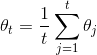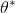Merge branch 'develop' of https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle into revert_callstack
Showing
doc/README.md
0 → 100644
doc/fluid/CMakeLists.txt
已删除
100644 → 0
doc/fluid/api/CMakeLists.txt
已删除
100644 → 0
doc/fluid/api/average.rst
已删除
100644 → 0
doc/fluid/api/backward.rst
已删除
100644 → 0
doc/fluid/api/clip.rst
已删除
100644 → 0
doc/fluid/api/data/image.rst
已删除
100644 → 0
doc/fluid/api/data_feeder.rst
已删除
100644 → 0
doc/fluid/api/executor.rst
已删除
100644 → 0
doc/fluid/api/fluid.rst
已删除
100644 → 0
doc/fluid/api/gen_doc.py
已删除
100644 → 0
doc/fluid/api/gen_doc.sh
已删除
100755 → 0
doc/fluid/api/index_en.rst
已删除
100644 → 0
doc/fluid/api/initializer.rst
已删除
100644 → 0
doc/fluid/api/io.rst
已删除
100644 → 0
doc/fluid/api/layers.rst
已删除
100644 → 0
此差异已折叠。
doc/fluid/api/metrics.rst
已删除
100644 → 0
doc/fluid/api/nets.rst
已删除
100644 → 0
doc/fluid/api/optimizer.rst
已删除
100644 → 0
doc/fluid/api/param_attr.rst
已删除
100644 → 0
doc/fluid/api/profiler.rst
已删除
100644 → 0
doc/fluid/api/regularizer.rst
已删除
100644 → 0
doc/fluid/api/transpiler.rst
已删除
100644 → 0
620 字节
156 字节
此差异已折叠。
160.0 KB
此差异已折叠。
175.1 KB
347.4 KB
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
133.4 KB
83.6 KB
99.1 KB
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
doc/fluid/design/index_cn.rst
已删除
100644 → 0
此差异已折叠。
doc/fluid/design/index_en.rst
已删除
100644 → 0
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
doc/fluid/dev/index_cn.rst
已删除
100644 → 0
此差异已折叠。
doc/fluid/dev/index_en.rst
已删除
100644 → 0
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
doc/fluid/dev/new_op_cn.md
已删除
100644 → 0
此差异已折叠。
doc/fluid/dev/new_op_en.md
已删除
100644 → 0
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
doc/fluid/dev/src/fc.py
已删除
100644 → 0
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
doc/fluid/dev/use_eigen_cn.md
已删除
100644 → 0
此差异已折叠。
doc/fluid/dev/use_eigen_en.md
已删除
100644 → 0
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
doc/fluid/faq/index_cn.rst
已删除
100644 → 0
此差异已折叠。
doc/fluid/faq/index_en.rst
已删除
100644 → 0
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
doc/fluid/howto/index_cn.rst
已删除
100644 → 0
此差异已折叠。
doc/fluid/howto/index_en.rst
已删除
100644 → 0
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
doc/fluid/images/1.png
已删除
100644 → 0
此差异已折叠。
doc/fluid/images/2.png
已删除
100644 → 0
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
doc/fluid/images/3.png
已删除
100644 → 0
此差异已折叠。
doc/fluid/images/4.png
已删除
100644 → 0
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
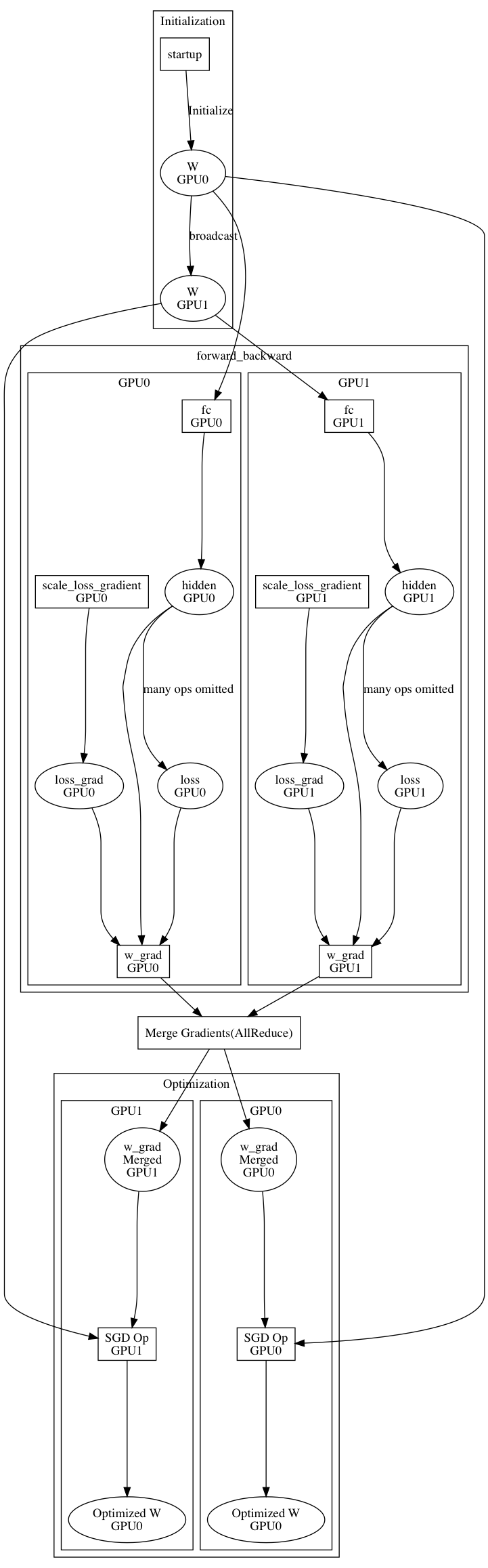
doc/fluid/images/asgd.gif
已删除
100644 → 0
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
doc/fluid/images/compiler.png
已删除
100644 → 0
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
doc/fluid/images/dcgan.png
已删除
100644 → 0
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
doc/fluid/images/executor.png
已删除
100644 → 0
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
doc/fluid/images/layer.png
已删除
100644 → 0
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
doc/fluid/images/op.dot
已删除
100644 → 0
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
doc/fluid/images/place.png
已删除
100644 → 0
此差异已折叠。
doc/fluid/images/pprof_1.png
已删除
100644 → 0
此差异已折叠。
doc/fluid/images/pprof_2.png
已删除
100644 → 0
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
doc/fluid/images/profiler.png
已删除
100644 → 0
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
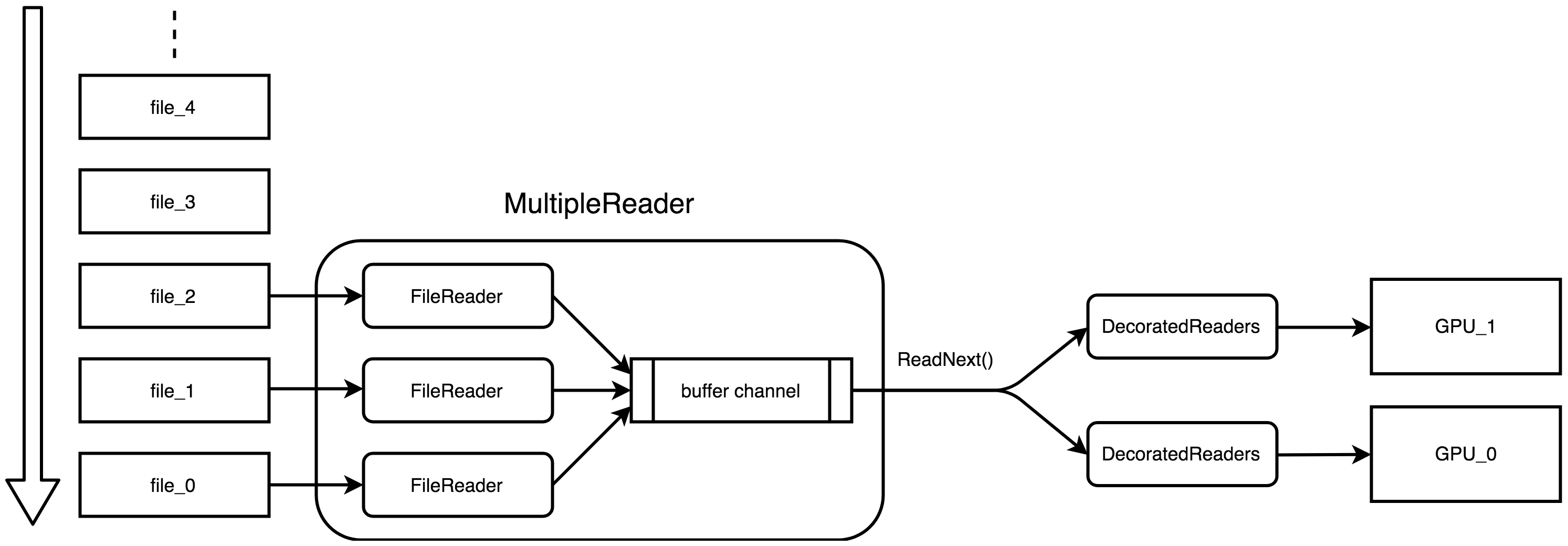
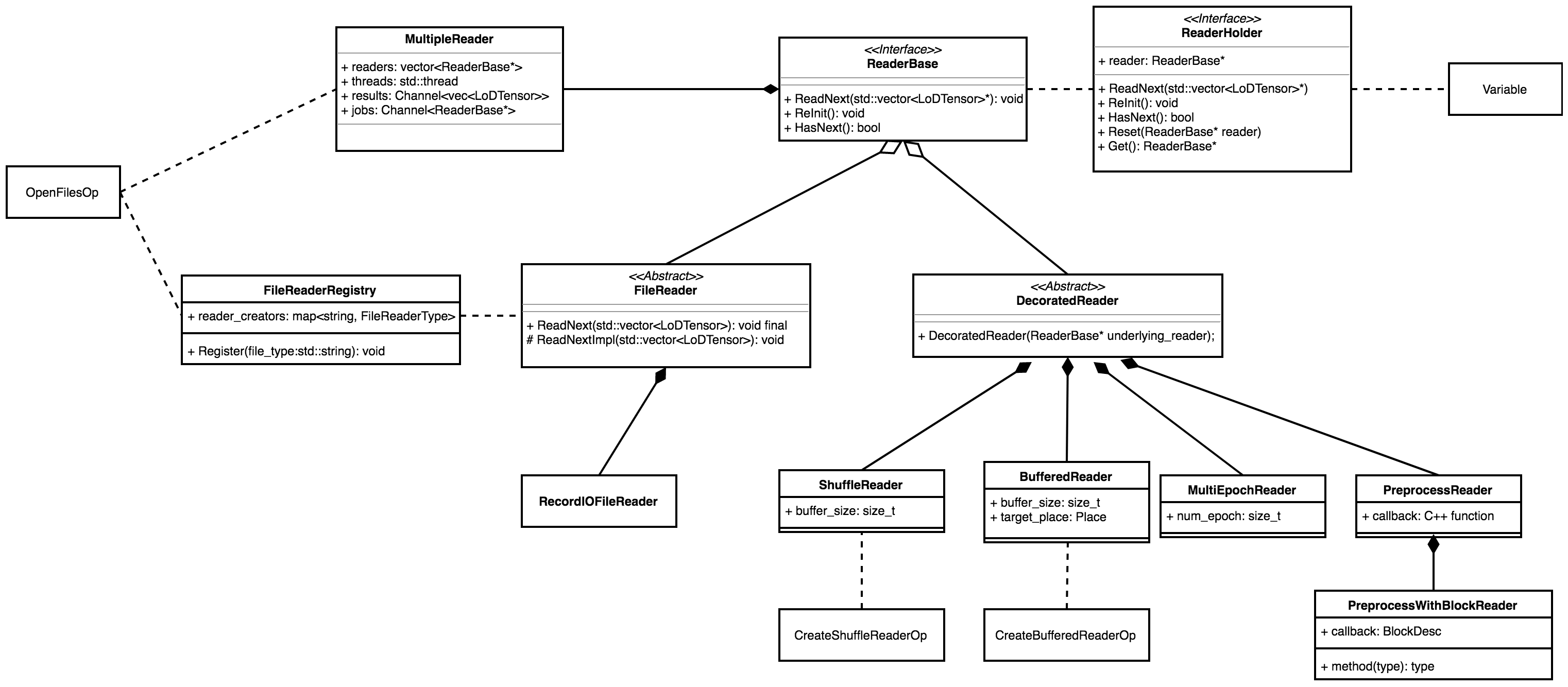
doc/fluid/images/readers.png
已删除
100644 → 0
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
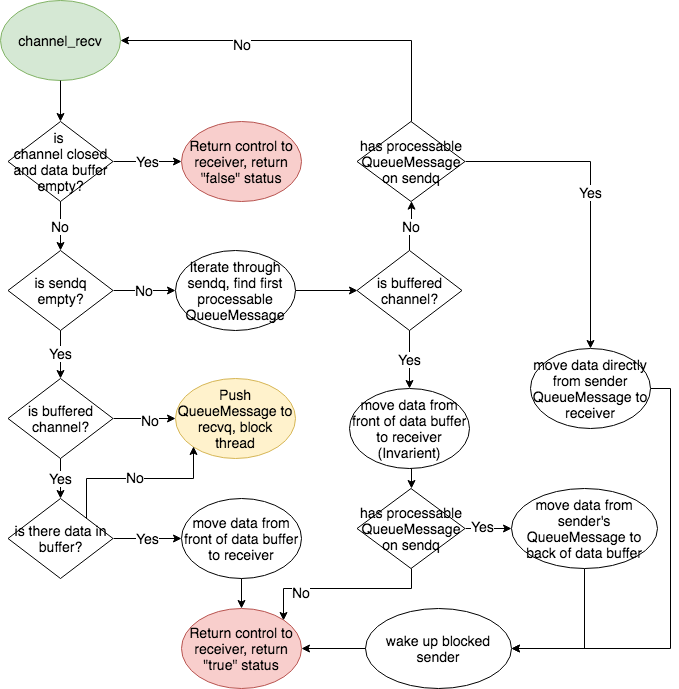
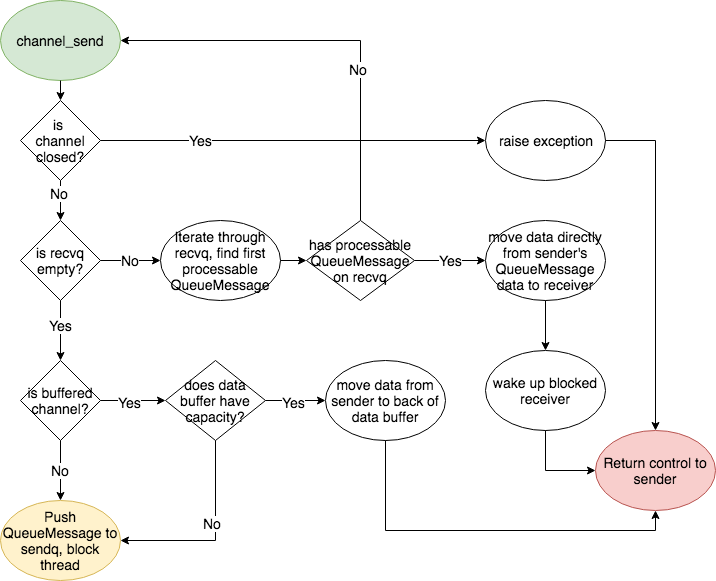
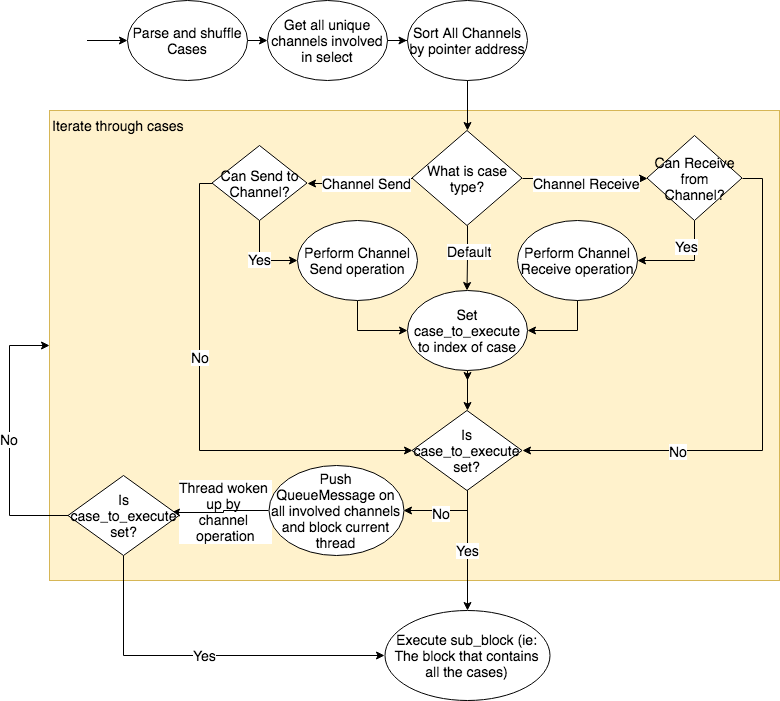
doc/fluid/images/rnn.dot
已删除
100644 → 0
此差异已折叠。
doc/fluid/images/rnn.jpg
已删除
100644 → 0
此差异已折叠。
doc/fluid/images/rnn.png
已删除
100644 → 0
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
doc/fluid/images/test.dot
已删除
100644 → 0
此差异已折叠。
doc/fluid/images/test.dot.png
已删除
100644 → 0
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
doc/fluid/images/tracing.jpeg
已删除
100644 → 0
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
doc/fluid/index_cn.rst
已删除
100644 → 0
此差异已折叠。
doc/fluid/index_en.rst
已删除
100644 → 0
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
doc/fluid/read_source.md
已删除
100644 → 0
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
paddle/fluid/framework/version.cc
0 → 100644
此差异已折叠。
paddle/fluid/framework/version.h
0 → 100644
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
文件已移动
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
paddle/fluid/string/pretty_log.cc
0 → 100644
此差异已折叠。
paddle/fluid/string/pretty_log.h
0 → 100644
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。