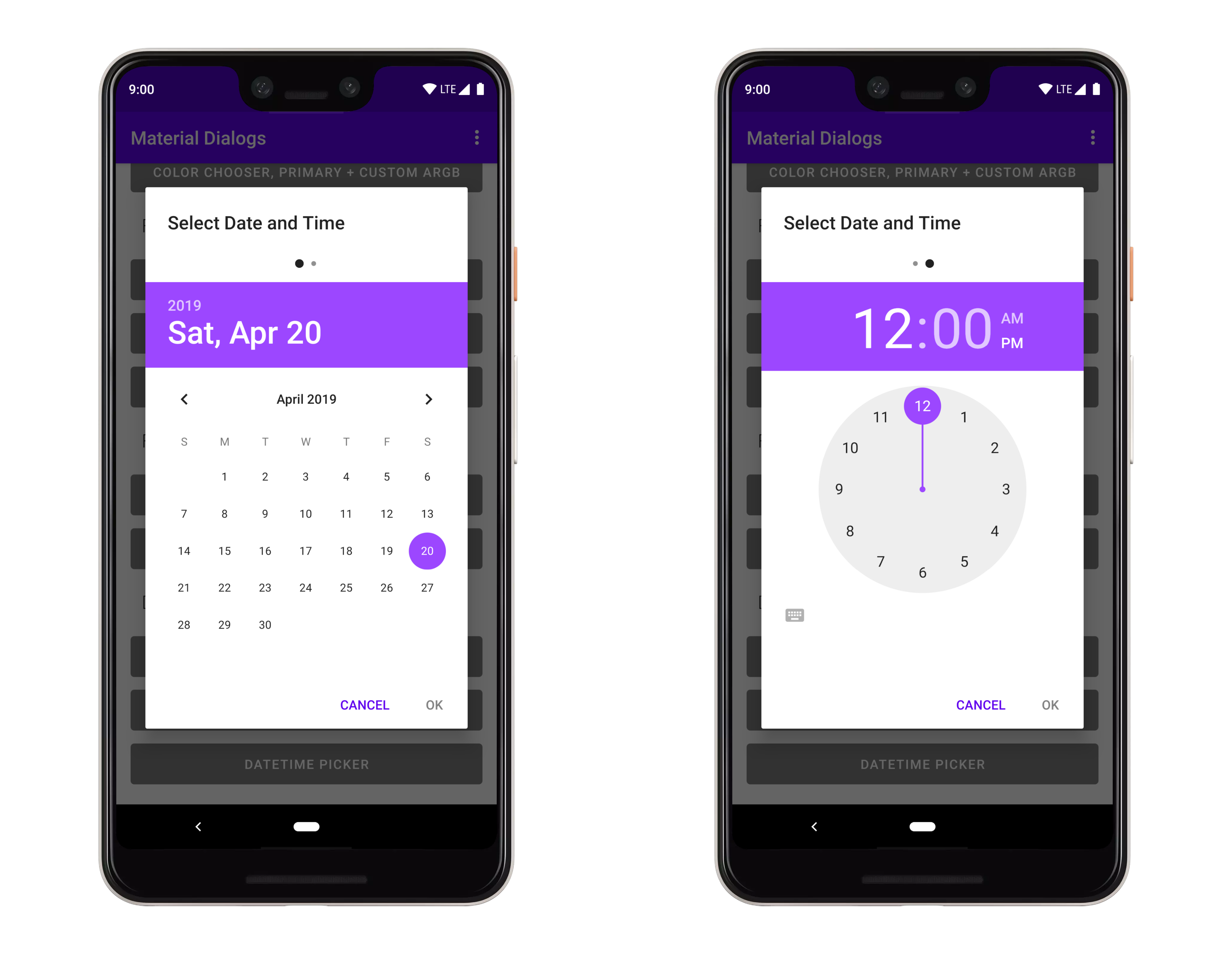
art/datetimepicker.png
0 → 100644
478.2 KB
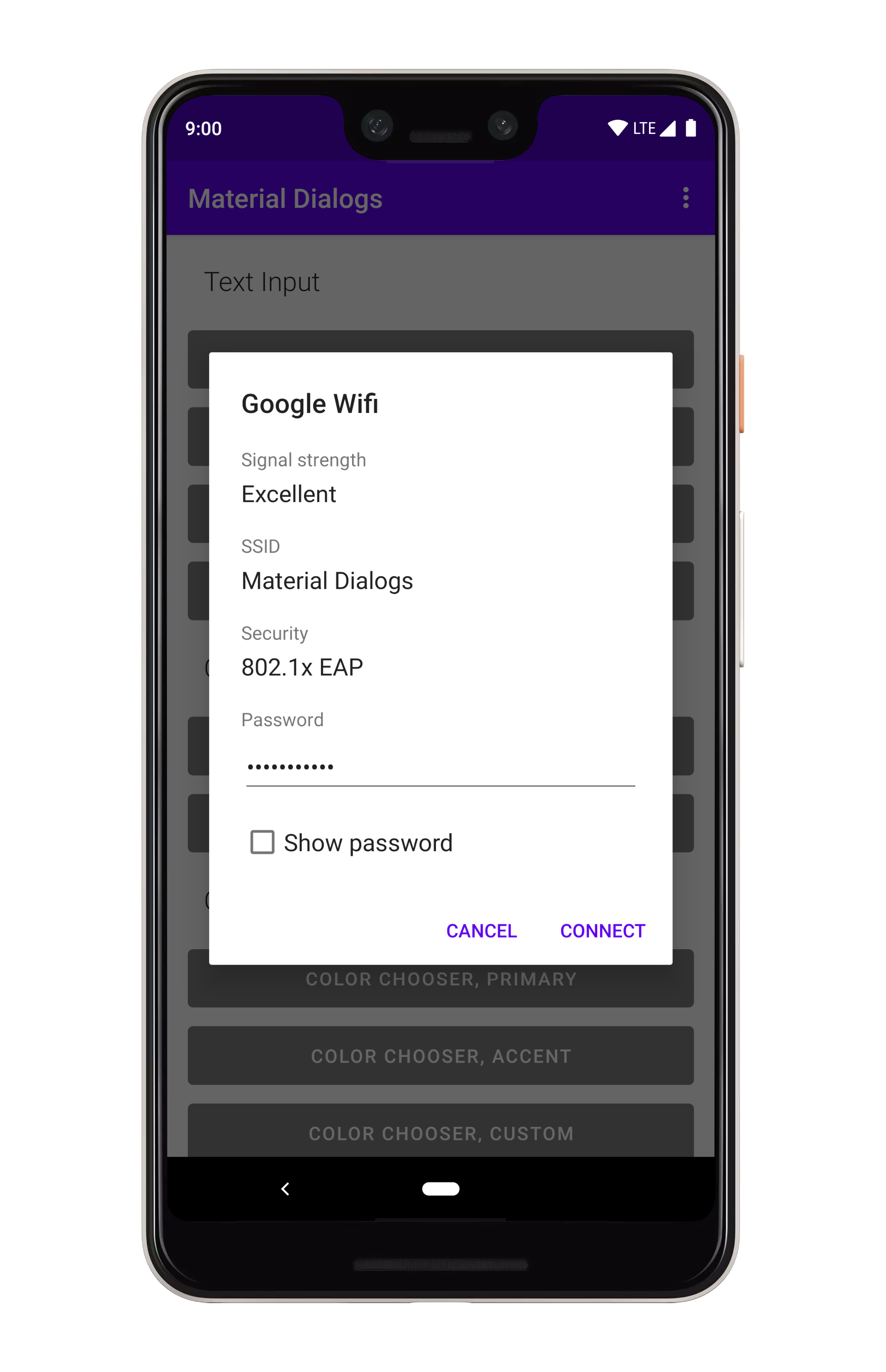
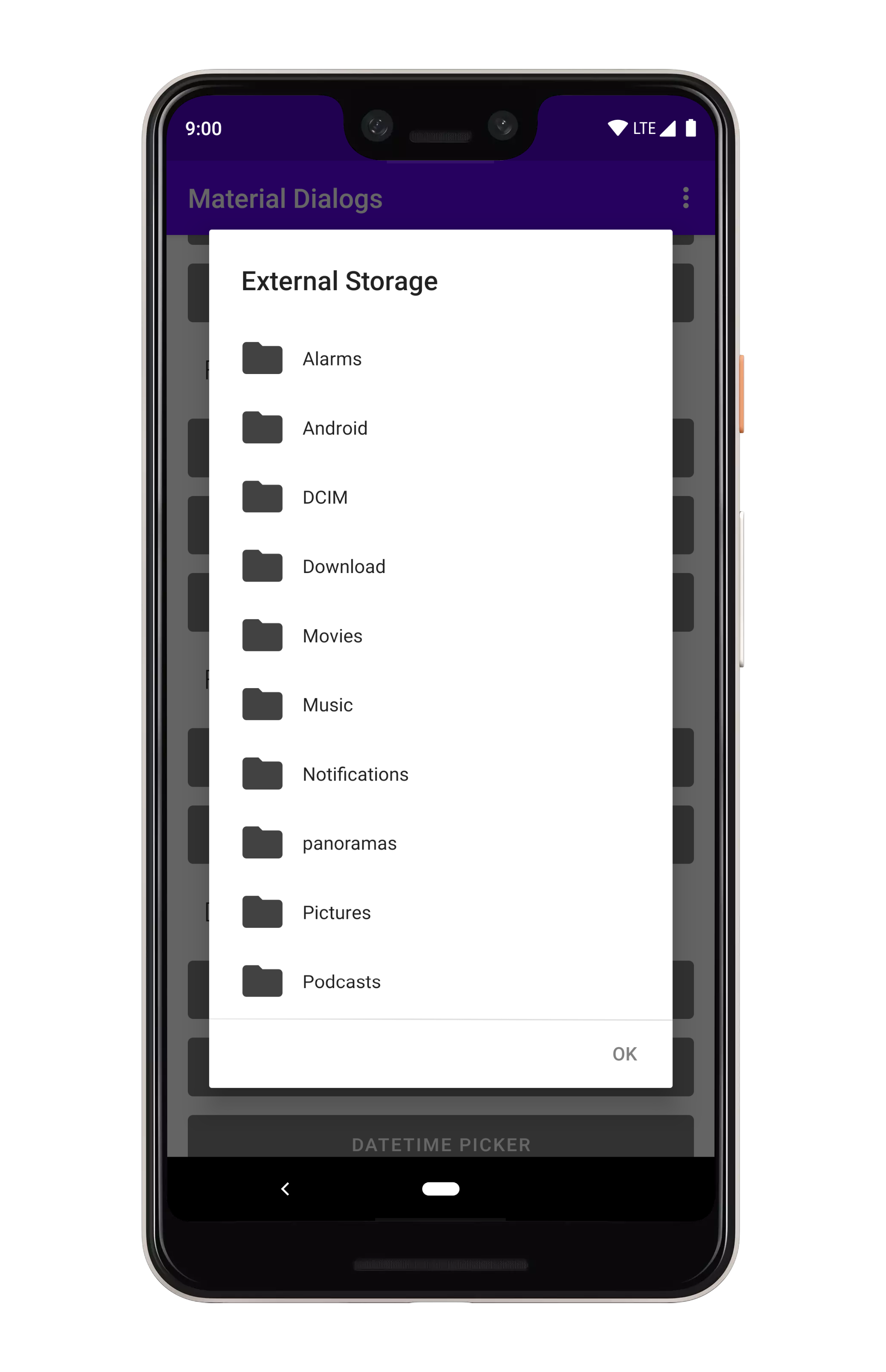
art/file_chooser.png
0 → 100644
356.2 KB
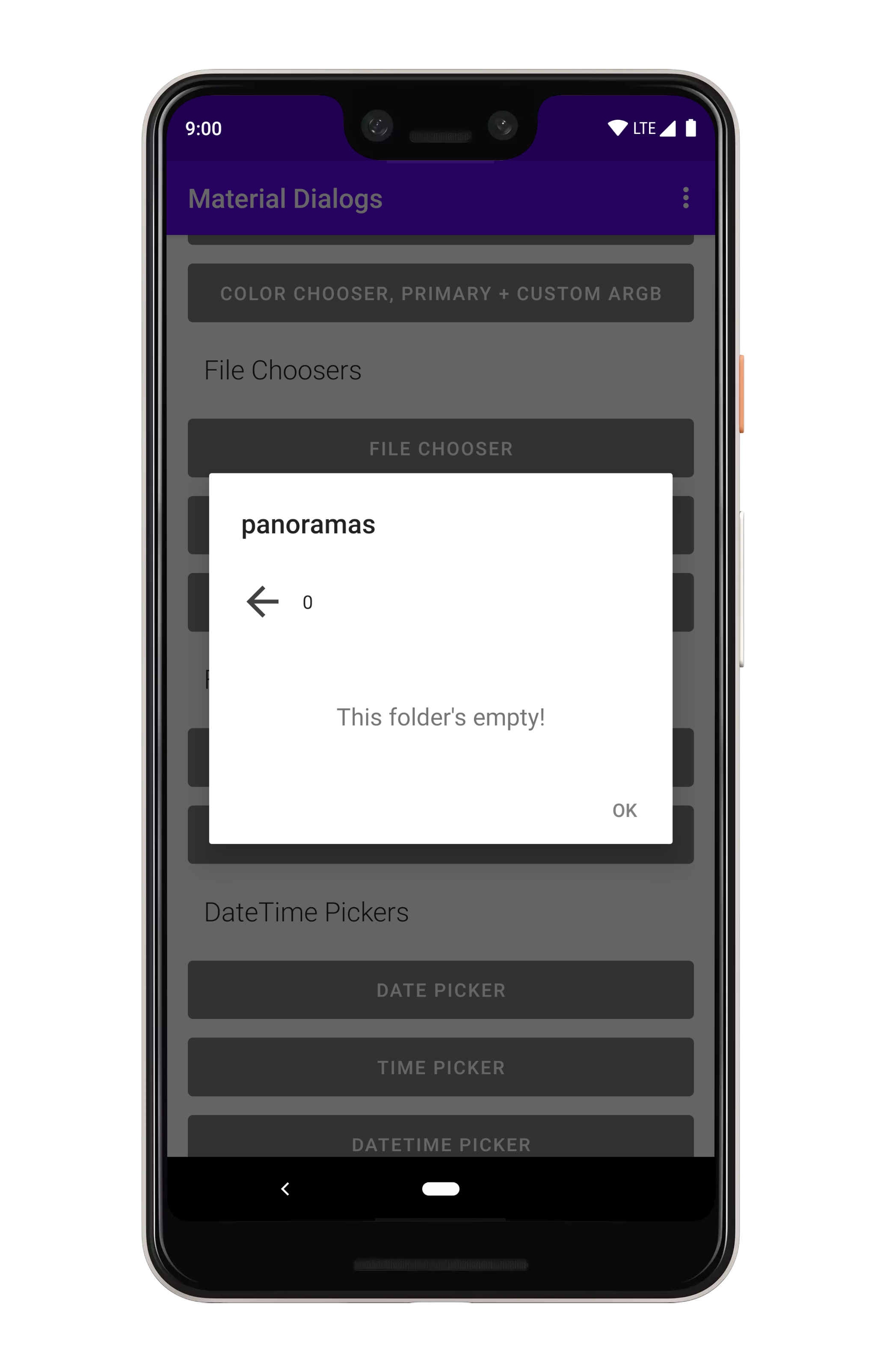
art/file_emptytext.png
0 → 100644
349.0 KB
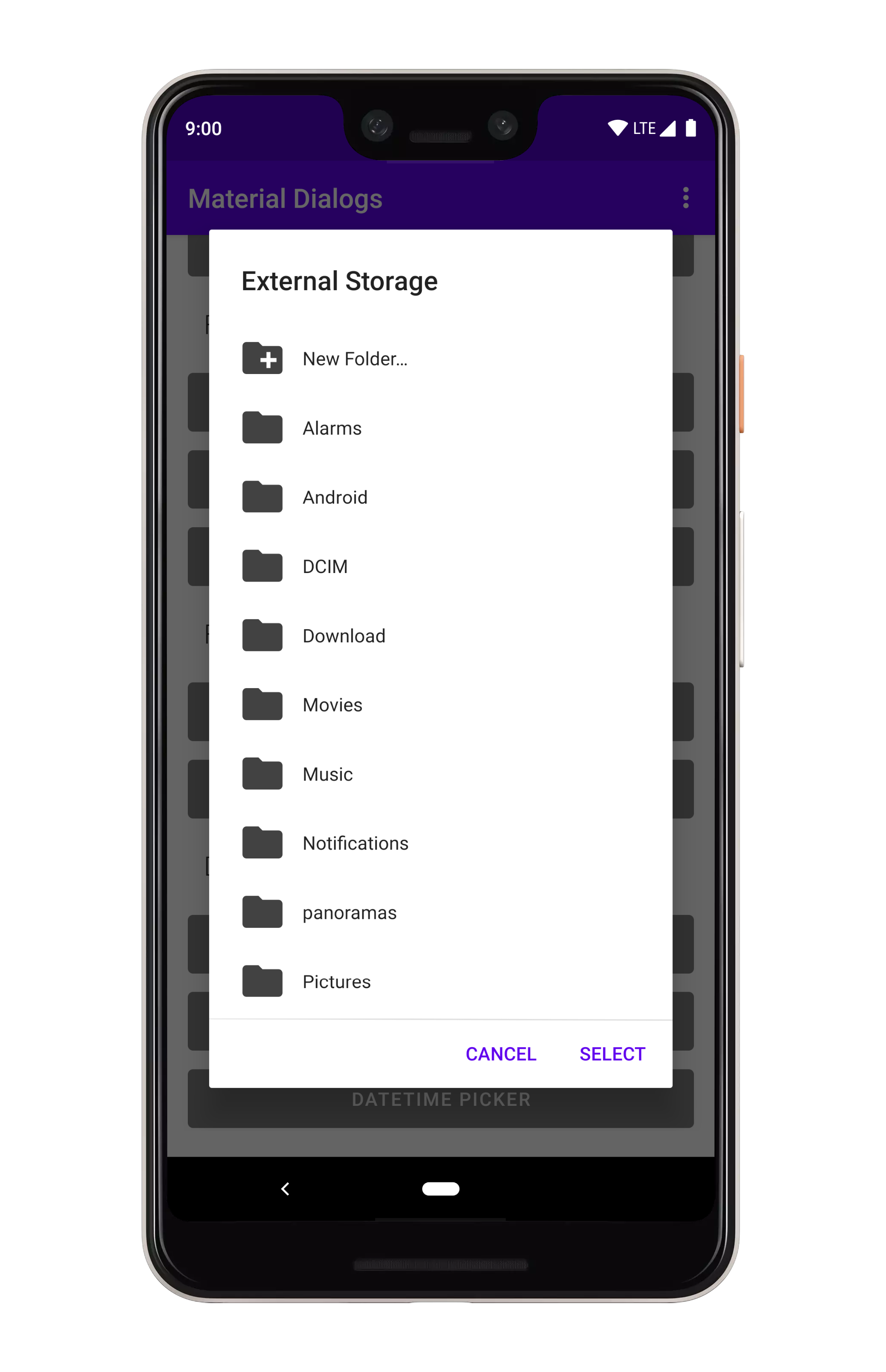
art/file_folder_creation.png
0 → 100644
361.6 KB
art/icon.png
0 → 100644
436.6 KB
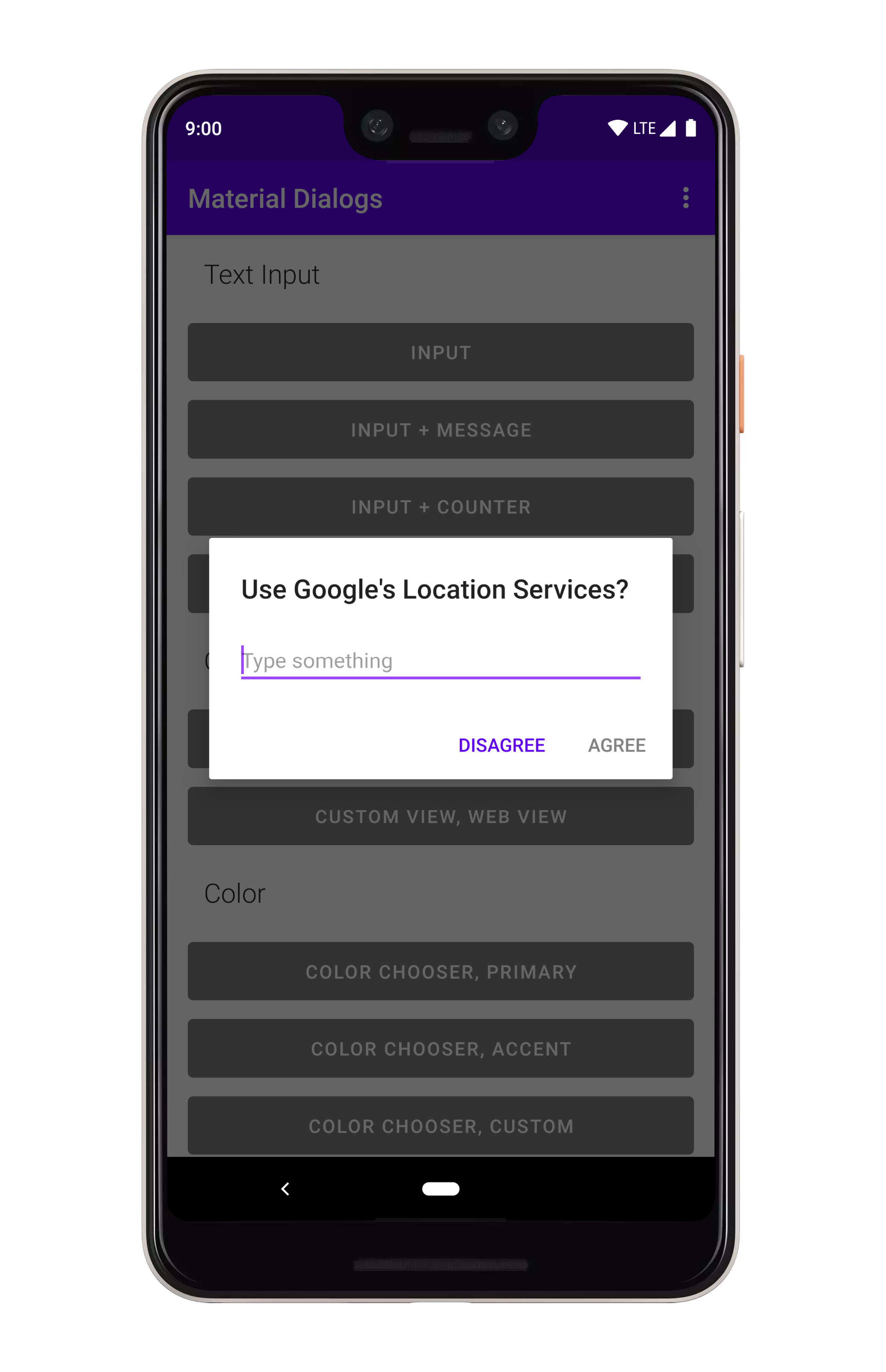
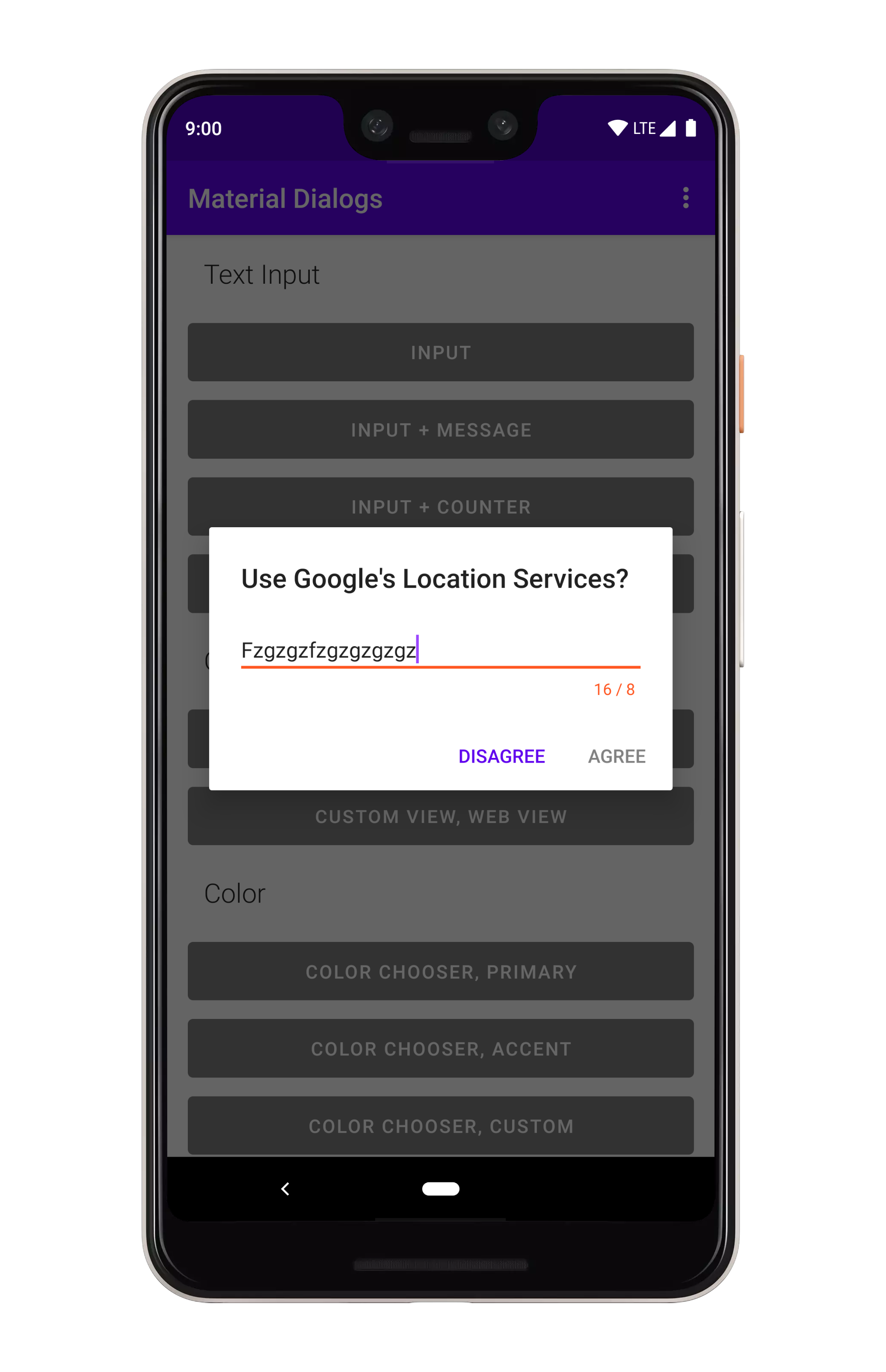
art/input.png
0 → 100644
373.4 KB
art/input_max_length.png
0 → 100644
379.0 KB
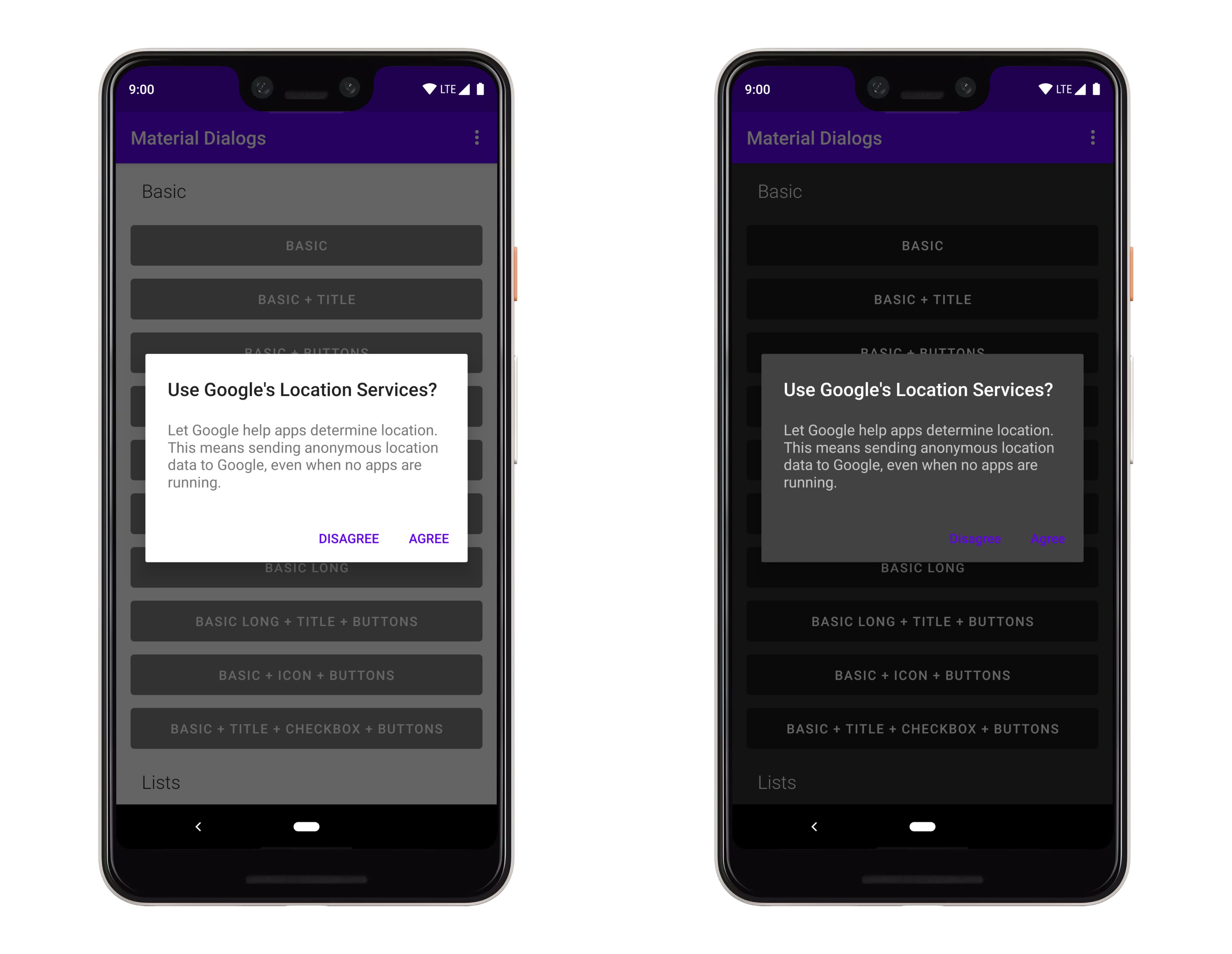
art/lightanddarkthemes.png
0 → 100644
630.9 KB
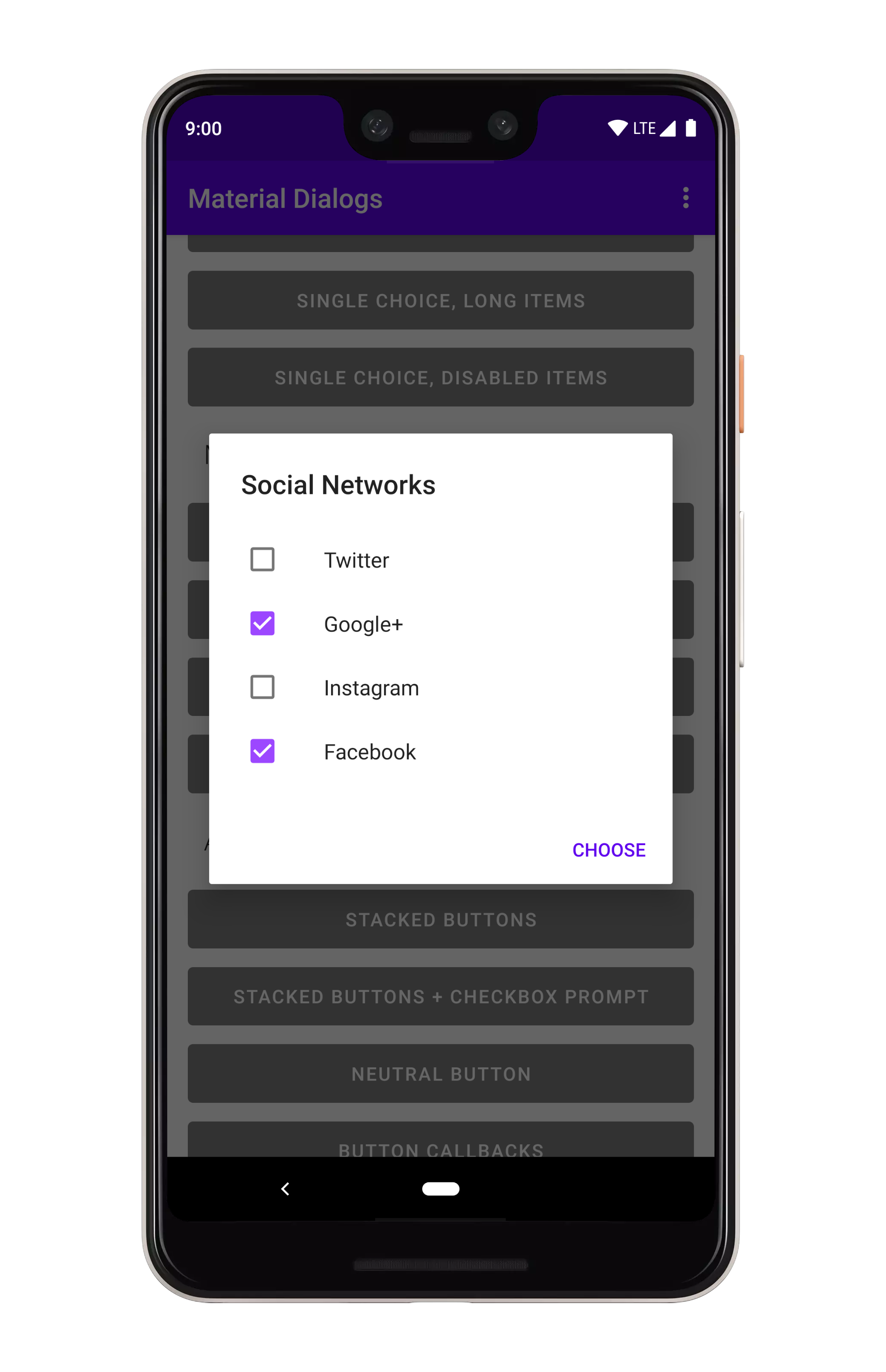
art/multi_choice_list.png
0 → 100644
376.0 KB
art/showcase4.png
0 → 100644
738.7 KB
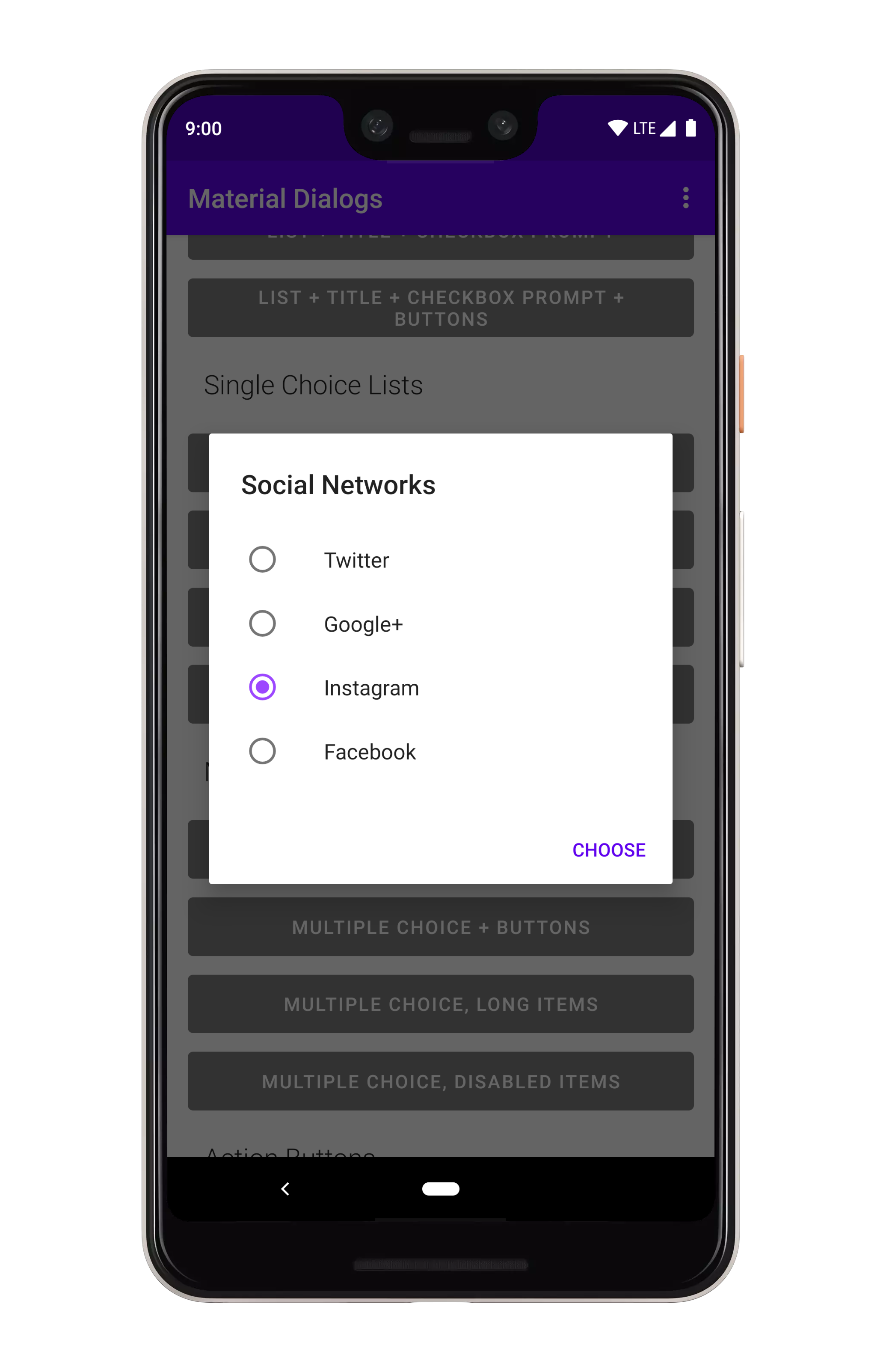
art/single_choice_list.png
0 → 100644
390.8 KB
art/stacked_buttons.png
0 → 100644
456.8 KB
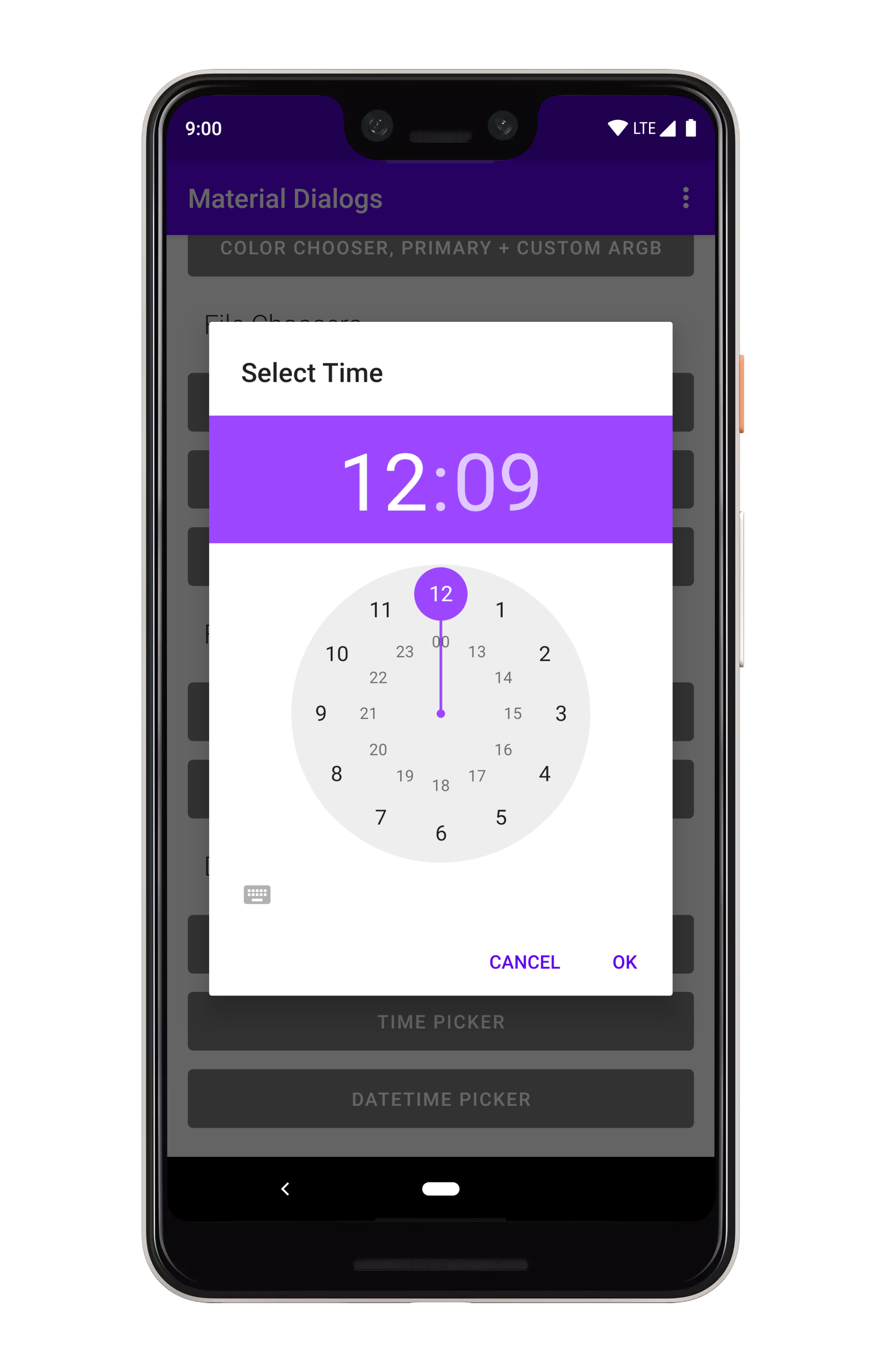
art/timepicker.png
0 → 100644
369.7 KB
5.7 KB
32.9 KB
documentation/BOTTOMSHEETS.md
0 → 100644
documentation/COLOR.md
0 → 100644
documentation/CORE.md
0 → 100644
documentation/DATETIME.md
0 → 100644
documentation/FILES.md
0 → 100644
documentation/INPUT.md
0 → 100644
documentation/LIFECYCLE.md
0 → 100644
documentation/en/BOTTOMSHEETS.md
0 → 100644
documentation/en/COLOR.md
0 → 100644
documentation/en/CORE.md
0 → 100644
documentation/en/DATETIME.md
0 → 100644
documentation/en/FILES.md
0 → 100644
documentation/en/INPUT.md
0 → 100644
documentation/en/LIFECYCLE.md
0 → 100644
en/README.md
0 → 100644
en/README_OLD.md
0 → 100644
此差异已折叠。
en/RELEASE_NOTES.md
0 → 100644
sample/ic_web.png
0 → 100644
19.0 KB
1.7 KB
1.6 KB
3.5 KB
1.2 KB
969 字节
2.3 KB
2.4 KB
2.2 KB
5.1 KB
3.6 KB
3.9 KB
8.0 KB
5.2 KB
5.9 KB
11.7 KB