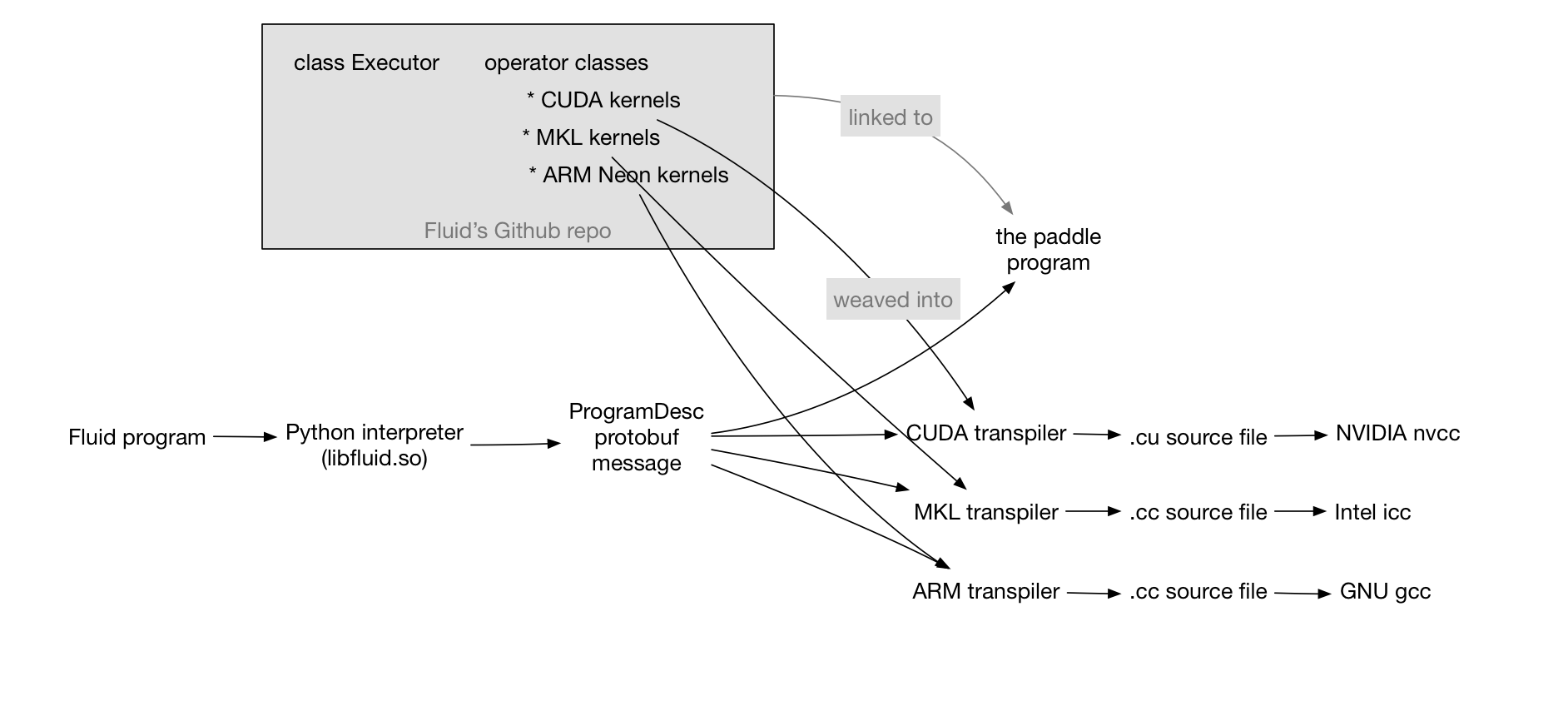
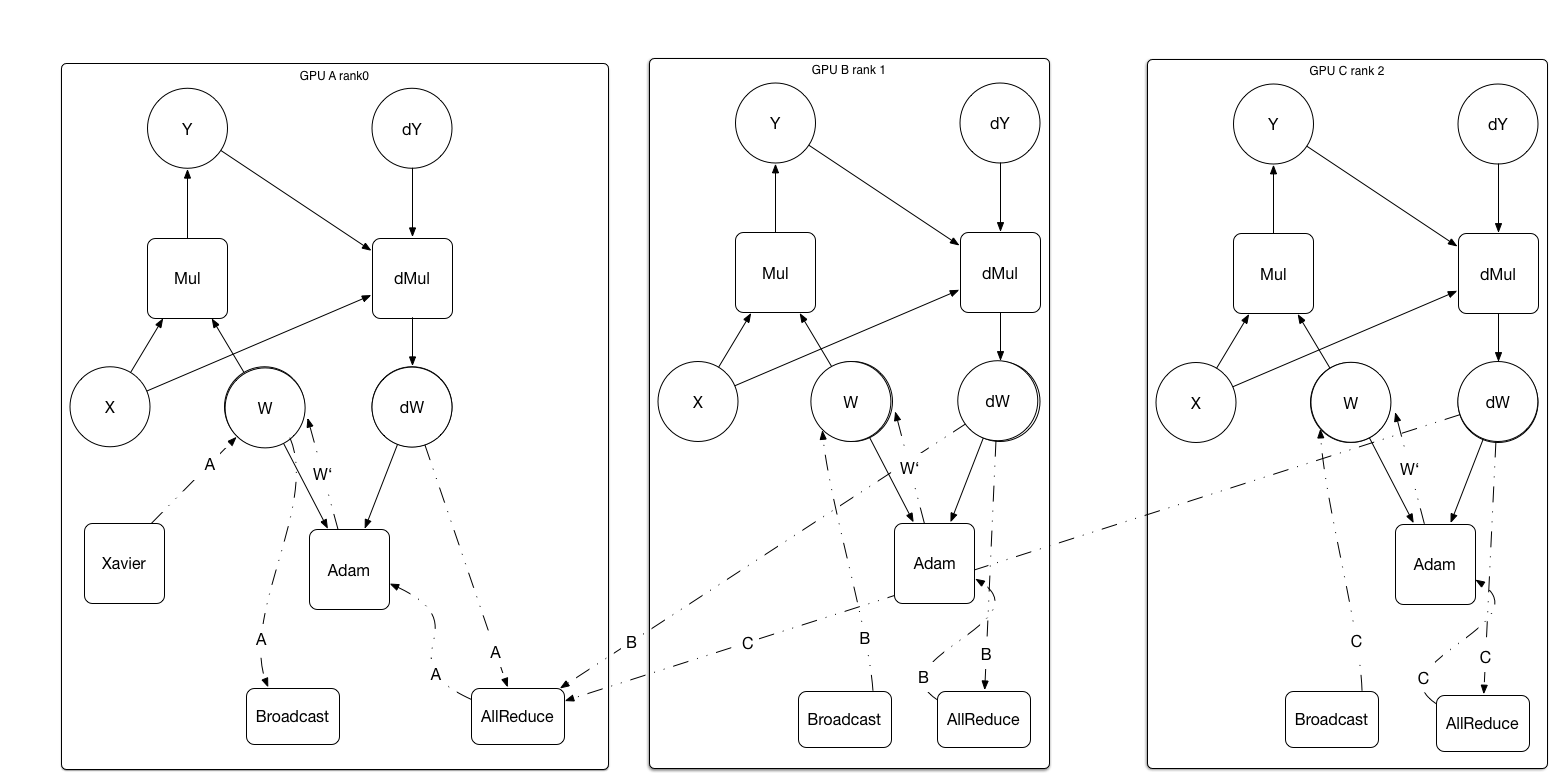
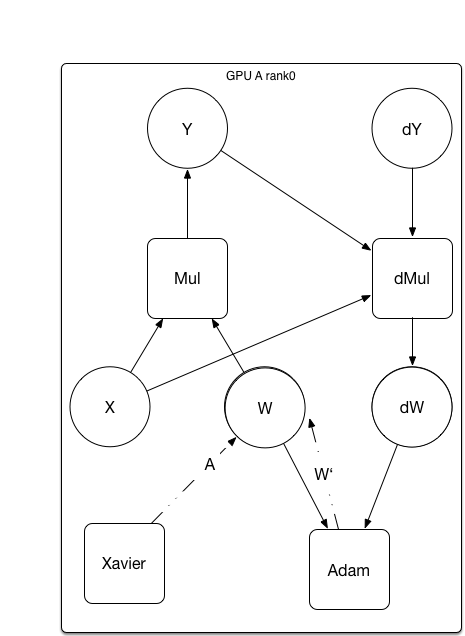
Merge branch 'develop' of https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle into fix-6590
Showing
doc/design/fluid-compiler.graffle
0 → 100644
文件已添加
doc/design/fluid-compiler.png
0 → 100644
121.2 KB
doc/design/fluid.md
0 → 100644
文件已添加
108.4 KB
文件已添加
32.8 KB
doc/design/mkl/mkl_packed.md
0 → 100644
doc/design/paddle_nccl.md
0 → 100644
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。