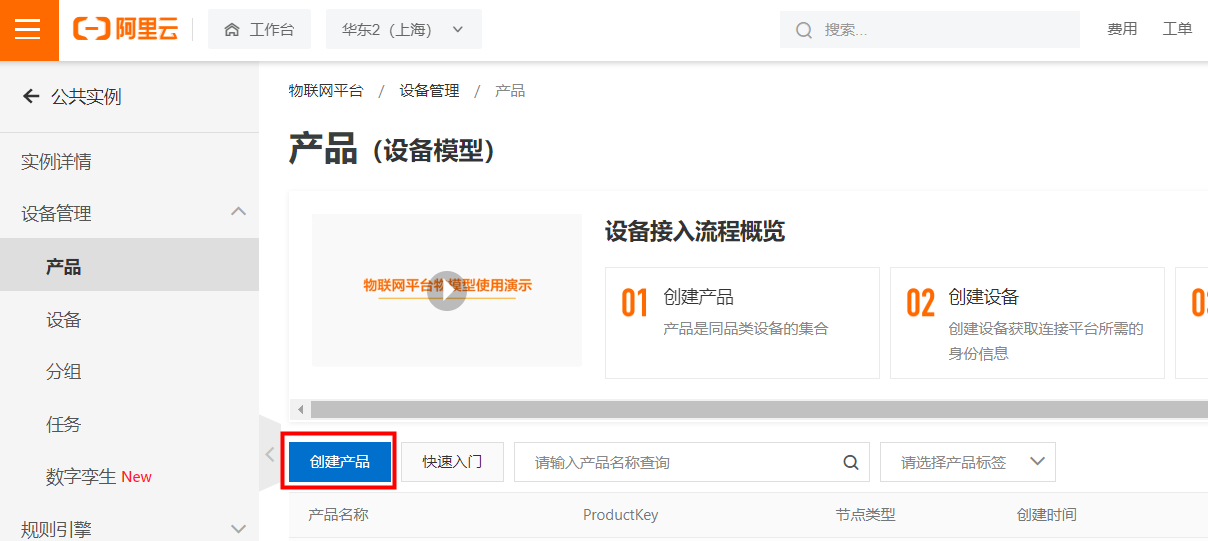
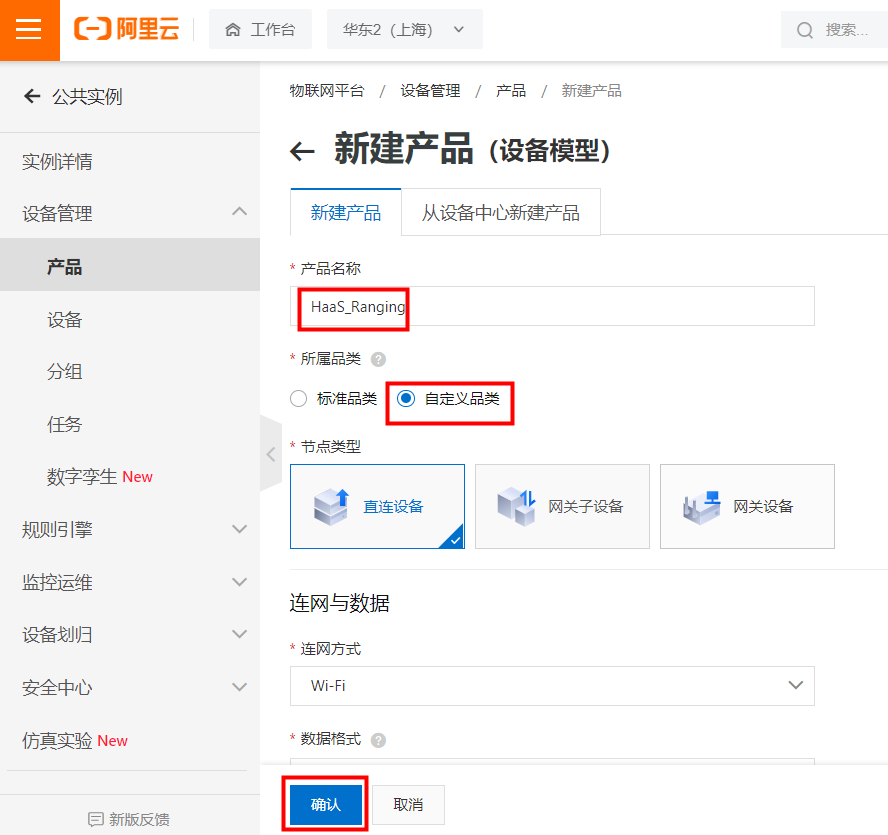
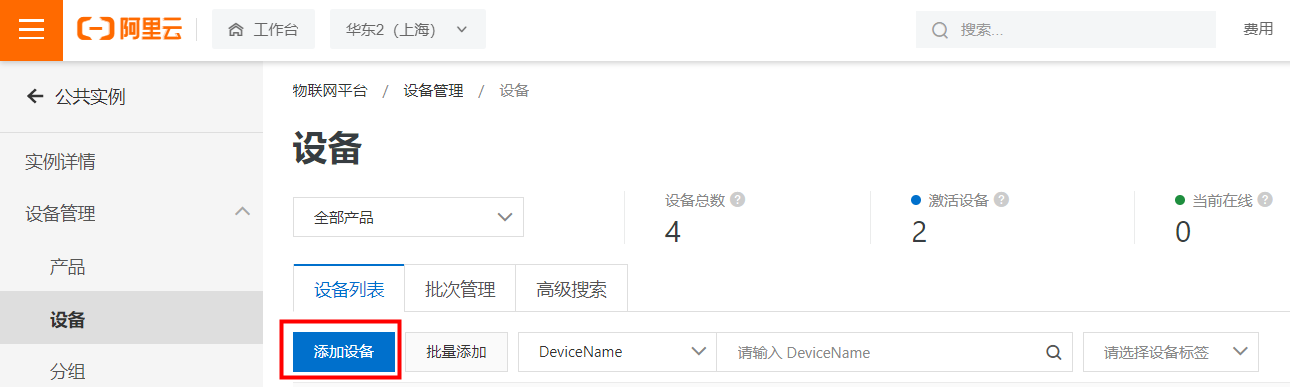
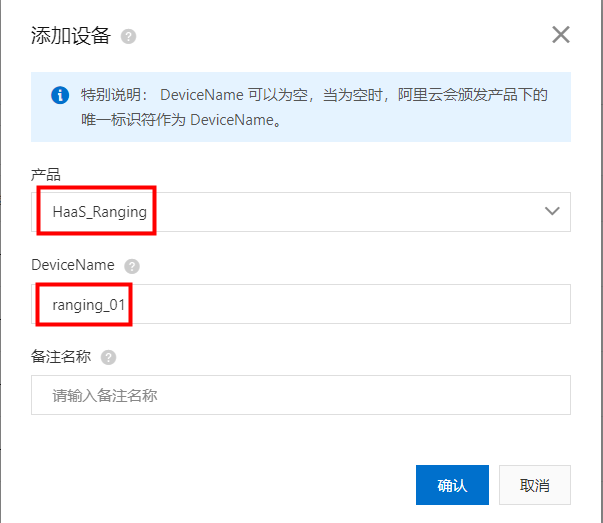
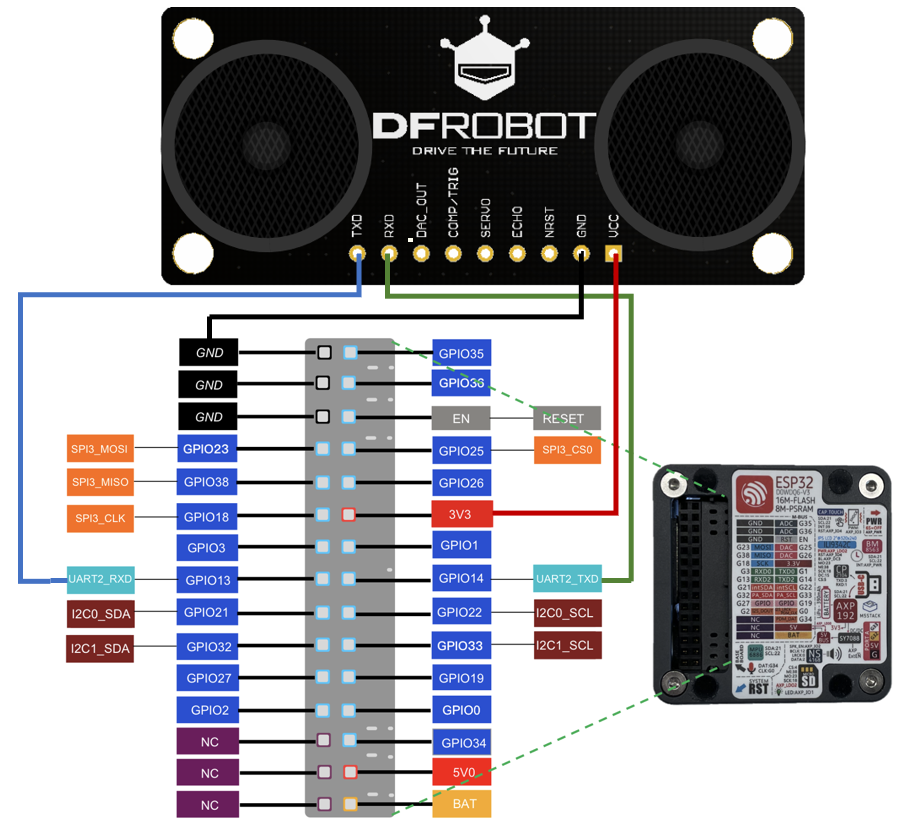
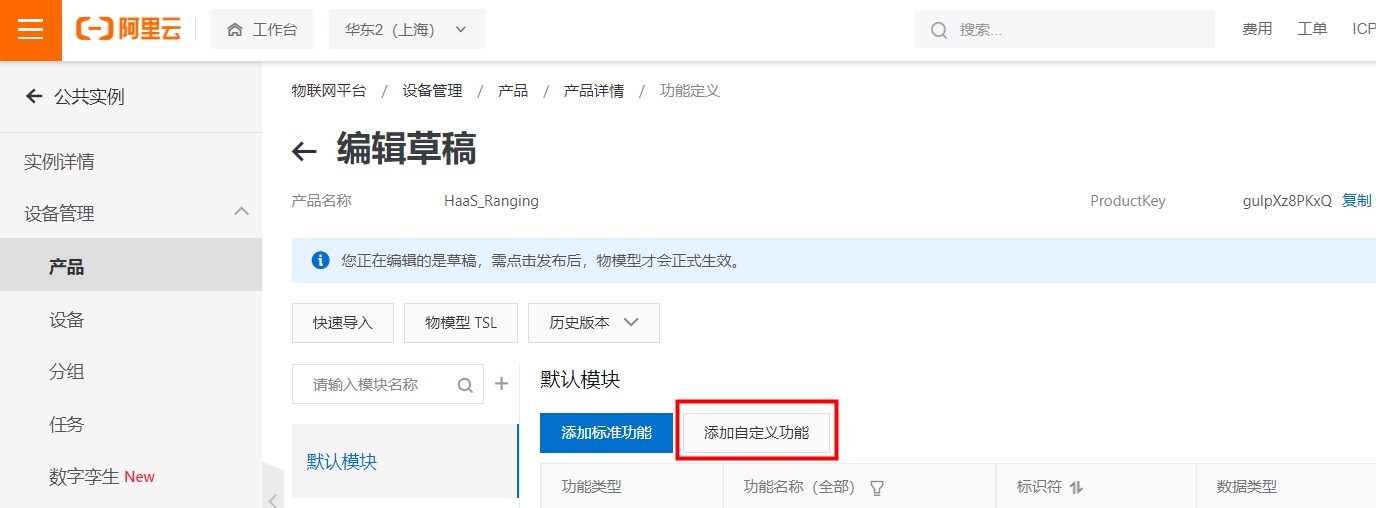
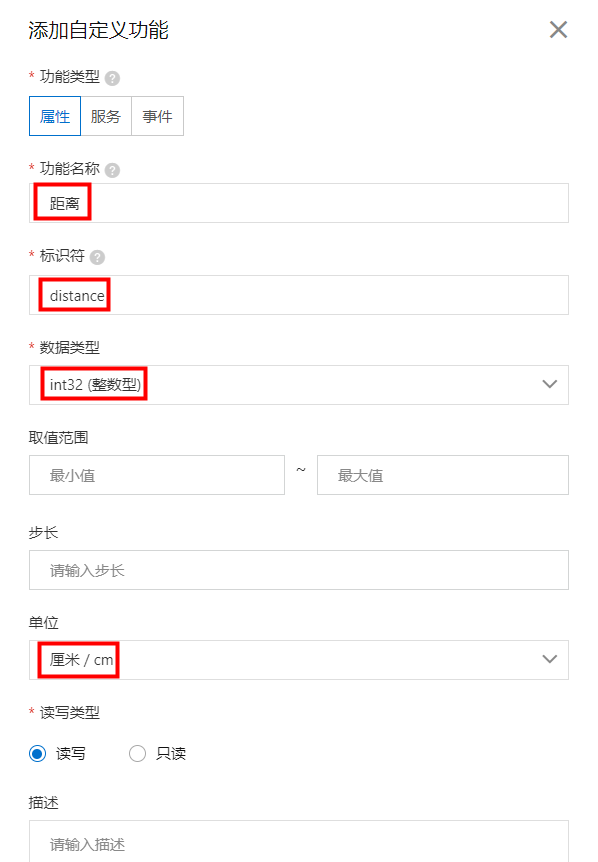
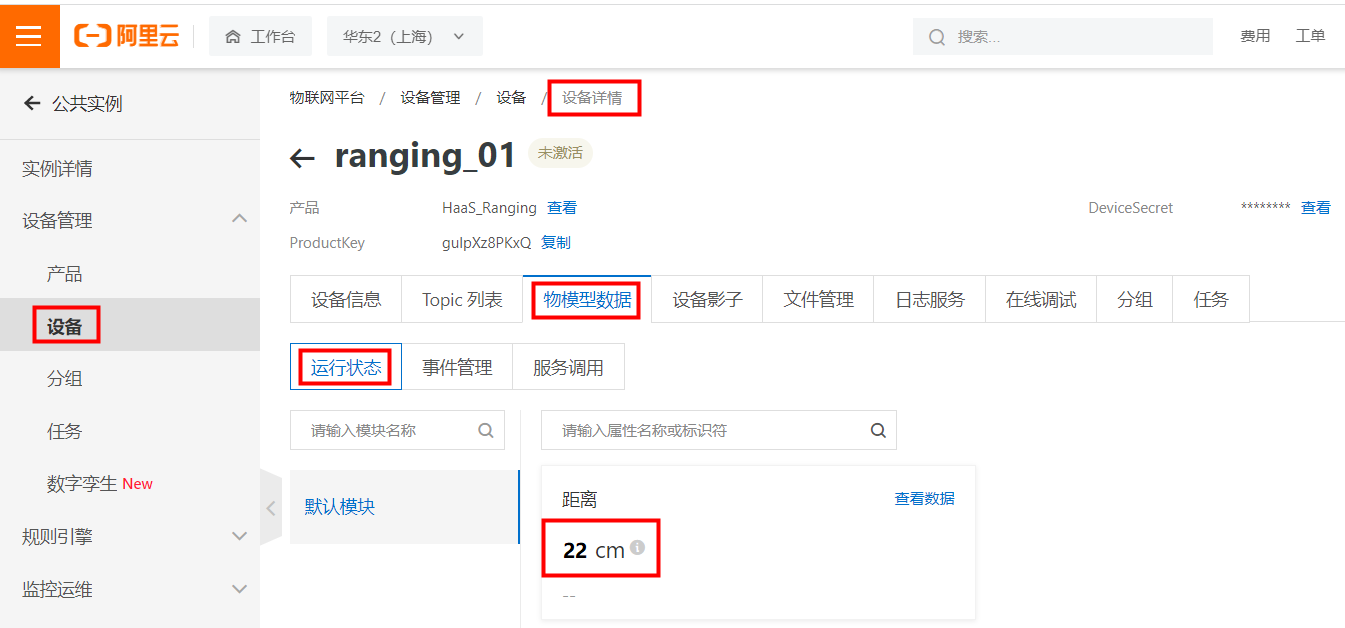
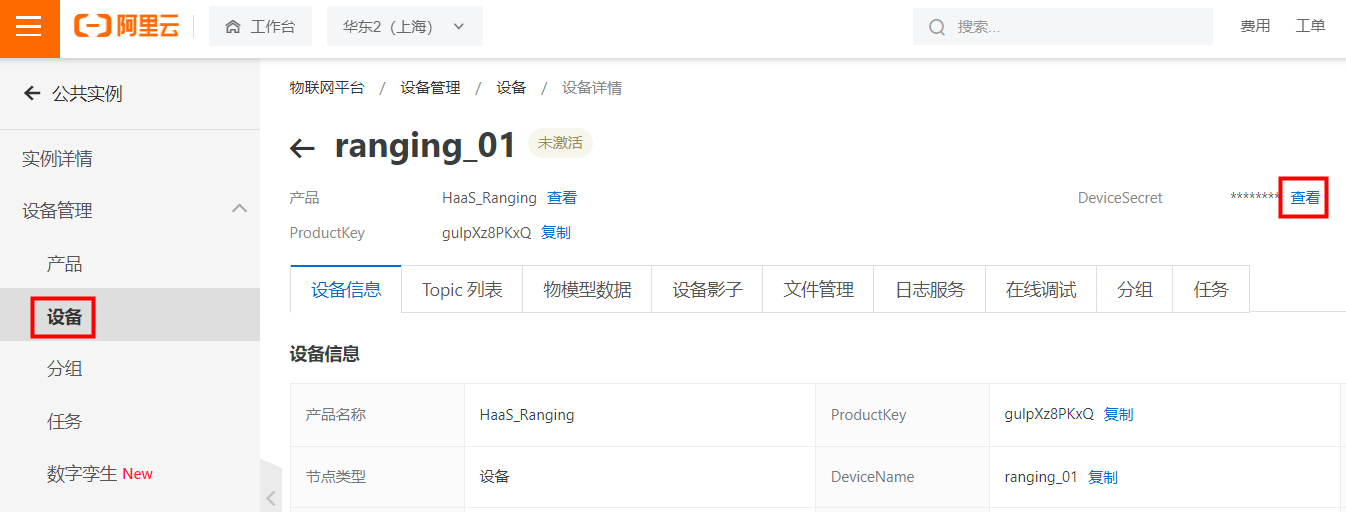
IssueID:1683:Python example ultrasonic ranging
[Detail] New Python example: ultrasonic ranging. [Verified Cases] Build Pass: <py_engine_demo> Test Pass: <py_engine_demo>
Showing
46.0 KB
47.9 KB
27.8 KB
14.2 KB
496.3 KB
407.4 KB
36.5 KB
37.9 KB
17.6 KB
60.0 KB
38.4 KB