Update to develop branch and resovle conflicts.
Showing
51.4 KB
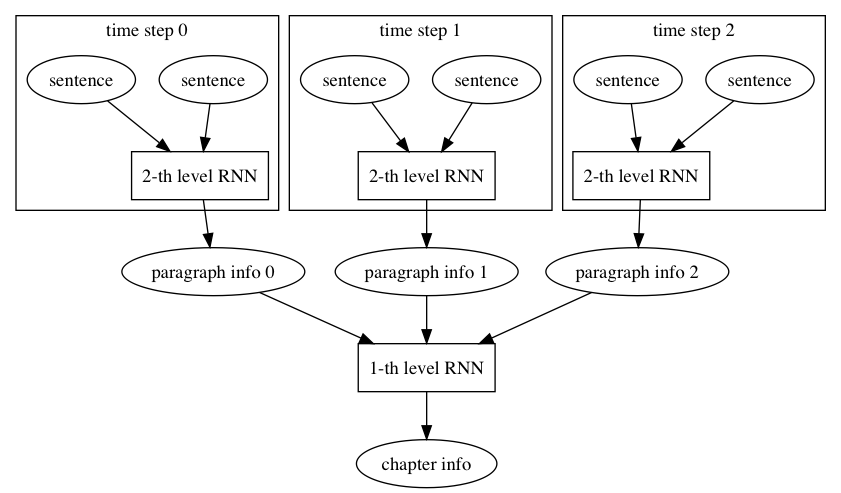
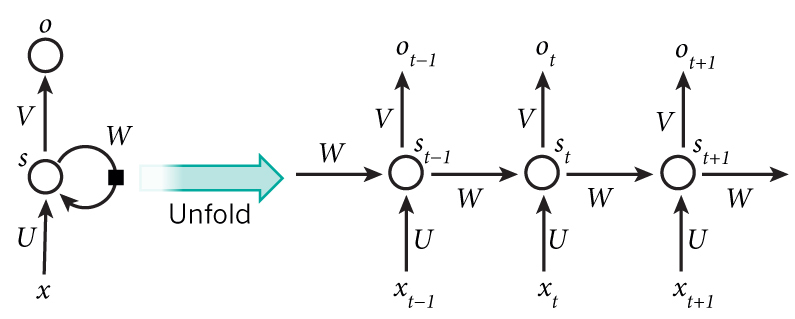
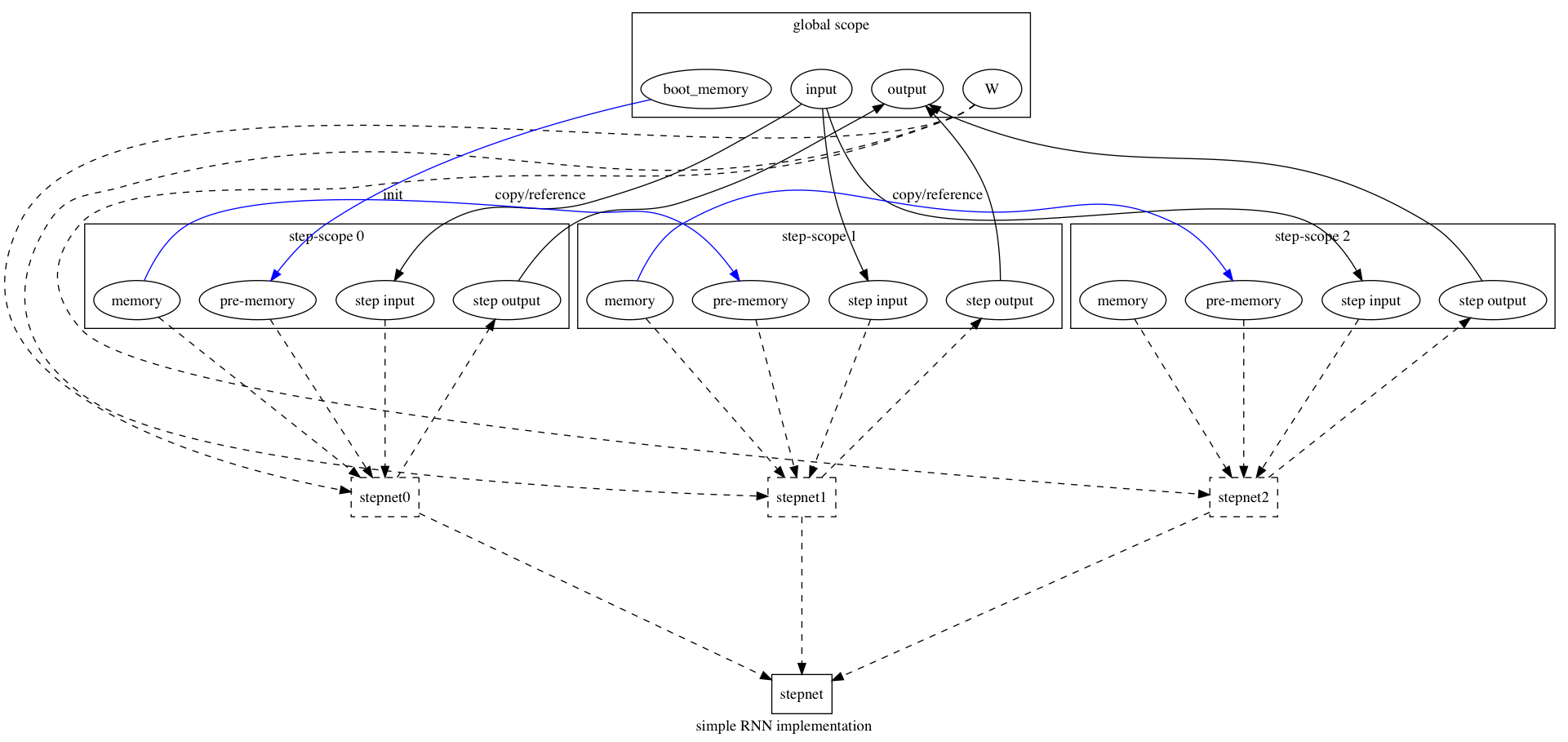
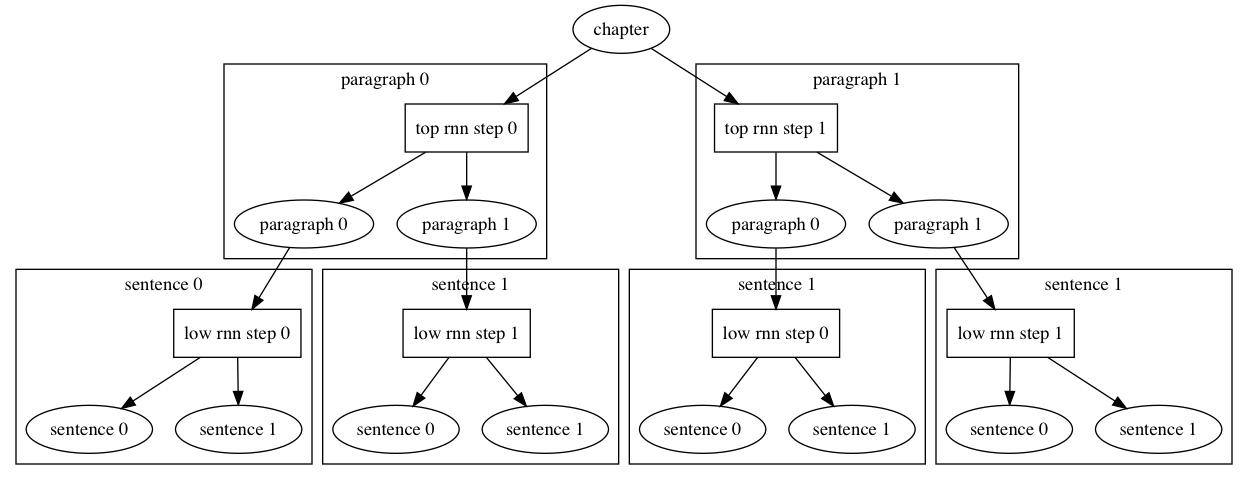
doc/design/ops/images/rnn.dot
0 → 100644
doc/design/ops/images/rnn.jpg
0 → 100644
43.3 KB
doc/design/ops/images/rnn.png
0 → 100644
180.8 KB
67.3 KB
doc/design/ops/rnn.md
0 → 100644
paddle/operators/accuracy_op.cc
0 → 100644
paddle/operators/accuracy_op.cu
0 → 100644
paddle/operators/accuracy_op.h
0 → 100644