Skip to content
体验新版
项目
组织
正在加载...
登录
切换导航
打开侧边栏
CSDN 技术社区
skill_tree_algorithm
提交
ceaae444
S
skill_tree_algorithm
项目概览
CSDN 技术社区
/
skill_tree_algorithm
通知
9
Star
8
Fork
1
代码
文件
提交
分支
Tags
贡献者
分支图
Diff
Issue
1
列表
看板
标记
里程碑
合并请求
0
DevOps
流水线
流水线任务
计划
Wiki
0
Wiki
分析
仓库
DevOps
项目成员
Pages
S
skill_tree_algorithm
项目概览
项目概览
详情
发布
仓库
仓库
文件
提交
分支
标签
贡献者
分支图
比较
Issue
1
Issue
1
列表
看板
标记
里程碑
合并请求
0
合并请求
0
Pages
DevOps
DevOps
流水线
流水线任务
计划
分析
分析
仓库分析
DevOps
Wiki
0
Wiki
成员
成员
收起侧边栏
关闭侧边栏
动态
分支图
创建新Issue
流水线任务
提交
Issue看板
提交
ceaae444
编写于
11月 09, 2021
作者:
F
feilong
浏览文件
操作
浏览文件
下载
电子邮件补丁
差异文件
fix bug
上级
9f06a56f
变更
204
展开全部
隐藏空白更改
内联
并排
Showing
204 changed file
with
939 addition
and
0 deletion
+939
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/100.第39级台阶/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/100.第39级台阶/solution.md
+9
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/104.9数算式/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/104.9数算式/solution.md
+9
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/106.错误票据/desc.md
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/106.错误票据/desc.md
+8
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/106.错误票据/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/106.错误票据/solution.md
+16
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/112.大数乘法/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/112.大数乘法/solution.md
+9
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/114.大衍数列/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/114.大衍数列/solution.md
+9
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/120.成绩统计/desc.md
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/120.成绩统计/desc.md
+5
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/120.成绩统计/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/120.成绩统计/solution.md
+14
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/126.比酒量/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/126.比酒量/solution.md
+9
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/134.第几天/desc.md
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/134.第几天/desc.md
+5
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/134.第几天/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/134.第几天/solution.md
+14
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/135.斐波那契/desc.md
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/135.斐波那契/desc.md
+7
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/135.斐波那契/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/135.斐波那契/solution.md
+15
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/149.方阵转置/desc.md
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/149.方阵转置/desc.md
+5
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/149.方阵转置/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/149.方阵转置/solution.md
+14
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/158.倍数问题/desc.md
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/158.倍数问题/desc.md
+7
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/158.倍数问题/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/158.倍数问题/solution.md
+15
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/24.乘积尾零/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/24.乘积尾零/solution.md
+9
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/3.分数/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/3.分数/solution.md
+9
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/4.等差素数列/desc.md
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/4.等差素数列/desc.md
+1
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/4.等差素数列/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/4.等差素数列/solution.md
+10
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/40.成绩分析/desc.md
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/40.成绩分析/desc.md
+5
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/40.成绩分析/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/40.成绩分析/solution.md
+14
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/41.乘积最大/desc.md
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/41.乘积最大/desc.md
+8
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/41.乘积最大/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/41.乘积最大/solution.md
+16
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/67.猜年龄/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/67.猜年龄/solution.md
+9
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/69.递增三元组/desc.md
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/69.递增三元组/desc.md
+4
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/69.递增三元组/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/69.递增三元组/solution.md
+13
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/77.第几个幸运数/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/77.第几个幸运数/solution.md
+9
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/88.次数差/desc.md
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/88.次数差/desc.md
+9
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/88.次数差/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/88.次数差/solution.md
+17
-0
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/99.猜字母/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/99.猜字母/solution.md
+9
-0
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/92.单词分析/desc.md
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/92.单词分析/desc.md
+8
-0
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/92.单词分析/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/92.单词分析/solution.md
+17
-0
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/97.分类计数/desc.md
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/97.分类计数/desc.md
+6
-0
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/97.分类计数/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/97.分类计数/solution.md
+15
-0
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/98.翻硬币/desc.md
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/98.翻硬币/desc.md
+8
-0
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/98.翻硬币/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/98.翻硬币/solution.md
+16
-0
data/1.算法初阶/3.蓝桥杯-递归/143.带分数/desc.md
data/1.算法初阶/3.蓝桥杯-递归/143.带分数/desc.md
+8
-0
data/1.算法初阶/3.蓝桥杯-递归/143.带分数/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/3.蓝桥杯-递归/143.带分数/solution.md
+16
-0
data/1.算法初阶/3.蓝桥杯-递归/163.等差数列/desc.md
data/1.算法初阶/3.蓝桥杯-递归/163.等差数列/desc.md
+7
-0
data/1.算法初阶/3.蓝桥杯-递归/163.等差数列/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/3.蓝桥杯-递归/163.等差数列/solution.md
+15
-0
data/1.算法初阶/3.蓝桥杯-递归/35.抽签/desc.md
data/1.算法初阶/3.蓝桥杯-递归/35.抽签/desc.md
+4
-0
data/1.算法初阶/3.蓝桥杯-递归/35.抽签/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/3.蓝桥杯-递归/35.抽签/solution.md
+13
-0
data/1.算法初阶/3.蓝桥杯-递归/58.打印图形/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/3.蓝桥杯-递归/58.打印图形/solution.md
+9
-0
data/1.算法初阶/4.蓝桥杯-堆栈队列链表/124.堆的计数/desc.md
data/1.算法初阶/4.蓝桥杯-堆栈队列链表/124.堆的计数/desc.md
+6
-0
data/1.算法初阶/4.蓝桥杯-堆栈队列链表/124.堆的计数/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/4.蓝桥杯-堆栈队列链表/124.堆的计数/solution.md
+15
-0
data/1.算法初阶/6.蓝桥杯-模拟/137.夺冠概率/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/6.蓝桥杯-模拟/137.夺冠概率/solution.md
+9
-0
data/1.算法初阶/6.蓝桥杯-模拟/14.方程整数解/desc.md
data/1.算法初阶/6.蓝桥杯-模拟/14.方程整数解/desc.md
+5
-0
data/1.算法初阶/6.蓝桥杯-模拟/14.方程整数解/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/6.蓝桥杯-模拟/14.方程整数解/solution.md
+14
-0
data/1.算法初阶/6.蓝桥杯-模拟/162.7段码/desc.md
data/1.算法初阶/6.蓝桥杯-模拟/162.7段码/desc.md
+1
-0
data/1.算法初阶/6.蓝桥杯-模拟/162.7段码/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/6.蓝桥杯-模拟/162.7段码/solution.md
+10
-0
data/1.算法初阶/6.蓝桥杯-模拟/175.颠倒的价牌/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/6.蓝桥杯-模拟/175.颠倒的价牌/solution.md
+9
-0
data/1.算法初阶/6.蓝桥杯-模拟/187.承压计算/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/6.蓝桥杯-模拟/187.承压计算/solution.md
+9
-0
data/1.算法初阶/6.蓝桥杯-模拟/23.放棋子/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/6.蓝桥杯-模拟/23.放棋子/solution.md
+9
-0
data/1.算法初阶/6.蓝桥杯-模拟/28.分巧克力/desc.md
data/1.算法初阶/6.蓝桥杯-模拟/28.分巧克力/desc.md
+4
-0
data/1.算法初阶/6.蓝桥杯-模拟/28.分巧克力/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/6.蓝桥杯-模拟/28.分巧克力/solution.md
+13
-0
data/1.算法初阶/6.蓝桥杯-模拟/53.等腰三角形/desc.md
data/1.算法初阶/6.蓝桥杯-模拟/53.等腰三角形/desc.md
+9
-0
data/1.算法初阶/6.蓝桥杯-模拟/53.等腰三角形/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/6.蓝桥杯-模拟/53.等腰三角形/solution.md
+18
-0
data/1.算法初阶/6.蓝桥杯-模拟/54.分糖果/desc.md
data/1.算法初阶/6.蓝桥杯-模拟/54.分糖果/desc.md
+6
-0
data/1.算法初阶/6.蓝桥杯-模拟/54.分糖果/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/6.蓝桥杯-模拟/54.分糖果/solution.md
+14
-0
data/1.算法初阶/6.蓝桥杯-模拟/63.方格填数/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/6.蓝桥杯-模拟/63.方格填数/solution.md
+9
-0
data/1.算法初阶/7.蓝桥杯-搜索/121.超级胶水/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/7.蓝桥杯-搜索/121.超级胶水/solution.md
+9
-0
data/1.算法初阶/7.蓝桥杯-搜索/156.凑算式/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/7.蓝桥杯-搜索/156.凑算式/solution.md
+9
-0
data/1.算法初阶/7.蓝桥杯-搜索/188.大臣的旅费/desc.md
data/1.算法初阶/7.蓝桥杯-搜索/188.大臣的旅费/desc.md
+7
-0
data/1.算法初阶/7.蓝桥杯-搜索/188.大臣的旅费/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/7.蓝桥杯-搜索/188.大臣的旅费/solution.md
+15
-0
data/1.算法初阶/7.蓝桥杯-搜索/51.分配口罩/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/7.蓝桥杯-搜索/51.分配口罩/solution.md
+9
-0
data/1.算法初阶/7.蓝桥杯-搜索/6.搭积木/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/7.蓝桥杯-搜索/6.搭积木/solution.md
+9
-0
data/1.算法初阶/7.蓝桥杯-搜索/65.方格分割/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/7.蓝桥杯-搜索/65.方格分割/solution.md
+9
-0
data/1.算法初阶/9.蓝桥杯-动态规划/117.地宫取宝/desc.md
data/1.算法初阶/9.蓝桥杯-动态规划/117.地宫取宝/desc.md
+8
-0
data/1.算法初阶/9.蓝桥杯-动态规划/117.地宫取宝/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/9.蓝桥杯-动态规划/117.地宫取宝/solution.md
+16
-0
data/1.算法初阶/9.蓝桥杯-动态规划/91.测试次数/solution.md
data/1.算法初阶/9.蓝桥杯-动态规划/91.测试次数/solution.md
+9
-0
data/2.算法中阶/1.leetcode-数组/0.两数之和/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/1.leetcode-数组/0.两数之和/solution.md
+9
-0
data/2.算法中阶/1.leetcode-数组/14.三数之和/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/1.leetcode-数组/14.三数之和/solution.md
+9
-0
data/2.算法中阶/1.leetcode-数组/17.四数之和/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/1.leetcode-数组/17.四数之和/solution.md
+9
-0
data/2.算法中阶/1.leetcode-数组/3.寻找两个正序数组的中位数/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/1.leetcode-数组/3.寻找两个正序数组的中位数/solution.md
+9
-0
data/2.算法中阶/1.leetcode-数组/32.搜索旋转排序数组/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/1.leetcode-数组/32.搜索旋转排序数组/solution.md
+9
-0
data/2.算法中阶/1.leetcode-数组/33.在排序数组中查找元素的第一个和最后一个位置/solution.md
...2.算法中阶/1.leetcode-数组/33.在排序数组中查找元素的第一个和最后一个位置/solution.md
+9
-0
data/2.算法中阶/1.leetcode-数组/34.搜索插入位置/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/1.leetcode-数组/34.搜索插入位置/solution.md
+9
-0
data/2.算法中阶/1.leetcode-数组/47.旋转图像/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/1.leetcode-数组/47.旋转图像/solution.md
+9
-0
data/2.算法中阶/1.leetcode-数组/53.螺旋矩阵/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/1.leetcode-数组/53.螺旋矩阵/solution.md
+9
-0
data/2.算法中阶/1.leetcode-数组/55.合并区间/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/1.leetcode-数组/55.合并区间/solution.md
+9
-0
data/2.算法中阶/1.leetcode-数组/56.插入区间/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/1.leetcode-数组/56.插入区间/solution.md
+9
-0
data/2.算法中阶/1.leetcode-数组/58.螺旋矩阵 II/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/1.leetcode-数组/58.螺旋矩阵 II/solution.md
+9
-0
data/2.算法中阶/1.leetcode-数组/72.矩阵置零/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/1.leetcode-数组/72.矩阵置零/solution.md
+9
-0
data/2.算法中阶/1.leetcode-数组/73.搜索二维矩阵/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/1.leetcode-数组/73.搜索二维矩阵/solution.md
+9
-0
data/2.算法中阶/1.leetcode-数组/77.子集/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/1.leetcode-数组/77.子集/solution.md
+9
-0
data/2.算法中阶/1.leetcode-数组/79.删除有序数组中的重复项 II/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/1.leetcode-数组/79.删除有序数组中的重复项 II/solution.md
+9
-0
data/2.算法中阶/1.leetcode-数组/80.搜索旋转排序数组 II/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/1.leetcode-数组/80.搜索旋转排序数组 II/solution.md
+9
-0
data/2.算法中阶/2.leetcode-链表/1.两数相加/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/2.leetcode-链表/1.两数相加/solution.md
+9
-0
data/2.算法中阶/2.leetcode-链表/18.删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/2.leetcode-链表/18.删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点/solution.md
+9
-0
data/2.算法中阶/2.leetcode-链表/20.合并两个有序链表/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/2.leetcode-链表/20.合并两个有序链表/solution.md
+9
-0
data/2.算法中阶/2.leetcode-链表/22.合并K个升序链表/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/2.leetcode-链表/22.合并K个升序链表/solution.md
+9
-0
data/2.算法中阶/2.leetcode-链表/23.两两交换链表中的节点/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/2.leetcode-链表/23.两两交换链表中的节点/solution.md
+9
-0
data/2.算法中阶/2.leetcode-链表/24.K 个一组翻转链表/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/2.leetcode-链表/24.K 个一组翻转链表/solution.md
+9
-0
data/2.算法中阶/2.leetcode-链表/81.删除排序链表中的重复元素 II/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/2.leetcode-链表/81.删除排序链表中的重复元素 II/solution.md
+9
-0
data/2.算法中阶/2.leetcode-链表/82.删除排序链表中的重复元素/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/2.leetcode-链表/82.删除排序链表中的重复元素/solution.md
+9
-0
data/2.算法中阶/2.leetcode-链表/85.分隔链表/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/2.leetcode-链表/85.分隔链表/solution.md
+0
-0
data/2.算法中阶/2.leetcode-链表/91.反转链表 II/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/2.leetcode-链表/91.反转链表 II/solution.md
+0
-0
data/2.算法中阶/3.leetcode-字符串/13.最长公共前缀/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/3.leetcode-字符串/13.最长公共前缀/solution.md
+0
-0
data/2.算法中阶/3.leetcode-字符串/2.无重复字符的最长子串/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/3.leetcode-字符串/2.无重复字符的最长子串/solution.md
+0
-0
data/2.算法中阶/3.leetcode-字符串/27.实现 strStr()/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/3.leetcode-字符串/27.实现 strStr()/solution.md
+0
-0
data/2.算法中阶/3.leetcode-字符串/37.外观数列/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/3.leetcode-字符串/37.外观数列/solution.md
+0
-0
data/2.算法中阶/3.leetcode-字符串/42.字符串相乘/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/3.leetcode-字符串/42.字符串相乘/solution.md
+0
-0
data/2.算法中阶/3.leetcode-字符串/5.Z 字形变换/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/3.leetcode-字符串/5.Z 字形变换/solution.md
+0
-0
data/2.算法中阶/3.leetcode-字符串/57.最后一个单词的长度/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/3.leetcode-字符串/57.最后一个单词的长度/solution.md
+0
-0
data/2.算法中阶/3.leetcode-字符串/64.有效数字/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/3.leetcode-字符串/64.有效数字/solution.md
+0
-0
data/2.算法中阶/3.leetcode-字符串/7.字符串转换整数 (atoi)/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/3.leetcode-字符串/7.字符串转换整数 (atoi)/solution.md
+0
-0
data/2.算法中阶/3.leetcode-字符串/92.复原 IP 地址/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/3.leetcode-字符串/92.复原 IP 地址/solution.md
+0
-0
data/2.算法中阶/3.leetcode-字符串/96.交错字符串/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/3.leetcode-字符串/96.交错字符串/solution.md
+0
-0
data/2.算法中阶/4.leetcode-栈与队列/149.逆波兰表达式求值/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/4.leetcode-栈与队列/149.逆波兰表达式求值/solution.md
+0
-0
data/2.算法中阶/4.leetcode-栈与队列/154.最小栈/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/4.leetcode-栈与队列/154.最小栈/solution.md
+0
-0
data/2.算法中阶/4.leetcode-栈与队列/19.有效的括号/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/4.leetcode-栈与队列/19.有效的括号/solution.md
+0
-0
data/2.算法中阶/4.leetcode-栈与队列/217.天际线问题/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/4.leetcode-栈与队列/217.天际线问题/solution.md
+0
-0
data/2.算法中阶/4.leetcode-栈与队列/223.基本计算器/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/4.leetcode-栈与队列/223.基本计算器/solution.md
+0
-0
data/2.算法中阶/4.leetcode-栈与队列/226.基本计算器 II/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/4.leetcode-栈与队列/226.基本计算器 II/solution.md
+0
-0
data/2.算法中阶/4.leetcode-栈与队列/31.最长有效括号/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/4.leetcode-栈与队列/31.最长有效括号/solution.md
+0
-0
data/2.算法中阶/4.leetcode-栈与队列/41.接雨水/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/4.leetcode-栈与队列/41.接雨水/solution.md
+0
-0
data/2.算法中阶/4.leetcode-栈与队列/70.简化路径/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/4.leetcode-栈与队列/70.简化路径/solution.md
+0
-0
data/2.算法中阶/4.leetcode-栈与队列/83.柱状图中最大的矩形/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/4.leetcode-栈与队列/83.柱状图中最大的矩形/solution.md
+0
-0
data/2.算法中阶/5.leetcode-排序算法/163.最大间距/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/5.leetcode-排序算法/163.最大间距/solution.md
+0
-0
data/2.算法中阶/5.leetcode-排序算法/273.H 指数/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/5.leetcode-排序算法/273.H 指数/solution.md
+0
-0
data/2.算法中阶/5.leetcode-排序算法/314.计算右侧小于当前元素的个数/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/5.leetcode-排序算法/314.计算右侧小于当前元素的个数/solution.md
+0
-0
data/2.算法中阶/5.leetcode-排序算法/323.摆动排序 II/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/5.leetcode-排序算法/323.摆动排序 II/solution.md
+0
-0
data/2.算法中阶/5.leetcode-排序算法/326.区间和的个数/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/5.leetcode-排序算法/326.区间和的个数/solution.md
+0
-0
data/2.算法中阶/5.leetcode-排序算法/346.前 K 个高频元素/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/5.leetcode-排序算法/346.前 K 个高频元素/solution.md
+0
-0
data/2.算法中阶/5.leetcode-排序算法/353.俄罗斯套娃信封问题/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/5.leetcode-排序算法/353.俄罗斯套娃信封问题/solution.md
+0
-0
data/2.算法中阶/5.leetcode-排序算法/377.有序矩阵中第 K 小的元素/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/5.leetcode-排序算法/377.有序矩阵中第 K 小的元素/solution.md
+0
-0
data/2.算法中阶/5.leetcode-排序算法/492.翻转对/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/5.leetcode-排序算法/492.翻转对/solution.md
+0
-0
data/2.算法中阶/5.leetcode-排序算法/911.排序数组/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/5.leetcode-排序算法/911.排序数组/solution.md
+0
-0
data/2.算法中阶/6.leetcode-双指针/10.盛最多水的容器/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/6.leetcode-双指针/10.盛最多水的容器/solution.md
+0
-0
data/2.算法中阶/6.leetcode-双指针/140.环形链表/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/6.leetcode-双指针/140.环形链表/solution.md
+0
-0
data/2.算法中阶/6.leetcode-双指针/141.环形链表 II/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/6.leetcode-双指针/141.环形链表 II/solution.md
+0
-0
data/2.算法中阶/6.leetcode-双指针/15.最接近的三数之和/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/6.leetcode-双指针/15.最接近的三数之和/solution.md
+0
-0
data/2.算法中阶/6.leetcode-双指针/25.删除有序数组中的重复项/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/6.leetcode-双指针/25.删除有序数组中的重复项/solution.md
+0
-0
data/2.算法中阶/6.leetcode-双指针/26.移除元素/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/6.leetcode-双指针/26.移除元素/solution.md
+0
-0
data/2.算法中阶/6.leetcode-双指针/30.下一个排列/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/6.leetcode-双指针/30.下一个排列/solution.md
+0
-0
data/2.算法中阶/6.leetcode-双指针/60.旋转链表/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/6.leetcode-双指针/60.旋转链表/solution.md
+0
-0
data/2.算法中阶/6.leetcode-双指针/74.颜色分类/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/6.leetcode-双指针/74.颜色分类/solution.md
+0
-0
data/2.算法中阶/6.leetcode-双指针/87.合并两个有序数组/solution.md
data/2.算法中阶/6.leetcode-双指针/87.合并两个有序数组/solution.md
+0
-0
data/3.算法高阶/1.leetcode-树/123.二叉树中的最大路径和/solution.md
data/3.算法高阶/1.leetcode-树/123.二叉树中的最大路径和/solution.md
+0
-0
data/3.算法高阶/1.leetcode-树/93.二叉树的中序遍历/solution.md
data/3.算法高阶/1.leetcode-树/93.二叉树的中序遍历/solution.md
+0
-0
data/3.算法高阶/1.leetcode-树/94.不同的二叉搜索树 II/solution.md
data/3.算法高阶/1.leetcode-树/94.不同的二叉搜索树 II/solution.md
+0
-0
data/3.算法高阶/1.leetcode-树/95.不同的二叉搜索树/solution.md
data/3.算法高阶/1.leetcode-树/95.不同的二叉搜索树/solution.md
+0
-0
data/3.算法高阶/1.leetcode-树/97.验证二叉搜索树/solution.md
data/3.算法高阶/1.leetcode-树/97.验证二叉搜索树/solution.md
+0
-0
data/3.算法高阶/1.leetcode-树/98.恢复二叉搜索树/solution.md
data/3.算法高阶/1.leetcode-树/98.恢复二叉搜索树/solution.md
+0
-0
data/3.算法高阶/1.leetcode-树/99.相同的树/solution.md
data/3.算法高阶/1.leetcode-树/99.相同的树/solution.md
+0
-0
data/3.算法高阶/2.leetcode-哈希表/204.同构字符串/solution.md
data/3.算法高阶/2.leetcode-哈希表/204.同构字符串/solution.md
+0
-0
data/3.算法高阶/2.leetcode-哈希表/29.串联所有单词的子串/solution.md
data/3.算法高阶/2.leetcode-哈希表/29.串联所有单词的子串/solution.md
+0
-0
data/3.算法高阶/2.leetcode-哈希表/35.有效的数独/solution.md
data/3.算法高阶/2.leetcode-哈希表/35.有效的数独/solution.md
+0
-0
data/3.算法高阶/2.leetcode-哈希表/40.缺失的第一个正数/solution.md
data/3.算法高阶/2.leetcode-哈希表/40.缺失的第一个正数/solution.md
+0
-0
data/3.算法高阶/2.leetcode-哈希表/48.字母异位词分组/solution.md
data/3.算法高阶/2.leetcode-哈希表/48.字母异位词分组/solution.md
+0
-0
data/3.算法高阶/2.leetcode-哈希表/75.最小覆盖子串/solution.md
data/3.算法高阶/2.leetcode-哈希表/75.最小覆盖子串/solution.md
+0
-0
data/3.算法高阶/3.leetcode-图与搜索/132.克隆图/solution.md
data/3.算法高阶/3.leetcode-图与搜索/132.克隆图/solution.md
+0
-0
data/3.算法高阶/3.leetcode-图与搜索/206.课程表/solution.md
data/3.算法高阶/3.leetcode-图与搜索/206.课程表/solution.md
+0
-0
data/3.算法高阶/3.leetcode-图与搜索/209.课程表 II/solution.md
data/3.算法高阶/3.leetcode-图与搜索/209.课程表 II/solution.md
+0
-0
data/3.算法高阶/3.leetcode-图与搜索/328.矩阵中的最长递增路径/solution.md
data/3.算法高阶/3.leetcode-图与搜索/328.矩阵中的最长递增路径/solution.md
+0
-0
data/3.算法高阶/3.leetcode-图与搜索/331.重新安排行程/solution.md
data/3.算法高阶/3.leetcode-图与搜索/331.重新安排行程/solution.md
+0
-0
data/3.算法高阶/3.leetcode-图与搜索/76.组合/solution.md
data/3.算法高阶/3.leetcode-图与搜索/76.组合/solution.md
+0
-0
data/3.算法高阶/3.leetcode-图与搜索/78.单词搜索/solution.md
data/3.算法高阶/3.leetcode-图与搜索/78.单词搜索/solution.md
+0
-0
data/3.算法高阶/4.leetcode-数学/11.整数转罗马数字/solution.md
data/3.算法高阶/4.leetcode-数学/11.整数转罗马数字/solution.md
+0
-0
data/3.算法高阶/4.leetcode-数学/12.罗马数字转整数/solution.md
data/3.算法高阶/4.leetcode-数学/12.罗马数字转整数/solution.md
+0
-0
data/3.算法高阶/4.leetcode-数学/28.两数相除/solution.md
data/3.算法高阶/4.leetcode-数学/28.两数相除/solution.md
+0
-0
data/3.算法高阶/4.leetcode-数学/49.Pow(x, n)/solution.md
data/3.算法高阶/4.leetcode-数学/49.Pow(x, n)/solution.md
+0
-0
data/3.算法高阶/4.leetcode-数学/59.排列序列/solution.md
data/3.算法高阶/4.leetcode-数学/59.排列序列/solution.md
+0
-0
data/3.算法高阶/4.leetcode-数学/6.整数反转/solution.md
data/3.算法高阶/4.leetcode-数学/6.整数反转/solution.md
+0
-0
data/3.算法高阶/4.leetcode-数学/65.加一/solution.md
data/3.算法高阶/4.leetcode-数学/65.加一/solution.md
+0
-0
data/3.算法高阶/4.leetcode-数学/66.二进制求和/solution.md
data/3.算法高阶/4.leetcode-数学/66.二进制求和/solution.md
+0
-0
data/3.算法高阶/4.leetcode-数学/68.x 的平方根/solution.md
data/3.算法高阶/4.leetcode-数学/68.x 的平方根/solution.md
+0
-0
data/3.算法高阶/4.leetcode-数学/8.回文数/solution.md
data/3.算法高阶/4.leetcode-数学/8.回文数/solution.md
+0
-0
data/3.算法高阶/5.leetcode-设计/145.LRU 缓存机制/solution.md
data/3.算法高阶/5.leetcode-设计/145.LRU 缓存机制/solution.md
+0
-0
data/3.算法高阶/5.leetcode-设计/354.设计推特/solution.md
data/3.算法高阶/5.leetcode-设计/354.设计推特/solution.md
+0
-0
data/3.算法高阶/5.leetcode-设计/379.O(1) 时间插入、删除和获取随机元素/solution.md
.../3.算法高阶/5.leetcode-设计/379.O(1) 时间插入、删除和获取随机元素/solution.md
+0
-0
data/3.算法高阶/5.leetcode-设计/380.O(1) 时间插入、删除和获取随机元素 - 允许重复/solution.md
.../5.leetcode-设计/380.O(1) 时间插入、删除和获取随机元素 - 允许重复/solution.md
+0
-0
data/3.算法高阶/5.leetcode-设计/459.LFU 缓存/solution.md
data/3.算法高阶/5.leetcode-设计/459.LFU 缓存/solution.md
+0
-0
data/3.算法高阶/6.leetcode-动态规划/21.括号生成/solution.md
data/3.算法高阶/6.leetcode-动态规划/21.括号生成/solution.md
+0
-0
data/3.算法高阶/6.leetcode-动态规划/4.最长回文子串/solution.md
data/3.算法高阶/6.leetcode-动态规划/4.最长回文子串/solution.md
+0
-0
data/3.算法高阶/6.leetcode-动态规划/43.通配符匹配/solution.md
data/3.算法高阶/6.leetcode-动态规划/43.通配符匹配/solution.md
+0
-0
data/3.算法高阶/6.leetcode-动态规划/52.最大子序和/solution.md
data/3.算法高阶/6.leetcode-动态规划/52.最大子序和/solution.md
+0
-0
data/3.算法高阶/6.leetcode-动态规划/61.不同路径/solution.md
data/3.算法高阶/6.leetcode-动态规划/61.不同路径/solution.md
+0
-0
data/3.算法高阶/6.leetcode-动态规划/62.不同路径 II/solution.md
data/3.算法高阶/6.leetcode-动态规划/62.不同路径 II/solution.md
+0
-0
data/3.算法高阶/6.leetcode-动态规划/63.最小路径和/solution.md
data/3.算法高阶/6.leetcode-动态规划/63.最小路径和/solution.md
+0
-0
data/3.算法高阶/6.leetcode-动态规划/69.爬楼梯/solution.md
data/3.算法高阶/6.leetcode-动态规划/69.爬楼梯/solution.md
+0
-0
data/3.算法高阶/6.leetcode-动态规划/71.编辑距离/solution.md
data/3.算法高阶/6.leetcode-动态规划/71.编辑距离/solution.md
+0
-0
data/3.算法高阶/6.leetcode-动态规划/84.最大矩形/solution.md
data/3.算法高阶/6.leetcode-动态规划/84.最大矩形/solution.md
+0
-0
data/3.算法高阶/6.leetcode-动态规划/86.扰乱字符串/solution.md
data/3.算法高阶/6.leetcode-动态规划/86.扰乱字符串/solution.md
+0
-0
data/3.算法高阶/6.leetcode-动态规划/9.正则表达式匹配/solution.md
data/3.算法高阶/6.leetcode-动态规划/9.正则表达式匹配/solution.md
+0
-0
data/3.算法高阶/6.leetcode-动态规划/90.解码方法/solution.md
data/3.算法高阶/6.leetcode-动态规划/90.解码方法/solution.md
+0
-0
data/3.算法高阶/7.leetcode-回溯算法/16.电话号码的字母组合/solution.md
data/3.算法高阶/7.leetcode-回溯算法/16.电话号码的字母组合/solution.md
+0
-0
data/3.算法高阶/7.leetcode-回溯算法/36.解数独/solution.md
data/3.算法高阶/7.leetcode-回溯算法/36.解数独/solution.md
+0
-0
data/3.算法高阶/7.leetcode-回溯算法/38.组合总和/solution.md
data/3.算法高阶/7.leetcode-回溯算法/38.组合总和/solution.md
+0
-0
data/3.算法高阶/7.leetcode-回溯算法/39.组合总和 II/solution.md
data/3.算法高阶/7.leetcode-回溯算法/39.组合总和 II/solution.md
+0
-0
data/3.算法高阶/7.leetcode-回溯算法/45.全排列/solution.md
data/3.算法高阶/7.leetcode-回溯算法/45.全排列/solution.md
+0
-0
data/3.算法高阶/7.leetcode-回溯算法/46.全排列 II/solution.md
data/3.算法高阶/7.leetcode-回溯算法/46.全排列 II/solution.md
+0
-0
data/3.算法高阶/7.leetcode-回溯算法/50.N 皇后/solution.md
data/3.算法高阶/7.leetcode-回溯算法/50.N 皇后/solution.md
+0
-0
data/3.算法高阶/7.leetcode-回溯算法/51.N皇后 II/solution.md
data/3.算法高阶/7.leetcode-回溯算法/51.N皇后 II/solution.md
+0
-0
data/3.算法高阶/7.leetcode-回溯算法/88.格雷编码/solution.md
data/3.算法高阶/7.leetcode-回溯算法/88.格雷编码/solution.md
+0
-0
data/3.算法高阶/7.leetcode-回溯算法/89.子集 II/solution.md
data/3.算法高阶/7.leetcode-回溯算法/89.子集 II/solution.md
+0
-0
data/3.算法高阶/8.leetcode-贪心/121.买卖股票的最佳时机 II/solution.md
data/3.算法高阶/8.leetcode-贪心/121.买卖股票的最佳时机 II/solution.md
+0
-0
data/3.算法高阶/8.leetcode-贪心/133.加油站/solution.md
data/3.算法高阶/8.leetcode-贪心/133.加油站/solution.md
+0
-0
data/3.算法高阶/8.leetcode-贪心/134.分发糖果/solution.md
data/3.算法高阶/8.leetcode-贪心/134.分发糖果/solution.md
+0
-0
data/3.算法高阶/8.leetcode-贪心/44.跳跃游戏 II/solution.md
data/3.算法高阶/8.leetcode-贪心/44.跳跃游戏 II/solution.md
+0
-0
data/3.算法高阶/8.leetcode-贪心/54.跳跃游戏/solution.md
data/3.算法高阶/8.leetcode-贪心/54.跳跃游戏/solution.md
+0
-0
data/3.算法高阶/8.leetcode-贪心/67.文本左右对齐/solution.md
data/3.算法高阶/8.leetcode-贪心/67.文本左右对齐/solution.md
+0
-0
未找到文件。
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/100.第39级台阶/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 第39级台阶
# 第39级台阶
小明刚刚看完电影《第39级台阶》,离开电影院的时候,他数了数礼堂前的台阶数,恰好是39级!
小明刚刚看完电影《第39级台阶》,离开电影院的时候,他数了数礼堂前的台阶数,恰好是39级!
站在台阶前,他突然又想着一个问题:
站在台阶前,他突然又想着一个问题:
...
@@ -9,7 +10,9 @@
...
@@ -9,7 +10,9 @@
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <iostream>
#define LEFT 0
#define LEFT 0
...
@@ -18,11 +21,13 @@ using namespace std;
...
@@ -18,11 +21,13 @@ using namespace std;
int
stage
[
40
][
2
];
int
stage
[
40
][
2
];
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -42,7 +47,9 @@ int main()
...
@@ -42,7 +47,9 @@ int main()
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -62,6 +69,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -62,6 +69,7 @@ int main()
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -81,6 +89,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -81,6 +89,7 @@ int main()
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
...
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/104.9数算式/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 9数算式
# 9数算式
观察如下的算式:
观察如下的算式:
```
```
9213 x 85674 = 789314562
9213 x 85674 = 789314562
...
@@ -14,7 +15,9 @@
...
@@ -14,7 +15,9 @@
2.
乘数和被乘数交换后作为同一方案来看待。
2.
乘数和被乘数交换后作为同一方案来看待。
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using
namespace
std
;
using
namespace
std
;
...
@@ -22,11 +25,13 @@ int bei[10];
...
@@ -22,11 +25,13 @@ int bei[10];
map
<
long
long
,
int
>
mp
;
map
<
long
long
,
int
>
mp
;
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -80,7 +85,9 @@ int main()
...
@@ -80,7 +85,9 @@ int main()
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -133,6 +140,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -133,6 +140,7 @@ int main()
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -185,6 +193,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -185,6 +193,7 @@ int main()
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
...
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/106.错误票据/desc.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
#### 问题描述
#### 问题描述
某涉密单位下发了某种票据,并要在年终全部收回。
某涉密单位下发了某种票据,并要在年终全部收回。
每张票据有唯一的ID号。全年所有票据的ID号是连续的,但ID的开始数码是随机选定的。
每张票据有唯一的ID号。全年所有票据的ID号是连续的,但ID的开始数码是随机选定的。
...
@@ -10,6 +11,7 @@
...
@@ -10,6 +11,7 @@
假设断号不可能发生在最大和最小号。
假设断号不可能发生在最大和最小号。
#### 输入格式
#### 输入格式
要求程序首先输入一个整数N(N<100)表示后面数据行数。
要求程序首先输入一个整数N(N<100)表示后面数据行数。
接着读入N行数据。
接着读入N行数据。
...
@@ -19,21 +21,25 @@
...
@@ -19,21 +21,25 @@
每个整数代表一个ID号。
每个整数代表一个ID号。
#### 输出格式
#### 输出格式
要求程序输出1行,含两个整数m n,用空格分隔。
要求程序输出1行,含两个整数m n,用空格分隔。
其中,m表示断号ID,n表示重号ID
其中,m表示断号ID,n表示重号ID
#### 样例输入1
#### 样例输入1
```
```
2
2
5 6 8 11 9
5 6 8 11 9
10 12 9
10 12 9
```
```
#### 样例输出1
#### 样例输出1
```
```
7 9
7 9
```
```
#### 样例输入2
#### 样例输入2
```
```
6
6
164 178 108 109 180 155 141 159 104 182 179 118 137 184 115 124 125 129 168 196
164 178 108 109 180 155 141 159 104 182 179 118 137 184 115 124 125 129 168 196
...
@@ -44,6 +50,7 @@
...
@@ -44,6 +50,7 @@
113 130 176 154 177 120 117 150 114 183 186 181 100 163 160 167 147 198 111 119
113 130 176 154 177 120 117 150 114 183 186 181 100 163 160 167 147 198 111 119
```
```
#### 样例输出2
#### 样例输出2
```
```
105 120
105 120
```
```
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/106.错误票据/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 错误票据
# 错误票据
#### 问题描述
#### 问题描述
某涉密单位下发了某种票据,并要在年终全部收回。
某涉密单位下发了某种票据,并要在年终全部收回。
每张票据有唯一的ID号。全年所有票据的ID号是连续的,但ID的开始数码是随机选定的。
每张票据有唯一的ID号。全年所有票据的ID号是连续的,但ID的开始数码是随机选定的。
...
@@ -11,6 +13,7 @@
...
@@ -11,6 +13,7 @@
假设断号不可能发生在最大和最小号。
假设断号不可能发生在最大和最小号。
#### 输入格式
#### 输入格式
要求程序首先输入一个整数N(N<100)表示后面数据行数。
要求程序首先输入一个整数N(N<100)表示后面数据行数。
接着读入N行数据。
接着读入N行数据。
...
@@ -20,21 +23,25 @@
...
@@ -20,21 +23,25 @@
每个整数代表一个ID号。
每个整数代表一个ID号。
#### 输出格式
#### 输出格式
要求程序输出1行,含两个整数m n,用空格分隔。
要求程序输出1行,含两个整数m n,用空格分隔。
其中,m表示断号ID,n表示重号ID
其中,m表示断号ID,n表示重号ID
#### 样例输入1
#### 样例输入1
```
```
2
2
5 6 8 11 9
5 6 8 11 9
10 12 9
10 12 9
```
```
#### 样例输出1
#### 样例输出1
```
```
7 9
7 9
```
```
#### 样例输入2
#### 样例输入2
```
```
6
6
164 178 108 109 180 155 141 159 104 182 179 118 137 184 115 124 125 129 168 196
164 178 108 109 180 155 141 159 104 182 179 118 137 184 115 124 125 129 168 196
...
@@ -45,12 +52,15 @@
...
@@ -45,12 +52,15 @@
113 130 176 154 177 120 117 150 114 183 186 181 100 163 160 167 147 198 111 119
113 130 176 154 177 120 117 150 114 183 186 181 100 163 160 167 147 198 111 119
```
```
#### 样例输出2
#### 样例输出2
```
```
105 120
105 120
```
```
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdio.h>
...
@@ -62,11 +72,13 @@ int ans[10005];
...
@@ -62,11 +72,13 @@ int ans[10005];
char
str
[
100001
];
char
str
[
100001
];
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -103,7 +115,9 @@ int main()
...
@@ -103,7 +115,9 @@ int main()
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -140,6 +154,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -140,6 +154,7 @@ int main()
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -176,6 +191,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -176,6 +191,7 @@ int main()
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
...
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/112.大数乘法/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 大数乘法
# 大数乘法
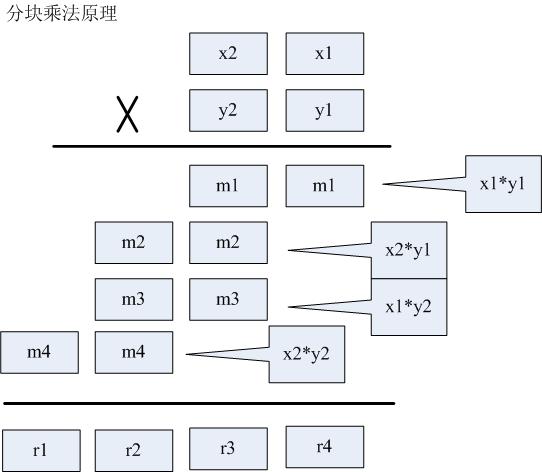
对于32位字长的机器,大约超过20亿,用int类型就无法表示了,我们可以选择int64类型,但无论怎样扩展,固定的整数类型总是有表达的极限!如果对超级大整数进行精确运算呢?一个简单的办法是:仅仅使用现有类型,但是把大整数的运算化解为若干小整数的运算,即所谓:“分块法”。
对于32位字长的机器,大约超过20亿,用int类型就无法表示了,我们可以选择int64类型,但无论怎样扩展,固定的整数类型总是有表达的极限!如果对超级大整数进行精确运算呢?一个简单的办法是:仅仅使用现有类型,但是把大整数的运算化解为若干小整数的运算,即所谓:“分块法”。

...
@@ -6,11 +7,14 @@
...
@@ -6,11 +7,14 @@
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdio.h>
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
(
int
argc
,
char
*
argv
[])
int
main
(
int
argc
,
char
*
argv
[])
{
{
...
@@ -25,6 +29,7 @@ int main(int argc, char *argv[])
...
@@ -25,6 +29,7 @@ int main(int argc, char *argv[])
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
void
bigmul
(
int
x
,
int
y
,
int
r
[])
void
bigmul
(
int
x
,
int
y
,
int
r
[])
{
{
...
@@ -52,7 +57,9 @@ void bigmul(int x, int y, int r[])
...
@@ -52,7 +57,9 @@ void bigmul(int x, int y, int r[])
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
void
bigmul
(
int
x
,
int
y
,
int
r
[])
void
bigmul
(
int
x
,
int
y
,
int
r
[])
{
{
...
@@ -80,6 +87,7 @@ void bigmul(int x, int y, int r[])
...
@@ -80,6 +87,7 @@ void bigmul(int x, int y, int r[])
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
void
bigmul
(
int
x
,
int
y
,
int
r
[])
void
bigmul
(
int
x
,
int
y
,
int
r
[])
{
{
...
@@ -107,6 +115,7 @@ void bigmul(int x, int y, int r[])
...
@@ -107,6 +115,7 @@ void bigmul(int x, int y, int r[])
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
void
bigmul
(
int
x
,
int
y
,
int
r
[])
void
bigmul
(
int
x
,
int
y
,
int
r
[])
{
{
...
...
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/114.大衍数列/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 大衍数列
# 大衍数列
中国古代文献中,曾记载过“大衍数列”, 主要用于解释中国传统文化中的太极衍生原理。
中国古代文献中,曾记载过“大衍数列”, 主要用于解释中国传统文化中的太极衍生原理。
它的前几项是:
```0、2、4、8、12、18、24、32、40、50 …```
它的前几项是:
```0、2、4、8、12、18、24、32、40、50 …```
...
@@ -8,16 +9,20 @@
...
@@ -8,16 +9,20 @@
以下的代码打印出了大衍数列的前 100 项。
以下的代码打印出了大衍数列的前 100 项。
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdio.h>
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -34,7 +39,9 @@ int main()
...
@@ -34,7 +39,9 @@ int main()
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -51,6 +58,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -51,6 +58,7 @@ int main()
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -67,6 +75,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -67,6 +75,7 @@ int main()
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
...
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/120.成绩统计/desc.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
#### 问题描述
#### 问题描述
编写一个程序,建立了一条单向链表,每个结点包含姓名、学号、英语成绩、数学成绩和C++成绩,并通过链表操作平均最高的学生和平均分最低的学生并且输出。
编写一个程序,建立了一条单向链表,每个结点包含姓名、学号、英语成绩、数学成绩和C++成绩,并通过链表操作平均最高的学生和平均分最低的学生并且输出。
#### 输入格式
#### 输入格式
输入n+1行,第一行输入一个正整数n,表示学生数量;接下来的n行每行输入5个数据,分别表示姓名、学号、英语成绩、数学成绩和C++成绩。注意成绩有可能会有小数。
输入n+1行,第一行输入一个正整数n,表示学生数量;接下来的n行每行输入5个数据,分别表示姓名、学号、英语成绩、数学成绩和C++成绩。注意成绩有可能会有小数。
#### 输出格式
#### 输出格式
输出两行,第一行输出平均成绩最高的学生姓名。第二行输出平均成绩最低的学生姓名。
输出两行,第一行输出平均成绩最高的学生姓名。第二行输出平均成绩最低的学生姓名。
#### 样例输入
#### 样例输入
```
```
2
2
yx1 1 45 67 87
yx1 1 45 67 87
yx2 2 88 90 99
yx2 2 88 90 99
```
```
#### 样例输出
#### 样例输出
```
```
yx2
yx2
yx1
yx1
...
...
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/120.成绩统计/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 成绩统计
# 成绩统计
#### 问题描述
#### 问题描述
编写一个程序,建立了一条单向链表,每个结点包含姓名、学号、英语成绩、数学成绩和C++成绩,并通过链表操作平均最高的学生和平均分最低的学生并且输出。
编写一个程序,建立了一条单向链表,每个结点包含姓名、学号、英语成绩、数学成绩和C++成绩,并通过链表操作平均最高的学生和平均分最低的学生并且输出。
#### 输入格式
#### 输入格式
输入n+1行,第一行输入一个正整数n,表示学生数量;接下来的n行每行输入5个数据,分别表示姓名、学号、英语成绩、数学成绩和C++成绩。注意成绩有可能会有小数。
输入n+1行,第一行输入一个正整数n,表示学生数量;接下来的n行每行输入5个数据,分别表示姓名、学号、英语成绩、数学成绩和C++成绩。注意成绩有可能会有小数。
#### 输出格式
#### 输出格式
输出两行,第一行输出平均成绩最高的学生姓名。第二行输出平均成绩最低的学生姓名。
输出两行,第一行输出平均成绩最高的学生姓名。第二行输出平均成绩最低的学生姓名。
#### 样例输入
#### 样例输入
```
```
2
2
yx1 1 45 67 87
yx1 1 45 67 87
yx2 2 88 90 99
yx2 2 88 90 99
```
```
#### 样例输出
#### 样例输出
```
```
yx2
yx2
yx1
yx1
```
```
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <iostream>
using
namespace
std
;
using
namespace
std
;
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -68,7 +78,9 @@ int main()
...
@@ -68,7 +78,9 @@ int main()
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -107,6 +119,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -107,6 +119,7 @@ int main()
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -145,6 +158,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -145,6 +158,7 @@ int main()
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
...
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/126.比酒量/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 比酒量
# 比酒量
有一群海盗(不多于20人),在船上比拼酒量。过程如下:打开一瓶酒,所有在场的人平分喝下,有几个人倒下了。再打开一瓶酒平分,又有倒下的,
有一群海盗(不多于20人),在船上比拼酒量。过程如下:打开一瓶酒,所有在场的人平分喝下,有几个人倒下了。再打开一瓶酒平分,又有倒下的,
再次重复......
再次重复......
...
@@ -17,7 +18,9 @@
...
@@ -17,7 +18,9 @@
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <iostream>
...
@@ -25,6 +28,7 @@ using namespace std;
...
@@ -25,6 +28,7 @@ using namespace std;
int
d
,
a1
[
4
];
int
d
,
a1
[
4
];
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -50,6 +54,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -50,6 +54,7 @@ int main()
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
d1
(
int
*
a1
)
int
d1
(
int
*
a1
)
{
{
...
@@ -79,7 +84,9 @@ int getS(int *a1)
...
@@ -79,7 +84,9 @@ int getS(int *a1)
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
d1
(
int
*
a1
)
int
d1
(
int
*
a1
)
{
{
...
@@ -109,6 +116,7 @@ int getS(int *a1)
...
@@ -109,6 +116,7 @@ int getS(int *a1)
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
d1
(
int
*
a1
)
int
d1
(
int
*
a1
)
{
{
...
@@ -138,6 +146,7 @@ int getS(int *a1)
...
@@ -138,6 +146,7 @@ int getS(int *a1)
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
d1
(
int
*
a1
)
int
d1
(
int
*
a1
)
{
{
...
...
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/134.第几天/desc.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
...
@@ -2,18 +2,23 @@ y年m月d日是哪一年的第几天。
...
@@ -2,18 +2,23 @@ y年m月d日是哪一年的第几天。
比如y年的1月1日是那一年的第一天,那么y年m月d日是哪一年的第几天。
比如y年的1月1日是那一年的第一天,那么y年m月d日是哪一年的第几天。
#### 输入
#### 输入
```
```
y m d
y m d
```
```
#### 输出
#### 输出
输出一个整数
输出一个整数
### 样例
### 样例
#### 输入
#### 输入
```
```
2000 7 7
2000 7 7
```
```
#### 输出
#### 输出
```
```
189
189
```
```
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/134.第几天/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 第几天
# 第几天
y年m月d日是哪一年的第几天。
y年m月d日是哪一年的第几天。
比如y年的1月1日是那一年的第一天,那么y年m月d日是哪一年的第几天。
比如y年的1月1日是那一年的第一天,那么y年m月d日是哪一年的第几天。
#### 输入
#### 输入
```
```
y m d
y m d
```
```
#### 输出
#### 输出
输出一个整数
输出一个整数
### 样例
### 样例
#### 输入
#### 输入
```
```
2000 7 7
2000 7 7
```
```
#### 输出
#### 输出
```
```
189
189
```
```
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <iostream>
using
namespace
std
;
using
namespace
std
;
...
@@ -31,11 +39,13 @@ bool is_leap(int year)
...
@@ -31,11 +39,13 @@ bool is_leap(int year)
}
}
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -67,7 +77,9 @@ int main()
...
@@ -67,7 +77,9 @@ int main()
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -98,6 +110,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -98,6 +110,7 @@ int main()
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -128,6 +141,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -128,6 +141,7 @@ int main()
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
...
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/135.斐波那契/desc.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
Fibonacci数列的递推公式为:Fn=Fn-1+Fn-2,其中F1=F2=1。
Fibonacci数列的递推公式为:Fn=Fn-1+Fn-2,其中F1=F2=1。
当n比较大时,Fn也非常大,现在我们想知道,Fn除以10007的余数是多少。
当n比较大时,Fn也非常大,现在我们想知道,Fn除以10007的余数是多少。
#### 输入格式
#### 输入格式
输入包含一个整数n。
输入包含一个整数n。
输出格式
输出格式
输出一行,包含一个整数,表示Fn除以10007的余数。
输出一行,包含一个整数,表示Fn除以10007的余数。
说明:在本题中,答案是要求Fn除以10007的余数,因此我们只要能算出这个余数即可,而不需要先计算出Fn的准确值,再将计算的结果除以10007取余数,直接计算余数往往比先算出原数再取余简单。
说明:在本题中,答案是要求Fn除以10007的余数,因此我们只要能算出这个余数即可,而不需要先计算出Fn的准确值,再将计算的结果除以10007取余数,直接计算余数往往比先算出原数再取余简单。
#### 样例输入
#### 样例输入
```
```
10
10
```
```
#### 样例输出
#### 样例输出
```
```
55
55
```
```
#### 样例输入
#### 样例输入
```
```
22
22
```
```
#### 样例输出
#### 样例输出
```
```
7704
7704
```
```
#### 数据规模与约定
#### 数据规模与约定
```
```
1 <= n <= 1,000,000。
1 <= n <= 1,000,000。
```
```
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/135.斐波那契/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 斐波那契
# 斐波那契
Fibonacci数列的递推公式为:Fn=Fn-1+Fn-2,其中F1=F2=1。
Fibonacci数列的递推公式为:Fn=Fn-1+Fn-2,其中F1=F2=1。
当n比较大时,Fn也非常大,现在我们想知道,Fn除以10007的余数是多少。
当n比较大时,Fn也非常大,现在我们想知道,Fn除以10007的余数是多少。
#### 输入格式
#### 输入格式
输入包含一个整数n。
输入包含一个整数n。
输出格式
输出格式
输出一行,包含一个整数,表示Fn除以10007的余数。
输出一行,包含一个整数,表示Fn除以10007的余数。
说明:在本题中,答案是要求Fn除以10007的余数,因此我们只要能算出这个余数即可,而不需要先计算出Fn的准确值,再将计算的结果除以10007取余数,直接计算余数往往比先算出原数再取余简单。
说明:在本题中,答案是要求Fn除以10007的余数,因此我们只要能算出这个余数即可,而不需要先计算出Fn的准确值,再将计算的结果除以10007取余数,直接计算余数往往比先算出原数再取余简单。
#### 样例输入
#### 样例输入
```
```
10
10
```
```
#### 样例输出
#### 样例输出
```
```
55
55
```
```
#### 样例输入
#### 样例输入
```
```
22
22
```
```
#### 样例输出
#### 样例输出
```
```
7704
7704
```
```
#### 数据规模与约定
#### 数据规模与约定
```
```
1 <= n <= 1,000,000。
1 <= n <= 1,000,000。
```
```
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdio.h>
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -60,7 +71,9 @@ int main()
...
@@ -60,7 +71,9 @@ int main()
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -83,6 +96,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -83,6 +96,7 @@ int main()
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -105,6 +119,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -105,6 +119,7 @@ int main()
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
...
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/149.方阵转置/desc.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
#### 问题描述
#### 问题描述
给定一个n×m矩阵相乘,求它的转置。其中1≤n≤20,1≤m≤20,矩阵中的每个元素都在整数类型(4字节)的表示范围内。
给定一个n×m矩阵相乘,求它的转置。其中1≤n≤20,1≤m≤20,矩阵中的每个元素都在整数类型(4字节)的表示范围内。
#### 输入格式
#### 输入格式
第一行两个整数n和m;
第一行两个整数n和m;
第二行起,每行m个整数,共n行,表示n×m的矩阵。数据之间都用一个空格分隔。
第二行起,每行m个整数,共n行,表示n×m的矩阵。数据之间都用一个空格分隔。
#### 输出格式
#### 输出格式
共m行,每行n个整数,数据间用一个空格分隔,表示转置后的矩阵。
共m行,每行n个整数,数据间用一个空格分隔,表示转置后的矩阵。
#### 样例输入
#### 样例输入
```
```
2 4
2 4
34 76 -54 7
34 76 -54 7
-4 5 23 9
-4 5 23 9
```
```
#### 样例输出
#### 样例输出
```
```
34 -4
34 -4
76 5
76 5
...
...
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/149.方阵转置/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 方阵转置
# 方阵转置
#### 问题描述
#### 问题描述
给定一个n×m矩阵相乘,求它的转置。其中1≤n≤20,1≤m≤20,矩阵中的每个元素都在整数类型(4字节)的表示范围内。
给定一个n×m矩阵相乘,求它的转置。其中1≤n≤20,1≤m≤20,矩阵中的每个元素都在整数类型(4字节)的表示范围内。
#### 输入格式
#### 输入格式
第一行两个整数n和m;
第一行两个整数n和m;
第二行起,每行m个整数,共n行,表示n×m的矩阵。数据之间都用一个空格分隔。
第二行起,每行m个整数,共n行,表示n×m的矩阵。数据之间都用一个空格分隔。
#### 输出格式
#### 输出格式
共m行,每行n个整数,数据间用一个空格分隔,表示转置后的矩阵。
共m行,每行n个整数,数据间用一个空格分隔,表示转置后的矩阵。
#### 样例输入
#### 样例输入
```
```
2 4
2 4
34 76 -54 7
34 76 -54 7
-4 5 23 9
-4 5 23 9
```
```
#### 样例输出
#### 样例输出
```
```
34 -4
34 -4
76 5
76 5
...
@@ -23,18 +29,22 @@
...
@@ -23,18 +29,22 @@
```
```
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using
namespace
std
;
using
namespace
std
;
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -63,7 +73,9 @@ int main()
...
@@ -63,7 +73,9 @@ int main()
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -91,6 +103,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -91,6 +103,7 @@ int main()
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -118,6 +131,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -118,6 +131,7 @@ int main()
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
...
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/158.倍数问题/desc.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
#### 题目描述
#### 题目描述
众所周知,小葱同学擅长计算,尤其擅长计算一个数是否是另外一个数的倍数。但小葱只擅长两个数的情况,当有很多个数之后就会比较苦恼。现在小葱给了你 n 个数,希望你从这 n 个数中找到三个数,使得这三个数的和是 K 的倍数,且这个和最大。数据保证一定有解。
众所周知,小葱同学擅长计算,尤其擅长计算一个数是否是另外一个数的倍数。但小葱只擅长两个数的情况,当有很多个数之后就会比较苦恼。现在小葱给了你 n 个数,希望你从这 n 个数中找到三个数,使得这三个数的和是 K 的倍数,且这个和最大。数据保证一定有解。
#### 输入格式
#### 输入格式
从标准输入读入数据。
从标准输入读入数据。
第一行包括 2 个正整数 n, K。
第一行包括 2 个正整数 n, K。
第二行 n 个正整数,代表给定的 n 个数。
第二行 n 个正整数,代表给定的 n 个数。
#### 输出格式
#### 输出格式
输出到标准输出。
输出到标准输出。
输出一行一个整数代表所求的和。
输出一行一个整数代表所求的和。
#### 样例输入
#### 样例输入
```
```
4 3
4 3
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4
```
```
#### 样例输出
#### 样例输出
```
```
9
9
```
```
#### 样例解释
#### 样例解释
```
```
选择2、3、4。
选择2、3、4。
```
```
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/158.倍数问题/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 倍数问题
# 倍数问题
#### 题目描述
#### 题目描述
众所周知,小葱同学擅长计算,尤其擅长计算一个数是否是另外一个数的倍数。但小葱只擅长两个数的情况,当有很多个数之后就会比较苦恼。现在小葱给了你 n 个数,希望你从这 n 个数中找到三个数,使得这三个数的和是 K 的倍数,且这个和最大。数据保证一定有解。
众所周知,小葱同学擅长计算,尤其擅长计算一个数是否是另外一个数的倍数。但小葱只擅长两个数的情况,当有很多个数之后就会比较苦恼。现在小葱给了你 n 个数,希望你从这 n 个数中找到三个数,使得这三个数的和是 K 的倍数,且这个和最大。数据保证一定有解。
#### 输入格式
#### 输入格式
从标准输入读入数据。
从标准输入读入数据。
第一行包括 2 个正整数 n, K。
第一行包括 2 个正整数 n, K。
第二行 n 个正整数,代表给定的 n 个数。
第二行 n 个正整数,代表给定的 n 个数。
#### 输出格式
#### 输出格式
输出到标准输出。
输出到标准输出。
输出一行一个整数代表所求的和。
输出一行一个整数代表所求的和。
#### 样例输入
#### 样例输入
```
```
4 3
4 3
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4
```
```
#### 样例输出
#### 样例输出
```
```
9
9
```
```
#### 样例解释
#### 样例解释
```
```
选择2、3、4。
选择2、3、4。
```
```
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <string>
#include <string>
...
@@ -44,6 +53,7 @@ int b[4];
...
@@ -44,6 +53,7 @@ int b[4];
int
flag
=
0
;
int
flag
=
0
;
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -59,6 +69,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -59,6 +69,7 @@ int main()
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
void
dfs
(
int
a
[],
int
n
,
int
s
)
void
dfs
(
int
a
[],
int
n
,
int
s
)
{
{
...
@@ -86,7 +97,9 @@ void dfs(int a[], int n, int s)
...
@@ -86,7 +97,9 @@ void dfs(int a[], int n, int s)
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
void
dfs
(
int
a
[],
int
n
,
int
s
)
void
dfs
(
int
a
[],
int
n
,
int
s
)
{
{
...
@@ -114,6 +127,7 @@ void dfs(int a[], int n, int s)
...
@@ -114,6 +127,7 @@ void dfs(int a[], int n, int s)
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
void
dfs
(
int
a
[],
int
n
,
int
s
)
void
dfs
(
int
a
[],
int
n
,
int
s
)
{
{
...
@@ -141,6 +155,7 @@ void dfs(int a[], int n, int s)
...
@@ -141,6 +155,7 @@ void dfs(int a[], int n, int s)
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
void
dfs
(
int
a
[],
int
n
,
int
s
)
void
dfs
(
int
a
[],
int
n
,
int
s
)
{
{
...
...
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/24.乘积尾零/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 乘积尾零
# 乘积尾零
如下的10行数据,每行有10个整数,请你求出它们的乘积的末尾有多少个零?
如下的10行数据,每行有10个整数,请你求出它们的乘积的末尾有多少个零?
```
```
5650 4542 3554 473 946 4114 3871 9073 90 4329
5650 4542 3554 473 946 4114 3871 9073 90 4329
...
@@ -14,17 +15,21 @@
...
@@ -14,17 +15,21 @@
```
```
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <iostream>
using
namespace
std
;
using
namespace
std
;
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -51,7 +56,9 @@ int main()
...
@@ -51,7 +56,9 @@ int main()
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -78,6 +85,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -78,6 +85,7 @@ int main()
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -105,6 +113,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -105,6 +113,7 @@ int main()
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
...
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/3.分数/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 分数
# 分数
1/1 + 1/2 + 1/4 + 1/8 + 1/16 + … 每项是前一项的一半,如果一共有20项,求这个和是多少,结果用分数表示出来。
1/1 + 1/2 + 1/4 + 1/8 + 1/16 + … 每项是前一项的一半,如果一共有20项,求这个和是多少,结果用分数表示出来。
类似:3/2
类似:3/2
当然,这只是加了前2项而已。分子分母要求互质。
当然,这只是加了前2项而已。分子分母要求互质。
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using
namespace
std
;
using
namespace
std
;
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
gcd
(
long
a
,
long
b
)
int
gcd
(
long
a
,
long
b
)
{
{
...
@@ -25,6 +29,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -25,6 +29,7 @@ int main()
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
long
pow_2
(
int
b
)
long
pow_2
(
int
b
)
{
{
...
@@ -42,7 +47,9 @@ long pow_2(int b)
...
@@ -42,7 +47,9 @@ long pow_2(int b)
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
long
pow_2
(
int
b
)
long
pow_2
(
int
b
)
{
{
...
@@ -60,6 +67,7 @@ long pow_2(int b)
...
@@ -60,6 +67,7 @@ long pow_2(int b)
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
long
pow_2
(
int
b
)
long
pow_2
(
int
b
)
{
{
...
@@ -77,6 +85,7 @@ long pow_2(int b)
...
@@ -77,6 +85,7 @@ long pow_2(int b)
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
long
pow_2
(
int
b
)
long
pow_2
(
int
b
)
{
{
...
...
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/4.等差素数列/desc.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
#### 题目描述
#### 题目描述
2,3,5,7,11,13,....是素数序列。
2,3,5,7,11,13,....是素数序列。
类似:7,37,67,97,127,157 这样完全由素数组成的等差数列,叫等差素数数列。
类似:7,37,67,97,127,157 这样完全由素数组成的等差数列,叫等差素数数列。
上边的数列公差为30,长度为6。
上边的数列公差为30,长度为6。
...
...
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/4.等差素数列/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 等差素数列
# 等差素数列
#### 题目描述
#### 题目描述
2,3,5,7,11,13,....是素数序列。
2,3,5,7,11,13,....是素数序列。
类似:7,37,67,97,127,157 这样完全由素数组成的等差数列,叫等差素数数列。
类似:7,37,67,97,127,157 这样完全由素数组成的等差数列,叫等差素数数列。
上边的数列公差为30,长度为6。
上边的数列公差为30,长度为6。
...
@@ -13,7 +15,9 @@
...
@@ -13,7 +15,9 @@
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <algorithm>
...
@@ -34,6 +38,7 @@ bool isPrimt(LL t)
...
@@ -34,6 +38,7 @@ bool isPrimt(LL t)
}
}
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
const
int
N
=
5000
;
const
int
N
=
5000
;
int
main
()
int
main
()
...
@@ -63,6 +68,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -63,6 +68,7 @@ int main()
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
f
(
LL
a
[],
int
n
)
int
f
(
LL
a
[],
int
n
)
{
{
...
@@ -89,7 +95,9 @@ int f(LL a[], int n)
...
@@ -89,7 +95,9 @@ int f(LL a[], int n)
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
f
(
LL
a
[],
int
n
)
int
f
(
LL
a
[],
int
n
)
{
{
...
@@ -116,6 +124,7 @@ int f(LL a[], int n)
...
@@ -116,6 +124,7 @@ int f(LL a[], int n)
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
f
(
LL
a
[],
int
n
)
int
f
(
LL
a
[],
int
n
)
{
{
...
@@ -142,6 +151,7 @@ int f(LL a[], int n)
...
@@ -142,6 +151,7 @@ int f(LL a[], int n)
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
f
(
LL
a
[],
int
n
)
int
f
(
LL
a
[],
int
n
)
{
{
...
...
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/40.成绩分析/desc.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
#### 问题描述
#### 问题描述
小蓝给学生们组织了一场考试,卷面总分为100分,每个学生的得分都是一个0到100的整数。
小蓝给学生们组织了一场考试,卷面总分为100分,每个学生的得分都是一个0到100的整数。
请计算这次考试的最高分、最低分和平均分。
请计算这次考试的最高分、最低分和平均分。
#### 输入格式
#### 输入格式
输入的第一行包含一个整数n,表示考试人数。
输入的第一行包含一个整数n,表示考试人数。
接下来n行,每行包含一个0至100的整数,表示一个学生的得分。
接下来n行,每行包含一个0至100的整数,表示一个学生的得分。
#### 输出格式
#### 输出格式
输出三行。
输出三行。
第一行包含一个整数,表示最高分。
第一行包含一个整数,表示最高分。
...
@@ -19,6 +22,7 @@
...
@@ -19,6 +22,7 @@
#### 样例输入
#### 样例输入
```
```
7
7
80
80
...
@@ -30,6 +34,7 @@
...
@@ -30,6 +34,7 @@
10
10
```
```
#### 样例输出
#### 样例输出
```
```
99
99
10
10
...
...
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/40.成绩分析/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 成绩分析
# 成绩分析
#### 问题描述
#### 问题描述
小蓝给学生们组织了一场考试,卷面总分为100分,每个学生的得分都是一个0到100的整数。
小蓝给学生们组织了一场考试,卷面总分为100分,每个学生的得分都是一个0到100的整数。
请计算这次考试的最高分、最低分和平均分。
请计算这次考试的最高分、最低分和平均分。
#### 输入格式
#### 输入格式
输入的第一行包含一个整数n,表示考试人数。
输入的第一行包含一个整数n,表示考试人数。
接下来n行,每行包含一个0至100的整数,表示一个学生的得分。
接下来n行,每行包含一个0至100的整数,表示一个学生的得分。
#### 输出格式
#### 输出格式
输出三行。
输出三行。
第一行包含一个整数,表示最高分。
第一行包含一个整数,表示最高分。
...
@@ -20,6 +24,7 @@
...
@@ -20,6 +24,7 @@
#### 样例输入
#### 样例输入
```
```
7
7
80
80
...
@@ -31,6 +36,7 @@
...
@@ -31,6 +36,7 @@
10
10
```
```
#### 样例输出
#### 样例输出
```
```
99
99
10
10
...
@@ -38,7 +44,9 @@
...
@@ -38,7 +44,9 @@
```
```
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <iostream>
...
@@ -46,11 +54,13 @@
...
@@ -46,11 +54,13 @@
using
namespace
std
;
using
namespace
std
;
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -77,7 +87,9 @@ int main()
...
@@ -77,7 +87,9 @@ int main()
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -103,6 +115,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -103,6 +115,7 @@ int main()
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -128,6 +141,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -128,6 +141,7 @@ int main()
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
...
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/41.乘积最大/desc.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
...
@@ -6,19 +6,23 @@
...
@@ -6,19 +6,23 @@
注意,如果 X<0, 我们定义 X 除以 1000000009 的余数是负(−X)除以 1000000009 的余数,即:0−((0−x)%1000000009)
注意,如果 X<0, 我们定义 X 除以 1000000009 的余数是负(−X)除以 1000000009 的余数,即:0−((0−x)%1000000009)
#### 输入格式
#### 输入格式
第一行包含两个整数 N 和 K。
第一行包含两个整数 N 和 K。
以下 N 行每行一个整数 Ai。
以下 N 行每行一个整数 Ai。
#### 输出格式
#### 输出格式
输出一个整数,表示答案。
输出一个整数,表示答案。
#### 数据范围
#### 数据范围
```
```
1≤K≤N≤105,
1≤K≤N≤105,
−105≤Ai≤105
−105≤Ai≤105
```
```
#### 输入样例1:
#### 输入样例1:
```
```
5 3
5 3
-100000
-100000
...
@@ -28,10 +32,12 @@
...
@@ -28,10 +32,12 @@
10000
10000
```
```
#### 输出样例1:
#### 输出样例1:
```
```
999100009
999100009
```
```
#### 输入样例2:
#### 输入样例2:
```
```
5 3
5 3
-100000
-100000
...
@@ -40,5 +46,6 @@
...
@@ -40,5 +46,6 @@
-100000
-100000
-100000
-100000
#### 输出样例2:
#### 输出样例2:
-999999829
-999999829
```
```
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/41.乘积最大/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 乘积最大
# 乘积最大
给定 N 个整数 A1,A2,…AN。
给定 N 个整数 A1,A2,…AN。
请你从中选出 K 个数,使其乘积最大。
请你从中选出 K 个数,使其乘积最大。
...
@@ -7,19 +8,23 @@
...
@@ -7,19 +8,23 @@
注意,如果 X<0, 我们定义 X 除以 1000000009 的余数是负(−X)除以 1000000009 的余数,即:0−((0−x)%1000000009)
注意,如果 X<0, 我们定义 X 除以 1000000009 的余数是负(−X)除以 1000000009 的余数,即:0−((0−x)%1000000009)
#### 输入格式
#### 输入格式
第一行包含两个整数 N 和 K。
第一行包含两个整数 N 和 K。
以下 N 行每行一个整数 Ai。
以下 N 行每行一个整数 Ai。
#### 输出格式
#### 输出格式
输出一个整数,表示答案。
输出一个整数,表示答案。
#### 数据范围
#### 数据范围
```
```
1≤K≤N≤105,
1≤K≤N≤105,
−105≤Ai≤105
−105≤Ai≤105
```
```
#### 输入样例1:
#### 输入样例1:
```
```
5 3
5 3
-100000
-100000
...
@@ -29,10 +34,12 @@
...
@@ -29,10 +34,12 @@
10000
10000
```
```
#### 输出样例1:
#### 输出样例1:
```
```
999100009
999100009
```
```
#### 输入样例2:
#### 输入样例2:
```
```
5 3
5 3
-100000
-100000
...
@@ -41,11 +48,14 @@
...
@@ -41,11 +48,14 @@
-100000
-100000
-100000
-100000
#### 输出样例2:
#### 输出样例2:
-999999829
-999999829
```
```
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <vector>
...
@@ -53,11 +63,13 @@
...
@@ -53,11 +63,13 @@
using
namespace
std
;
using
namespace
std
;
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -102,7 +114,9 @@ int main()
...
@@ -102,7 +114,9 @@ int main()
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -146,6 +160,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -146,6 +160,7 @@ int main()
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -189,6 +204,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -189,6 +204,7 @@ int main()
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
...
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/67.猜年龄/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 猜年龄
# 猜年龄
美国数学家维纳(N.Wiener)智力早熟,11岁就上了大学。他曾在1935~1936年应邀来中国清华大学讲学。
美国数学家维纳(N.Wiener)智力早熟,11岁就上了大学。他曾在1935~1936年应邀来中国清华大学讲学。
一次,他参加某个重要会议,年轻的脸孔引人注目。于是有人询问他的年龄,他回答说:“我年龄的立方是个4位数。我年龄的4次方是个6位数。这10个数字正好包含了从0到9这10个数字,每个都恰好出现1次。”
一次,他参加某个重要会议,年轻的脸孔引人注目。于是有人询问他的年龄,他回答说:“我年龄的立方是个4位数。我年龄的4次方是个6位数。这10个数字正好包含了从0到9这10个数字,每个都恰好出现1次。”
请你推算一下,他当时到底有多年轻。
请你推算一下,他当时到底有多年轻。
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <iostream>
using
namespace
std
;
using
namespace
std
;
...
@@ -27,22 +31,27 @@ int main()
...
@@ -27,22 +31,27 @@ int main()
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
18
18
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
19
19
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
20
20
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
21
21
```
```
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/69.递增三元组/desc.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
...
@@ -7,6 +7,7 @@ C = [C1, C2, ... CN],
...
@@ -7,6 +7,7 @@ C = [C1, C2, ... CN],
2.
Ai < Bj < Ck
2.
Ai < Bj < Ck
#### 输入格式
#### 输入格式
第一行包含一个整数N。
第一行包含一个整数N。
第二行包含N个整数A1, A2, ... AN。
第二行包含N个整数A1, A2, ... AN。
第三行包含N个整数B1, B2, ... BN。
第三行包含N个整数B1, B2, ... BN。
...
@@ -17,8 +18,10 @@ C = [C1, C2, ... CN],
...
@@ -17,8 +18,10 @@ C = [C1, C2, ... CN],
对于100%的数据,1 <= N <= 100000 0 <= Ai, Bi, Ci <= 100000
对于100%的数据,1 <= N <= 100000 0 <= Ai, Bi, Ci <= 100000
#### 输出格式
#### 输出格式
一个整数表示答案
一个整数表示答案
#### 样例输入
#### 样例输入
```
```
3
3
1 1 1
1 1 1
...
@@ -26,6 +29,7 @@ C = [C1, C2, ... CN],
...
@@ -26,6 +29,7 @@ C = [C1, C2, ... CN],
3 3 3
3 3 3
```
```
#### 样例输出
#### 样例输出
```
```
27
27
```
```
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/69.递增三元组/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 递增三元组
# 递增三元组
给定三个整数数组
给定三个整数数组
A = [A1, A2, ... AN],
A = [A1, A2, ... AN],
B = [B1, B2, ... BN],
B = [B1, B2, ... BN],
...
@@ -8,6 +9,7 @@ C = [C1, C2, ... CN],
...
@@ -8,6 +9,7 @@ C = [C1, C2, ... CN],
2.
Ai < Bj < Ck
2.
Ai < Bj < Ck
#### 输入格式
#### 输入格式
第一行包含一个整数N。
第一行包含一个整数N。
第二行包含N个整数A1, A2, ... AN。
第二行包含N个整数A1, A2, ... AN。
第三行包含N个整数B1, B2, ... BN。
第三行包含N个整数B1, B2, ... BN。
...
@@ -18,8 +20,10 @@ C = [C1, C2, ... CN],
...
@@ -18,8 +20,10 @@ C = [C1, C2, ... CN],
对于100%的数据,1 <= N <= 100000 0 <= Ai, Bi, Ci <= 100000
对于100%的数据,1 <= N <= 100000 0 <= Ai, Bi, Ci <= 100000
#### 输出格式
#### 输出格式
一个整数表示答案
一个整数表示答案
#### 样例输入
#### 样例输入
```
```
3
3
1 1 1
1 1 1
...
@@ -27,13 +31,16 @@ C = [C1, C2, ... CN],
...
@@ -27,13 +31,16 @@ C = [C1, C2, ... CN],
3 3 3
3 3 3
```
```
#### 样例输出
#### 样例输出
```
```
27
27
```
```
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstring>
...
@@ -47,11 +54,13 @@ int a[N], b[N], c[N], sa[N], sc[N], s[N];
...
@@ -47,11 +54,13 @@ int a[N], b[N], c[N], sa[N], sc[N], s[N];
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -88,7 +97,9 @@ int main()
...
@@ -88,7 +97,9 @@ int main()
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -125,6 +136,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -125,6 +136,7 @@ int main()
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -161,6 +173,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -161,6 +173,7 @@ int main()
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
...
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/77.第几个幸运数/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 第几个幸运数
# 第几个幸运数
到x星球旅行的游客都被发给一个整数,作为游客编号。
到x星球旅行的游客都被发给一个整数,作为游客编号。
x星的国王有个怪癖,他只喜欢数字3,5和7。
x星的国王有个怪癖,他只喜欢数字3,5和7。
国王规定,游客的编号如果只含有因子:3,5,7,就可以获得一份奖品。
国王规定,游客的编号如果只含有因子:3,5,7,就可以获得一份奖品。
...
@@ -14,7 +15,9 @@ x星的国王有个怪癖,他只喜欢数字3,5和7。
...
@@ -14,7 +15,9 @@ x星的国王有个怪癖,他只喜欢数字3,5和7。
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
#include <cmath>
...
@@ -23,11 +26,13 @@ x星的国王有个怪癖,他只喜欢数字3,5和7。
...
@@ -23,11 +26,13 @@ x星的国王有个怪癖,他只喜欢数字3,5和7。
using
namespace
std
;
using
namespace
std
;
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -62,7 +67,9 @@ int main()
...
@@ -62,7 +67,9 @@ int main()
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -97,6 +104,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -97,6 +104,7 @@ int main()
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -132,6 +140,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -132,6 +140,7 @@ int main()
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
...
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/88.次数差/desc.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
#### 问题描述
#### 问题描述
x星球有26只球队,分别用 a ~ z 的26个字母代表。他们总是不停地比赛。
x星球有26只球队,分别用 a ~ z 的26个字母代表。他们总是不停地比赛。
在某一赛段,哪个球队获胜了,就记录下代表它的字母,这样就形成一个长长的串。
在某一赛段,哪个球队获胜了,就记录下代表它的字母,这样就形成一个长长的串。
国王总是询问:获胜次数最多的和获胜次数最少的有多大差距?
国王总是询问:获胜次数最多的和获胜次数最少的有多大差距?
(当然,他不关心那些一次也没获胜的,认为他们在怠工罢了)
(当然,他不关心那些一次也没获胜的,认为他们在怠工罢了)
#### 输入格式
#### 输入格式
一个串,表示球队获胜情况(保证串的长度<1000)
一个串,表示球队获胜情况(保证串的长度<1000)
#### 输出格式
#### 输出格式
要求输出一个数字,表示出现次数最多的字母比出现次数最少的字母多了多少次。
要求输出一个数字,表示出现次数最多的字母比出现次数最少的字母多了多少次。
#### 样例输入1
#### 样例输入1
```
```
abaabcaa
abaabcaa
```
```
#### 样例输出1
#### 样例输出1
```
```
4
4
```
```
#### 提示
#### 提示
```
```
a 出现 5 次,最多;c 出现1次,最少。
a 出现 5 次,最多;c 出现1次,最少。
5 - 1 = 4
5 - 1 = 4
```
```
#### 样例输入2
#### 样例输入2
```
```
bbccccddaaaacccc
bbccccddaaaacccc
```
```
#### 样例输出2
#### 样例输出2
```
```
6
6
```
```
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/88.次数差/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 次数差
# 次数差
#### 问题描述
#### 问题描述
x星球有26只球队,分别用 a ~ z 的26个字母代表。他们总是不停地比赛。
x星球有26只球队,分别用 a ~ z 的26个字母代表。他们总是不停地比赛。
在某一赛段,哪个球队获胜了,就记录下代表它的字母,这样就形成一个长长的串。
在某一赛段,哪个球队获胜了,就记录下代表它的字母,这样就形成一个长长的串。
国王总是询问:获胜次数最多的和获胜次数最少的有多大差距?
国王总是询问:获胜次数最多的和获胜次数最少的有多大差距?
(当然,他不关心那些一次也没获胜的,认为他们在怠工罢了)
(当然,他不关心那些一次也没获胜的,认为他们在怠工罢了)
#### 输入格式
#### 输入格式
一个串,表示球队获胜情况(保证串的长度<1000)
一个串,表示球队获胜情况(保证串的长度<1000)
#### 输出格式
#### 输出格式
要求输出一个数字,表示出现次数最多的字母比出现次数最少的字母多了多少次。
要求输出一个数字,表示出现次数最多的字母比出现次数最少的字母多了多少次。
#### 样例输入1
#### 样例输入1
```
```
abaabcaa
abaabcaa
```
```
#### 样例输出1
#### 样例输出1
```
```
4
4
```
```
#### 提示
#### 提示
```
```
a 出现 5 次,最多;c 出现1次,最少。
a 出现 5 次,最多;c 出现1次,最少。
5 - 1 = 4
5 - 1 = 4
```
```
#### 样例输入2
#### 样例输入2
```
```
bbccccddaaaacccc
bbccccddaaaacccc
```
```
#### 样例输出2
#### 样例输出2
```
```
6
6
```
```
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <string.h>
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -75,7 +88,9 @@ int main()
...
@@ -75,7 +88,9 @@ int main()
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -105,6 +120,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -105,6 +120,7 @@ int main()
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -134,6 +150,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -134,6 +150,7 @@ int main()
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
...
data/1.算法初阶/1.蓝桥杯-基础/99.猜字母/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 猜字母
# 猜字母
把abcd...s共19个字母组成的序列重复拼接106次,得到长度为2014的串。
把abcd...s共19个字母组成的序列重复拼接106次,得到长度为2014的串。
接下来删除第1个字母(即开头的字母a),以及第3个,第5个等所有奇数位置的字母。
接下来删除第1个字母(即开头的字母a),以及第3个,第5个等所有奇数位置的字母。
得到的新串再进行删除奇数位置字母的动作。如此下去,最后只剩下一个字母,请写出该字母。
得到的新串再进行删除奇数位置字母的动作。如此下去,最后只剩下一个字母,请写出该字母。
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <vector>
using
namespace
std
;
using
namespace
std
;
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -38,7 +43,9 @@ int main()
...
@@ -38,7 +43,9 @@ int main()
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -61,6 +68,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -61,6 +68,7 @@ int main()
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -83,6 +91,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -83,6 +91,7 @@ int main()
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
...
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/92.单词分析/desc.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
#### 问题描述
#### 问题描述
小蓝正在学习一门神奇的语言,这门语言中的单词都是由小写英文字母组成,有些单词很长,远远超过正常英文单词的长度。小蓝学了很长时间也记不住一些单词,他准备不再完全记忆这些单词,而是根据单词中哪个字母出现得最多来分辨单词。
小蓝正在学习一门神奇的语言,这门语言中的单词都是由小写英文字母组成,有些单词很长,远远超过正常英文单词的长度。小蓝学了很长时间也记不住一些单词,他准备不再完全记忆这些单词,而是根据单词中哪个字母出现得最多来分辨单词。
现在,请你帮助小蓝,给了一个单词后,帮助他找到出现最多的字母和这个字母出现的次数。
现在,请你帮助小蓝,给了一个单词后,帮助他找到出现最多的字母和这个字母出现的次数。
#### 输入格式
#### 输入格式
输入一行包含一个单词,单词只由小写英文字母组成。
输入一行包含一个单词,单词只由小写英文字母组成。
#### 输出格式
#### 输出格式
输出两行,第一行包含一个英文字母,表示单词中出现得最多的字母是哪
输出两行,第一行包含一个英文字母,表示单词中出现得最多的字母是哪
个。如果有多个字母出现的次数相等,输出字典序最小的那个。
个。如果有多个字母出现的次数相等,输出字典序最小的那个。
第二行包含一个整数,表示出现得最多的那个字母在单词中出现的次数。
第二行包含一个整数,表示出现得最多的那个字母在单词中出现的次数。
#### 样例输入
#### 样例输入
```
```
lanqiao
lanqiao
```
```
#### 样例输出
#### 样例输出
```
```
a 2
a 2
```
```
#### 样例输入
#### 样例输入
```
```
longlonglongistoolong
longlonglongistoolong
```
```
#### 样例输出
#### 样例输出
```
```
o 6
o 6
```
```
#### 评测用例规模与约定
#### 评测用例规模与约定
对于所有的评测用例,输入的单词长度不超过 1000。
对于所有的评测用例,输入的单词长度不超过 1000。
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/92.单词分析/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 单词分析
# 单词分析
#### 问题描述
#### 问题描述
小蓝正在学习一门神奇的语言,这门语言中的单词都是由小写英文字母组成,有些单词很长,远远超过正常英文单词的长度。小蓝学了很长时间也记不住一些单词,他准备不再完全记忆这些单词,而是根据单词中哪个字母出现得最多来分辨单词。
小蓝正在学习一门神奇的语言,这门语言中的单词都是由小写英文字母组成,有些单词很长,远远超过正常英文单词的长度。小蓝学了很长时间也记不住一些单词,他准备不再完全记忆这些单词,而是根据单词中哪个字母出现得最多来分辨单词。
现在,请你帮助小蓝,给了一个单词后,帮助他找到出现最多的字母和这个字母出现的次数。
现在,请你帮助小蓝,给了一个单词后,帮助他找到出现最多的字母和这个字母出现的次数。
#### 输入格式
#### 输入格式
输入一行包含一个单词,单词只由小写英文字母组成。
输入一行包含一个单词,单词只由小写英文字母组成。
#### 输出格式
#### 输出格式
输出两行,第一行包含一个英文字母,表示单词中出现得最多的字母是哪
输出两行,第一行包含一个英文字母,表示单词中出现得最多的字母是哪
个。如果有多个字母出现的次数相等,输出字典序最小的那个。
个。如果有多个字母出现的次数相等,输出字典序最小的那个。
第二行包含一个整数,表示出现得最多的那个字母在单词中出现的次数。
第二行包含一个整数,表示出现得最多的那个字母在单词中出现的次数。
#### 样例输入
#### 样例输入
```
```
lanqiao
lanqiao
```
```
#### 样例输出
#### 样例输出
```
```
a 2
a 2
```
```
#### 样例输入
#### 样例输入
```
```
longlonglongistoolong
longlonglongistoolong
```
```
#### 样例输出
#### 样例输出
```
```
o 6
o 6
```
```
#### 评测用例规模与约定
#### 评测用例规模与约定
对于所有的评测用例,输入的单词长度不超过 1000。
对于所有的评测用例,输入的单词长度不超过 1000。
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdio.h"
#include "string.h"
#include "string.h"
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -73,7 +86,9 @@ int main()
...
@@ -73,7 +86,9 @@ int main()
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -107,6 +122,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -107,6 +122,7 @@ int main()
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -140,6 +156,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -140,6 +156,7 @@ int main()
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
...
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/97.分类计数/desc.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
#### 问题描述
#### 问题描述
输入一个字符串,请输出这个字符串包含多少个大写字母,多少个小写字母,多少个数字。
输入一个字符串,请输出这个字符串包含多少个大写字母,多少个小写字母,多少个数字。
#### 输入格式
#### 输入格式
输入一行包含一个字符串。
输入一行包含一个字符串。
#### 输出格式
#### 输出格式
输出三行,每行一个整数,分别表示大写字母、小写字母和数字的个数。
输出三行,每行一个整数,分别表示大写字母、小写字母和数字的个数。
#### 样例输入
#### 样例输入
```
```
1+a=Aab
1+a=Aab
```
```
#### 样例输出
#### 样例输出
```
```
1
1
3
3
1
1
```
```
#### 评测用例规模与约定
#### 评测用例规模与约定
对于所有评测用例,字符串由可见字符组成,长度不超过 100。
对于所有评测用例,字符串由可见字符组成,长度不超过 100。
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/97.分类计数/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 分类计数
# 分类计数
#### 问题描述
#### 问题描述
输入一个字符串,请输出这个字符串包含多少个大写字母,多少个小写字母,多少个数字。
输入一个字符串,请输出这个字符串包含多少个大写字母,多少个小写字母,多少个数字。
#### 输入格式
#### 输入格式
输入一行包含一个字符串。
输入一行包含一个字符串。
#### 输出格式
#### 输出格式
输出三行,每行一个整数,分别表示大写字母、小写字母和数字的个数。
输出三行,每行一个整数,分别表示大写字母、小写字母和数字的个数。
#### 样例输入
#### 样例输入
```
```
1+a=Aab
1+a=Aab
```
```
#### 样例输出
#### 样例输出
```
```
1
1
3
3
1
1
```
```
#### 评测用例规模与约定
#### 评测用例规模与约定
对于所有评测用例,字符串由可见字符组成,长度不超过 100。
对于所有评测用例,字符串由可见字符组成,长度不超过 100。
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <iostream>
using
namespace
std
;
using
namespace
std
;
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
(
int
argc
,
char
**
argv
)
int
main
(
int
argc
,
char
**
argv
)
{
{
...
@@ -66,7 +77,9 @@ int main(int argc, char **argv)
...
@@ -66,7 +77,9 @@ int main(int argc, char **argv)
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
(
int
argc
,
char
**
argv
)
int
main
(
int
argc
,
char
**
argv
)
{
{
...
@@ -97,6 +110,7 @@ int main(int argc, char **argv)
...
@@ -97,6 +110,7 @@ int main(int argc, char **argv)
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
(
int
argc
,
char
**
argv
)
int
main
(
int
argc
,
char
**
argv
)
{
{
...
@@ -127,6 +141,7 @@ int main(int argc, char **argv)
...
@@ -127,6 +141,7 @@ int main(int argc, char **argv)
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
(
int
argc
,
char
**
argv
)
int
main
(
int
argc
,
char
**
argv
)
{
{
...
...
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/98.翻硬币/desc.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
#### 问题描述
#### 问题描述
小明正在玩一个“翻硬币”的游戏。
小明正在玩一个“翻硬币”的游戏。
桌上放着排成一排的若干硬币。我们用
*
表示正面,用 o 表示反面(是小写字母,不是零)。
桌上放着排成一排的若干硬币。我们用
*
表示正面,用 o 表示反面(是小写字母,不是零)。
...
@@ -12,26 +13,32 @@
...
@@ -12,26 +13,32 @@
我们约定:把翻动相邻的两个硬币叫做一步操作,那么要求:
我们约定:把翻动相邻的两个硬币叫做一步操作,那么要求:
#### 输入格式
#### 输入格式
两行等长的字符串,分别表示初始状态和要达到的目标状态。每行的长度<1000
两行等长的字符串,分别表示初始状态和要达到的目标状态。每行的长度<1000
#### 输出格式
#### 输出格式
一个整数,表示最小操作步数。
一个整数,表示最小操作步数。
#### 样例输入1
#### 样例输入1
```
```
**********
**********
o****o****
o****o****
```
```
#### 样例输出1
#### 样例输出1
```
```
5
5
```
```
#### 样例输入2
#### 样例输入2
```
```
*o**o***o***
*o**o***o***
*o***o**o***
*o***o**o***
```
```
#### 样例输出2
#### 样例输出2
```
```
1
1
```
```
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/2.蓝桥杯-字符串/98.翻硬币/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 翻硬币
# 翻硬币
#### 问题描述
#### 问题描述
小明正在玩一个“翻硬币”的游戏。
小明正在玩一个“翻硬币”的游戏。
桌上放着排成一排的若干硬币。我们用
*
表示正面,用 o 表示反面(是小写字母,不是零)。
桌上放着排成一排的若干硬币。我们用
*
表示正面,用 o 表示反面(是小写字母,不是零)。
...
@@ -13,42 +15,52 @@
...
@@ -13,42 +15,52 @@
我们约定:把翻动相邻的两个硬币叫做一步操作,那么要求:
我们约定:把翻动相邻的两个硬币叫做一步操作,那么要求:
#### 输入格式
#### 输入格式
两行等长的字符串,分别表示初始状态和要达到的目标状态。每行的长度<1000
两行等长的字符串,分别表示初始状态和要达到的目标状态。每行的长度<1000
#### 输出格式
#### 输出格式
一个整数,表示最小操作步数。
一个整数,表示最小操作步数。
#### 样例输入1
#### 样例输入1
```
```
**********
**********
o****o****
o****o****
```
```
#### 样例输出1
#### 样例输出1
```
```
5
5
```
```
#### 样例输入2
#### 样例输入2
```
```
*o**o***o***
*o**o***o***
*o***o**o***
*o***o**o***
```
```
#### 样例输出2
#### 样例输出2
```
```
1
1
```
```
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using
namespace
std
;
using
namespace
std
;
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -81,7 +93,9 @@ int main()
...
@@ -81,7 +93,9 @@ int main()
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -114,6 +128,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -114,6 +128,7 @@ int main()
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -146,6 +161,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -146,6 +161,7 @@ int main()
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
...
data/1.算法初阶/3.蓝桥杯-递归/143.带分数/desc.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
#### 问题描述
#### 问题描述
100 可以表示为带分数的形式:100 = 3 + 69258 / 714。
100 可以表示为带分数的形式:100 = 3 + 69258 / 714。
还可以表示为:100 = 82 + 3546 / 197。
还可以表示为:100 = 82 + 3546 / 197。
...
@@ -8,26 +9,32 @@
...
@@ -8,26 +9,32 @@
类似这样的带分数,100 有 11 种表示法。
类似这样的带分数,100 有 11 种表示法。
#### 输入格式
#### 输入格式
从标准输入读入一个正整数N (N<1000
*
1000)
从标准输入读入一个正整数N (N<1000
*
1000)
#### 输出格式
#### 输出格式
程序输出该数字用数码1~9不重复不遗漏地组成带分数表示的全部种数。
程序输出该数字用数码1~9不重复不遗漏地组成带分数表示的全部种数。
注意:不要求输出每个表示,只统计有多少表示法!
注意:不要求输出每个表示,只统计有多少表示法!
#### 样例输入1
#### 样例输入1
```
```
100
100
```
```
#### 样例输出1
#### 样例输出1
```
```
11
11
```
```
#### 样例输入2
#### 样例输入2
```
```
105
105
```
```
#### 样例输出2
#### 样例输出2
```
```
6
6
```
```
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/3.蓝桥杯-递归/143.带分数/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 带分数
# 带分数
#### 问题描述
#### 问题描述
100 可以表示为带分数的形式:100 = 3 + 69258 / 714。
100 可以表示为带分数的形式:100 = 3 + 69258 / 714。
还可以表示为:100 = 82 + 3546 / 197。
还可以表示为:100 = 82 + 3546 / 197。
...
@@ -9,32 +11,40 @@
...
@@ -9,32 +11,40 @@
类似这样的带分数,100 有 11 种表示法。
类似这样的带分数,100 有 11 种表示法。
#### 输入格式
#### 输入格式
从标准输入读入一个正整数N (N<1000
*
1000)
从标准输入读入一个正整数N (N<1000
*
1000)
#### 输出格式
#### 输出格式
程序输出该数字用数码1~9不重复不遗漏地组成带分数表示的全部种数。
程序输出该数字用数码1~9不重复不遗漏地组成带分数表示的全部种数。
注意:不要求输出每个表示,只统计有多少表示法!
注意:不要求输出每个表示,只统计有多少表示法!
#### 样例输入1
#### 样例输入1
```
```
100
100
```
```
#### 样例输出1
#### 样例输出1
```
```
11
11
```
```
#### 样例输入2
#### 样例输入2
```
```
105
105
```
```
#### 样例输出2
#### 样例输出2
```
```
6
6
```
```
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int
x
=
0
,
number
=
0
,
count
=
0
;
int
x
=
0
,
number
=
0
,
count
=
0
;
...
@@ -56,6 +66,7 @@ int getNum(int list[], int f, int r)
...
@@ -56,6 +66,7 @@ int getNum(int list[], int f, int r)
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -75,6 +86,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -75,6 +86,7 @@ int main()
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
void
Prim
(
int
list
[],
int
k
,
int
m
)
void
Prim
(
int
list
[],
int
k
,
int
m
)
{
{
...
@@ -116,7 +128,9 @@ void Prim(int list[], int k, int m)
...
@@ -116,7 +128,9 @@ void Prim(int list[], int k, int m)
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
void
Prim
(
int
list
[],
int
k
,
int
m
)
void
Prim
(
int
list
[],
int
k
,
int
m
)
{
{
...
@@ -158,6 +172,7 @@ void Prim(int list[], int k, int m)
...
@@ -158,6 +172,7 @@ void Prim(int list[], int k, int m)
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
void
Prim
(
int
list
[],
int
k
,
int
m
)
void
Prim
(
int
list
[],
int
k
,
int
m
)
{
{
...
@@ -197,6 +212,7 @@ void Prim(int list[], int k, int m)
...
@@ -197,6 +212,7 @@ void Prim(int list[], int k, int m)
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
void
Prim
(
int
list
[],
int
k
,
int
m
)
void
Prim
(
int
list
[],
int
k
,
int
m
)
{
{
...
...
data/1.算法初阶/3.蓝桥杯-递归/163.等差数列/desc.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
#### 题目描述
#### 题目描述
数学老师给小明出了一道等差数列求和的题目。
数学老师给小明出了一道等差数列求和的题目。
但是粗心的小明忘记了一部分的数列,只记得其中 N 个整数。
但是粗心的小明忘记了一部分的数列,只记得其中 N 个整数。
...
@@ -6,15 +7,18 @@
...
@@ -6,15 +7,18 @@
现在给出这 N 个整数,小明想知道包含这 N 个整数的最短的等差数列有几项?
现在给出这 N 个整数,小明想知道包含这 N 个整数的最短的等差数列有几项?
#### 输入格式
#### 输入格式
输入的第一行包含一个整数 N。
输入的第一行包含一个整数 N。
第二行包含 N 个整数 A1,A2,⋅⋅⋅,AN。(注意 A1∼AN 并不一定是按等差数
第二行包含 N 个整数 A1,A2,⋅⋅⋅,AN。(注意 A1∼AN 并不一定是按等差数
列中的顺序给出)
列中的顺序给出)
#### 输出格式
#### 输出格式
输出一个整数表示答案。
输出一个整数表示答案。
#### 数据范围
#### 数据范围
```
```
2≤N≤100000,
2≤N≤100000,
0≤Ai≤109
0≤Ai≤109
...
@@ -22,6 +26,7 @@
...
@@ -22,6 +26,7 @@
2
2
```
```
#### 输入样例:
#### 输入样例:
```
```
5
5
2 6 4 10 20
2 6 4 10 20
...
@@ -29,9 +34,11 @@
...
@@ -29,9 +34,11 @@
2
2
```
```
#### 输出样例:
#### 输出样例:
```
```
10
10
1
1
```
```
#### 样例解释
#### 样例解释
包含 2、6、4、10、20 的最短的等差数列是 2、4、6、8、10、12、14、16、18、20。
包含 2、6、4、10、20 的最短的等差数列是 2、4、6、8、10、12、14、16、18、20。
data/1.算法初阶/3.蓝桥杯-递归/163.等差数列/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 等差数列
# 等差数列
#### 题目描述
#### 题目描述
数学老师给小明出了一道等差数列求和的题目。
数学老师给小明出了一道等差数列求和的题目。
但是粗心的小明忘记了一部分的数列,只记得其中 N 个整数。
但是粗心的小明忘记了一部分的数列,只记得其中 N 个整数。
...
@@ -7,29 +9,36 @@
...
@@ -7,29 +9,36 @@
现在给出这 N 个整数,小明想知道包含这 N 个整数的最短的等差数列有几项?
现在给出这 N 个整数,小明想知道包含这 N 个整数的最短的等差数列有几项?
#### 输入格式
#### 输入格式
输入的第一行包含一个整数 N。
输入的第一行包含一个整数 N。
第二行包含 N 个整数 A1,A2,⋅⋅⋅,AN。(注意 A1∼AN 并不一定是按等差数
第二行包含 N 个整数 A1,A2,⋅⋅⋅,AN。(注意 A1∼AN 并不一定是按等差数
列中的顺序给出)
列中的顺序给出)
#### 输出格式
#### 输出格式
输出一个整数表示答案。
输出一个整数表示答案。
#### 输入样例:
#### 输入样例:
```
```
5
5
2 6 4 10 20
2 6 4 10 20
```
```
#### 输出样例:
#### 输出样例:
```
```
10
10
```
```
#### 样例解释
#### 样例解释
包含 2、6、4、10、20 的最短的等差数列是 2、4、6、8、10、12、14、16、18、20。
包含 2、6、4、10、20 的最短的等差数列是 2、4、6、8、10、12、14、16、18、20。
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <algorithm>
...
@@ -44,11 +53,13 @@ int gcd(int a, int b)
...
@@ -44,11 +53,13 @@ int gcd(int a, int b)
}
}
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -74,7 +85,9 @@ int main()
...
@@ -74,7 +85,9 @@ int main()
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -99,6 +112,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -99,6 +112,7 @@ int main()
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -123,6 +137,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -123,6 +137,7 @@ int main()
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
...
data/1.算法初阶/3.蓝桥杯-递归/35.抽签/desc.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
...
@@ -8,15 +8,19 @@ C国最多可以派出2人。
...
@@ -8,15 +8,19 @@ C国最多可以派出2人。
那么最终派往W星的观察团会有多少种国别的不同组合呢?
那么最终派往W星的观察团会有多少种国别的不同组合呢?
#### 输入格式
#### 输入格式
第一行N,以下N行代表N个国家最多可派出人数Ai。
第一行N,以下N行代表N个国家最多可派出人数Ai。
#### 输出格式
#### 输出格式
最多多少种派法ANS,ANS为一个整数。
最多多少种派法ANS,ANS为一个整数。
#### 输出规模
#### 输出规模
```
```
1<N<10000
1<N<10000
1<AI<10000
1<AI<10000
```
```
#### 示例输入
#### 示例输入
```
```
6
6
4
4
...
...
data/1.算法初阶/3.蓝桥杯-递归/35.抽签/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 抽签
# 抽签
X星球要派出一个5人组成的观察团前往W星。
X星球要派出一个5人组成的观察团前往W星。
其中:
其中:
A国最多可以派出4人。
A国最多可以派出4人。
...
@@ -9,15 +10,19 @@ C国最多可以派出2人。
...
@@ -9,15 +10,19 @@ C国最多可以派出2人。
那么最终派往W星的观察团会有多少种国别的不同组合呢?
那么最终派往W星的观察团会有多少种国别的不同组合呢?
#### 输入格式
#### 输入格式
第一行N,以下N行代表N个国家最多可派出人数Ai。
第一行N,以下N行代表N个国家最多可派出人数Ai。
#### 输出格式
#### 输出格式
最多多少种派法ANS,ANS为一个整数。
最多多少种派法ANS,ANS为一个整数。
#### 输出规模
#### 输出规模
```
```
1<N<10000
1<N<10000
1<AI<10000
1<AI<10000
```
```
#### 示例输入
#### 示例输入
```
```
6
6
4
4
...
@@ -34,13 +39,16 @@ C国最多可以派出2人。
...
@@ -34,13 +39,16 @@ C国最多可以派出2人。
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <iostream>
using
namespace
std
;
using
namespace
std
;
int
a
[
10000
],
N
,
i
,
ans
=
0
;
int
a
[
10000
],
N
,
i
,
ans
=
0
;
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -58,6 +66,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -58,6 +66,7 @@ int main()
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
void
findAns
(
int
a
[],
int
start
,
int
An
)
void
findAns
(
int
a
[],
int
start
,
int
An
)
{
{
...
@@ -76,7 +85,9 @@ void findAns(int a[], int start, int An)
...
@@ -76,7 +85,9 @@ void findAns(int a[], int start, int An)
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
void
findAns
(
int
a
[],
int
start
,
int
An
)
void
findAns
(
int
a
[],
int
start
,
int
An
)
{
{
...
@@ -95,6 +106,7 @@ void findAns(int a[], int start, int An)
...
@@ -95,6 +106,7 @@ void findAns(int a[], int start, int An)
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
void
findAns
(
int
a
[],
int
start
,
int
An
)
void
findAns
(
int
a
[],
int
start
,
int
An
)
{
{
...
@@ -113,6 +125,7 @@ void findAns(int a[], int start, int An)
...
@@ -113,6 +125,7 @@ void findAns(int a[], int start, int An)
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
void
findAns
(
int
a
[],
int
start
,
int
An
)
void
findAns
(
int
a
[],
int
start
,
int
An
)
{
{
...
...
data/1.算法初阶/3.蓝桥杯-递归/58.打印图形/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 打印图形
# 打印图形
小明在X星球的城堡中发现了如下图形和文字:
小明在X星球的城堡中发现了如下图形和文字:
```
```
rank=3
rank=3
...
@@ -61,13 +62,16 @@ ran=6
...
@@ -61,13 +62,16 @@ ran=6
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdio>
#define N 70
#define N 70
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -92,6 +96,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -92,6 +96,7 @@ int main()
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
void
f
(
char
a
[][
N
],
int
rank
,
int
row
,
int
col
)
void
f
(
char
a
[][
N
],
int
rank
,
int
row
,
int
col
)
{
{
...
@@ -112,7 +117,9 @@ void f(char a[][N], int rank, int row, int col)
...
@@ -112,7 +117,9 @@ void f(char a[][N], int rank, int row, int col)
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
void
f
(
char
a
[][
N
],
int
rank
,
int
row
,
int
col
)
void
f
(
char
a
[][
N
],
int
rank
,
int
row
,
int
col
)
{
{
...
@@ -133,6 +140,7 @@ void f(char a[][N], int rank, int row, int col)
...
@@ -133,6 +140,7 @@ void f(char a[][N], int rank, int row, int col)
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
void
f
(
char
a
[][
N
],
int
rank
,
int
row
,
int
col
)
void
f
(
char
a
[][
N
],
int
rank
,
int
row
,
int
col
)
{
{
...
@@ -153,6 +161,7 @@ void f(char a[][N], int rank, int row, int col)
...
@@ -153,6 +161,7 @@ void f(char a[][N], int rank, int row, int col)
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
void
f
(
char
a
[][
N
],
int
rank
,
int
row
,
int
col
)
void
f
(
char
a
[][
N
],
int
rank
,
int
row
,
int
col
)
{
{
...
...
data/1.算法初阶/4.蓝桥杯-堆栈队列链表/124.堆的计数/desc.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
#### 题目描述
#### 题目描述
我们知道包含N个元素的堆可以看成是一棵包含N个节点的完全二叉树。
我们知道包含N个元素的堆可以看成是一棵包含N个节点的完全二叉树。
每个节点有一个权值。对于小根堆来说,父节点的权值一定小于其子节点的权值。
每个节点有一个权值。对于小根堆来说,父节点的权值一定小于其子节点的权值。
...
@@ -29,24 +30,29 @@
...
@@ -29,24 +30,29 @@
#### 输入格式
#### 输入格式
一个整数N。
一个整数N。
对于40%的数据,1 <= N <= 1000
对于40%的数据,1 <= N <= 1000
对于70%的数据,1 <= N <= 10000
对于70%的数据,1 <= N <= 10000
对于100%的数据,1 <= N <= 100000
对于100%的数据,1 <= N <= 100000
#### 输出格式
#### 输出格式
一个整数表示答案。
一个整数表示答案。
#### 输入样例
#### 输入样例
```
```
4
4
```
```
#### 输出样例
#### 输出样例
```
```
3
3
```
```
#### 资源约定:
#### 资源约定:
峰值内存消耗(含虚拟机) < 256M
峰值内存消耗(含虚拟机) < 256M
CPU消耗 < 1000ms
CPU消耗 < 1000ms
data/1.算法初阶/4.蓝桥杯-堆栈队列链表/124.堆的计数/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 堆的计数
# 堆的计数
#### 题目描述
#### 题目描述
我们知道包含N个元素的堆可以看成是一棵包含N个节点的完全二叉树。
我们知道包含N个元素的堆可以看成是一棵包含N个节点的完全二叉树。
每个节点有一个权值。对于小根堆来说,父节点的权值一定小于其子节点的权值。
每个节点有一个权值。对于小根堆来说,父节点的权值一定小于其子节点的权值。
...
@@ -30,31 +32,38 @@
...
@@ -30,31 +32,38 @@
#### 输入格式
#### 输入格式
一个整数N。
一个整数N。
对于40%的数据,1 <= N <= 1000
对于40%的数据,1 <= N <= 1000
对于70%的数据,1 <= N <= 10000
对于70%的数据,1 <= N <= 10000
对于100%的数据,1 <= N <= 100000
对于100%的数据,1 <= N <= 100000
#### 输出格式
#### 输出格式
一个整数表示答案。
一个整数表示答案。
#### 输入样例
#### 输入样例
```
```
4
4
```
```
#### 输出样例
#### 输出样例
```
```
3
3
```
```
#### 资源约定:
#### 资源约定:
峰值内存消耗(含虚拟机) < 256M
峰值内存消耗(含虚拟机) < 256M
CPU消耗 < 1000ms
CPU消耗 < 1000ms
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using
namespace
std
;
using
namespace
std
;
...
@@ -83,11 +92,13 @@ ll C(ll n, ll m)
...
@@ -83,11 +92,13 @@ ll C(ll n, ll m)
}
}
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -119,7 +130,9 @@ int main()
...
@@ -119,7 +130,9 @@ int main()
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -151,6 +164,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -151,6 +164,7 @@ int main()
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -182,6 +196,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -182,6 +196,7 @@ int main()
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
...
data/1.算法初阶/6.蓝桥杯-模拟/137.夺冠概率/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 夺冠概率
# 夺冠概率
足球比赛具有一定程度的偶然性,弱队也有战胜强队的可能。
足球比赛具有一定程度的偶然性,弱队也有战胜强队的可能。
假设有甲、乙、丙、丁四个球队。根据他们过去比赛的成绩,得出每个队与另一个队对阵时取胜的概率表:
假设有甲、乙、丙、丁四个球队。根据他们过去比赛的成绩,得出每个队与另一个队对阵时取胜的概率表:
...
@@ -20,7 +21,9 @@
...
@@ -20,7 +21,9 @@
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <iostream>
using
namespace
std
;
using
namespace
std
;
...
@@ -31,11 +34,13 @@ double rate[4][4] = {
...
@@ -31,11 +34,13 @@ double rate[4][4] = {
{
0.5
,
0.6
,
0.8
,
0
}};
{
0.5
,
0.6
,
0.8
,
0
}};
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -63,7 +68,9 @@ int main()
...
@@ -63,7 +68,9 @@ int main()
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -91,6 +98,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -91,6 +98,7 @@ int main()
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -118,6 +126,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -118,6 +126,7 @@ int main()
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
...
data/1.算法初阶/6.蓝桥杯-模拟/14.方程整数解/desc.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
#### 题目描述
#### 题目描述
方程: a^2 + b^2 + c^2 = 1000
方程: a^2 + b^2 + c^2 = 1000
这个方程有正整数解吗?有:a,b,c=6,8,30 就是一组解。
这个方程有正整数解吗?有:a,b,c=6,8,30 就是一组解。
求出 a^2 + b^2 + c^2 = n(1
<
=
n
<=10000)
的所有解
,
解要保证c
>
=b>=a>=1。
求出 a^2 + b^2 + c^2 = n(1
<
=
n
<=10000)
的所有解
,
解要保证c
>
=b>=a>=1。
#### 输入
#### 输入
存在多组测试数据,每组测试数据一行包含一个正整数n(1<=n<=10000)
存在多组测试数据,每组测试数据一行包含一个正整数n(1<=n<=10000)
#### 输出
#### 输出
如果无解则输出"No Solution"。
如果无解则输出"No Solution"。
如果存在多解,每组解输出1行,输出格式:a b c,以一个空格分隔
如果存在多解,每组解输出1行,输出格式:a b c,以一个空格分隔
按照a从小到大的顺序输出,如果a相同则按照b从小到大的顺序输出,如果a,b都相同则按照c从小到大的顺序输出。
按照a从小到大的顺序输出,如果a相同则按照b从小到大的顺序输出,如果a,b都相同则按照c从小到大的顺序输出。
#### 样例输入
#### 样例输入
```
```
4
4
1000
1000
```
```
#### 样例输出
#### 样例输出
```
```
No Solution
No Solution
6 8 30
6 8 30
...
...
data/1.算法初阶/6.蓝桥杯-模拟/14.方程整数解/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 方程整数解
# 方程整数解
#### 题目描述
#### 题目描述
方程: a^2 + b^2 + c^2 = 1000
方程: a^2 + b^2 + c^2 = 1000
这个方程有正整数解吗?有:a,b,c=6,8,30 就是一组解。
这个方程有正整数解吗?有:a,b,c=6,8,30 就是一组解。
求出 a^2 + b^2 + c^2 = n(1
<
=
n
<=10000)
的所有解
,
解要保证c
>
=b>=a>=1。
求出 a^2 + b^2 + c^2 = n(1
<
=
n
<=10000)
的所有解
,
解要保证c
>
=b>=a>=1。
#### 输入
#### 输入
存在多组测试数据,每组测试数据一行包含一个正整数n(1<=n<=10000)
存在多组测试数据,每组测试数据一行包含一个正整数n(1<=n<=10000)
#### 输出
#### 输出
如果无解则输出"No Solution"。
如果无解则输出"No Solution"。
如果存在多解,每组解输出1行,输出格式:a b c,以一个空格分隔
如果存在多解,每组解输出1行,输出格式:a b c,以一个空格分隔
按照a从小到大的顺序输出,如果a相同则按照b从小到大的顺序输出,如果a,b都相同则按照c从小到大的顺序输出。
按照a从小到大的顺序输出,如果a相同则按照b从小到大的顺序输出,如果a,b都相同则按照c从小到大的顺序输出。
#### 样例输入
#### 样例输入
```
```
4
4
1000
1000
```
```
#### 样例输出
#### 样例输出
```
```
No Solution
No Solution
6 8 30
6 8 30
...
@@ -23,18 +29,22 @@ No Solution
...
@@ -23,18 +29,22 @@ No Solution
```
```
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
#include <cmath>
using
namespace
std
;
using
namespace
std
;
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -69,7 +79,9 @@ int main()
...
@@ -69,7 +79,9 @@ int main()
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -103,6 +115,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -103,6 +115,7 @@ int main()
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -136,6 +149,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -136,6 +149,7 @@ int main()
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
...
data/1.算法初阶/6.蓝桥杯-模拟/162.7段码/desc.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
#### 题目描述
#### 题目描述
小蓝要用七段码数码管来表示一种特殊的文字。
小蓝要用七段码数码管来表示一种特殊的文字。

...
...
data/1.算法初阶/6.蓝桥杯-模拟/162.7段码/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 7段码
# 7段码
#### 题目描述
#### 题目描述
小蓝要用七段码数码管来表示一种特殊的文字。
小蓝要用七段码数码管来表示一种特殊的文字。


上图给出了七段码数码管的一个图示,数码管中一共有 7 段可以发光的二极管,分别标记为 a, b, c, d, e, f, g。
上图给出了七段码数码管的一个图示,数码管中一共有 7 段可以发光的二极管,分别标记为 a, b, c, d, e, f, g。
...
@@ -19,7 +21,9 @@
...
@@ -19,7 +21,9 @@
请问,小蓝可以用七段码数码管表达多少种不同的字符?
请问,小蓝可以用七段码数码管表达多少种不同的字符?
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <iostream>
using
namespace
std
;
using
namespace
std
;
...
@@ -45,6 +49,7 @@ int find(int a)
...
@@ -45,6 +49,7 @@ int find(int a)
}
}
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -57,6 +62,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -57,6 +62,7 @@ int main()
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
void
dfs
(
int
d
)
void
dfs
(
int
d
)
{
{
...
@@ -105,7 +111,9 @@ void dfs(int d)
...
@@ -105,7 +111,9 @@ void dfs(int d)
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
void
dfs
(
int
d
)
void
dfs
(
int
d
)
{
{
...
@@ -154,6 +162,7 @@ void dfs(int d)
...
@@ -154,6 +162,7 @@ void dfs(int d)
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
void
dfs
(
int
d
)
void
dfs
(
int
d
)
{
{
...
@@ -202,6 +211,7 @@ void dfs(int d)
...
@@ -202,6 +211,7 @@ void dfs(int d)
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
void
dfs
(
int
d
)
void
dfs
(
int
d
)
{
{
...
...
data/1.算法初阶/6.蓝桥杯-模拟/175.颠倒的价牌/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 颠倒的价牌
# 颠倒的价牌
小李的店里专卖其它店中下架的样品电视机,可称为:样品电视专卖店。
小李的店里专卖其它店中下架的样品电视机,可称为:样品电视专卖店。
其标价都是4位数字(即千元不等)。
其标价都是4位数字(即千元不等)。
小李为了标价清晰、方便,使用了预制的类似数码管的标价签,只要用颜色笔涂数字就可以了(参见图片)。
小李为了标价清晰、方便,使用了预制的类似数码管的标价签,只要用颜色笔涂数字就可以了(参见图片)。
...
@@ -12,17 +13,21 @@
...
@@ -12,17 +13,21 @@
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <iostream>
using
namespace
std
;
using
namespace
std
;
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -80,7 +85,9 @@ int main()
...
@@ -80,7 +85,9 @@ int main()
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -138,6 +145,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -138,6 +145,7 @@ int main()
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -195,6 +203,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -195,6 +203,7 @@ int main()
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
...
data/1.算法初阶/6.蓝桥杯-模拟/187.承压计算/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 承压计算
# 承压计算
X星球的高科技实验室中整齐地堆放着某批珍贵金属原料。
X星球的高科技实验室中整齐地堆放着某批珍贵金属原料。
每块金属原料的外形、尺寸完全一致,但重量不同。
每块金属原料的外形、尺寸完全一致,但重量不同。
...
@@ -52,7 +53,9 @@ X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X
...
@@ -52,7 +53,9 @@ X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <string.h>
...
@@ -65,11 +68,13 @@ double a[1050][1050];
...
@@ -65,11 +68,13 @@ double a[1050][1050];
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -100,7 +105,9 @@ int main()
...
@@ -100,7 +105,9 @@ int main()
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
...
@@ -132,6 +139,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -132,6 +139,7 @@ int main()
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -162,6 +170,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -162,6 +170,7 @@ int main()
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
...
data/1.算法初阶/6.蓝桥杯-模拟/23.放棋子/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 放棋子
# 放棋子
今有6×6的棋盘,其中某些格子已预放了棋子。现在要再放上去一些,使得每行每列都正好有3颗棋子。我们希望推算出所有可能的放法,下面的代码就实现了这个功能。初始数组中,“1”表示放有棋子,“0”表示空白。
今有6×6的棋盘,其中某些格子已预放了棋子。现在要再放上去一些,使得每行每列都正好有3颗棋子。我们希望推算出所有可能的放法,下面的代码就实现了这个功能。初始数组中,“1”表示放有棋子,“0”表示空白。

## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdio>
...
@@ -71,6 +74,7 @@ void GoNext(int x[][6], int r, int c)
...
@@ -71,6 +74,7 @@ void GoNext(int x[][6], int r, int c)
}
}
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -89,6 +93,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -89,6 +93,7 @@ int main()
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
void
f
(
int
x
[][
6
],
int
r
,
int
c
)
void
f
(
int
x
[][
6
],
int
r
,
int
c
)
{
{
...
@@ -130,7 +135,9 @@ void f(int x[][6], int r, int c)
...
@@ -130,7 +135,9 @@ void f(int x[][6], int r, int c)
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
void
f
(
int
x
[][
6
],
int
r
,
int
c
)
void
f
(
int
x
[][
6
],
int
r
,
int
c
)
{
{
...
@@ -168,6 +175,7 @@ void f(int x[][6], int r, int c)
...
@@ -168,6 +175,7 @@ void f(int x[][6], int r, int c)
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
void
f
(
int
x
[][
6
],
int
r
,
int
c
)
void
f
(
int
x
[][
6
],
int
r
,
int
c
)
{
{
...
@@ -206,6 +214,7 @@ void f(int x[][6], int r, int c)
...
@@ -206,6 +214,7 @@ void f(int x[][6], int r, int c)
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
void
f
(
int
x
[][
6
],
int
r
,
int
c
)
void
f
(
int
x
[][
6
],
int
r
,
int
c
)
{
{
...
...
data/1.算法初阶/6.蓝桥杯-模拟/28.分巧克力/desc.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
...
@@ -7,18 +7,22 @@
...
@@ -7,18 +7,22 @@
例如一块6x5的巧克力可以切出6块2x2的巧克力或者2块3x3的巧克力。
例如一块6x5的巧克力可以切出6块2x2的巧克力或者2块3x3的巧克力。
当然小朋友们都希望得到的巧克力尽可能大,你能帮小Hi计算出最大的边长是多少么?
当然小朋友们都希望得到的巧克力尽可能大,你能帮小Hi计算出最大的边长是多少么?
#### 输入
#### 输入
第一行包含两个整数N和K。(1 <= N, K <= 100000)
第一行包含两个整数N和K。(1 <= N, K <= 100000)
以下N行每行包含两个整数Hi和Wi。(1 <= Hi, Wi <= 100000)
以下N行每行包含两个整数Hi和Wi。(1 <= Hi, Wi <= 100000)
输入保证每位小朋友至少能获得一块1x1的巧克力。
输入保证每位小朋友至少能获得一块1x1的巧克力。
#### 输出
#### 输出
输出切出的正方形巧克力最大可能的边长。
输出切出的正方形巧克力最大可能的边长。
#### 样例输入:
#### 样例输入:
```
```
2 10
2 10
6 5
6 5
5 6
5 6
```
```
#### 样例输出:
#### 样例输出:
```
```
2
2
```
```
...
...
data/1.算法初阶/6.蓝桥杯-模拟/28.分巧克力/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 分巧克力
# 分巧克力
儿童节那天有K位小朋友到小明家做客。小明拿出了珍藏的巧克力招待小朋友们。
儿童节那天有K位小朋友到小明家做客。小明拿出了珍藏的巧克力招待小朋友们。
小明一共有N块巧克力,其中第i块是Hi x Wi的方格组成的长方形。
小明一共有N块巧克力,其中第i块是Hi x Wi的方格组成的长方形。
为了公平起见,小明需要从这 N 块巧克力中切出K块巧克力分给小朋友们。切出的巧克力需要满足:
为了公平起见,小明需要从这 N 块巧克力中切出K块巧克力分给小朋友们。切出的巧克力需要满足:
...
@@ -8,18 +9,22 @@
...
@@ -8,18 +9,22 @@
例如一块6x5的巧克力可以切出6块2x2的巧克力或者2块3x3的巧克力。
例如一块6x5的巧克力可以切出6块2x2的巧克力或者2块3x3的巧克力。
当然小朋友们都希望得到的巧克力尽可能大,你能帮小Hi计算出最大的边长是多少么?
当然小朋友们都希望得到的巧克力尽可能大,你能帮小Hi计算出最大的边长是多少么?
#### 输入
#### 输入
第一行包含两个整数N和K。(1 <= N, K <= 100000)
第一行包含两个整数N和K。(1 <= N, K <= 100000)
以下N行每行包含两个整数Hi和Wi。(1 <= Hi, Wi <= 100000)
以下N行每行包含两个整数Hi和Wi。(1 <= Hi, Wi <= 100000)
输入保证每位小朋友至少能获得一块1x1的巧克力。
输入保证每位小朋友至少能获得一块1x1的巧克力。
#### 输出
#### 输出
输出切出的正方形巧克力最大可能的边长。
输出切出的正方形巧克力最大可能的边长。
#### 样例输入:
#### 样例输入:
```
```
2 10
2 10
6 5
6 5
5 6
5 6
```
```
#### 样例输出:
#### 样例输出:
```
```
2
2
```
```
...
@@ -27,7 +32,9 @@
...
@@ -27,7 +32,9 @@
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <string.h>
...
@@ -45,6 +52,7 @@ int coun(int n, int x)
...
@@ -45,6 +52,7 @@ int coun(int n, int x)
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -58,6 +66,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -58,6 +66,7 @@ int main()
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
binary
(
int
n
,
int
k
)
int
binary
(
int
n
,
int
k
)
{
{
...
@@ -77,7 +86,9 @@ int binary(int n, int k)
...
@@ -77,7 +86,9 @@ int binary(int n, int k)
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
binary
(
int
n
,
int
k
)
int
binary
(
int
n
,
int
k
)
{
{
...
@@ -97,6 +108,7 @@ int binary(int n, int k)
...
@@ -97,6 +108,7 @@ int binary(int n, int k)
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
binary
(
int
n
,
int
k
)
int
binary
(
int
n
,
int
k
)
{
{
...
@@ -116,6 +128,7 @@ int binary(int n, int k)
...
@@ -116,6 +128,7 @@ int binary(int n, int k)
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
binary
(
int
n
,
int
k
)
int
binary
(
int
n
,
int
k
)
{
{
...
...
data/1.算法初阶/6.蓝桥杯-模拟/53.等腰三角形/desc.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
...
@@ -10,21 +10,30 @@
...
@@ -10,21 +10,30 @@
为了便于测评,我们要求空格一律用"."代替。
为了便于测评,我们要求空格一律用"."代替。
### 例如:
### 例如:
#### 输入:
#### 输入:
5
5
#### 程序应该输出:
#### 程序应该输出:


### 再例如:
### 再例如:
#### 输入:
#### 输入:
10
10
#### 程序应该输出:
#### 程序应该输出:


### 再例如:
### 再例如:
#### 输入:
#### 输入:
15
15
#### 程序应该输出:
#### 程序应该输出:


data/1.算法初阶/6.蓝桥杯-模拟/53.等腰三角形/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 等腰三角形
# 等腰三角形
本题目要求你在控制台输出一个由数字组成的等腰三角形。具体的步骤是:
本题目要求你在控制台输出一个由数字组成的等腰三角形。具体的步骤是:
先用1,2,3,…的自然数拼一个足够长的串
先用1,2,3,…的自然数拼一个足够长的串
...
@@ -11,28 +12,39 @@
...
@@ -11,28 +12,39 @@
为了便于测评,我们要求空格一律用"."代替。
为了便于测评,我们要求空格一律用"."代替。
### 例如:
### 例如:
#### 输入:
#### 输入:
5
5
#### 程序应该输出:
#### 程序应该输出:


### 再例如:
### 再例如:
#### 输入:
#### 输入:
10
10
#### 程序应该输出:
#### 程序应该输出:


### 再例如:
### 再例如:
#### 输入:
#### 输入:
15
15
#### 程序应该输出:
#### 程序应该输出:


## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using
namespace
std
;
using
namespace
std
;
...
@@ -40,11 +52,13 @@ string str;
...
@@ -40,11 +52,13 @@ string str;
stringstream
ss
;
stringstream
ss
;
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -107,7 +121,9 @@ int main()
...
@@ -107,7 +121,9 @@ int main()
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -170,6 +186,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -170,6 +186,7 @@ int main()
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -232,6 +249,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -232,6 +249,7 @@ int main()
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
...
data/1.算法初阶/6.蓝桥杯-模拟/54.分糖果/desc.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
#### 问题描述
#### 问题描述
有n个小朋友围坐成一圈。老师给每个小朋友随机发偶数个糖果,然后进行下面的游戏:
有n个小朋友围坐成一圈。老师给每个小朋友随机发偶数个糖果,然后进行下面的游戏:
每个小朋友都把自己的糖果分一半给左手边的孩子。
每个小朋友都把自己的糖果分一半给左手边的孩子。
一轮分糖后,拥有奇数颗糖的孩子由老师补给1个糖果,从而变成偶数。
一轮分糖后,拥有奇数颗糖的孩子由老师补给1个糖果,从而变成偶数。
...
@@ -6,18 +7,22 @@
...
@@ -6,18 +7,22 @@
你的任务是预测在已知的初始糖果情形下,老师一共需要补发多少个糖果。
你的任务是预测在已知的初始糖果情形下,老师一共需要补发多少个糖果。
#### 输入格式
#### 输入格式
程序首先读入一个整数N(2<N<100),表示小朋友的人数。
程序首先读入一个整数N(2<N<100),表示小朋友的人数。
接着是一行用空格分开的N个偶数(每个偶数不大于1000,不小于2)
接着是一行用空格分开的N个偶数(每个偶数不大于1000,不小于2)
#### 输出格式
#### 输出格式
要求程序输出一个整数,表示老师需要补发的糖果数。
要求程序输出一个整数,表示老师需要补发的糖果数。
#### 样例输入
#### 样例输入
```
```
3
3
2 2 4
2 2 4
```
```
#### 样例输出
#### 样例输出
```
```
4
4
```
```
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/6.蓝桥杯-模拟/54.分糖果/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 分糖果
# 分糖果
#### 问题描述
#### 问题描述
有n个小朋友围坐成一圈。老师给每个小朋友随机发偶数个糖果,然后进行下面的游戏:
有n个小朋友围坐成一圈。老师给每个小朋友随机发偶数个糖果,然后进行下面的游戏:
每个小朋友都把自己的糖果分一半给左手边的孩子。
每个小朋友都把自己的糖果分一半给左手边的孩子。
一轮分糖后,拥有奇数颗糖的孩子由老师补给1个糖果,从而变成偶数。
一轮分糖后,拥有奇数颗糖的孩子由老师补给1个糖果,从而变成偶数。
...
@@ -7,34 +9,42 @@
...
@@ -7,34 +9,42 @@
你的任务是预测在已知的初始糖果情形下,老师一共需要补发多少个糖果。
你的任务是预测在已知的初始糖果情形下,老师一共需要补发多少个糖果。
#### 输入格式
#### 输入格式
程序首先读入一个整数N(2<N<100),表示小朋友的人数。
程序首先读入一个整数N(2<N<100),表示小朋友的人数。
接着是一行用空格分开的N个偶数(每个偶数不大于1000,不小于2)
接着是一行用空格分开的N个偶数(每个偶数不大于1000,不小于2)
#### 输出格式
#### 输出格式
要求程序输出一个整数,表示老师需要补发的糖果数。
要求程序输出一个整数,表示老师需要补发的糖果数。
#### 样例输入
#### 样例输入
```
```
3
3
2 2 4
2 2 4
```
```
#### 样例输出
#### 样例输出
```
```
4
4
```
```
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <iostream>
using
namespace
std
;
using
namespace
std
;
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -80,7 +90,9 @@ int main()
...
@@ -80,7 +90,9 @@ int main()
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -126,6 +138,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -126,6 +138,7 @@ int main()
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -171,6 +184,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -171,6 +184,7 @@ int main()
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
...
data/1.算法初阶/6.蓝桥杯-模拟/63.方格填数/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 方格填数
# 方格填数
如下图
如下图

填入0~9的数字。要求:连续的两个数字不能相邻。
填入0~9的数字。要求:连续的两个数字不能相邻。
...
@@ -7,7 +8,9 @@
...
@@ -7,7 +8,9 @@
一共有多少种可能的填数方案?
一共有多少种可能的填数方案?
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <algorithm>
...
@@ -19,6 +22,7 @@ int ans;
...
@@ -19,6 +22,7 @@ int ans;
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -36,6 +40,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -36,6 +40,7 @@ int main()
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
bool
check
()
bool
check
()
{
{
...
@@ -60,7 +65,9 @@ bool check()
...
@@ -60,7 +65,9 @@ bool check()
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
bool
check
()
bool
check
()
{
{
...
@@ -85,6 +92,7 @@ bool check()
...
@@ -85,6 +92,7 @@ bool check()
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
bool
check
()
bool
check
()
{
{
...
@@ -111,6 +119,7 @@ bool check()
...
@@ -111,6 +119,7 @@ bool check()
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
bool
check
()
bool
check
()
{
{
...
...
data/1.算法初阶/7.蓝桥杯-搜索/121.超级胶水/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 超级胶水
# 超级胶水
小明有n颗石子,按顺序摆成一排。他准备用胶水将这些石子粘在一起。每颗石子有自己的重量,如果将两颗石子粘在一起,将合并成一颗新的石子,重量是这两颗石子的重量之和。
小明有n颗石子,按顺序摆成一排。他准备用胶水将这些石子粘在一起。每颗石子有自己的重量,如果将两颗石子粘在一起,将合并成一颗新的石子,重量是这两颗石子的重量之和。
为了保证石子粘贴牢固,粘贴两颗石子所需要的胶水与两颗石子的重量乘积成正比,本题不考虑物理单位,认为所需要的胶水在数值上等于两颗石子重量的乘积。
为了保证石子粘贴牢固,粘贴两颗石子所需要的胶水与两颗石子的重量乘积成正比,本题不考虑物理单位,认为所需要的胶水在数值上等于两颗石子重量的乘积。
每次合并,小明只能合并位置相邻的两颗石子,并将合并出的新石子放在原来的位置。
每次合并,小明只能合并位置相邻的两颗石子,并将合并出的新石子放在原来的位置。
...
@@ -19,7 +20,9 @@
...
@@ -19,7 +20,9 @@
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using
namespace
std
;
using
namespace
std
;
...
@@ -32,6 +35,7 @@ int v[maxn];
...
@@ -32,6 +35,7 @@ int v[maxn];
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
(){
int
main
(){
...
@@ -50,6 +54,7 @@ int main(){
...
@@ -50,6 +54,7 @@ int main(){
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
dfs
(
int
idx
){
int
dfs
(
int
idx
){
...
@@ -69,7 +74,9 @@ int dfs(int idx){
...
@@ -69,7 +74,9 @@ int dfs(int idx){
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
dfs
(
int
idx
)
int
dfs
(
int
idx
)
{
{
...
@@ -89,6 +96,7 @@ int dfs(int idx)
...
@@ -89,6 +96,7 @@ int dfs(int idx)
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
dfs
(
int
idx
)
int
dfs
(
int
idx
)
{
{
...
@@ -108,6 +116,7 @@ int dfs(int idx)
...
@@ -108,6 +116,7 @@ int dfs(int idx)
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
dfs
(
int
idx
)
int
dfs
(
int
idx
)
{
{
...
...
data/1.算法初阶/7.蓝桥杯-搜索/156.凑算式/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 凑算式
# 凑算式
```
```
B DEF
B DEF
A + —- + ——–- = 10
A + —- + ——–- = 10
...
@@ -14,7 +15,9 @@ A + —- + ——–- = 10
...
@@ -14,7 +15,9 @@ A + —- + ——–- = 10
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
...
@@ -35,6 +38,7 @@ void judge()
...
@@ -35,6 +38,7 @@ void judge()
}
}
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -46,6 +50,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -46,6 +50,7 @@ int main()
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
void
dfs
(
int
index
)
void
dfs
(
int
index
)
{
{
...
@@ -69,7 +74,9 @@ void dfs(int index)
...
@@ -69,7 +74,9 @@ void dfs(int index)
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
void
dfs
(
int
index
)
void
dfs
(
int
index
)
{
{
...
@@ -93,6 +100,7 @@ void dfs(int index)
...
@@ -93,6 +100,7 @@ void dfs(int index)
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
void
dfs
(
int
index
)
void
dfs
(
int
index
)
{
{
...
@@ -116,6 +124,7 @@ void dfs(int index)
...
@@ -116,6 +124,7 @@ void dfs(int index)
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
void
dfs
(
int
index
)
void
dfs
(
int
index
)
{
{
...
...
data/1.算法初阶/7.蓝桥杯-搜索/188.大臣的旅费/desc.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
#### 问题描述
#### 问题描述
很久以前,T王国空前繁荣。为了更好地管理国家,王国修建了大量的快速路,用于连接首都和王国内的各大城市。
很久以前,T王国空前繁荣。为了更好地管理国家,王国修建了大量的快速路,用于连接首都和王国内的各大城市。
为节省经费,T国的大臣们经过思考,制定了一套优秀的修建方案,使得任何一个大城市都能从首都直接或者通过其他大城市间接到达。同时,如果不重复经过大城市,从首都到达每个大城市的方案都是唯一的。
为节省经费,T国的大臣们经过思考,制定了一套优秀的修建方案,使得任何一个大城市都能从首都直接或者通过其他大城市间接到达。同时,如果不重复经过大城市,从首都到达每个大城市的方案都是唯一的。
...
@@ -10,6 +11,7 @@ J是T国重要大臣,他巡查于各大城市之间,体察民情。所以,
...
@@ -10,6 +11,7 @@ J是T国重要大臣,他巡查于各大城市之间,体察民情。所以,
J大臣想知道:他从某一个城市出发,中间不休息,到达另一个城市,所有可能花费的路费中最多是多少呢?
J大臣想知道:他从某一个城市出发,中间不休息,到达另一个城市,所有可能花费的路费中最多是多少呢?
#### 输入格式
#### 输入格式
输入的第一行包含一个整数n,表示包括首都在内的T王国的城市数
输入的第一行包含一个整数n,表示包括首都在内的T王国的城市数
城市从1开始依次编号,1号城市为首都。
城市从1开始依次编号,1号城市为首都。
...
@@ -19,9 +21,11 @@ J大臣想知道:他从某一个城市出发,中间不休息,到达另一
...
@@ -19,9 +21,11 @@ J大臣想知道:他从某一个城市出发,中间不休息,到达另一
每行三个整数Pi, Qi, Di,表示城市Pi和城市Qi之间有一条高速路,长度为Di千米。
每行三个整数Pi, Qi, Di,表示城市Pi和城市Qi之间有一条高速路,长度为Di千米。
#### 输出格式
#### 输出格式
输出一个整数,表示大臣J最多花费的路费是多少。
输出一个整数,表示大臣J最多花费的路费是多少。
#### 样例输入1
#### 样例输入1
```
```
5
5
1 2 2
1 2 2
...
@@ -30,10 +34,12 @@ J大臣想知道:他从某一个城市出发,中间不休息,到达另一
...
@@ -30,10 +34,12 @@ J大臣想知道:他从某一个城市出发,中间不休息,到达另一
2 5 4
2 5 4
```
```
#### 样例输出1
#### 样例输出1
```
```
135
135
```
```
#### 输出格式
#### 输出格式
```
```
大臣J从城市4到城市5要花费135的路费。
大臣J从城市4到城市5要花费135的路费。
```
```
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/7.蓝桥杯-搜索/188.大臣的旅费/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 大臣的旅费
# 大臣的旅费
#### 问题描述
#### 问题描述
很久以前,T王国空前繁荣。为了更好地管理国家,王国修建了大量的快速路,用于连接首都和王国内的各大城市。
很久以前,T王国空前繁荣。为了更好地管理国家,王国修建了大量的快速路,用于连接首都和王国内的各大城市。
为节省经费,T国的大臣们经过思考,制定了一套优秀的修建方案,使得任何一个大城市都能从首都直接或者通过其他大城市间接到达。同时,如果不重复经过大城市,从首都到达每个大城市的方案都是唯一的。
为节省经费,T国的大臣们经过思考,制定了一套优秀的修建方案,使得任何一个大城市都能从首都直接或者通过其他大城市间接到达。同时,如果不重复经过大城市,从首都到达每个大城市的方案都是唯一的。
...
@@ -11,6 +13,7 @@ J是T国重要大臣,他巡查于各大城市之间,体察民情。所以,
...
@@ -11,6 +13,7 @@ J是T国重要大臣,他巡查于各大城市之间,体察民情。所以,
J大臣想知道:他从某一个城市出发,中间不休息,到达另一个城市,所有可能花费的路费中最多是多少呢?
J大臣想知道:他从某一个城市出发,中间不休息,到达另一个城市,所有可能花费的路费中最多是多少呢?
#### 输入格式
#### 输入格式
输入的第一行包含一个整数n,表示包括首都在内的T王国的城市数
输入的第一行包含一个整数n,表示包括首都在内的T王国的城市数
城市从1开始依次编号,1号城市为首都。
城市从1开始依次编号,1号城市为首都。
...
@@ -20,9 +23,11 @@ J大臣想知道:他从某一个城市出发,中间不休息,到达另一
...
@@ -20,9 +23,11 @@ J大臣想知道:他从某一个城市出发,中间不休息,到达另一
每行三个整数Pi, Qi, Di,表示城市Pi和城市Qi之间有一条高速路,长度为Di千米。
每行三个整数Pi, Qi, Di,表示城市Pi和城市Qi之间有一条高速路,长度为Di千米。
#### 输出格式
#### 输出格式
输出一个整数,表示大臣J最多花费的路费是多少。
输出一个整数,表示大臣J最多花费的路费是多少。
#### 样例输入1
#### 样例输入1
```
```
5
5
1 2 2
1 2 2
...
@@ -31,16 +36,20 @@ J大臣想知道:他从某一个城市出发,中间不休息,到达另一
...
@@ -31,16 +36,20 @@ J大臣想知道:他从某一个城市出发,中间不休息,到达另一
2 5 4
2 5 4
```
```
#### 样例输出1
#### 样例输出1
```
```
135
135
```
```
#### 输出格式
#### 输出格式
```
```
大臣J从城市4到城市5要花费135的路费。
大臣J从城市4到城市5要花费135的路费。
```
```
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using
namespace
std
;
using
namespace
std
;
...
@@ -55,6 +64,7 @@ ll dis[maxn];
...
@@ -55,6 +64,7 @@ ll dis[maxn];
ll
sum
=
0
;
ll
sum
=
0
;
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -83,6 +93,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -83,6 +93,7 @@ int main()
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
bfs
(
int
node
)
int
bfs
(
int
node
)
{
{
...
@@ -115,7 +126,9 @@ int bfs(int node)
...
@@ -115,7 +126,9 @@ int bfs(int node)
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
bfs
(
int
node
)
int
bfs
(
int
node
)
{
{
...
@@ -145,6 +158,7 @@ int bfs(int node)
...
@@ -145,6 +158,7 @@ int bfs(int node)
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
bfs
(
int
node
)
int
bfs
(
int
node
)
{
{
...
@@ -174,6 +188,7 @@ int bfs(int node)
...
@@ -174,6 +188,7 @@ int bfs(int node)
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
bfs
(
int
node
)
int
bfs
(
int
node
)
{
{
...
...
data/1.算法初阶/7.蓝桥杯-搜索/51.分配口罩/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 分配口罩
# 分配口罩
某市市长获得了若干批口罩,给定每批口罩的数量,市长要把口罩分配给市内的2所医院。
某市市长获得了若干批口罩,给定每批口罩的数量,市长要把口罩分配给市内的2所医院。
```
```
...
@@ -12,7 +13,9 @@ masks = [9090400, 8499400, 5926800, 8547000, 4958200, 4422600, 5751200, 4175600,
...
@@ -12,7 +13,9 @@ masks = [9090400, 8499400, 5926800, 8547000, 4958200, 4422600, 5751200, 4175600,
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <algorithm>
...
@@ -25,6 +28,7 @@ long int masks[15] = {9090400, 8499400, 5926800, 8547000, 4958200,
...
@@ -25,6 +28,7 @@ long int masks[15] = {9090400, 8499400, 5926800, 8547000, 4958200,
long
ans
=
1000000000
;
long
ans
=
1000000000
;
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -35,6 +39,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -35,6 +39,7 @@ int main()
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
void
dfs
(
int
n
,
long
h1
,
long
h2
)
void
dfs
(
int
n
,
long
h1
,
long
h2
)
{
{
...
@@ -50,7 +55,9 @@ void dfs(int n, long h1, long h2)
...
@@ -50,7 +55,9 @@ void dfs(int n, long h1, long h2)
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
void
dfs
(
int
n
,
long
h1
,
long
h2
)
void
dfs
(
int
n
,
long
h1
,
long
h2
)
{
{
...
@@ -65,6 +72,7 @@ void dfs(int n, long h1, long h2)
...
@@ -65,6 +72,7 @@ void dfs(int n, long h1, long h2)
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
void
dfs
(
int
n
,
long
h1
,
long
h2
)
void
dfs
(
int
n
,
long
h1
,
long
h2
)
{
{
...
@@ -79,6 +87,7 @@ void dfs(int n, long h1, long h2)
...
@@ -79,6 +87,7 @@ void dfs(int n, long h1, long h2)
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
void
dfs
(
int
n
,
long
h1
,
long
h2
)
void
dfs
(
int
n
,
long
h1
,
long
h2
)
{
{
...
...
data/1.算法初阶/7.蓝桥杯-搜索/6.搭积木/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 搭积木
# 搭积木
小明最近喜欢搭数字积木,
小明最近喜欢搭数字积木,
一共有10块积木,每个积木上有一个数字,0~9。
一共有10块积木,每个积木上有一个数字,0~9。
...
@@ -23,7 +24,9 @@
...
@@ -23,7 +24,9 @@
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using
namespace
std
;
using
namespace
std
;
...
@@ -60,6 +63,7 @@ bool judge()
...
@@ -60,6 +63,7 @@ bool judge()
int
ans
=
0
;
int
ans
=
0
;
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -71,6 +75,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -71,6 +75,7 @@ int main()
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
void
dfs
(
int
idx
)
void
dfs
(
int
idx
)
{
{
...
@@ -99,7 +104,9 @@ void dfs(int idx)
...
@@ -99,7 +104,9 @@ void dfs(int idx)
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
void
dfs
(
int
idx
)
void
dfs
(
int
idx
)
{
{
...
@@ -128,6 +135,7 @@ void dfs(int idx)
...
@@ -128,6 +135,7 @@ void dfs(int idx)
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
void
dfs
(
int
idx
)
void
dfs
(
int
idx
)
{
{
...
@@ -156,6 +164,7 @@ void dfs(int idx)
...
@@ -156,6 +164,7 @@ void dfs(int idx)
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
void
dfs
(
int
idx
)
void
dfs
(
int
idx
)
{
{
...
...
data/1.算法初阶/7.蓝桥杯-搜索/65.方格分割/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 方格分割
# 方格分割
6x6的方格,沿着格子的边线剪开成两部分。
6x6的方格,沿着格子的边线剪开成两部分。
要求这两部分的形状完全相同。
要求这两部分的形状完全相同。
...
@@ -13,7 +14,9 @@
...
@@ -13,7 +14,9 @@
注意:旋转对称的属于同一种分割法。
注意:旋转对称的属于同一种分割法。
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <iostream>
using
namespace
std
;
using
namespace
std
;
...
@@ -23,6 +26,7 @@ int dire[][2] = {{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}};
...
@@ -23,6 +26,7 @@ int dire[][2] = {{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}};
int
vis
[
7
][
7
];
int
vis
[
7
][
7
];
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -33,6 +37,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -33,6 +37,7 @@ int main()
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
void
dfs
(
int
x
,
int
y
)
void
dfs
(
int
x
,
int
y
)
{
{
...
@@ -63,7 +68,9 @@ void dfs(int x, int y)
...
@@ -63,7 +68,9 @@ void dfs(int x, int y)
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
void
dfs
(
int
x
,
int
y
)
void
dfs
(
int
x
,
int
y
)
{
{
...
@@ -94,6 +101,7 @@ void dfs(int x, int y)
...
@@ -94,6 +101,7 @@ void dfs(int x, int y)
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
void
dfs
(
int
x
,
int
y
)
void
dfs
(
int
x
,
int
y
)
{
{
...
@@ -124,6 +132,7 @@ void dfs(int x, int y)
...
@@ -124,6 +132,7 @@ void dfs(int x, int y)
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
void
dfs
(
int
x
,
int
y
)
void
dfs
(
int
x
,
int
y
)
{
{
...
...
data/1.算法初阶/9.蓝桥杯-动态规划/117.地宫取宝/desc.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
...
@@ -6,36 +6,43 @@ X 国王有一个地宫宝库,是 n×m 个格子的矩阵,每个格子放一
...
@@ -6,36 +6,43 @@ X 国王有一个地宫宝库,是 n×m 个格子的矩阵,每个格子放一
请你帮小明算一算,在给定的局面下,他有多少种不同的行动方案能获得这 k 件宝贝。
请你帮小明算一算,在给定的局面下,他有多少种不同的行动方案能获得这 k 件宝贝。
#### 输入格式
#### 输入格式
第一行 3 个整数,n,m,k,含义见题目描述。
第一行 3 个整数,n,m,k,含义见题目描述。
接下来 n 行,每行有 m 个整数 Ci 用来描述宝库矩阵每个格子的宝贝价值。
接下来 n 行,每行有 m 个整数 Ci 用来描述宝库矩阵每个格子的宝贝价值。
#### 输出格式
#### 输出格式
输出一个整数,表示正好取 k 个宝贝的行动方案数。
输出一个整数,表示正好取 k 个宝贝的行动方案数。
该数字可能很大,输出它对 1000000007 取模的结果。
该数字可能很大,输出它对 1000000007 取模的结果。
#### 数据范围
#### 数据范围
```
```
1≤n,m≤50,
1≤n,m≤50,
1≤k≤12,
1≤k≤12,
0≤Ci≤12
0≤Ci≤12
```
```
#### 输入样例1:
#### 输入样例1:
```
```
2 2 2
2 2 2
1 2
1 2
2 1
2 1
```
```
#### 输出样例1:
#### 输出样例1:
```
```
2
2
```
```
#### 输入样例2:
#### 输入样例2:
```
```
2 3 2
2 3 2
1 2 3
1 2 3
2 1 5
2 1 5
```
```
#### 输出样例2:
#### 输出样例2:
```
```
14
14
```
```
\ No newline at end of file
data/1.算法初阶/9.蓝桥杯-动态规划/117.地宫取宝/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 地宫取宝
# 地宫取宝
X 国王有一个地宫宝库,是 n×m 个格子的矩阵,每个格子放一件宝贝,每个宝贝贴着价值标签。
X 国王有一个地宫宝库,是 n×m 个格子的矩阵,每个格子放一件宝贝,每个宝贝贴着价值标签。
地宫的入口在左上角,出口在右下角。
地宫的入口在左上角,出口在右下角。
小明被带到地宫的入口,国王要求他只能向右或向下行走。
小明被带到地宫的入口,国王要求他只能向右或向下行走。
...
@@ -7,42 +8,51 @@ X 国王有一个地宫宝库,是 n×m 个格子的矩阵,每个格子放一
...
@@ -7,42 +8,51 @@ X 国王有一个地宫宝库,是 n×m 个格子的矩阵,每个格子放一
请你帮小明算一算,在给定的局面下,他有多少种不同的行动方案能获得这 k 件宝贝。
请你帮小明算一算,在给定的局面下,他有多少种不同的行动方案能获得这 k 件宝贝。
#### 输入格式
#### 输入格式
第一行 3 个整数,n,m,k,含义见题目描述。
第一行 3 个整数,n,m,k,含义见题目描述。
接下来 n 行,每行有 m 个整数 Ci 用来描述宝库矩阵每个格子的宝贝价值。
接下来 n 行,每行有 m 个整数 Ci 用来描述宝库矩阵每个格子的宝贝价值。
#### 输出格式
#### 输出格式
输出一个整数,表示正好取 k 个宝贝的行动方案数。
输出一个整数,表示正好取 k 个宝贝的行动方案数。
该数字可能很大,输出它对 1000000007 取模的结果。
该数字可能很大,输出它对 1000000007 取模的结果。
#### 数据范围
#### 数据范围
```
```
1≤n,m≤50,
1≤n,m≤50,
1≤k≤12,
1≤k≤12,
0≤Ci≤12
0≤Ci≤12
```
```
#### 输入样例1:
#### 输入样例1:
```
```
2 2 2
2 2 2
1 2
1 2
2 1
2 1
```
```
#### 输出样例1:
#### 输出样例1:
```
```
2
2
```
```
#### 输入样例2:
#### 输入样例2:
```
```
2 3 2
2 3 2
1 2 3
1 2 3
2 1 5
2 1 5
```
```
#### 输出样例2:
#### 输出样例2:
```
```
14
14
```
```
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <iostream>
using
namespace
std
;
using
namespace
std
;
...
@@ -53,11 +63,13 @@ int g[N][N];
...
@@ -53,11 +63,13 @@ int g[N][N];
int
n
,
m
,
k
;
int
n
,
m
,
k
;
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -104,7 +116,9 @@ int main()
...
@@ -104,7 +116,9 @@ int main()
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -150,6 +164,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -150,6 +164,7 @@ int main()
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -195,6 +210,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -195,6 +210,7 @@ int main()
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
...
data/1.算法初阶/9.蓝桥杯-动态规划/91.测试次数/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 测试次数
# 测试次数
x星球的居民脾气不太好,但好在他们生气的时候唯一的异常举动是:摔手机。
x星球的居民脾气不太好,但好在他们生气的时候唯一的异常举动是:摔手机。
各大厂商也就纷纷推出各种耐摔型手机。x星球的质监局规定了手机必须经过耐摔测试,并且评定出一个耐摔指数来,之后才允许上市流通。
各大厂商也就纷纷推出各种耐摔型手机。x星球的质监局规定了手机必须经过耐摔测试,并且评定出一个耐摔指数来,之后才允许上市流通。
...
@@ -14,13 +15,16 @@ x星球有很多高耸入云的高塔,刚好可以用来做耐摔测试。塔
...
@@ -14,13 +15,16 @@ x星球有很多高耸入云的高塔,刚好可以用来做耐摔测试。塔
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <iostream>
using
namespace
std
;
using
namespace
std
;
int
num
[
5
][
1010
]
=
{
0
};
int
num
[
5
][
1010
]
=
{
0
};
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -30,6 +34,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -30,6 +34,7 @@ int main()
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
dp
(
int
k
,
int
n
)
int
dp
(
int
k
,
int
n
)
{
{
...
@@ -50,7 +55,9 @@ int dp(int k, int n)
...
@@ -50,7 +55,9 @@ int dp(int k, int n)
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
dp
(
int
k
,
int
n
)
int
dp
(
int
k
,
int
n
)
{
{
...
@@ -71,6 +78,7 @@ int dp(int k, int n)
...
@@ -71,6 +78,7 @@ int dp(int k, int n)
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
dp
(
int
k
,
int
n
)
int
dp
(
int
k
,
int
n
)
{
{
...
@@ -91,6 +99,7 @@ int dp(int k, int n)
...
@@ -91,6 +99,7 @@ int dp(int k, int n)
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
dp
(
int
k
,
int
n
)
int
dp
(
int
k
,
int
n
)
{
{
...
...
data/2.算法中阶/1.leetcode-数组/0.两数之和/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 两数之和
# 两数之和
<p>
给定一个整数数组
<code>
nums
</code>
和一个整数目标值
<code>
target
</code>
,请你在该数组中找出
<strong>
和为目标值
</strong>
的那
<strong>
两个
</strong>
整数,并返回它们的数组下标。
</p><p>
你可以假设每种输入只会对应一个答案。但是,数组中同一个元素在答案里不能重复出现。
</p><p>
你可以按任意顺序返回答案。
</p><p>
</p><p><strong>
示例 1:
</strong></p><pre><strong>
输入:
</strong>
nums = [2,7,11,15], target = 9
<strong><br
/>
输出:
</strong>
[0,1]
<strong><br
/>
解释:
</strong>
因为 nums[0] + nums[1] == 9 ,返回 [0, 1] 。
</pre><p><strong>
示例 2:
</strong></p><pre><strong>
输入:
</strong>
nums = [3,2,4], target = 6
<strong><br
/>
输出:
</strong>
[1,2]
</pre><p><strong>
示例 3:
</strong></p><pre><strong>
输入:
</strong>
nums = [3,3], target = 6
<strong><br
/>
输出:
</strong>
[0,1]
</pre><p>
</p><p><strong>
提示:
</strong></p><ul>
<li><code>
2
<
=
nums.length
<=
10<
sup
>
3
</sup></code></li>
<li><code>
-10
<sup>
9
</sup>
<
=
nums
[
i
]
<=
10<
sup
>
9
</sup></code></li>
<li><code>
-10
<sup>
9
</sup>
<
=
target
<=
10<
sup
>
9
</sup></code></li>
<li><strong>
只会存在一个有效答案
</strong></li></ul>
<p>
给定一个整数数组
<code>
nums
</code>
和一个整数目标值
<code>
target
</code>
,请你在该数组中找出
<strong>
和为目标值
</strong>
的那
<strong>
两个
</strong>
整数,并返回它们的数组下标。
</p><p>
你可以假设每种输入只会对应一个答案。但是,数组中同一个元素在答案里不能重复出现。
</p><p>
你可以按任意顺序返回答案。
</p><p>
</p><p><strong>
示例 1:
</strong></p><pre><strong>
输入:
</strong>
nums = [2,7,11,15], target = 9
<strong><br
/>
输出:
</strong>
[0,1]
<strong><br
/>
解释:
</strong>
因为 nums[0] + nums[1] == 9 ,返回 [0, 1] 。
</pre><p><strong>
示例 2:
</strong></p><pre><strong>
输入:
</strong>
nums = [3,2,4], target = 6
<strong><br
/>
输出:
</strong>
[1,2]
</pre><p><strong>
示例 3:
</strong></p><pre><strong>
输入:
</strong>
nums = [3,3], target = 6
<strong><br
/>
输出:
</strong>
[0,1]
</pre><p>
</p><p><strong>
提示:
</strong></p><ul>
<li><code>
2
<
=
nums.length
<=
10<
sup
>
3
</sup></code></li>
<li><code>
-10
<sup>
9
</sup>
<
=
nums
[
i
]
<=
10<
sup
>
9
</sup></code></li>
<li><code>
-10
<sup>
9
</sup>
<
=
target
<=
10<
sup
>
9
</sup></code></li>
<li><strong>
只会存在一个有效答案
</strong></li></ul>
<p>
以下错误的选项是?
</p>
<p>
以下错误的选项是?
</p>
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <unordered_map>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <vector>
#include <vector>
...
@@ -12,6 +15,7 @@
...
@@ -12,6 +15,7 @@
using
namespace
std
;
using
namespace
std
;
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -29,6 +33,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -29,6 +33,7 @@ int main()
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -56,7 +61,9 @@ public:
...
@@ -56,7 +61,9 @@ public:
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -84,6 +91,7 @@ public:
...
@@ -84,6 +91,7 @@ public:
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -111,6 +119,7 @@ public:
...
@@ -111,6 +119,7 @@ public:
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
...
data/2.算法中阶/1.leetcode-数组/14.三数之和/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 三数之和
# 三数之和
<p>
给你一个包含
<code>
n
</code>
个整数的数组
<code>
nums
</code>
,判断
<code>
nums
</code>
中是否存在三个元素
<em>
a,b,c ,
</em>
使得
<em>
a + b + c =
</em>
0 ?请你找出所有和为
<code>
0
</code>
且不重复的三元组。
</p><p><strong>
注意:
</strong>
答案中不可以包含重复的三元组。
</p><p>
</p><p><strong>
示例 1:
</strong></p><pre><strong>
输入:
</strong>
nums = [-1,0,1,2,-1,-4]
<strong><br
/>
输出:
</strong>
[[-1,-1,2],[-1,0,1]]
</pre><p><strong>
示例 2:
</strong></p><pre><strong>
输入:
</strong>
nums = []
<strong><br
/>
输出:
</strong>
[]
</pre><p><strong>
示例 3:
</strong></p><pre><strong>
输入:
</strong>
nums = [0]
<strong><br
/>
输出:
</strong>
[]
</pre><p>
</p><p><strong>
提示:
</strong></p><ul>
<li><code>
0
<
=
nums.length
<=
3000</
code
></li>
<li><code>
-10
<sup>
5
</sup>
<
=
nums
[
i
]
<=
10<
sup
>
5
</sup></code></li></ul>
<p>
给你一个包含
<code>
n
</code>
个整数的数组
<code>
nums
</code>
,判断
<code>
nums
</code>
中是否存在三个元素
<em>
a,b,c ,
</em>
使得
<em>
a + b + c =
</em>
0 ?请你找出所有和为
<code>
0
</code>
且不重复的三元组。
</p><p><strong>
注意:
</strong>
答案中不可以包含重复的三元组。
</p><p>
</p><p><strong>
示例 1:
</strong></p><pre><strong>
输入:
</strong>
nums = [-1,0,1,2,-1,-4]
<strong><br
/>
输出:
</strong>
[[-1,-1,2],[-1,0,1]]
</pre><p><strong>
示例 2:
</strong></p><pre><strong>
输入:
</strong>
nums = []
<strong><br
/>
输出:
</strong>
[]
</pre><p><strong>
示例 3:
</strong></p><pre><strong>
输入:
</strong>
nums = [0]
<strong><br
/>
输出:
</strong>
[]
</pre><p>
</p><p><strong>
提示:
</strong></p><ul>
<li><code>
0
<
=
nums.length
<=
3000</
code
></li>
<li><code>
-10
<sup>
5
</sup>
<
=
nums
[
i
]
<=
10<
sup
>
5
</sup></code></li></ul>
<p>
以下错误的选项是?
</p>
<p>
以下错误的选项是?
</p>
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <vector>
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
#include <iostream>
...
@@ -12,6 +15,7 @@
...
@@ -12,6 +15,7 @@
using
namespace
std
;
using
namespace
std
;
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -34,6 +38,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -34,6 +38,7 @@ int main()
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -72,7 +77,9 @@ public:
...
@@ -72,7 +77,9 @@ public:
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -125,6 +132,7 @@ public:
...
@@ -125,6 +132,7 @@ public:
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -166,6 +174,7 @@ public:
...
@@ -166,6 +174,7 @@ public:
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
...
data/2.算法中阶/1.leetcode-数组/17.四数之和/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 四数之和
# 四数之和
<p>
给定一个包含
<em>
n
</em>
个整数的数组
<code>
nums
</code>
和一个目标值
<code>
target
</code>
,判断
<code>
nums
</code>
中是否存在四个元素
<em>
a,
</em><em>
b,c
</em>
和
<em>
d
</em>
,使得
<em>
a
</em>
+
<em>
b
</em>
+
<em>
c
</em>
+
<em>
d
</em>
的值与
<code>
target
</code>
相等?找出所有满足条件且不重复的四元组。
</p><p><strong>
注意:
</strong>
答案中不可以包含重复的四元组。
</p><p>
</p><p><strong>
示例 1:
</strong></p><pre><strong>
输入:
</strong>
nums = [1,0,-1,0,-2,2], target = 0
<strong><br
/>
输出:
</strong>
[[-2,-1,1,2],[-2,0,0,2],[-1,0,0,1]]
</pre><p><strong>
示例 2:
</strong></p><pre><strong>
输入:
</strong>
nums = [], target = 0
<strong><br
/>
输出:
</strong>
[]
</pre><p>
</p><p><strong>
提示:
</strong></p><ul>
<li><code>
0
<
=
nums.length
<=
200</
code
></li>
<li><code>
-10
<sup>
9
</sup>
<
=
nums
[
i
]
<=
10<
sup
>
9
</sup></code></li>
<li><code>
-10
<sup>
9
</sup>
<
=
target
<=
10<
sup
>
9
</sup></code></li></ul>
<p>
给定一个包含
<em>
n
</em>
个整数的数组
<code>
nums
</code>
和一个目标值
<code>
target
</code>
,判断
<code>
nums
</code>
中是否存在四个元素
<em>
a,
</em><em>
b,c
</em>
和
<em>
d
</em>
,使得
<em>
a
</em>
+
<em>
b
</em>
+
<em>
c
</em>
+
<em>
d
</em>
的值与
<code>
target
</code>
相等?找出所有满足条件且不重复的四元组。
</p><p><strong>
注意:
</strong>
答案中不可以包含重复的四元组。
</p><p>
</p><p><strong>
示例 1:
</strong></p><pre><strong>
输入:
</strong>
nums = [1,0,-1,0,-2,2], target = 0
<strong><br
/>
输出:
</strong>
[[-2,-1,1,2],[-2,0,0,2],[-1,0,0,1]]
</pre><p><strong>
示例 2:
</strong></p><pre><strong>
输入:
</strong>
nums = [], target = 0
<strong><br
/>
输出:
</strong>
[]
</pre><p>
</p><p><strong>
提示:
</strong></p><ul>
<li><code>
0
<
=
nums.length
<=
200</
code
></li>
<li><code>
-10
<sup>
9
</sup>
<
=
nums
[
i
]
<=
10<
sup
>
9
</sup></code></li>
<li><code>
-10
<sup>
9
</sup>
<
=
target
<=
10<
sup
>
9
</sup></code></li></ul>
<p>
以下错误的选项是?
</p>
<p>
以下错误的选项是?
</p>
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using
namespace
std
;
using
namespace
std
;
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -34,6 +38,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -34,6 +38,7 @@ int main()
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -82,7 +87,9 @@ public:
...
@@ -82,7 +87,9 @@ public:
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -140,6 +147,7 @@ public:
...
@@ -140,6 +147,7 @@ public:
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -185,6 +193,7 @@ public:
...
@@ -185,6 +193,7 @@ public:
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
...
data/2.算法中阶/1.leetcode-数组/3.寻找两个正序数组的中位数/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 寻找两个正序数组的中位数
# 寻找两个正序数组的中位数
<p>
给定两个大小分别为
<code>
m
</code>
和
<code>
n
</code>
的正序(从小到大)数组
<code>
nums1
</code>
和
<code>
nums2
</code>
。请你找出并返回这两个正序数组的
<strong>
中位数
</strong>
。
</p><p>
</p><p><strong>
示例 1:
</strong></p><pre><strong>
输入:
</strong>
nums1 = [1,3], nums2 = [2]
<strong><br
/>
输出:
</strong>
2.00000
<strong><br
/>
解释:
</strong>
合并数组 = [1,2,3] ,中位数 2
</pre><p><strong>
示例 2:
</strong></p><pre><strong>
输入:
</strong>
nums1 = [1,2], nums2 = [3,4]
<strong><br
/>
输出:
</strong>
2.50000
<strong><br
/>
解释:
</strong>
合并数组 = [1,2,3,4] ,中位数 (2 + 3) / 2 = 2.5
</pre><p><strong>
示例 3:
</strong></p><pre><strong>
输入:
</strong>
nums1 = [0,0], nums2 = [0,0]
<strong><br
/>
输出:
</strong>
0.00000
</pre><p><strong>
示例 4:
</strong></p><pre><strong>
输入:
</strong>
nums1 = [], nums2 = [1]
<strong><br
/>
输出:
</strong>
1.00000
</pre><p><strong>
示例 5:
</strong></p><pre><strong>
输入:
</strong>
nums1 = [2], nums2 = []
<strong><br
/>
输出:
</strong>
2.00000
</pre><p>
</p><p><strong>
提示:
</strong></p><ul>
<li><code>
nums1.length == m
</code></li>
<li><code>
nums2.length == n
</code></li>
<li><code>
0
<
=
m
<=
1000</
code
></li>
<li><code>
0
<
=
n
<=
1000</
code
></li>
<li><code>
1
<
=
m
+
n
<=
2000</
code
></li>
<li><code>
-10
<sup>
6
</sup>
<
=
nums1
[
i
],
nums2
[
i
]
<=
10<
sup
>
6
</sup></code></li></ul><p>
</p><p><strong>
进阶:
</strong>
你能设计一个时间复杂度为
<code>
O(log (m+n))
</code>
的算法解决此问题吗?
</p>
<p>
给定两个大小分别为
<code>
m
</code>
和
<code>
n
</code>
的正序(从小到大)数组
<code>
nums1
</code>
和
<code>
nums2
</code>
。请你找出并返回这两个正序数组的
<strong>
中位数
</strong>
。
</p><p>
</p><p><strong>
示例 1:
</strong></p><pre><strong>
输入:
</strong>
nums1 = [1,3], nums2 = [2]
<strong><br
/>
输出:
</strong>
2.00000
<strong><br
/>
解释:
</strong>
合并数组 = [1,2,3] ,中位数 2
</pre><p><strong>
示例 2:
</strong></p><pre><strong>
输入:
</strong>
nums1 = [1,2], nums2 = [3,4]
<strong><br
/>
输出:
</strong>
2.50000
<strong><br
/>
解释:
</strong>
合并数组 = [1,2,3,4] ,中位数 (2 + 3) / 2 = 2.5
</pre><p><strong>
示例 3:
</strong></p><pre><strong>
输入:
</strong>
nums1 = [0,0], nums2 = [0,0]
<strong><br
/>
输出:
</strong>
0.00000
</pre><p><strong>
示例 4:
</strong></p><pre><strong>
输入:
</strong>
nums1 = [], nums2 = [1]
<strong><br
/>
输出:
</strong>
1.00000
</pre><p><strong>
示例 5:
</strong></p><pre><strong>
输入:
</strong>
nums1 = [2], nums2 = []
<strong><br
/>
输出:
</strong>
2.00000
</pre><p>
</p><p><strong>
提示:
</strong></p><ul>
<li><code>
nums1.length == m
</code></li>
<li><code>
nums2.length == n
</code></li>
<li><code>
0
<
=
m
<=
1000</
code
></li>
<li><code>
0
<
=
n
<=
1000</
code
></li>
<li><code>
1
<
=
m
+
n
<=
2000</
code
></li>
<li><code>
-10
<sup>
6
</sup>
<
=
nums1
[
i
],
nums2
[
i
]
<=
10<
sup
>
6
</sup></code></li></ul><p>
</p><p><strong>
进阶:
</strong>
你能设计一个时间复杂度为
<code>
O(log (m+n))
</code>
的算法解决此问题吗?
</p>
<p>
以下错误的选项是?
</p>
<p>
以下错误的选项是?
</p>
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using
namespace
std
;
using
namespace
std
;
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -30,6 +34,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -30,6 +34,7 @@ int main()
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -87,7 +92,9 @@ public:
...
@@ -87,7 +92,9 @@ public:
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -124,6 +131,7 @@ public:
...
@@ -124,6 +131,7 @@ public:
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -143,6 +151,7 @@ public:
...
@@ -143,6 +151,7 @@ public:
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
...
data/2.算法中阶/1.leetcode-数组/32.搜索旋转排序数组/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 搜索旋转排序数组
# 搜索旋转排序数组
<p>
整数数组
<code>
nums
</code>
按升序排列,数组中的值
<strong>
互不相同
</strong>
。
</p>
<p>
整数数组
<code>
nums
</code>
按升序排列,数组中的值
<strong>
互不相同
</strong>
。
</p>
<p>
在传递给函数之前,
<code>
nums
</code>
在预先未知的某个下标
<code>
k
</code>
(
<code>
0
<
=
k
<
nums.length
</
code
>
)上进行了
<strong>
旋转
</strong>
,使数组变为
<p>
在传递给函数之前,
<code>
nums
</code>
在预先未知的某个下标
<code>
k
</code>
(
<code>
0
<
=
k
<
nums.length
</
code
>
)上进行了
<strong>
旋转
</strong>
,使数组变为
<code>
[nums[k], nums[k+1], ..., nums[n-1], nums[0], nums[1], ..., nums[k-1]]
</code>
(下标
<strong>
从 0 开始
</strong>
<code>
[nums[k], nums[k+1], ..., nums[n-1], nums[0], nums[1], ..., nums[k-1]]
</code>
(下标
<strong>
从 0 开始
</strong>
...
@@ -28,12 +29,15 @@
...
@@ -28,12 +29,15 @@
<p>
以下错误的选项是?
</p>
<p>
以下错误的选项是?
</p>
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using
namespace
std
;
using
namespace
std
;
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -50,6 +54,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -50,6 +54,7 @@ int main()
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -84,7 +89,9 @@ public:
...
@@ -84,7 +89,9 @@ public:
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -129,6 +136,7 @@ public:
...
@@ -129,6 +136,7 @@ public:
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -155,6 +163,7 @@ public:
...
@@ -155,6 +163,7 @@ public:
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
...
data/2.算法中阶/1.leetcode-数组/33.在排序数组中查找元素的第一个和最后一个位置/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 在排序数组中查找元素的第一个和最后一个位置
# 在排序数组中查找元素的第一个和最后一个位置
<p>
给定一个按照升序排列的整数数组
<code>
nums
</code>
,和一个目标值
<code>
target
</code>
。找出给定目标值在数组中的开始位置和结束位置。
</p>
<p>
给定一个按照升序排列的整数数组
<code>
nums
</code>
,和一个目标值
<code>
target
</code>
。找出给定目标值在数组中的开始位置和结束位置。
</p>
<p>
如果数组中不存在目标值
<code>
target
</code>
,返回
<code>
[-1, -1]
</code>
。
</p>
<p>
如果数组中不存在目标值
<code>
target
</code>
,返回
<code>
[-1, -1]
</code>
。
</p>
<p><strong>
进阶:
</strong></p>
<p><strong>
进阶:
</strong></p>
...
@@ -23,12 +24,15 @@
...
@@ -23,12 +24,15 @@
<p>
以下错误的选项是?
</p>
<p>
以下错误的选项是?
</p>
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using
namespace
std
;
using
namespace
std
;
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -46,6 +50,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -46,6 +50,7 @@ int main()
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -114,7 +119,9 @@ public:
...
@@ -114,7 +119,9 @@ public:
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -170,6 +177,7 @@ public:
...
@@ -170,6 +177,7 @@ public:
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -237,6 +245,7 @@ private:
...
@@ -237,6 +245,7 @@ private:
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
...
data/2.算法中阶/1.leetcode-数组/34.搜索插入位置/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 搜索插入位置
# 搜索插入位置
<p>
给定一个排序数组和一个目标值,在数组中找到目标值,并返回其索引。如果目标值不存在于数组中,返回它将会被按顺序插入的位置。
</p><p>
你可以假设数组中无重复元素。
</p><p><strong>
示例 1:
</strong></p><pre><strong>
输入:
</strong>
[1,3,5,6], 5
<strong><br
/>
输出:
</strong>
2
</pre><p><strong>
示例
2:
</strong></p><pre><strong>
输入:
</strong>
[1,3,5,6], 2
<strong><br
/>
输出:
</strong>
1
</pre><p><strong>
示例 3:
</strong></p><pre><strong>
输入:
</strong>
[1,3,5,6], 7
<strong><br
/>
输出:
</strong>
4
</pre><p><strong>
示例 4:
</strong></p><pre><strong>
输入:
</strong>
[1,3,5,6], 0
<strong><br
/>
输出:
</strong>
0
</pre>
<p>
给定一个排序数组和一个目标值,在数组中找到目标值,并返回其索引。如果目标值不存在于数组中,返回它将会被按顺序插入的位置。
</p><p>
你可以假设数组中无重复元素。
</p><p><strong>
示例 1:
</strong></p><pre><strong>
输入:
</strong>
[1,3,5,6], 5
<strong><br
/>
输出:
</strong>
2
</pre><p><strong>
示例
2:
</strong></p><pre><strong>
输入:
</strong>
[1,3,5,6], 2
<strong><br
/>
输出:
</strong>
1
</pre><p><strong>
示例 3:
</strong></p><pre><strong>
输入:
</strong>
[1,3,5,6], 7
<strong><br
/>
输出:
</strong>
4
</pre><p><strong>
示例 4:
</strong></p><pre><strong>
输入:
</strong>
[1,3,5,6], 0
<strong><br
/>
输出:
</strong>
0
</pre>
<p>
以下错误的选项是?
</p>
<p>
以下错误的选项是?
</p>
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using
namespace
std
;
using
namespace
std
;
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -25,6 +29,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -25,6 +29,7 @@ int main()
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -50,7 +55,9 @@ public:
...
@@ -50,7 +55,9 @@ public:
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -77,6 +84,7 @@ public:
...
@@ -77,6 +84,7 @@ public:
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -97,6 +105,7 @@ public:
...
@@ -97,6 +105,7 @@ public:
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
...
data/2.算法中阶/1.leetcode-数组/47.旋转图像/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 旋转图像
# 旋转图像
<p>给定一个 <em>n </em>× <em>n</em> 的二维矩阵 <code>matrix</code> 表示一个图像。请你将图像顺时针旋转 90 度。</p><p>你必须在<strong><a href="https://baike.baidu.com/item/%E5%8E%9F%E5%9C%B0%E7%AE%97%E6%B3%95" target="_blank"> 原地</a></strong> 旋转图像,这意味着你需要直接修改输入的二维矩阵。<strong>请不要 </strong>使用另一个矩阵来旋转图像。</p><p> </p><p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p><img alt="" src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/doocs/leetcode@main/solution/0000-0099/0048.Rotate%20Image/images/mat1.jpg" style="width: 642px; height: 242px;" /><pre><strong>输入:</strong>matrix = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]]<strong><br />输出:</strong>[[7,4,1],[8,5,2],[9,6,3]]</pre><p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p><img alt="" src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/doocs/leetcode@main/solution/0000-0099/0048.Rotate%20Image/images/mat2.jpg" style="width: 800px; height: 321px;" /><pre><strong>输入:</strong>matrix = [[5,1,9,11],[2,4,8,10],[13,3,6,7],[15,14,12,16]]<strong><br />输出:</strong>[[15,13,2,5],[14,3,4,1],[12,6,8,9],[16,7,10,11]]</pre><p><strong>示例 3:</strong></p><pre><strong>输入:</strong>matrix = [[1]]<strong><br />输出:</strong>[[1]]</pre><p><strong>示例 4:</strong></p><pre><strong>输入:</strong>matrix = [[1,2],[3,4]]<strong><br />输出:</strong>[[3,1],[4,2]]</pre><p> </p><p><strong>提示:</strong></p><ul> <li><code>matrix.length == n</code></li> <li><code>matrix[i].length == n</code></li> <li><code>1 <= n <= 20</code></li> <li><code>-1000 <= matrix[i][j] <= 1000</code></li></ul>
<p>给定一个 <em>n </em>× <em>n</em> 的二维矩阵 <code>matrix</code> 表示一个图像。请你将图像顺时针旋转 90 度。</p><p>你必须在<strong><a href="https://baike.baidu.com/item/%E5%8E%9F%E5%9C%B0%E7%AE%97%E6%B3%95" target="_blank"> 原地</a></strong> 旋转图像,这意味着你需要直接修改输入的二维矩阵。<strong>请不要 </strong>使用另一个矩阵来旋转图像。</p><p> </p><p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p><img alt="" src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/doocs/leetcode@main/solution/0000-0099/0048.Rotate%20Image/images/mat1.jpg" style="width: 642px; height: 242px;" /><pre><strong>输入:</strong>matrix = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]]<strong><br />输出:</strong>[[7,4,1],[8,5,2],[9,6,3]]</pre><p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p><img alt="" src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/doocs/leetcode@main/solution/0000-0099/0048.Rotate%20Image/images/mat2.jpg" style="width: 800px; height: 321px;" /><pre><strong>输入:</strong>matrix = [[5,1,9,11],[2,4,8,10],[13,3,6,7],[15,14,12,16]]<strong><br />输出:</strong>[[15,13,2,5],[14,3,4,1],[12,6,8,9],[16,7,10,11]]</pre><p><strong>示例 3:</strong></p><pre><strong>输入:</strong>matrix = [[1]]<strong><br />输出:</strong>[[1]]</pre><p><strong>示例 4:</strong></p><pre><strong>输入:</strong>matrix = [[1,2],[3,4]]<strong><br />输出:</strong>[[3,1],[4,2]]</pre><p> </p><p><strong>提示:</strong></p><ul> <li><code>matrix.length == n</code></li> <li><code>matrix[i].length == n</code></li> <li><code>1 <= n <= 20</code></li> <li><code>-1000 <= matrix[i][j] <= 1000</code></li></ul>
<p>
以下错误的选项是?
</p>
<p>
以下错误的选项是?
</p>
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -39,7 +44,9 @@ public:
...
@@ -39,7 +44,9 @@ public:
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -64,6 +71,7 @@ public:
...
@@ -64,6 +71,7 @@ public:
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -91,6 +99,7 @@ public:
...
@@ -91,6 +99,7 @@ public:
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
...
data/2.算法中阶/1.leetcode-数组/53.螺旋矩阵/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 螺旋矩阵
# 螺旋矩阵
<p>给你一个 <code>m</code> 行 <code>n</code> 列的矩阵 <code>matrix</code> ,请按照 <strong>顺时针螺旋顺序</strong> ,返回矩阵中的所有元素。</p><p> </p><p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p><img alt="" src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/doocs/leetcode@main/solution/0000-0099/0054.Spiral%20Matrix/images/spiral1.jpg" style="width: 242px; height: 242px;" /><pre><strong>输入:</strong>matrix = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]]<strong><br />输出:</strong>[1,2,3,6,9,8,7,4,5]</pre><p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p><img alt="" src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/doocs/leetcode@main/solution/0000-0099/0054.Spiral%20Matrix/images/spiral.jpg" style="width: 322px; height: 242px;" /><pre><strong>输入:</strong>matrix = [[1,2,3,4],[5,6,7,8],[9,10,11,12]]<strong><br />输出:</strong>[1,2,3,4,8,12,11,10,9,5,6,7]</pre><p> </p><p><strong>提示:</strong></p><ul> <li><code>m == matrix.length</code></li> <li><code>n == matrix[i].length</code></li> <li><code>1 <= m, n <= 10</code></li> <li><code>-100 <= matrix[i][j] <= 100</code></li></ul>
<p>给你一个 <code>m</code> 行 <code>n</code> 列的矩阵 <code>matrix</code> ,请按照 <strong>顺时针螺旋顺序</strong> ,返回矩阵中的所有元素。</p><p> </p><p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p><img alt="" src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/doocs/leetcode@main/solution/0000-0099/0054.Spiral%20Matrix/images/spiral1.jpg" style="width: 242px; height: 242px;" /><pre><strong>输入:</strong>matrix = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]]<strong><br />输出:</strong>[1,2,3,6,9,8,7,4,5]</pre><p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p><img alt="" src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/doocs/leetcode@main/solution/0000-0099/0054.Spiral%20Matrix/images/spiral.jpg" style="width: 322px; height: 242px;" /><pre><strong>输入:</strong>matrix = [[1,2,3,4],[5,6,7,8],[9,10,11,12]]<strong><br />输出:</strong>[1,2,3,4,8,12,11,10,9,5,6,7]</pre><p> </p><p><strong>提示:</strong></p><ul> <li><code>m == matrix.length</code></li> <li><code>n == matrix[i].length</code></li> <li><code>1 <= m, n <= 10</code></li> <li><code>-100 <= matrix[i][j] <= 100</code></li></ul>
<p>
以下错误的选项是?
</p>
<p>
以下错误的选项是?
</p>
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using
namespace
std
;
using
namespace
std
;
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -68,7 +73,9 @@ public:
...
@@ -68,7 +73,9 @@ public:
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -125,6 +132,7 @@ public:
...
@@ -125,6 +132,7 @@ public:
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -159,6 +167,7 @@ public:
...
@@ -159,6 +167,7 @@ public:
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
...
data/2.算法中阶/1.leetcode-数组/55.合并区间/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 合并区间
# 合并区间
<p>
以数组
<code>
intervals
</code>
表示若干个区间的集合,其中单个区间为
<code>
intervals[i] = [start
<sub>
i
</sub>
, end
<sub>
i
</sub>
]
</code>
。请你合并所有重叠的区间,并返回一个不重叠的区间数组,该数组需恰好覆盖输入中的所有区间。
</p><p>
</p><p><strong>
示例 1:
</strong></p><pre><strong>
输入:
</strong>
intervals = [[1,3],[2,6],[8,10],[15,18]]
<strong><br
/>
输出:
</strong>
[[1,6],[8,10],[15,18]]
<strong><br
/>
解释:
</strong>
区间 [1,3] 和 [2,6] 重叠, 将它们合并为 [1,6].
</pre><p><strong>
示例 2:
</strong></p><pre><strong>
输入:
</strong>
intervals = [[1,4],[4,5]]
<strong><br
/>
输出:
</strong>
[[1,5]]
<strong><br
/>
解释:
</strong>
区间 [1,4] 和 [4,5] 可被视为重叠区间。
</pre><p>
</p><p><strong>
提示:
</strong></p><ul>
<li><code>
1
<
=
intervals.length
<=
10<
sup
>
4
</sup></code></li>
<li><code>
intervals[i].length == 2
</code></li>
<li><code>
0
<
=
start
<
sub
>
i
</sub>
<
=
end
<
sub
>
i
</sub>
<
=
10<
sup
>
4
</sup></code></li></ul>
<p>
以数组
<code>
intervals
</code>
表示若干个区间的集合,其中单个区间为
<code>
intervals[i] = [start
<sub>
i
</sub>
, end
<sub>
i
</sub>
]
</code>
。请你合并所有重叠的区间,并返回一个不重叠的区间数组,该数组需恰好覆盖输入中的所有区间。
</p><p>
</p><p><strong>
示例 1:
</strong></p><pre><strong>
输入:
</strong>
intervals = [[1,3],[2,6],[8,10],[15,18]]
<strong><br
/>
输出:
</strong>
[[1,6],[8,10],[15,18]]
<strong><br
/>
解释:
</strong>
区间 [1,3] 和 [2,6] 重叠, 将它们合并为 [1,6].
</pre><p><strong>
示例 2:
</strong></p><pre><strong>
输入:
</strong>
intervals = [[1,4],[4,5]]
<strong><br
/>
输出:
</strong>
[[1,5]]
<strong><br
/>
解释:
</strong>
区间 [1,4] 和 [4,5] 可被视为重叠区间。
</pre><p>
</p><p><strong>
提示:
</strong></p><ul>
<li><code>
1
<
=
intervals.length
<=
10<
sup
>
4
</sup></code></li>
<li><code>
intervals[i].length == 2
</code></li>
<li><code>
0
<
=
start
<
sub
>
i
</sub>
<
=
end
<
sub
>
i
</sub>
<
=
10<
sup
>
4
</sup></code></li></ul>
<p>
以下错误的选项是?
</p>
<p>
以下错误的选项是?
</p>
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using
namespace
std
;
using
namespace
std
;
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -48,7 +53,9 @@ public:
...
@@ -48,7 +53,9 @@ public:
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -71,6 +78,7 @@ public:
...
@@ -71,6 +78,7 @@ public:
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -97,6 +105,7 @@ public:
...
@@ -97,6 +105,7 @@ public:
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
...
data/2.算法中阶/1.leetcode-数组/56.插入区间/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 插入区间
# 插入区间
<p>
给你一个
<strong>
无重叠的
</strong><em>
,
</em>
按照区间起始端点排序的区间列表。
</p>
<p>
给你一个
<strong>
无重叠的
</strong><em>
,
</em>
按照区间起始端点排序的区间列表。
</p>
<p>
在列表中插入一个新的区间,你需要确保列表中的区间仍然有序且不重叠(如果有必要的话,可以合并区间)。
</p>
<p>
在列表中插入一个新的区间,你需要确保列表中的区间仍然有序且不重叠(如果有必要的话,可以合并区间)。
</p>
<p>
</p>
<p>
</p>
...
@@ -25,17 +26,21 @@
...
@@ -25,17 +26,21 @@
<p>
以下错误的选项是?
</p>
<p>
以下错误的选项是?
</p>
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using
namespace
std
;
using
namespace
std
;
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -60,7 +65,9 @@ public:
...
@@ -60,7 +65,9 @@ public:
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -197,6 +204,7 @@ public:
...
@@ -197,6 +204,7 @@ public:
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -235,6 +243,7 @@ public:
...
@@ -235,6 +243,7 @@ public:
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
...
data/2.算法中阶/1.leetcode-数组/58.螺旋矩阵 II/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 螺旋矩阵 II
# 螺旋矩阵 II
<p>给你一个正整数 <code>n</code> ,生成一个包含 <code>1</code> 到 <code>n<sup>2</sup></code> 所有元素,且元素按顺时针顺序螺旋排列的 <code>n x n</code> 正方形矩阵 <code>matrix</code> 。</p><p> </p><p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p><img alt="" src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/doocs/leetcode@main/solution/0000-0099/0059.Spiral%20Matrix%20II/images/spiraln.jpg" style="width: 242px; height: 242px;" /><pre><strong>输入:</strong>n = 3<strong><br />输出:</strong>[[1,2,3],[8,9,4],[7,6,5]]</pre><p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p><pre><strong>输入:</strong>n = 1<strong><br />输出:</strong>[[1]]</pre><p> </p><p><strong>提示:</strong></p><ul> <li><code>1 <= n <= 20</code></li></ul>
<p>给你一个正整数 <code>n</code> ,生成一个包含 <code>1</code> 到 <code>n<sup>2</sup></code> 所有元素,且元素按顺时针顺序螺旋排列的 <code>n x n</code> 正方形矩阵 <code>matrix</code> 。</p><p> </p><p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p><img alt="" src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/doocs/leetcode@main/solution/0000-0099/0059.Spiral%20Matrix%20II/images/spiraln.jpg" style="width: 242px; height: 242px;" /><pre><strong>输入:</strong>n = 3<strong><br />输出:</strong>[[1,2,3],[8,9,4],[7,6,5]]</pre><p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p><pre><strong>输入:</strong>n = 1<strong><br />输出:</strong>[[1]]</pre><p> </p><p><strong>提示:</strong></p><ul> <li><code>1 <= n <= 20</code></li></ul>
<p>
以下错误的选项是?
</p>
<p>
以下错误的选项是?
</p>
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using
namespace
std
;
using
namespace
std
;
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -28,6 +32,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -28,6 +32,7 @@ int main()
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -56,7 +61,9 @@ public:
...
@@ -56,7 +61,9 @@ public:
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
...
@@ -97,6 +104,7 @@ public:
...
@@ -97,6 +104,7 @@ public:
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -128,6 +136,7 @@ public:
...
@@ -128,6 +136,7 @@ public:
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
...
data/2.算法中阶/1.leetcode-数组/72.矩阵置零/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 矩阵置零
# 矩阵置零
<p>给定一个 <code><em>m</em> x <em>n</em></code> 的矩阵,如果一个元素为 <strong>0 </strong>,则将其所在行和列的所有元素都设为 <strong>0</strong> 。请使用 <strong><a href="http://baike.baidu.com/item/%E5%8E%9F%E5%9C%B0%E7%AE%97%E6%B3%95" target="_blank">原地</a></strong> 算法<strong>。</strong></p><p><strong>进阶:</strong></p><ul> <li>一个直观的解决方案是使用 <code>O(<em>m</em><em>n</em>)</code> 的额外空间,但这并不是一个好的解决方案。</li> <li>一个简单的改进方案是使用 <code>O(<em>m</em> + <em>n</em>)</code> 的额外空间,但这仍然不是最好的解决方案。</li> <li>你能想出一个仅使用常量空间的解决方案吗?</li></ul><p> </p><p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p><img alt="" src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/doocs/leetcode@main/solution/0000-0099/0073.Set%20Matrix%20Zeroes/images/mat1.jpg" style="width: 450px; height: 169px;" /><pre><strong>输入:</strong>matrix = [[1,1,1],[1,0,1],[1,1,1]]<strong><br />输出:</strong>[[1,0,1],[0,0,0],[1,0,1]]</pre><p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p><img alt="" src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/doocs/leetcode@main/solution/0000-0099/0073.Set%20Matrix%20Zeroes/images/mat2.jpg" style="width: 450px; height: 137px;" /><pre><strong>输入:</strong>matrix = [[0,1,2,0],[3,4,5,2],[1,3,1,5]]<strong><br />输出:</strong>[[0,0,0,0],[0,4,5,0],[0,3,1,0]]</pre><p> </p><p><strong>提示:</strong></p><ul> <li><code>m == matrix.length</code></li> <li><code>n == matrix[0].length</code></li> <li><code>1 <= m, n <= 200</code></li> <li><code>-2<sup>31</sup> <= matrix[i][j] <= 2<sup>31</sup> - 1</code></li></ul>
<p>给定一个 <code><em>m</em> x <em>n</em></code> 的矩阵,如果一个元素为 <strong>0 </strong>,则将其所在行和列的所有元素都设为 <strong>0</strong> 。请使用 <strong><a href="http://baike.baidu.com/item/%E5%8E%9F%E5%9C%B0%E7%AE%97%E6%B3%95" target="_blank">原地</a></strong> 算法<strong>。</strong></p><p><strong>进阶:</strong></p><ul> <li>一个直观的解决方案是使用 <code>O(<em>m</em><em>n</em>)</code> 的额外空间,但这并不是一个好的解决方案。</li> <li>一个简单的改进方案是使用 <code>O(<em>m</em> + <em>n</em>)</code> 的额外空间,但这仍然不是最好的解决方案。</li> <li>你能想出一个仅使用常量空间的解决方案吗?</li></ul><p> </p><p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p><img alt="" src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/doocs/leetcode@main/solution/0000-0099/0073.Set%20Matrix%20Zeroes/images/mat1.jpg" style="width: 450px; height: 169px;" /><pre><strong>输入:</strong>matrix = [[1,1,1],[1,0,1],[1,1,1]]<strong><br />输出:</strong>[[1,0,1],[0,0,0],[1,0,1]]</pre><p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p><img alt="" src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/doocs/leetcode@main/solution/0000-0099/0073.Set%20Matrix%20Zeroes/images/mat2.jpg" style="width: 450px; height: 137px;" /><pre><strong>输入:</strong>matrix = [[0,1,2,0],[3,4,5,2],[1,3,1,5]]<strong><br />输出:</strong>[[0,0,0,0],[0,4,5,0],[0,3,1,0]]</pre><p> </p><p><strong>提示:</strong></p><ul> <li><code>m == matrix.length</code></li> <li><code>n == matrix[0].length</code></li> <li><code>1 <= m, n <= 200</code></li> <li><code>-2<sup>31</sup> <= matrix[i][j] <= 2<sup>31</sup> - 1</code></li></ul>
<p>
以下错误的选项是?
</p>
<p>
以下错误的选项是?
</p>
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using
namespace
std
;
using
namespace
std
;
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -28,6 +32,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -28,6 +32,7 @@ int main()
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -69,7 +74,9 @@ public:
...
@@ -69,7 +74,9 @@ public:
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -140,6 +147,7 @@ public:
...
@@ -140,6 +147,7 @@ public:
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -185,6 +193,7 @@ public:
...
@@ -185,6 +193,7 @@ public:
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
...
data/2.算法中阶/1.leetcode-数组/73.搜索二维矩阵/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 搜索二维矩阵
# 搜索二维矩阵
<p>编写一个高效的算法来判断 <code>m x n</code> 矩阵中,是否存在一个目标值。该矩阵具有如下特性:</p><ul> <li>每行中的整数从左到右按升序排列。</li> <li>每行的第一个整数大于前一行的最后一个整数。</li></ul><p> </p><p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p><img alt="" src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/doocs/leetcode@main/solution/0000-0099/0074.Search%20a%202D%20Matrix/images/mat.jpg" style="width: 322px; height: 242px;" /><pre><strong>输入:</strong>matrix = [[1,3,5,7],[10,11,16,20],[23,30,34,60]], target = 3<strong><br />输出:</strong>true</pre><p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p><img alt="" src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/doocs/leetcode@main/solution/0000-0099/0074.Search%20a%202D%20Matrix/images/mat2.jpg" style="width: 322px; height: 242px;" /><pre><strong>输入:</strong>matrix = [[1,3,5,7],[10,11,16,20],[23,30,34,60]], target = 13<strong><br />输出:</strong>false</pre><p> </p><p><strong>提示:</strong></p><ul> <li><code>m == matrix.length</code></li> <li><code>n == matrix[i].length</code></li> <li><code>1 <= m, n <= 100</code></li> <li><code>-10<sup>4</sup> <= matrix[i][j], target <= 10<sup>4</sup></code></li></ul>
<p>编写一个高效的算法来判断 <code>m x n</code> 矩阵中,是否存在一个目标值。该矩阵具有如下特性:</p><ul> <li>每行中的整数从左到右按升序排列。</li> <li>每行的第一个整数大于前一行的最后一个整数。</li></ul><p> </p><p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p><img alt="" src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/doocs/leetcode@main/solution/0000-0099/0074.Search%20a%202D%20Matrix/images/mat.jpg" style="width: 322px; height: 242px;" /><pre><strong>输入:</strong>matrix = [[1,3,5,7],[10,11,16,20],[23,30,34,60]], target = 3<strong><br />输出:</strong>true</pre><p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p><img alt="" src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/doocs/leetcode@main/solution/0000-0099/0074.Search%20a%202D%20Matrix/images/mat2.jpg" style="width: 322px; height: 242px;" /><pre><strong>输入:</strong>matrix = [[1,3,5,7],[10,11,16,20],[23,30,34,60]], target = 13<strong><br />输出:</strong>false</pre><p> </p><p><strong>提示:</strong></p><ul> <li><code>m == matrix.length</code></li> <li><code>n == matrix[i].length</code></li> <li><code>1 <= m, n <= 100</code></li> <li><code>-10<sup>4</sup> <= matrix[i][j], target <= 10<sup>4</sup></code></li></ul>
<p>
以下错误的选项是?
</p>
<p>
以下错误的选项是?
</p>
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using
namespace
std
;
using
namespace
std
;
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -27,6 +31,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -27,6 +31,7 @@ int main()
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -64,7 +69,9 @@ public:
...
@@ -64,7 +69,9 @@ public:
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -117,6 +124,7 @@ public:
...
@@ -117,6 +124,7 @@ public:
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -148,6 +156,7 @@ public:
...
@@ -148,6 +156,7 @@ public:
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
...
data/2.算法中阶/1.leetcode-数组/77.子集/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 子集
# 子集
<p>
给你一个整数数组
<code>
nums
</code>
,数组中的元素
<strong>
互不相同
</strong>
。返回该数组所有可能的子集(幂集)。
</p><p>
解集
<strong>
不能
</strong>
包含重复的子集。你可以按
<strong>
任意顺序
</strong>
返回解集。
</p><p>
</p><p><strong>
示例 1:
</strong></p><pre><strong>
输入:
</strong>
nums = [1,2,3]
<strong><br
/>
输出:
</strong>
[[],[1],[2],[1,2],[3],[1,3],[2,3],[1,2,3]]
</pre><p><strong>
示例 2:
</strong></p><pre><strong>
输入:
</strong>
nums = [0]
<strong><br
/>
输出:
</strong>
[[],[0]]
</pre><p>
</p><p><strong>
提示:
</strong></p><ul>
<li><code>
1
<
=
nums.length
<=
10</
code
></li>
<li><code>
-10
<
=
nums
[
i
]
<=
10</
code
></li>
<li><code>
nums
</code>
中的所有元素
<strong>
互不相同
</strong></li></ul>
<p>
给你一个整数数组
<code>
nums
</code>
,数组中的元素
<strong>
互不相同
</strong>
。返回该数组所有可能的子集(幂集)。
</p><p>
解集
<strong>
不能
</strong>
包含重复的子集。你可以按
<strong>
任意顺序
</strong>
返回解集。
</p><p>
</p><p><strong>
示例 1:
</strong></p><pre><strong>
输入:
</strong>
nums = [1,2,3]
<strong><br
/>
输出:
</strong>
[[],[1],[2],[1,2],[3],[1,3],[2,3],[1,2,3]]
</pre><p><strong>
示例 2:
</strong></p><pre><strong>
输入:
</strong>
nums = [0]
<strong><br
/>
输出:
</strong>
[[],[0]]
</pre><p>
</p><p><strong>
提示:
</strong></p><ul>
<li><code>
1
<
=
nums.length
<=
10</
code
></li>
<li><code>
-10
<
=
nums
[
i
]
<=
10</
code
></li>
<li><code>
nums
</code>
中的所有元素
<strong>
互不相同
</strong></li></ul>
<p>
以下错误的选项是?
</p>
<p>
以下错误的选项是?
</p>
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using
namespace
std
;
using
namespace
std
;
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -27,6 +31,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -27,6 +31,7 @@ int main()
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -57,7 +62,9 @@ public:
...
@@ -57,7 +62,9 @@ public:
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -87,6 +94,7 @@ public:
...
@@ -87,6 +94,7 @@ public:
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -117,6 +125,7 @@ public:
...
@@ -117,6 +125,7 @@ public:
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
...
data/2.算法中阶/1.leetcode-数组/79.删除有序数组中的重复项 II/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 删除有序数组中的重复项 II
# 删除有序数组中的重复项 II
<p>
给你一个有序数组
<code>
nums
</code>
,请你
<strong>
<a href="http://baike.baidu.com/item/%E5%8E%9F%E5%9C%B0%E7%AE%97%E6%B3%95"
<p>
给你一个有序数组
<code>
nums
</code>
,请你
<strong>
<a href="http://baike.baidu.com/item/%E5%8E%9F%E5%9C%B0%E7%AE%97%E6%B3%95"
target="_blank"> 原地
</a></strong>
删除重复出现的元素,使每个元素
<strong>
最多出现两次
</strong>
,返回删除后数组的新长度。
</p>
target="_blank"> 原地
</a></strong>
删除重复出现的元素,使每个元素
<strong>
最多出现两次
</strong>
,返回删除后数组的新长度。
</p>
<p>
不要使用额外的数组空间,你必须在
<strong>
<a href="https://baike.baidu.com/item/%E5%8E%9F%E5%9C%B0%E7%AE%97%E6%B3%95"
<p>
不要使用额外的数组空间,你必须在
<strong>
<a href="https://baike.baidu.com/item/%E5%8E%9F%E5%9C%B0%E7%AE%97%E6%B3%95"
...
@@ -30,12 +31,15 @@
...
@@ -30,12 +31,15 @@
<p>
以下错误的选项是?
</p>
<p>
以下错误的选项是?
</p>
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using
namespace
std
;
using
namespace
std
;
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -52,6 +56,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -52,6 +56,7 @@ int main()
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -77,7 +82,9 @@ public:
...
@@ -77,7 +82,9 @@ public:
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -105,6 +112,7 @@ public:
...
@@ -105,6 +112,7 @@ public:
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -129,6 +137,7 @@ public:
...
@@ -129,6 +137,7 @@ public:
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
...
data/2.算法中阶/1.leetcode-数组/80.搜索旋转排序数组 II/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 搜索旋转排序数组 II
# 搜索旋转排序数组 II
<p>
已知存在一个按非降序排列的整数数组
<code>
nums
</code>
,数组中的值不必互不相同。
</p>
<p>
已知存在一个按非降序排列的整数数组
<code>
nums
</code>
,数组中的值不必互不相同。
</p>
<p>
在传递给函数之前,
<code>
nums
</code>
在预先未知的某个下标
<code>
k
</code>
(
<code>
0
<
=
k
<
nums.length
</
code
>
)上进行了
<strong>
旋转
<p>
在传递给函数之前,
<code>
nums
</code>
在预先未知的某个下标
<code>
k
</code>
(
<code>
0
<
=
k
<
nums.length
</
code
>
)上进行了
<strong>
旋转
</strong>
,使数组变为
<code>
[nums[k], nums[k+1], ..., nums[n-1], nums[0], nums[1], ..., nums[k-1]]
</code>
(下标
<strong>
从 0
</strong>
,使数组变为
<code>
[nums[k], nums[k+1], ..., nums[n-1], nums[0], nums[1], ..., nums[k-1]]
</code>
(下标
<strong>
从 0
...
@@ -32,12 +33,15 @@
...
@@ -32,12 +33,15 @@
<p>
以下错误的选项是?
</p>
<p>
以下错误的选项是?
</p>
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using
namespace
std
;
using
namespace
std
;
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -52,6 +56,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -52,6 +56,7 @@ int main()
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -104,7 +109,9 @@ public:
...
@@ -104,7 +109,9 @@ public:
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -152,6 +159,7 @@ public:
...
@@ -152,6 +159,7 @@ public:
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -219,6 +227,7 @@ public:
...
@@ -219,6 +227,7 @@ public:
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
...
data/2.算法中阶/2.leetcode-链表/1.两数相加/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 两数相加
# 两数相加
<p>给你两个 <strong>非空</strong> 的链表,表示两个非负的整数。它们每位数字都是按照 <strong>逆序</strong> 的方式存储的,并且每个节点只能存储 <strong>一位</strong> 数字。</p><p>请你将两个数相加,并以相同形式返回一个表示和的链表。</p><p>你可以假设除了数字 0 之外,这两个数都不会以 0 开头。</p><p> </p><p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p><img alt="" src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/doocs/leetcode@main/solution/0000-0099/0002.Add%20Two%20Numbers/images/addtwonumber1.jpg" style="width: 483px; height: 342px;" /><pre><strong>输入:</strong>l1 = [2,4,3], l2 = [5,6,4]<strong><br />输出:</strong>[7,0,8]<strong><br />解释:</strong>342 + 465 = 807.</pre><p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p><pre><strong>输入:</strong>l1 = [0], l2 = [0]<strong><br />输出:</strong>[0]</pre><p><strong>示例 3:</strong></p><pre><strong>输入:</strong>l1 = [9,9,9,9,9,9,9], l2 = [9,9,9,9]<strong><br />输出:</strong>[8,9,9,9,0,0,0,1]</pre><p> </p><p><strong>提示:</strong></p><ul> <li>每个链表中的节点数在范围 <code>[1, 100]</code> 内</li> <li><code>0 <= Node.val <= 9</code></li> <li>题目数据保证列表表示的数字不含前导零</li></ul>
<p>给你两个 <strong>非空</strong> 的链表,表示两个非负的整数。它们每位数字都是按照 <strong>逆序</strong> 的方式存储的,并且每个节点只能存储 <strong>一位</strong> 数字。</p><p>请你将两个数相加,并以相同形式返回一个表示和的链表。</p><p>你可以假设除了数字 0 之外,这两个数都不会以 0 开头。</p><p> </p><p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p><img alt="" src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/doocs/leetcode@main/solution/0000-0099/0002.Add%20Two%20Numbers/images/addtwonumber1.jpg" style="width: 483px; height: 342px;" /><pre><strong>输入:</strong>l1 = [2,4,3], l2 = [5,6,4]<strong><br />输出:</strong>[7,0,8]<strong><br />解释:</strong>342 + 465 = 807.</pre><p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p><pre><strong>输入:</strong>l1 = [0], l2 = [0]<strong><br />输出:</strong>[0]</pre><p><strong>示例 3:</strong></p><pre><strong>输入:</strong>l1 = [9,9,9,9,9,9,9], l2 = [9,9,9,9]<strong><br />输出:</strong>[8,9,9,9,0,0,0,1]</pre><p> </p><p><strong>提示:</strong></p><ul> <li>每个链表中的节点数在范围 <code>[1, 100]</code> 内</li> <li><code>0 <= Node.val <= 9</code></li> <li>题目数据保证列表表示的数字不含前导零</li></ul>
<p>
以下错误的选项是?
</p>
<p>
以下错误的选项是?
</p>
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <unordered_map>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <vector>
#include <vector>
...
@@ -21,6 +24,7 @@ struct ListNode
...
@@ -21,6 +24,7 @@ struct ListNode
};
};
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
...
@@ -61,6 +65,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -61,6 +65,7 @@ int main()
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -101,7 +106,9 @@ public:
...
@@ -101,7 +106,9 @@ public:
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -146,6 +153,7 @@ public:
...
@@ -146,6 +153,7 @@ public:
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -198,6 +206,7 @@ public:
...
@@ -198,6 +206,7 @@ public:
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
...
data/2.算法中阶/2.leetcode-链表/18.删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点
# 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点
<p>给你一个链表,删除链表的倒数第 <code>n</code><em> </em>个结点,并且返回链表的头结点。</p><p><strong>进阶:</strong>你能尝试使用一趟扫描实现吗?</p><p> </p><p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p><img alt="" src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/doocs/leetcode@main/solution/0000-0099/0019.Remove%20Nth%20Node%20From%20End%20of%20List/images/remove_ex1.jpg" style="width: 542px; height: 222px;" /><pre><strong>输入:</strong>head = [1,2,3,4,5], n = 2<strong><br />输出:</strong>[1,2,3,5]</pre><p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p><pre><strong>输入:</strong>head = [1], n = 1<strong><br />输出:</strong>[]</pre><p><strong>示例 3:</strong></p><pre><strong>输入:</strong>head = [1,2], n = 1<strong><br />输出:</strong>[1]</pre><p> </p><p><strong>提示:</strong></p><ul> <li>链表中结点的数目为 <code>sz</code></li> <li><code>1 <= sz <= 30</code></li> <li><code>0 <= Node.val <= 100</code></li> <li><code>1 <= n <= sz</code></li></ul>
<p>给你一个链表,删除链表的倒数第 <code>n</code><em> </em>个结点,并且返回链表的头结点。</p><p><strong>进阶:</strong>你能尝试使用一趟扫描实现吗?</p><p> </p><p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p><img alt="" src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/doocs/leetcode@main/solution/0000-0099/0019.Remove%20Nth%20Node%20From%20End%20of%20List/images/remove_ex1.jpg" style="width: 542px; height: 222px;" /><pre><strong>输入:</strong>head = [1,2,3,4,5], n = 2<strong><br />输出:</strong>[1,2,3,5]</pre><p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p><pre><strong>输入:</strong>head = [1], n = 1<strong><br />输出:</strong>[]</pre><p><strong>示例 3:</strong></p><pre><strong>输入:</strong>head = [1,2], n = 1<strong><br />输出:</strong>[1]</pre><p> </p><p><strong>提示:</strong></p><ul> <li>链表中结点的数目为 <code>sz</code></li> <li><code>1 <= sz <= 30</code></li> <li><code>0 <= Node.val <= 100</code></li> <li><code>1 <= n <= sz</code></li></ul>
<p>
以下错误的选项是?
</p>
<p>
以下错误的选项是?
</p>
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using
namespace
std
;
using
namespace
std
;
...
@@ -18,6 +21,7 @@ struct ListNode
...
@@ -18,6 +21,7 @@ struct ListNode
};
};
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -53,6 +57,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -53,6 +57,7 @@ int main()
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
...
@@ -92,7 +97,9 @@ public:
...
@@ -92,7 +97,9 @@ public:
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -128,6 +135,7 @@ public:
...
@@ -128,6 +135,7 @@ public:
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -156,6 +164,7 @@ public:
...
@@ -156,6 +164,7 @@ public:
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
...
data/2.算法中阶/2.leetcode-链表/20.合并两个有序链表/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 合并两个有序链表
# 合并两个有序链表
<p>将两个升序链表合并为一个新的 <strong>升序</strong> 链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。 </p><p> </p><p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p><img alt="" src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/doocs/leetcode@main/solution/0000-0099/0021.Merge%20Two%20Sorted%20Lists/images/merge_ex1.jpg" style="width: 662px; height: 302px;" /><pre><strong>输入:</strong>l1 = [1,2,4], l2 = [1,3,4]<strong><br />输出:</strong>[1,1,2,3,4,4]</pre><p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p><pre><strong>输入:</strong>l1 = [], l2 = []<strong><br />输出:</strong>[]</pre><p><strong>示例 3:</strong></p><pre><strong>输入:</strong>l1 = [], l2 = [0]<strong><br />输出:</strong>[0]</pre><p> </p><p><strong>提示:</strong></p><ul> <li>两个链表的节点数目范围是 <code>[0, 50]</code></li> <li><code>-100 <= Node.val <= 100</code></li> <li><code>l1</code> 和 <code>l2</code> 均按 <strong>非递减顺序</strong> 排列</li></ul>
<p>将两个升序链表合并为一个新的 <strong>升序</strong> 链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。 </p><p> </p><p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p><img alt="" src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/doocs/leetcode@main/solution/0000-0099/0021.Merge%20Two%20Sorted%20Lists/images/merge_ex1.jpg" style="width: 662px; height: 302px;" /><pre><strong>输入:</strong>l1 = [1,2,4], l2 = [1,3,4]<strong><br />输出:</strong>[1,1,2,3,4,4]</pre><p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p><pre><strong>输入:</strong>l1 = [], l2 = []<strong><br />输出:</strong>[]</pre><p><strong>示例 3:</strong></p><pre><strong>输入:</strong>l1 = [], l2 = [0]<strong><br />输出:</strong>[0]</pre><p> </p><p><strong>提示:</strong></p><ul> <li>两个链表的节点数目范围是 <code>[0, 50]</code></li> <li><code>-100 <= Node.val <= 100</code></li> <li><code>l1</code> 和 <code>l2</code> 均按 <strong>非递减顺序</strong> 排列</li></ul>
<p>
以下错误的选项是?
</p>
<p>
以下错误的选项是?
</p>
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using
namespace
std
;
using
namespace
std
;
...
@@ -18,6 +21,7 @@ struct ListNode
...
@@ -18,6 +21,7 @@ struct ListNode
};
};
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -57,6 +61,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -57,6 +61,7 @@ int main()
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -82,7 +87,9 @@ public:
...
@@ -82,7 +87,9 @@ public:
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -134,6 +141,7 @@ public:
...
@@ -134,6 +141,7 @@ public:
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -179,6 +187,7 @@ public:
...
@@ -179,6 +187,7 @@ public:
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
...
data/2.算法中阶/2.leetcode-链表/22.合并K个升序链表/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 合并K个升序链表
# 合并K个升序链表
<p>
给你一个链表数组,每个链表都已经按升序排列。
</p><p>
请你将所有链表合并到一个升序链表中,返回合并后的链表。
</p><p>
</p><p><strong>
示例 1:
</strong></p><pre><strong>
输入:
</strong>
lists =
[
[1,4,5],[1,3,4],[2,6]]<strong><br />输出:</strong>[1,1,2,3,4,4,5,6]<strong><br />解释:</strong>链表数组如下:[ 1->4->5, 1->3->4, 2->6]将它们合并到一个有序链表中得到。1->1->2->3->4->4->5->6</pre><p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p><pre><strong>输入:</strong>lists = []<strong><br />输出:</strong>[]</pre><p><strong>示例 3:</strong></p><pre><strong>输入:</strong>lists = [[]]<strong><br />输出:</strong>[]</pre><p> </p><p><strong>提示:</strong></p><ul> <li><code>k == lists.length</code></li> <li><code>0 <= k <= 10^4</code></li> <li><code>0 <= lists[i].length <= 500</code></li> <li><code>-10^4 <= lists[i
][
j
]
<
= 10^4
</code></li>
<li><code>
lists[i]
</code>
按
<strong>
升序
</strong>
排列
</li>
<li><code>
lists[i].length
</code>
的总和不超过
<code>
10^4
</code></li></ul>
<p>
给你一个链表数组,每个链表都已经按升序排列。
</p><p>
请你将所有链表合并到一个升序链表中,返回合并后的链表。
</p><p>
</p><p><strong>
示例 1:
</strong></p><pre><strong>
输入:
</strong>
lists =
[
[1,4,5],[1,3,4],[2,6]]<strong><br />输出:</strong>[1,1,2,3,4,4,5,6]<strong><br />解释:</strong>链表数组如下:[ 1->4->5, 1->3->4, 2->6]将它们合并到一个有序链表中得到。1->1->2->3->4->4->5->6</pre><p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p><pre><strong>输入:</strong>lists = []<strong><br />输出:</strong>[]</pre><p><strong>示例 3:</strong></p><pre><strong>输入:</strong>lists = [[]]<strong><br />输出:</strong>[]</pre><p> </p><p><strong>提示:</strong></p><ul> <li><code>k == lists.length</code></li> <li><code>0 <= k <= 10^4</code></li> <li><code>0 <= lists[i].length <= 500</code></li> <li><code>-10^4 <= lists[i
][
j
]
<
= 10^4
</code></li>
<li><code>
lists[i]
</code>
按
<strong>
升序
</strong>
排列
</li>
<li><code>
lists[i].length
</code>
的总和不超过
<code>
10^4
</code></li></ul>
<p>
以下错误的选项是?
</p>
<p>
以下错误的选项是?
</p>
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using
namespace
std
;
using
namespace
std
;
...
@@ -18,6 +21,7 @@ struct ListNode
...
@@ -18,6 +21,7 @@ struct ListNode
};
};
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
int
main
()
int
main
()
{
{
...
@@ -66,6 +70,7 @@ int main()
...
@@ -66,6 +70,7 @@ int main()
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
struct
cmp
struct
cmp
{
{
...
@@ -106,7 +111,9 @@ public:
...
@@ -106,7 +111,9 @@ public:
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -158,6 +165,7 @@ public:
...
@@ -158,6 +165,7 @@ public:
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -203,6 +211,7 @@ public:
...
@@ -203,6 +211,7 @@ public:
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
...
data/2.算法中阶/2.leetcode-链表/23.两两交换链表中的节点/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 两两交换链表中的节点
# 两两交换链表中的节点
<p>给定一个链表,两两交换其中相邻的节点,并返回交换后的链表。</p><p><strong>你不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值</strong>,而是需要实际的进行节点交换。</p><p> </p><p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p><img alt="" src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/doocs/leetcode@main/solution/0000-0099/0024.Swap%20Nodes%20in%20Pairs/images/swap_ex1.jpg" style="width: 422px; height: 222px;" /><pre><strong>输入:</strong>head = [1,2,3,4]<strong><br />输出:</strong>[2,1,4,3]</pre><p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p><pre><strong>输入:</strong>head = []<strong><br />输出:</strong>[]</pre><p><strong>示例 3:</strong></p><pre><strong>输入:</strong>head = [1]<strong><br />输出:</strong>[1]</pre><p> </p><p><strong>提示:</strong></p><ul> <li>链表中节点的数目在范围 <code>[0, 100]</code> 内</li> <li><code>0 <= Node.val <= 100</code></li></ul><p> </p><p><strong>进阶:</strong>你能在不修改链表节点值的情况下解决这个问题吗?(也就是说,仅修改节点本身。)</p>
<p>给定一个链表,两两交换其中相邻的节点,并返回交换后的链表。</p><p><strong>你不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值</strong>,而是需要实际的进行节点交换。</p><p> </p><p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p><img alt="" src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/doocs/leetcode@main/solution/0000-0099/0024.Swap%20Nodes%20in%20Pairs/images/swap_ex1.jpg" style="width: 422px; height: 222px;" /><pre><strong>输入:</strong>head = [1,2,3,4]<strong><br />输出:</strong>[2,1,4,3]</pre><p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p><pre><strong>输入:</strong>head = []<strong><br />输出:</strong>[]</pre><p><strong>示例 3:</strong></p><pre><strong>输入:</strong>head = [1]<strong><br />输出:</strong>[1]</pre><p> </p><p><strong>提示:</strong></p><ul> <li>链表中节点的数目在范围 <code>[0, 100]</code> 内</li> <li><code>0 <= Node.val <= 100</code></li></ul><p> </p><p><strong>进阶:</strong>你能在不修改链表节点值的情况下解决这个问题吗?(也就是说,仅修改节点本身。)</p>
<p>
以下错误的选项是?
</p>
<p>
以下错误的选项是?
</p>
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using
namespace
std
;
using
namespace
std
;
...
@@ -18,11 +21,13 @@ struct ListNode
...
@@ -18,11 +21,13 @@ struct ListNode
};
};
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -54,7 +59,9 @@ public:
...
@@ -54,7 +59,9 @@ public:
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
...
@@ -90,6 +97,7 @@ public:
...
@@ -90,6 +97,7 @@ public:
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
{
class
Solution
{
public:
public:
...
@@ -106,6 +114,7 @@ public:
...
@@ -106,6 +114,7 @@ public:
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
...
data/2.算法中阶/2.leetcode-链表/24.K 个一组翻转链表/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# K 个一组翻转链表
# K 个一组翻转链表
<p>给你一个链表,每 <em>k </em>个节点一组进行翻转,请你返回翻转后的链表。</p><p><em>k </em>是一个正整数,它的值小于或等于链表的长度。</p><p>如果节点总数不是 <em>k </em>的整数倍,那么请将最后剩余的节点保持原有顺序。</p><p><strong>进阶:</strong></p><ul> <li>你可以设计一个只使用常数额外空间的算法来解决此问题吗?</li> <li><strong>你不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值</strong>,而是需要实际进行节点交换。</li></ul><p> </p><p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p><img alt="" src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/doocs/leetcode@main/solution/0000-0099/0025.Reverse%20Nodes%20in%20k-Group/images/reverse_ex1.jpg" style="width: 542px; height: 222px;" /><pre><strong>输入:</strong>head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2<strong><br />输出:</strong>[2,1,4,3,5]</pre><p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p><img alt="" src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/doocs/leetcode@main/solution/0000-0099/0025.Reverse%20Nodes%20in%20k-Group/images/reverse_ex2.jpg" style="width: 542px; height: 222px;" /><pre><strong>输入:</strong>head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 3<strong><br />输出:</strong>[3,2,1,4,5]</pre><p><strong>示例 3:</strong></p><pre><strong>输入:</strong>head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 1<strong><br />输出:</strong>[1,2,3,4,5]</pre><p><strong>示例 4:</strong></p><pre><strong>输入:</strong>head = [1], k = 1<strong><br />输出:</strong>[1]</pre><ul></ul><p><strong>提示:</strong></p><ul> <li>列表中节点的数量在范围 <code>sz</code> 内</li> <li><code>1 <= sz <= 5000</code></li> <li><code>0 <= Node.val <= 1000</code></li> <li><code>1 <= k <= sz</code></li></ul>
<p>给你一个链表,每 <em>k </em>个节点一组进行翻转,请你返回翻转后的链表。</p><p><em>k </em>是一个正整数,它的值小于或等于链表的长度。</p><p>如果节点总数不是 <em>k </em>的整数倍,那么请将最后剩余的节点保持原有顺序。</p><p><strong>进阶:</strong></p><ul> <li>你可以设计一个只使用常数额外空间的算法来解决此问题吗?</li> <li><strong>你不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值</strong>,而是需要实际进行节点交换。</li></ul><p> </p><p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p><img alt="" src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/doocs/leetcode@main/solution/0000-0099/0025.Reverse%20Nodes%20in%20k-Group/images/reverse_ex1.jpg" style="width: 542px; height: 222px;" /><pre><strong>输入:</strong>head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2<strong><br />输出:</strong>[2,1,4,3,5]</pre><p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p><img alt="" src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/doocs/leetcode@main/solution/0000-0099/0025.Reverse%20Nodes%20in%20k-Group/images/reverse_ex2.jpg" style="width: 542px; height: 222px;" /><pre><strong>输入:</strong>head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 3<strong><br />输出:</strong>[3,2,1,4,5]</pre><p><strong>示例 3:</strong></p><pre><strong>输入:</strong>head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 1<strong><br />输出:</strong>[1,2,3,4,5]</pre><p><strong>示例 4:</strong></p><pre><strong>输入:</strong>head = [1], k = 1<strong><br />输出:</strong>[1]</pre><ul></ul><p><strong>提示:</strong></p><ul> <li>列表中节点的数量在范围 <code>sz</code> 内</li> <li><code>1 <= sz <= 5000</code></li> <li><code>0 <= Node.val <= 1000</code></li> <li><code>1 <= k <= sz</code></li></ul>
<p>
以下错误的选项是?
</p>
<p>
以下错误的选项是?
</p>
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
struct
ListNode
struct
ListNode
{
{
...
@@ -15,11 +18,13 @@ struct ListNode
...
@@ -15,11 +18,13 @@ struct ListNode
};
};
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -89,7 +94,9 @@ public:
...
@@ -89,7 +94,9 @@ public:
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -151,6 +158,7 @@ public:
...
@@ -151,6 +158,7 @@ public:
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -193,6 +201,7 @@ public:
...
@@ -193,6 +201,7 @@ public:
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
...
data/2.算法中阶/2.leetcode-链表/81.删除排序链表中的重复元素 II/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 删除排序链表中的重复元素 II
# 删除排序链表中的重复元素 II
<p>存在一个按升序排列的链表,给你这个链表的头节点 <code>head</code> ,请你删除链表中所有存在数字重复情况的节点,只保留原始链表中 <strong>没有重复出现</strong><em> </em>的数字。</p><p>返回同样按升序排列的结果链表。</p><p> </p><p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p><img alt="" src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/doocs/leetcode@main/solution/0000-0099/0082.Remove%20Duplicates%20from%20Sorted%20List%20II/images/linkedlist1.jpg" style="width: 500px; height: 142px;" /><pre><strong>输入:</strong>head = [1,2,3,3,4,4,5]<strong><br />输出:</strong>[1,2,5]</pre><p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p><img alt="" src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/doocs/leetcode@main/solution/0000-0099/0082.Remove%20Duplicates%20from%20Sorted%20List%20II/images/linkedlist2.jpg" style="width: 500px; height: 205px;" /><pre><strong>输入:</strong>head = [1,1,1,2,3]<strong><br />输出:</strong>[2,3]</pre><p> </p><p><strong>提示:</strong></p><ul> <li>链表中节点数目在范围 <code>[0, 300]</code> 内</li> <li><code>-100 <= Node.val <= 100</code></li> <li>题目数据保证链表已经按升序排列</li></ul>
<p>存在一个按升序排列的链表,给你这个链表的头节点 <code>head</code> ,请你删除链表中所有存在数字重复情况的节点,只保留原始链表中 <strong>没有重复出现</strong><em> </em>的数字。</p><p>返回同样按升序排列的结果链表。</p><p> </p><p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p><img alt="" src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/doocs/leetcode@main/solution/0000-0099/0082.Remove%20Duplicates%20from%20Sorted%20List%20II/images/linkedlist1.jpg" style="width: 500px; height: 142px;" /><pre><strong>输入:</strong>head = [1,2,3,3,4,4,5]<strong><br />输出:</strong>[1,2,5]</pre><p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p><img alt="" src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/doocs/leetcode@main/solution/0000-0099/0082.Remove%20Duplicates%20from%20Sorted%20List%20II/images/linkedlist2.jpg" style="width: 500px; height: 205px;" /><pre><strong>输入:</strong>head = [1,1,1,2,3]<strong><br />输出:</strong>[2,3]</pre><p> </p><p><strong>提示:</strong></p><ul> <li>链表中节点数目在范围 <code>[0, 300]</code> 内</li> <li><code>-100 <= Node.val <= 100</code></li> <li>题目数据保证链表已经按升序排列</li></ul>
<p>
以下错误的选项是?
</p>
<p>
以下错误的选项是?
</p>
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using
namespace
std
;
using
namespace
std
;
...
@@ -16,11 +19,13 @@ struct ListNode
...
@@ -16,11 +19,13 @@ struct ListNode
};
};
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -53,7 +58,9 @@ public:
...
@@ -53,7 +58,9 @@ public:
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -78,6 +85,7 @@ public:
...
@@ -78,6 +85,7 @@ public:
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -118,6 +126,7 @@ public:
...
@@ -118,6 +126,7 @@ public:
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
...
data/2.算法中阶/2.leetcode-链表/82.删除排序链表中的重复元素/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
# 删除排序链表中的重复元素
# 删除排序链表中的重复元素
<p>存在一个按升序排列的链表,给你这个链表的头节点 <code>head</code> ,请你删除所有重复的元素,使每个元素 <strong>只出现一次</strong> 。</p><p>返回同样按升序排列的结果链表。</p><p> </p><p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p><img alt="" src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/doocs/leetcode@main/solution/0000-0099/0083.Remove%20Duplicates%20from%20Sorted%20List/images/list1.jpg" style="width: 302px; height: 242px;" /><pre><strong>输入:</strong>head = [1,1,2]<strong><br />输出:</strong>[1,2]</pre><p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p><img alt="" src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/doocs/leetcode@main/solution/0000-0099/0083.Remove%20Duplicates%20from%20Sorted%20List/images/list2.jpg" style="width: 542px; height: 222px;" /><pre><strong>输入:</strong>head = [1,1,2,3,3]<strong><br />输出:</strong>[1,2,3]</pre><p> </p><p><strong>提示:</strong></p><ul> <li>链表中节点数目在范围 <code>[0, 300]</code> 内</li> <li><code>-100 <= Node.val <= 100</code></li> <li>题目数据保证链表已经按升序排列</li></ul>
<p>存在一个按升序排列的链表,给你这个链表的头节点 <code>head</code> ,请你删除所有重复的元素,使每个元素 <strong>只出现一次</strong> 。</p><p>返回同样按升序排列的结果链表。</p><p> </p><p><strong>示例 1:</strong></p><img alt="" src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/doocs/leetcode@main/solution/0000-0099/0083.Remove%20Duplicates%20from%20Sorted%20List/images/list1.jpg" style="width: 302px; height: 242px;" /><pre><strong>输入:</strong>head = [1,1,2]<strong><br />输出:</strong>[1,2]</pre><p><strong>示例 2:</strong></p><img alt="" src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/doocs/leetcode@main/solution/0000-0099/0083.Remove%20Duplicates%20from%20Sorted%20List/images/list2.jpg" style="width: 542px; height: 222px;" /><pre><strong>输入:</strong>head = [1,1,2,3,3]<strong><br />输出:</strong>[1,2,3]</pre><p> </p><p><strong>提示:</strong></p><ul> <li>链表中节点数目在范围 <code>[0, 300]</code> 内</li> <li><code>-100 <= Node.val <= 100</code></li> <li>题目数据保证链表已经按升序排列</li></ul>
<p>
以下错误的选项是?
</p>
<p>
以下错误的选项是?
</p>
## aop
## aop
### before
### before
```
cpp
```
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using
namespace
std
;
using
namespace
std
;
...
@@ -16,11 +19,13 @@ struct ListNode
...
@@ -16,11 +19,13 @@ struct ListNode
};
};
```
```
### after
### after
```
cpp
```
cpp
```
```
## 答案
## 答案
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -38,7 +43,9 @@ public:
...
@@ -38,7 +43,9 @@ public:
```
```
## 选项
## 选项
### A
### A
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -73,6 +80,7 @@ public:
...
@@ -73,6 +80,7 @@ public:
```
```
### B
### B
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
@@ -96,6 +104,7 @@ public:
...
@@ -96,6 +104,7 @@ public:
```
```
### C
### C
```
cpp
```
cpp
class
Solution
class
Solution
{
{
...
...
data/2.算法中阶/2.leetcode-链表/85.分隔链表/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/2.算法中阶/2.leetcode-链表/91.反转链表 II/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/2.算法中阶/3.leetcode-字符串/13.最长公共前缀/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/2.算法中阶/3.leetcode-字符串/2.无重复字符的最长子串/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/2.算法中阶/3.leetcode-字符串/27.实现 strStr()/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/2.算法中阶/3.leetcode-字符串/37.外观数列/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/2.算法中阶/3.leetcode-字符串/42.字符串相乘/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/2.算法中阶/3.leetcode-字符串/5.Z 字形变换/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/2.算法中阶/3.leetcode-字符串/57.最后一个单词的长度/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/2.算法中阶/3.leetcode-字符串/64.有效数字/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/2.算法中阶/3.leetcode-字符串/7.字符串转换整数 (atoi)/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/2.算法中阶/3.leetcode-字符串/92.复原 IP 地址/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/2.算法中阶/3.leetcode-字符串/96.交错字符串/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/2.算法中阶/4.leetcode-栈与队列/149.逆波兰表达式求值/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/2.算法中阶/4.leetcode-栈与队列/154.最小栈/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/2.算法中阶/4.leetcode-栈与队列/19.有效的括号/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/2.算法中阶/4.leetcode-栈与队列/217.天际线问题/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/2.算法中阶/4.leetcode-栈与队列/223.基本计算器/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/2.算法中阶/4.leetcode-栈与队列/226.基本计算器 II/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/2.算法中阶/4.leetcode-栈与队列/31.最长有效括号/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/2.算法中阶/4.leetcode-栈与队列/41.接雨水/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/2.算法中阶/4.leetcode-栈与队列/70.简化路径/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/2.算法中阶/4.leetcode-栈与队列/83.柱状图中最大的矩形/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/2.算法中阶/5.leetcode-排序算法/163.最大间距/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/2.算法中阶/5.leetcode-排序算法/273.H 指数/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/2.算法中阶/5.leetcode-排序算法/314.计算右侧小于当前元素的个数/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/2.算法中阶/5.leetcode-排序算法/323.摆动排序 II/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/2.算法中阶/5.leetcode-排序算法/326.区间和的个数/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/2.算法中阶/5.leetcode-排序算法/346.前 K 个高频元素/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/2.算法中阶/5.leetcode-排序算法/353.俄罗斯套娃信封问题/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/2.算法中阶/5.leetcode-排序算法/377.有序矩阵中第 K 小的元素/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/2.算法中阶/5.leetcode-排序算法/492.翻转对/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/2.算法中阶/5.leetcode-排序算法/911.排序数组/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/2.算法中阶/6.leetcode-双指针/10.盛最多水的容器/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/2.算法中阶/6.leetcode-双指针/140.环形链表/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/2.算法中阶/6.leetcode-双指针/141.环形链表 II/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/2.算法中阶/6.leetcode-双指针/15.最接近的三数之和/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/2.算法中阶/6.leetcode-双指针/25.删除有序数组中的重复项/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/2.算法中阶/6.leetcode-双指针/26.移除元素/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/2.算法中阶/6.leetcode-双指针/30.下一个排列/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/2.算法中阶/6.leetcode-双指针/60.旋转链表/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/2.算法中阶/6.leetcode-双指针/74.颜色分类/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/2.算法中阶/6.leetcode-双指针/87.合并两个有序数组/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/3.算法高阶/1.leetcode-树/123.二叉树中的最大路径和/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/3.算法高阶/1.leetcode-树/93.二叉树的中序遍历/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/3.算法高阶/1.leetcode-树/94.不同的二叉搜索树 II/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/3.算法高阶/1.leetcode-树/95.不同的二叉搜索树/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/3.算法高阶/1.leetcode-树/97.验证二叉搜索树/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/3.算法高阶/1.leetcode-树/98.恢复二叉搜索树/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/3.算法高阶/1.leetcode-树/99.相同的树/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/3.算法高阶/2.leetcode-哈希表/204.同构字符串/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/3.算法高阶/2.leetcode-哈希表/29.串联所有单词的子串/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/3.算法高阶/2.leetcode-哈希表/35.有效的数独/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/3.算法高阶/2.leetcode-哈希表/40.缺失的第一个正数/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/3.算法高阶/2.leetcode-哈希表/48.字母异位词分组/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/3.算法高阶/2.leetcode-哈希表/75.最小覆盖子串/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/3.算法高阶/3.leetcode-图与搜索/132.克隆图/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/3.算法高阶/3.leetcode-图与搜索/206.课程表/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/3.算法高阶/3.leetcode-图与搜索/209.课程表 II/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/3.算法高阶/3.leetcode-图与搜索/328.矩阵中的最长递增路径/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/3.算法高阶/3.leetcode-图与搜索/331.重新安排行程/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/3.算法高阶/3.leetcode-图与搜索/76.组合/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/3.算法高阶/3.leetcode-图与搜索/78.单词搜索/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/3.算法高阶/4.leetcode-数学/11.整数转罗马数字/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/3.算法高阶/4.leetcode-数学/12.罗马数字转整数/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/3.算法高阶/4.leetcode-数学/28.两数相除/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/3.算法高阶/4.leetcode-数学/49.Pow(x, n)/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/3.算法高阶/4.leetcode-数学/59.排列序列/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/3.算法高阶/4.leetcode-数学/6.整数反转/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/3.算法高阶/4.leetcode-数学/65.加一/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/3.算法高阶/4.leetcode-数学/66.二进制求和/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/3.算法高阶/4.leetcode-数学/68.x 的平方根/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/3.算法高阶/4.leetcode-数学/8.回文数/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/3.算法高阶/5.leetcode-设计/145.LRU 缓存机制/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/3.算法高阶/5.leetcode-设计/354.设计推特/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/3.算法高阶/5.leetcode-设计/379.O(1) 时间插入、删除和获取随机元素/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/3.算法高阶/5.leetcode-设计/380.O(1) 时间插入、删除和获取随机元素 - 允许重复/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/3.算法高阶/5.leetcode-设计/459.LFU 缓存/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/3.算法高阶/6.leetcode-动态规划/21.括号生成/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/3.算法高阶/6.leetcode-动态规划/4.最长回文子串/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/3.算法高阶/6.leetcode-动态规划/43.通配符匹配/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/3.算法高阶/6.leetcode-动态规划/52.最大子序和/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/3.算法高阶/6.leetcode-动态规划/61.不同路径/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/3.算法高阶/6.leetcode-动态规划/62.不同路径 II/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/3.算法高阶/6.leetcode-动态规划/63.最小路径和/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/3.算法高阶/6.leetcode-动态规划/69.爬楼梯/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/3.算法高阶/6.leetcode-动态规划/71.编辑距离/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/3.算法高阶/6.leetcode-动态规划/84.最大矩形/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/3.算法高阶/6.leetcode-动态规划/86.扰乱字符串/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/3.算法高阶/6.leetcode-动态规划/9.正则表达式匹配/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/3.算法高阶/6.leetcode-动态规划/90.解码方法/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/3.算法高阶/7.leetcode-回溯算法/16.电话号码的字母组合/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/3.算法高阶/7.leetcode-回溯算法/36.解数独/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/3.算法高阶/7.leetcode-回溯算法/38.组合总和/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/3.算法高阶/7.leetcode-回溯算法/39.组合总和 II/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/3.算法高阶/7.leetcode-回溯算法/45.全排列/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/3.算法高阶/7.leetcode-回溯算法/46.全排列 II/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/3.算法高阶/7.leetcode-回溯算法/50.N 皇后/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/3.算法高阶/7.leetcode-回溯算法/51.N皇后 II/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/3.算法高阶/7.leetcode-回溯算法/88.格雷编码/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/3.算法高阶/7.leetcode-回溯算法/89.子集 II/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/3.算法高阶/8.leetcode-贪心/121.买卖股票的最佳时机 II/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/3.算法高阶/8.leetcode-贪心/133.加油站/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/3.算法高阶/8.leetcode-贪心/134.分发糖果/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/3.算法高阶/8.leetcode-贪心/44.跳跃游戏 II/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/3.算法高阶/8.leetcode-贪心/54.跳跃游戏/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
data/3.算法高阶/8.leetcode-贪心/67.文本左右对齐/solution.md
浏览文件 @
ceaae444
此差异已折叠。
点击以展开。
编辑
预览
Markdown
is supported
0%
请重试
或
添加新附件
.
添加附件
取消
You are about to add
0
people
to the discussion. Proceed with caution.
先完成此消息的编辑!
取消
想要评论请
注册
或
登录