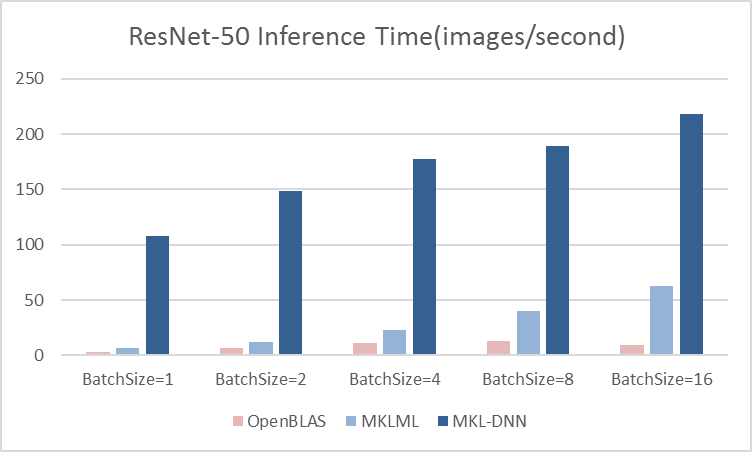
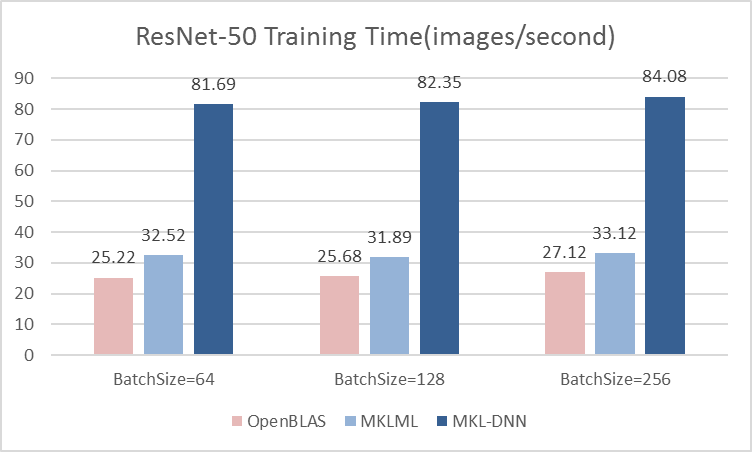
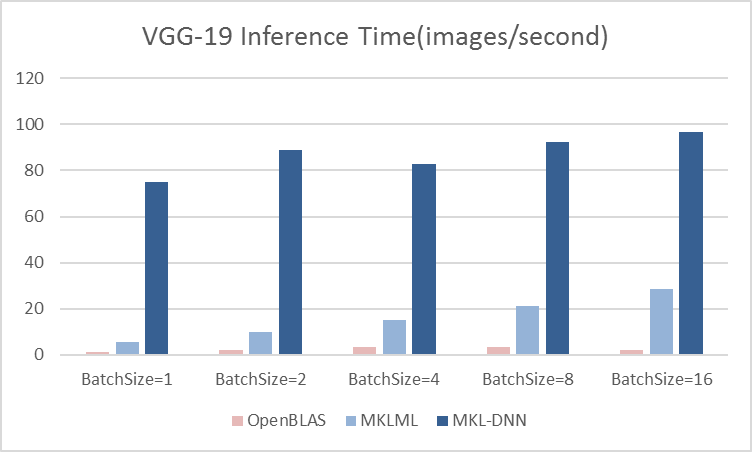
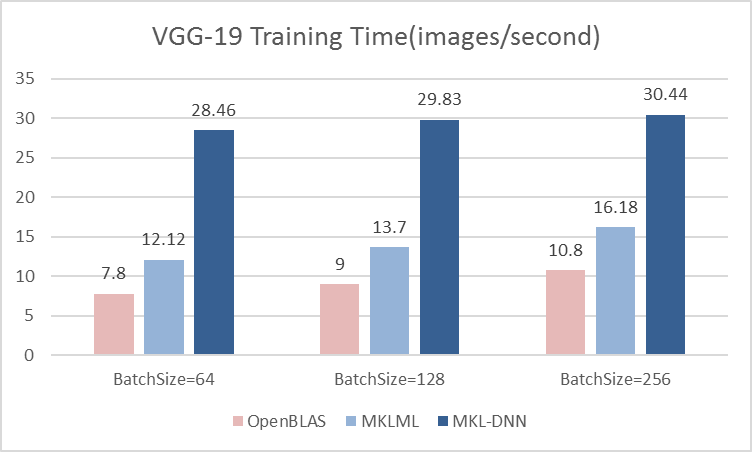
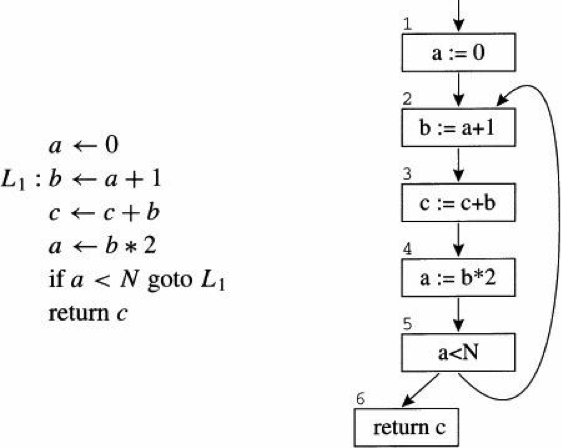
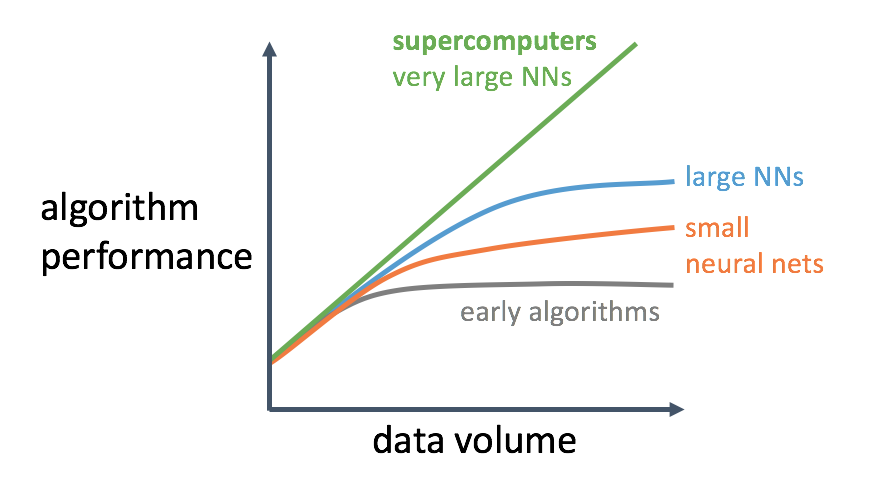
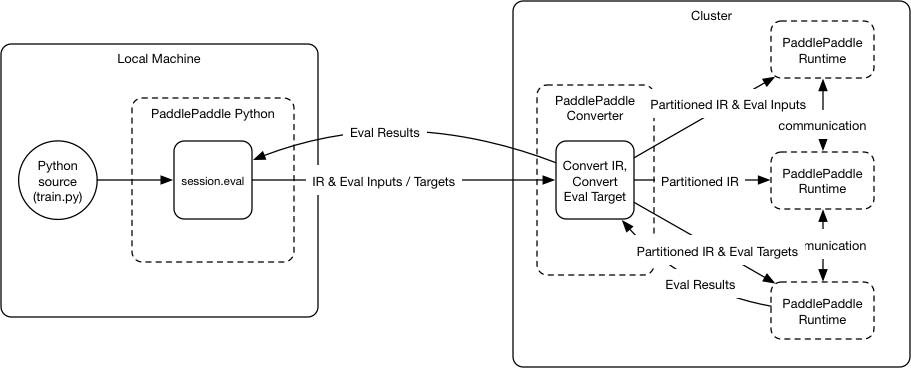
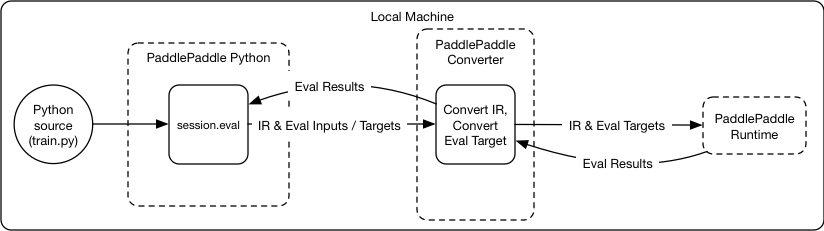
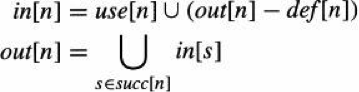Merge branch 'develop' of github.com:PaddlePaddle/Paddle into hsigmoid_op
Showing
15.1 KB
15.6 KB
14.1 KB
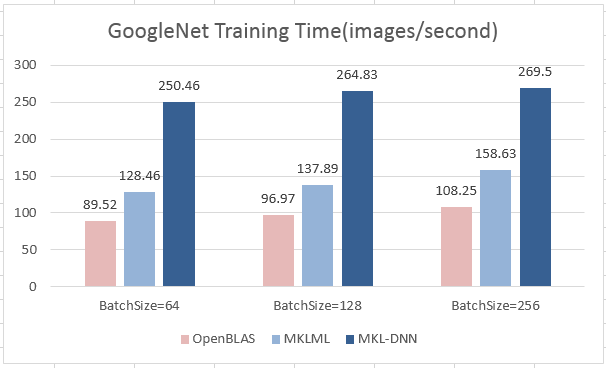
| W: | H:
| W: | H:


13.7 KB
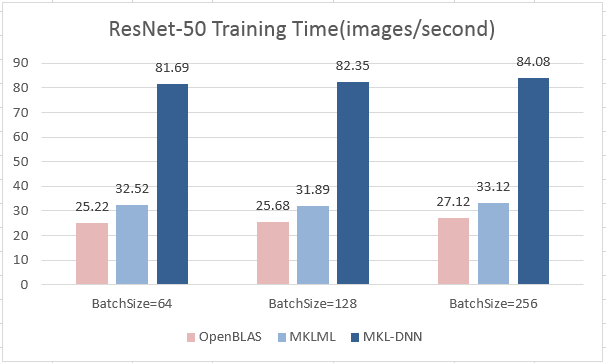
| W: | H:
| W: | H:


benchmark/figs/vgg-cpu-infer.png
0 → 100644
13.7 KB
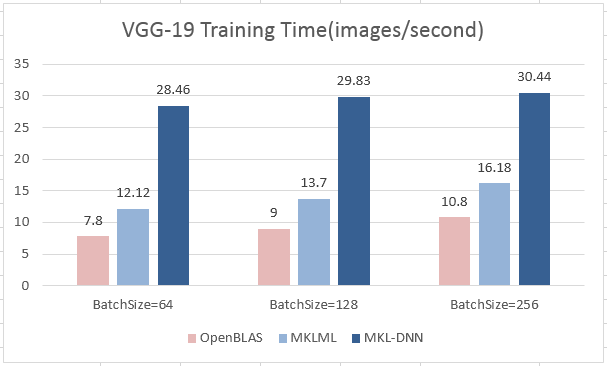
| W: | H:
| W: | H:


doc/design/ci_build_whl.png
0 → 100644
280.4 KB
文件已移动
文件已移动
文件已移动
文件已移动
189.2 KB
文件已移动
文件已移动
文件已添加
102.5 KB
文件已移动
文件已移动
文件已移动
文件已移动
文件已移动
文件已添加
134.5 KB
doc/design/error_clip.md
0 → 100644
83.3 KB
22.5 KB
39.7 KB
doc/design/memory_optimization.md
0 → 100644
46.5 KB
文件已删除
28.3 KB
paddle/inference/CMakeLists.txt
0 → 100644
此差异已折叠。
paddle/inference/example.cc
0 → 100644
此差异已折叠。
paddle/inference/inference.cc
0 → 100644
此差异已折叠。
paddle/inference/inference.h
0 → 100644
此差异已折叠。
paddle/operators/get_places_op.cc
0 → 100644
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
paddle/operators/tensor.save
已删除
100644 → 0
此差异已折叠。
paddle/operators/warpctc_op.cc
0 → 100644
此差异已折叠。
paddle/operators/warpctc_op.cu.cc
0 → 100644
此差异已折叠。
paddle/operators/warpctc_op.h
0 → 100644
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
paddle/platform/dynload/warpctc.h
0 → 100644
此差异已折叠。
paddle/platform/mkldnn_helper.h
0 → 100644
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。