Skip to content
体验新版
项目
组织
正在加载...
登录
切换导航
打开侧边栏
s920243400
PaddleOCR
提交
6c09c0d9
P
PaddleOCR
项目概览
s920243400
/
PaddleOCR
与 Fork 源项目一致
Fork自
PaddlePaddle / PaddleOCR
通知
1
Star
1
Fork
0
代码
文件
提交
分支
Tags
贡献者
分支图
Diff
Issue
0
列表
看板
标记
里程碑
合并请求
0
Wiki
0
Wiki
分析
仓库
DevOps
项目成员
Pages
P
PaddleOCR
项目概览
项目概览
详情
发布
仓库
仓库
文件
提交
分支
标签
贡献者
分支图
比较
Issue
0
Issue
0
列表
看板
标记
里程碑
合并请求
0
合并请求
0
Pages
分析
分析
仓库分析
DevOps
Wiki
0
Wiki
成员
成员
收起侧边栏
关闭侧边栏
动态
分支图
创建新Issue
提交
Issue看板
未验证
提交
6c09c0d9
编写于
9月 22, 2022
作者:
S
shaohua.zhang
提交者:
GitHub
9月 22, 2022
浏览文件
操作
浏览文件
下载
电子邮件补丁
差异文件
add a new applaction introduce
上级
4f49ea33
变更
1
隐藏空白更改
内联
并排
Showing
1 changed file
with
782 addition
and
0 deletion
+782
-0
applications/快速构建卡证类OCR.md
applications/快速构建卡证类OCR.md
+782
-0
未找到文件。
applications/快速构建卡证类OCR.md
0 → 100644
浏览文件 @
6c09c0d9
# 快速构建卡证类OCR
-
[
快速构建卡证类OCR
](
#快速构建卡证类ocr
)
-
[
1. 金融行业卡证识别应用
](
#1-金融行业卡证识别应用
)
-
[
1.1 金融行业中的OCR相关技术
](
#11-金融行业中的ocr相关技术
)
-
[
1.2 金融行业中的卡证识别场景介绍
](
#12-金融行业中的卡证识别场景介绍
)
-
[
1.3 OCR落地挑战
](
#13-ocr落地挑战
)
-
[
2. 卡证识别技术解析
](
#2-卡证识别技术解析
)
-
[
2.1 卡证分类模型
](
#21-卡证分类模型
)
-
[
2.2 卡证识别模型
](
#22-卡证识别模型
)
-
[
3. OCR技术拆解
](
#3-ocr技术拆解
)
-
[
3.1技术流程
](
#31技术流程
)
-
[
3.2 OCR技术拆解---卡证分类
](
#32-ocr技术拆解---卡证分类
)
-
[
卡证分类:数据、模型准备
](
#卡证分类数据模型准备
)
-
[
卡证分类---修改配置文件
](
#卡证分类---修改配置文件
)
-
[
卡证分类---训练
](
#卡证分类---训练
)
-
[
3.2 OCR技术拆解---卡证识别
](
#32-ocr技术拆解---卡证识别
)
-
[
身份证识别:检测+分类
](
#身份证识别检测分类
)
-
[
数据标注
](
#数据标注
)
-
[
4 . 项目实践
](
#4--项目实践
)
-
[
4.1 环境准备
](
#41-环境准备
)
-
[
4.2 配置文件修改
](
#42-配置文件修改
)
-
[
4.3 代码修改
](
#43-代码修改
)
-
[
4.3.1 数据读取
](
#431-数据读取
)
-
[
4.3.2 head修改
](
#432--head修改
)
-
[
4.3.3 修改loss
](
#433-修改loss
)
-
[
4.3.4 后处理
](
#434-后处理
)
-
[
4.4. 模型启动
](
#44-模型启动
)
-
[
5 总结
](
#5-总结
)
-
[
References
](
#references
)
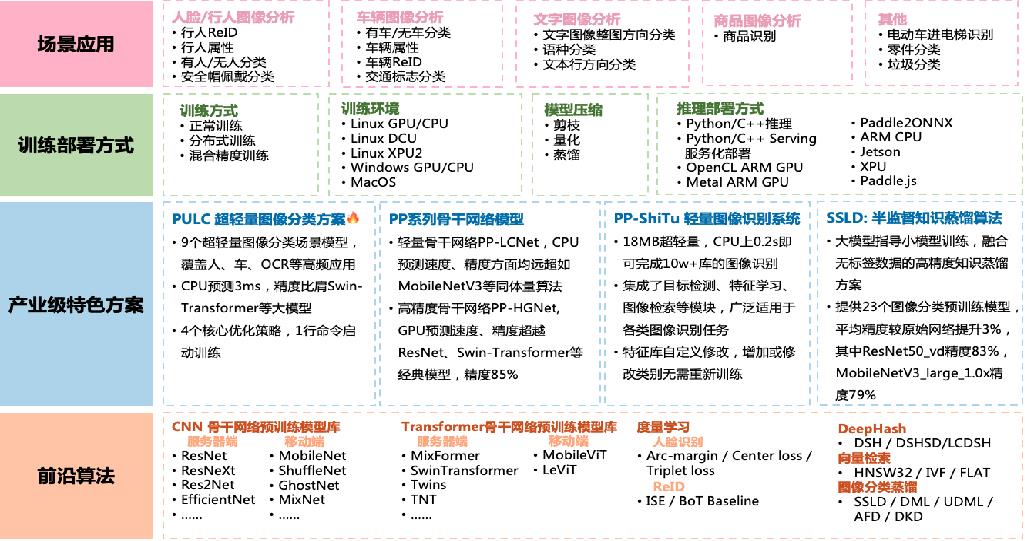
## 1. 金融行业卡证识别应用
### 1.1 金融行业中的OCR相关技术
*
《“十四五”数字经济发展规划》指出,2020年我国数字经济核心产业增加值占GDP比重达7.8%,随着数字经济迈向全面扩展,到2025年该比例将提升至10%。
*
在过去数年的跨越发展与积累沉淀中,数字金融、金融科技已在对金融业的重塑与再造中充分印证了其自身价值。
*
以智能为目标,提升金融数字化水平,实现业务流程自动化,降低人力成本。

### 1.2 金融行业中的卡证识别场景介绍
应用场景:身份证、银行卡、营业执照、驾驶证等。
应用难点:由于数据的采集来源多样,以及实际采集数据各种噪声:反光、褶皱、模糊、倾斜等各种问题干扰。

### 1.3 OCR落地挑战
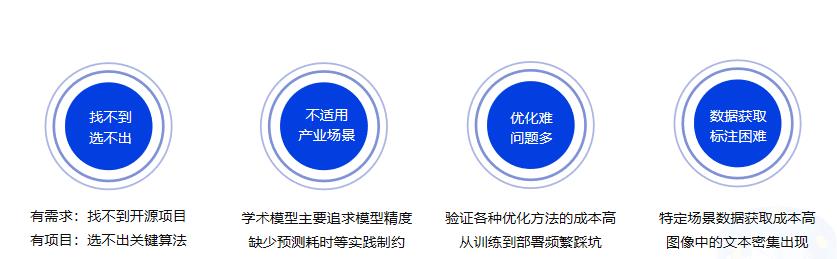
## 2. 卡证识别技术解析
### 2.1 卡证分类模型
卡证分类:基于PPLCNet
与其他轻量级模型相比在CPU环境下ImageNet数据集上的表现
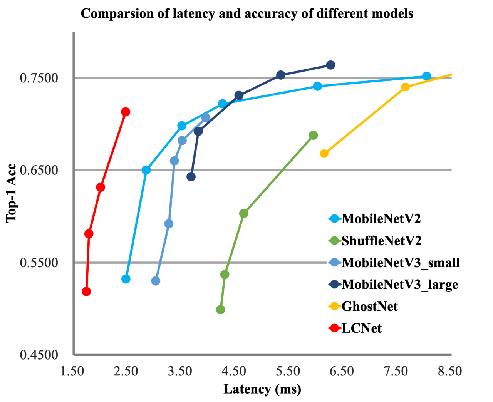
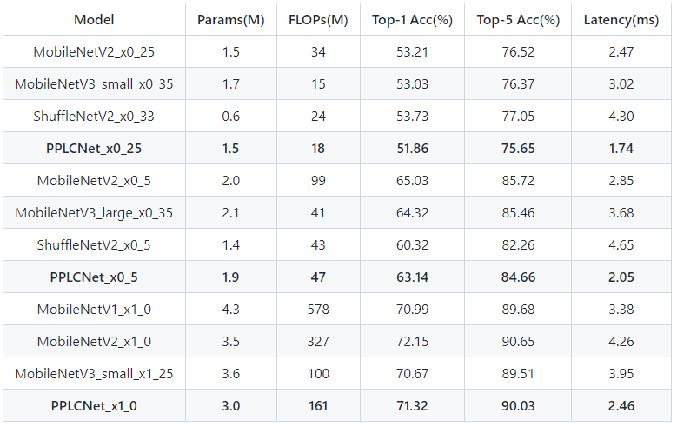
*
模型来自模型库PaddleClas,它是一个图像识别和图像分类任务的工具集,助力使用者训练出更好的视觉模型和应用落地。
### 2.2 卡证识别模型
*
检测:DBNet 识别:SVRT

*
PPOCRv3在文本检测、识别进行了一系列改进优化,在保证精度的同时提升预测效率
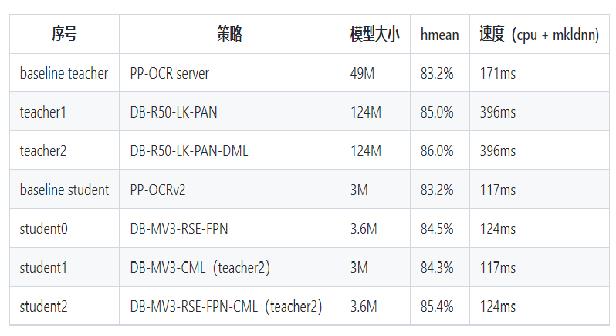
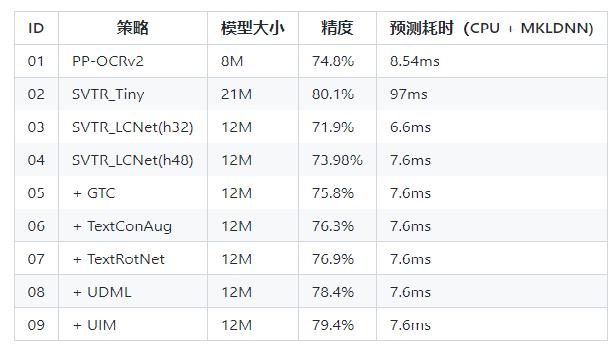
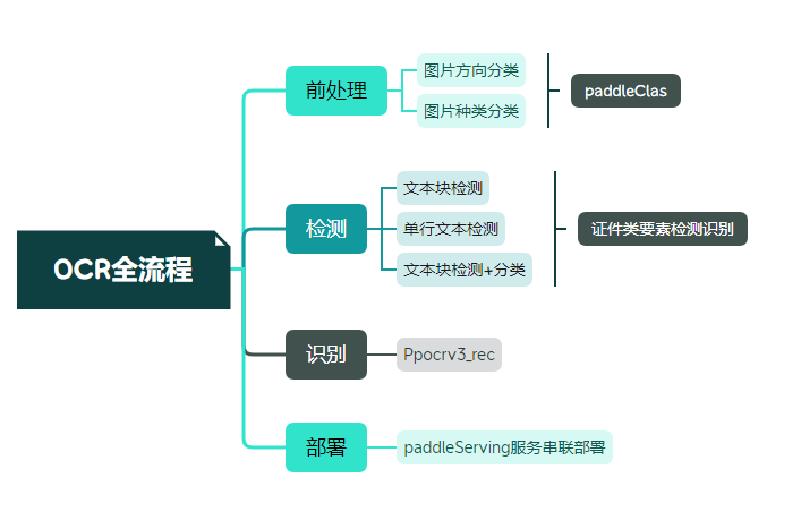
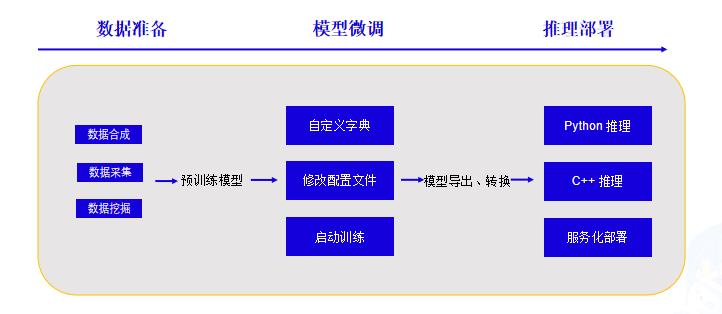
## 3. OCR技术拆解
### 3.1技术流程
### 3.2 OCR技术拆解---卡证分类
#### 卡证分类:数据、模型准备
A 使用爬虫获取无标注数据,将相同类别的放在同一文件夹下,文件名从0开始命名。具体格式如下图所示。
注:卡证类数据,建议每个类别数据量在500张以上

B 一行命令生成标签文件
```
tree -r -i -f | grep -E "jpg|JPG|jpeg|JPEG|png|PNG|webp" | awk -F "/" '{print $0" "$2}' > train_list.txt
```
C
[
下载预训练模型
](
https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleClas/blob/release/2.4/docs/zh_CN/models/PP-LCNet.md
)
#### 卡证分类---修改配置文件
配置文件主要修改三个部分:
全局参数:预训练模型路径/训练轮次/图像尺寸
模型结构:分类数
数据处理:训练/评估数据路径
!
[](
https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/e0dc05039c7444c5ab1260ff550a408748df8d4cfe864223adf390e51058dbd5
)
#### 卡证分类---训练
指定配置文件启动训练:
```
!python /home/aistudio/work/PaddleClas/tools/train.py -c /home/aistudio/work/PaddleClas/ppcls/configs/PULC/text_image_orientation/PPLCNet_x1_0.yaml
```
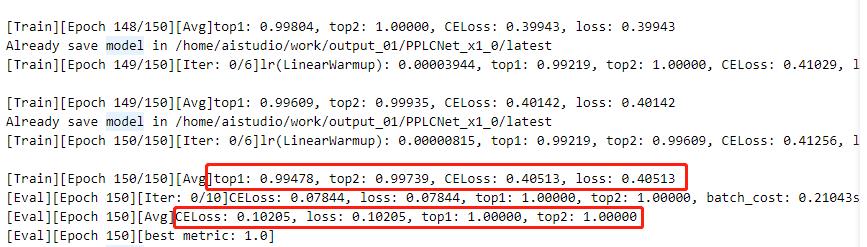
注:日志中显示了训练结果和评估结果(训练时可以设置固定轮数评估一次)
### 3.2 OCR技术拆解---卡证识别
卡证识别(以身份证检测为例)
存在的困难及问题:
*
在自然场景下,由于各种拍摄设备以及光线、角度不同等影响导致实际得到的证件影像千差万别。
*
如何快速提取需要的关键信息
*
多行的文本信息,检测结果如何正确拼接
!
[](
https://ai-studio-static-online.cdn.bcebos.com/4f8f5533a2914e0a821f4a639677843c32ec1f08a1b1488d94c0b8bfb6e72d2d
)
*
OCR技术拆解---OCR工具库
PaddleOCR是一个丰富、领先且实用的OCR工具库,助力开发者训练出更好的模型并应用落地
身份证识别:用现有的方法识别

#### 身份证识别:检测+分类
> 方法:基于现有的dbnet检测模型,加入分类方法。检测同时进行分类,从一定程度上优化识别流程


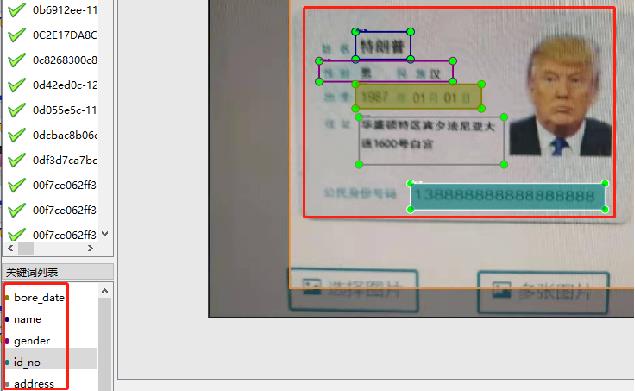
#### 数据标注
使用PaddleOCRLable进行快速标注
*
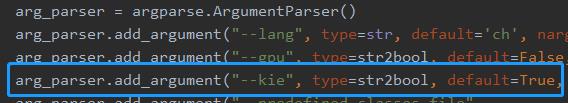
修改PPOCRLabel.py,将下图中的kie参数设置为True
*
数据标注踩坑分享

注:两者只有标注有差别,训练参数数据集都相同
## 4 . 项目实践
AIStudio项目链接:
[
快速构建卡证类OCR
](
https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/projectdetail/4459116
)
### 4.1 环境准备
1)拉取
[
paddleocr
](
https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR
)
项目,如果从github上拉取速度慢可以选择从gitee上获取。
```
!git clone https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR.git -b release/2.6 /home/aistudio/work/
```
2)获取并解压预训练模型,如果要使用其他模型可以从模型库里自主选择合适模型。
```
!wget -P work/pre_trained/ https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train.tar
!tar -vxf /home/aistudio/work/pre_trained/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train.tar -C /home/aistudio/work/pre_trained
```
3) 安装必要依赖
```
!pip install -r /home/aistudio/work/requirements.txt
```
### 4.2 配置文件修改
修改配置文件
*work/configs/det/detmv3db.yml*
具体修改说明如下:
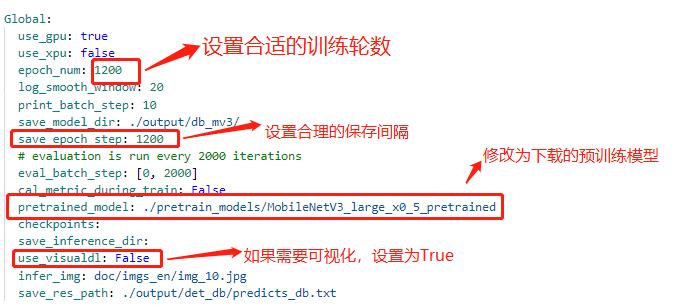
注:在上述的配置文件的Global变量中需要添加以下两个参数:
label_list 为标签表
num_classes 为分类数
上述两个参数根据实际的情况配置即可
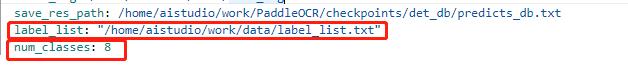
其中lable_list内容如下例所示,
***建议第一个参数设置为 background,不要设置为实际要提取的关键信息种类**
*
:
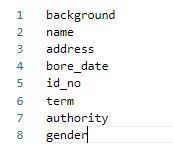
配置文件中的其他设置说明

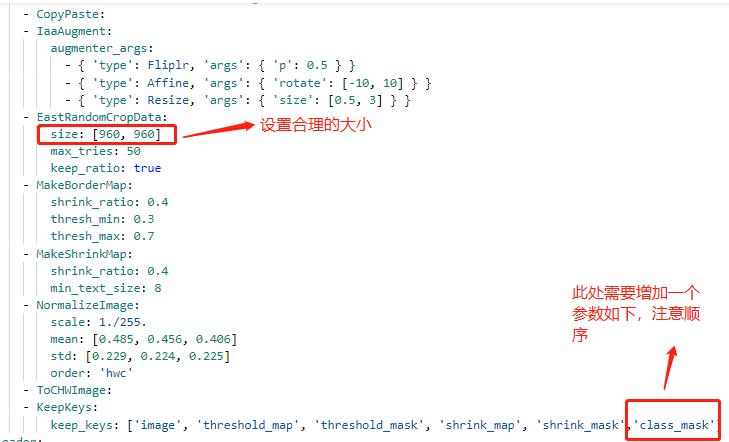
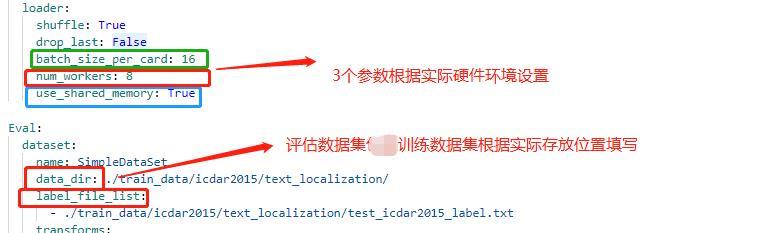
### 4.3 代码修改
#### 4.3.1 数据读取
*
修改 PaddleOCR/ppocr/data/imaug/label_ops.py中的DetLabelEncode
```
python
class
DetLabelEncode
(
object
):
# 修改检测标签的编码处,新增了参数分类数:num_classes,重写初始化方法,以及分类标签的读取
def
__init__
(
self
,
label_list
,
num_classes
=
8
,
**
kwargs
):
self
.
num_classes
=
num_classes
self
.
label_list
=
[]
if
label_list
:
if
isinstance
(
label_list
,
str
):
with
open
(
label_list
,
'r+'
,
encoding
=
'utf-8'
)
as
f
:
for
line
in
f
.
readlines
():
self
.
label_list
.
append
(
line
.
replace
(
"
\n
"
,
""
))
else
:
self
.
label_list
=
label_list
else
:
assert
' please check label_list whether it is none or config is right'
if
num_classes
!=
len
(
self
.
label_list
):
# 校验分类数和标签的一致性
assert
'label_list length is not equal to the num_classes'
def
__call__
(
self
,
data
):
label
=
data
[
'label'
]
label
=
json
.
loads
(
label
)
nBox
=
len
(
label
)
boxes
,
txts
,
txt_tags
,
classes
=
[],
[],
[],
[]
for
bno
in
range
(
0
,
nBox
):
box
=
label
[
bno
][
'points'
]
txt
=
label
[
bno
][
'key_cls'
]
# 此处将kie中的参数作为分类读取
boxes
.
append
(
box
)
txts
.
append
(
txt
)
if
txt
in
[
'*'
,
'###'
]:
txt_tags
.
append
(
True
)
if
self
.
num_classes
>
1
:
classes
.
append
(
-
2
)
else
:
txt_tags
.
append
(
False
)
if
self
.
num_classes
>
1
:
# 将KIE内容的key标签作为分类标签使用
classes
.
append
(
int
(
self
.
label_list
.
index
(
txt
)))
if
len
(
boxes
)
==
0
:
return
None
boxes
=
self
.
expand_points_num
(
boxes
)
boxes
=
np
.
array
(
boxes
,
dtype
=
np
.
float32
)
txt_tags
=
np
.
array
(
txt_tags
,
dtype
=
np
.
bool
)
classes
=
classes
data
[
'polys'
]
=
boxes
data
[
'texts'
]
=
txts
data
[
'ignore_tags'
]
=
txt_tags
if
self
.
num_classes
>
1
:
data
[
'classes'
]
=
classes
return
data
```
*
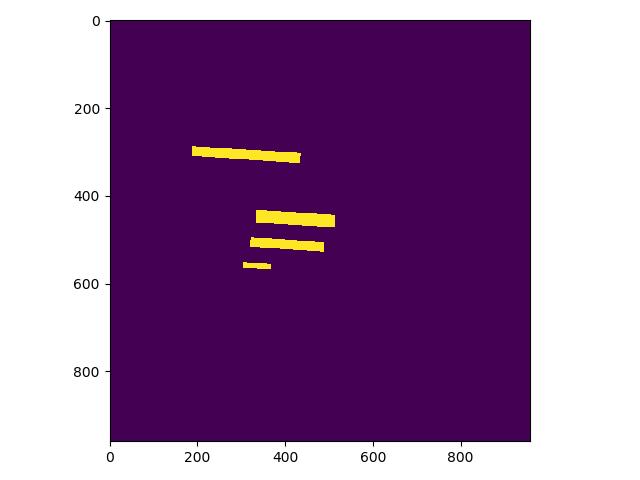
修改 PaddleOCR/ppocr/data/imaug/make_shrink_map.py中的MakeShrinkMap类。这里需要注意的是,如果我们设置的label_list中的第一个参数为要检测的信息那么会得到如下的mask,
举例说明:
这是检测的mask图,图中有四个mask那么实际对应的分类应该是4类
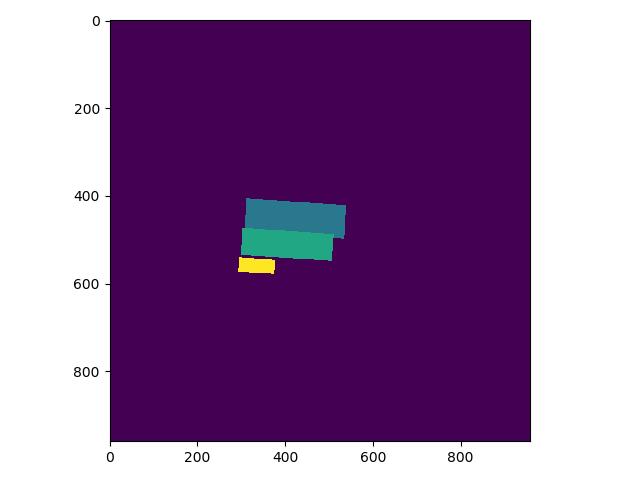
label_list中第一个为关键分类,则得到的分类Mask实际如下,与上图相比,少了一个box:
```
python
class
MakeShrinkMap
(
object
):
r
'''
Making binary mask from detection data with ICDAR format.
Typically following the process of class `MakeICDARData`.
'''
def
__init__
(
self
,
min_text_size
=
8
,
shrink_ratio
=
0.4
,
num_classes
=
8
,
**
kwargs
):
self
.
min_text_size
=
min_text_size
self
.
shrink_ratio
=
shrink_ratio
self
.
num_classes
=
num_classes
# 添加了分类
def
__call__
(
self
,
data
):
image
=
data
[
'image'
]
text_polys
=
data
[
'polys'
]
ignore_tags
=
data
[
'ignore_tags'
]
if
self
.
num_classes
>
1
:
classes
=
data
[
'classes'
]
h
,
w
=
image
.
shape
[:
2
]
text_polys
,
ignore_tags
=
self
.
validate_polygons
(
text_polys
,
ignore_tags
,
h
,
w
)
gt
=
np
.
zeros
((
h
,
w
),
dtype
=
np
.
float32
)
mask
=
np
.
ones
((
h
,
w
),
dtype
=
np
.
float32
)
gt_class
=
np
.
zeros
((
h
,
w
),
dtype
=
np
.
float32
)
# 新增分类
for
i
in
range
(
len
(
text_polys
)):
polygon
=
text_polys
[
i
]
height
=
max
(
polygon
[:,
1
])
-
min
(
polygon
[:,
1
])
width
=
max
(
polygon
[:,
0
])
-
min
(
polygon
[:,
0
])
if
ignore_tags
[
i
]
or
min
(
height
,
width
)
<
self
.
min_text_size
:
cv2
.
fillPoly
(
mask
,
polygon
.
astype
(
np
.
int32
)[
np
.
newaxis
,
:,
:],
0
)
ignore_tags
[
i
]
=
True
else
:
polygon_shape
=
Polygon
(
polygon
)
subject
=
[
tuple
(
l
)
for
l
in
polygon
]
padding
=
pyclipper
.
PyclipperOffset
()
padding
.
AddPath
(
subject
,
pyclipper
.
JT_ROUND
,
pyclipper
.
ET_CLOSEDPOLYGON
)
shrinked
=
[]
# Increase the shrink ratio every time we get multiple polygon returned back
possible_ratios
=
np
.
arange
(
self
.
shrink_ratio
,
1
,
self
.
shrink_ratio
)
np
.
append
(
possible_ratios
,
1
)
for
ratio
in
possible_ratios
:
distance
=
polygon_shape
.
area
*
(
1
-
np
.
power
(
ratio
,
2
))
/
polygon_shape
.
length
shrinked
=
padding
.
Execute
(
-
distance
)
if
len
(
shrinked
)
==
1
:
break
if
shrinked
==
[]:
cv2
.
fillPoly
(
mask
,
polygon
.
astype
(
np
.
int32
)[
np
.
newaxis
,
:,
:],
0
)
ignore_tags
[
i
]
=
True
continue
for
each_shirnk
in
shrinked
:
shirnk
=
np
.
array
(
each_shirnk
).
reshape
(
-
1
,
2
)
cv2
.
fillPoly
(
gt
,
[
shirnk
.
astype
(
np
.
int32
)],
1
)
if
self
.
num_classes
>
1
:
# 绘制分类的mask
cv2
.
fillPoly
(
gt_class
,
polygon
.
astype
(
np
.
int32
)[
np
.
newaxis
,
:,
:],
classes
[
i
])
data
[
'shrink_map'
]
=
gt
if
self
.
num_classes
>
1
:
data
[
'class_mask'
]
=
gt_class
data
[
'shrink_mask'
]
=
mask
return
data
```
由于在训练数据中会对数据进行resize设置,yml中的操作为:EastRandomCropData,所以需要修改PaddleOCR/ppocr/data/imaug/random_crop_data.py中的EastRandomCropData
```
python
class
EastRandomCropData
(
object
):
def
__init__
(
self
,
size
=
(
640
,
640
),
max_tries
=
10
,
min_crop_side_ratio
=
0.1
,
keep_ratio
=
True
,
num_classes
=
8
,
**
kwargs
):
self
.
size
=
size
self
.
max_tries
=
max_tries
self
.
min_crop_side_ratio
=
min_crop_side_ratio
self
.
keep_ratio
=
keep_ratio
self
.
num_classes
=
num_classes
def
__call__
(
self
,
data
):
img
=
data
[
'image'
]
text_polys
=
data
[
'polys'
]
ignore_tags
=
data
[
'ignore_tags'
]
texts
=
data
[
'texts'
]
if
self
.
num_classes
>
1
:
classes
=
data
[
'classes'
]
all_care_polys
=
[
text_polys
[
i
]
for
i
,
tag
in
enumerate
(
ignore_tags
)
if
not
tag
]
# 计算crop区域
crop_x
,
crop_y
,
crop_w
,
crop_h
=
crop_area
(
img
,
all_care_polys
,
self
.
min_crop_side_ratio
,
self
.
max_tries
)
# crop 图片 保持比例填充
scale_w
=
self
.
size
[
0
]
/
crop_w
scale_h
=
self
.
size
[
1
]
/
crop_h
scale
=
min
(
scale_w
,
scale_h
)
h
=
int
(
crop_h
*
scale
)
w
=
int
(
crop_w
*
scale
)
if
self
.
keep_ratio
:
padimg
=
np
.
zeros
((
self
.
size
[
1
],
self
.
size
[
0
],
img
.
shape
[
2
]),
img
.
dtype
)
padimg
[:
h
,
:
w
]
=
cv2
.
resize
(
img
[
crop_y
:
crop_y
+
crop_h
,
crop_x
:
crop_x
+
crop_w
],
(
w
,
h
))
img
=
padimg
else
:
img
=
cv2
.
resize
(
img
[
crop_y
:
crop_y
+
crop_h
,
crop_x
:
crop_x
+
crop_w
],
tuple
(
self
.
size
))
# crop 文本框
text_polys_crop
=
[]
ignore_tags_crop
=
[]
texts_crop
=
[]
classes_crop
=
[]
for
poly
,
text
,
tag
,
class_index
in
zip
(
text_polys
,
texts
,
ignore_tags
,
classes
):
poly
=
((
poly
-
(
crop_x
,
crop_y
))
*
scale
).
tolist
()
if
not
is_poly_outside_rect
(
poly
,
0
,
0
,
w
,
h
):
text_polys_crop
.
append
(
poly
)
ignore_tags_crop
.
append
(
tag
)
texts_crop
.
append
(
text
)
if
self
.
num_classes
>
1
:
classes_crop
.
append
(
class_index
)
data
[
'image'
]
=
img
data
[
'polys'
]
=
np
.
array
(
text_polys_crop
)
data
[
'ignore_tags'
]
=
ignore_tags_crop
data
[
'texts'
]
=
texts_crop
if
self
.
num_classes
>
1
:
data
[
'classes'
]
=
classes_crop
return
data
```
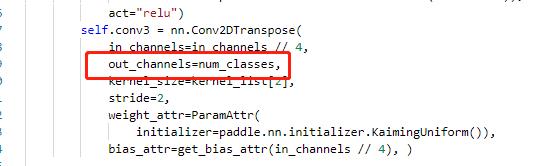
#### 4.3.2 head修改
主要修改 ppocr/modeling/heads/det_db_head.py,将Head类中的最后一层的输出修改为实际的分类数,同时在DBHead中新增分类的head。
#### 4.3.3 修改loss
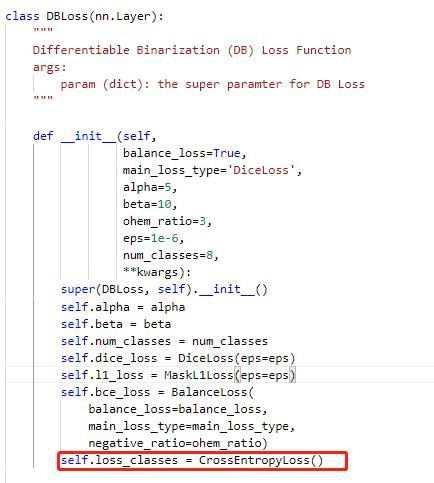
修改PaddleOCR/ppocr/losses/det_db_loss.py中的DBLoss类,分类采用交叉熵损失函数进行计算。
#### 4.3.4 后处理
由于涉及到eval以及后续推理能否正常使用,我们需要修改后处理的相关代码,修改位置 PaddleOCR/ppocr/postprocess/db_postprocess.py中的DBPostProcess类
```
python
class
DBPostProcess
(
object
):
"""
The post process for Differentiable Binarization (DB).
"""
def
__init__
(
self
,
thresh
=
0.3
,
box_thresh
=
0.7
,
max_candidates
=
1000
,
unclip_ratio
=
2.0
,
use_dilation
=
False
,
score_mode
=
"fast"
,
**
kwargs
):
self
.
thresh
=
thresh
self
.
box_thresh
=
box_thresh
self
.
max_candidates
=
max_candidates
self
.
unclip_ratio
=
unclip_ratio
self
.
min_size
=
3
self
.
score_mode
=
score_mode
assert
score_mode
in
[
"slow"
,
"fast"
],
"Score mode must be in [slow, fast] but got: {}"
.
format
(
score_mode
)
self
.
dilation_kernel
=
None
if
not
use_dilation
else
np
.
array
(
[[
1
,
1
],
[
1
,
1
]])
def
boxes_from_bitmap
(
self
,
pred
,
_bitmap
,
classes
,
dest_width
,
dest_height
):
"""
_bitmap: single map with shape (1, H, W),
whose values are binarized as {0, 1}
"""
bitmap
=
_bitmap
height
,
width
=
bitmap
.
shape
outs
=
cv2
.
findContours
((
bitmap
*
255
).
astype
(
np
.
uint8
),
cv2
.
RETR_LIST
,
cv2
.
CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE
)
if
len
(
outs
)
==
3
:
img
,
contours
,
_
=
outs
[
0
],
outs
[
1
],
outs
[
2
]
elif
len
(
outs
)
==
2
:
contours
,
_
=
outs
[
0
],
outs
[
1
]
num_contours
=
min
(
len
(
contours
),
self
.
max_candidates
)
boxes
=
[]
scores
=
[]
class_indexes
=
[]
class_scores
=
[]
for
index
in
range
(
num_contours
):
contour
=
contours
[
index
]
points
,
sside
=
self
.
get_mini_boxes
(
contour
)
if
sside
<
self
.
min_size
:
continue
points
=
np
.
array
(
points
)
if
self
.
score_mode
==
"fast"
:
score
,
class_index
,
class_score
=
self
.
box_score_fast
(
pred
,
points
.
reshape
(
-
1
,
2
),
classes
)
else
:
score
,
class_index
,
class_score
=
self
.
box_score_slow
(
pred
,
contour
,
classes
)
if
self
.
box_thresh
>
score
:
continue
box
=
self
.
unclip
(
points
).
reshape
(
-
1
,
1
,
2
)
box
,
sside
=
self
.
get_mini_boxes
(
box
)
if
sside
<
self
.
min_size
+
2
:
continue
box
=
np
.
array
(
box
)
box
[:,
0
]
=
np
.
clip
(
np
.
round
(
box
[:,
0
]
/
width
*
dest_width
),
0
,
dest_width
)
box
[:,
1
]
=
np
.
clip
(
np
.
round
(
box
[:,
1
]
/
height
*
dest_height
),
0
,
dest_height
)
boxes
.
append
(
box
.
astype
(
np
.
int16
))
scores
.
append
(
score
)
class_indexes
.
append
(
class_index
)
class_scores
.
append
(
class_score
)
if
classes
is
None
:
return
np
.
array
(
boxes
,
dtype
=
np
.
int16
),
scores
else
:
return
np
.
array
(
boxes
,
dtype
=
np
.
int16
),
scores
,
class_indexes
,
class_scores
def
unclip
(
self
,
box
):
unclip_ratio
=
self
.
unclip_ratio
poly
=
Polygon
(
box
)
distance
=
poly
.
area
*
unclip_ratio
/
poly
.
length
offset
=
pyclipper
.
PyclipperOffset
()
offset
.
AddPath
(
box
,
pyclipper
.
JT_ROUND
,
pyclipper
.
ET_CLOSEDPOLYGON
)
expanded
=
np
.
array
(
offset
.
Execute
(
distance
))
return
expanded
def
get_mini_boxes
(
self
,
contour
):
bounding_box
=
cv2
.
minAreaRect
(
contour
)
points
=
sorted
(
list
(
cv2
.
boxPoints
(
bounding_box
)),
key
=
lambda
x
:
x
[
0
])
index_1
,
index_2
,
index_3
,
index_4
=
0
,
1
,
2
,
3
if
points
[
1
][
1
]
>
points
[
0
][
1
]:
index_1
=
0
index_4
=
1
else
:
index_1
=
1
index_4
=
0
if
points
[
3
][
1
]
>
points
[
2
][
1
]:
index_2
=
2
index_3
=
3
else
:
index_2
=
3
index_3
=
2
box
=
[
points
[
index_1
],
points
[
index_2
],
points
[
index_3
],
points
[
index_4
]
]
return
box
,
min
(
bounding_box
[
1
])
def
box_score_fast
(
self
,
bitmap
,
_box
,
classes
):
'''
box_score_fast: use bbox mean score as the mean score
'''
h
,
w
=
bitmap
.
shape
[:
2
]
box
=
_box
.
copy
()
xmin
=
np
.
clip
(
np
.
floor
(
box
[:,
0
].
min
()).
astype
(
np
.
int
),
0
,
w
-
1
)
xmax
=
np
.
clip
(
np
.
ceil
(
box
[:,
0
].
max
()).
astype
(
np
.
int
),
0
,
w
-
1
)
ymin
=
np
.
clip
(
np
.
floor
(
box
[:,
1
].
min
()).
astype
(
np
.
int
),
0
,
h
-
1
)
ymax
=
np
.
clip
(
np
.
ceil
(
box
[:,
1
].
max
()).
astype
(
np
.
int
),
0
,
h
-
1
)
mask
=
np
.
zeros
((
ymax
-
ymin
+
1
,
xmax
-
xmin
+
1
),
dtype
=
np
.
uint8
)
box
[:,
0
]
=
box
[:,
0
]
-
xmin
box
[:,
1
]
=
box
[:,
1
]
-
ymin
cv2
.
fillPoly
(
mask
,
box
.
reshape
(
1
,
-
1
,
2
).
astype
(
np
.
int32
),
1
)
if
classes
is
None
:
return
cv2
.
mean
(
bitmap
[
ymin
:
ymax
+
1
,
xmin
:
xmax
+
1
],
mask
)[
0
],
None
,
None
else
:
k
=
999
class_mask
=
np
.
full
((
ymax
-
ymin
+
1
,
xmax
-
xmin
+
1
),
k
,
dtype
=
np
.
int32
)
cv2
.
fillPoly
(
class_mask
,
box
.
reshape
(
1
,
-
1
,
2
).
astype
(
np
.
int32
),
0
)
classes
=
classes
[
ymin
:
ymax
+
1
,
xmin
:
xmax
+
1
]
new_classes
=
classes
+
class_mask
a
=
new_classes
.
reshape
(
-
1
)
b
=
np
.
where
(
a
>=
k
)
classes
=
np
.
delete
(
a
,
b
[
0
].
tolist
())
class_index
=
np
.
argmax
(
np
.
bincount
(
classes
))
class_score
=
np
.
sum
(
classes
==
class_index
)
/
len
(
classes
)
return
cv2
.
mean
(
bitmap
[
ymin
:
ymax
+
1
,
xmin
:
xmax
+
1
],
mask
)[
0
],
class_index
,
class_score
def
box_score_slow
(
self
,
bitmap
,
contour
,
classes
):
"""
box_score_slow: use polyon mean score as the mean score
"""
h
,
w
=
bitmap
.
shape
[:
2
]
contour
=
contour
.
copy
()
contour
=
np
.
reshape
(
contour
,
(
-
1
,
2
))
xmin
=
np
.
clip
(
np
.
min
(
contour
[:,
0
]),
0
,
w
-
1
)
xmax
=
np
.
clip
(
np
.
max
(
contour
[:,
0
]),
0
,
w
-
1
)
ymin
=
np
.
clip
(
np
.
min
(
contour
[:,
1
]),
0
,
h
-
1
)
ymax
=
np
.
clip
(
np
.
max
(
contour
[:,
1
]),
0
,
h
-
1
)
mask
=
np
.
zeros
((
ymax
-
ymin
+
1
,
xmax
-
xmin
+
1
),
dtype
=
np
.
uint8
)
contour
[:,
0
]
=
contour
[:,
0
]
-
xmin
contour
[:,
1
]
=
contour
[:,
1
]
-
ymin
cv2
.
fillPoly
(
mask
,
contour
.
reshape
(
1
,
-
1
,
2
).
astype
(
np
.
int32
),
1
)
if
classes
is
None
:
return
cv2
.
mean
(
bitmap
[
ymin
:
ymax
+
1
,
xmin
:
xmax
+
1
],
mask
)[
0
],
None
,
None
else
:
k
=
999
class_mask
=
np
.
full
((
ymax
-
ymin
+
1
,
xmax
-
xmin
+
1
),
k
,
dtype
=
np
.
int32
)
cv2
.
fillPoly
(
class_mask
,
contour
.
reshape
(
1
,
-
1
,
2
).
astype
(
np
.
int32
),
0
)
classes
=
classes
[
ymin
:
ymax
+
1
,
xmin
:
xmax
+
1
]
new_classes
=
classes
+
class_mask
a
=
new_classes
.
reshape
(
-
1
)
b
=
np
.
where
(
a
>=
k
)
classes
=
np
.
delete
(
a
,
b
[
0
].
tolist
())
class_index
=
np
.
argmax
(
np
.
bincount
(
classes
))
class_score
=
np
.
sum
(
classes
==
class_index
)
/
len
(
classes
)
return
cv2
.
mean
(
bitmap
[
ymin
:
ymax
+
1
,
xmin
:
xmax
+
1
],
mask
)[
0
],
class_index
,
class_score
def
__call__
(
self
,
outs_dict
,
shape_list
):
pred
=
outs_dict
[
'maps'
]
if
isinstance
(
pred
,
paddle
.
Tensor
):
pred
=
pred
.
numpy
()
pred
=
pred
[:,
0
,
:,
:]
segmentation
=
pred
>
self
.
thresh
if
"classes"
in
outs_dict
:
classes
=
outs_dict
[
'classes'
]
if
isinstance
(
classes
,
paddle
.
Tensor
):
classes
=
classes
.
numpy
()
classes
=
classes
[:,
0
,
:,
:]
else
:
classes
=
None
boxes_batch
=
[]
for
batch_index
in
range
(
pred
.
shape
[
0
]):
src_h
,
src_w
,
ratio_h
,
ratio_w
=
shape_list
[
batch_index
]
if
self
.
dilation_kernel
is
not
None
:
mask
=
cv2
.
dilate
(
np
.
array
(
segmentation
[
batch_index
]).
astype
(
np
.
uint8
),
self
.
dilation_kernel
)
else
:
mask
=
segmentation
[
batch_index
]
if
classes
is
None
:
boxes
,
scores
=
self
.
boxes_from_bitmap
(
pred
[
batch_index
],
mask
,
None
,
src_w
,
src_h
)
boxes_batch
.
append
({
'points'
:
boxes
})
else
:
boxes
,
scores
,
class_indexes
,
class_scores
=
self
.
boxes_from_bitmap
(
pred
[
batch_index
],
mask
,
classes
[
batch_index
],
src_w
,
src_h
)
boxes_batch
.
append
({
'points'
:
boxes
,
"classes"
:
class_indexes
,
"class_scores"
:
class_scores
})
return
boxes_batch
```
### 4.4. 模型启动
在完成上述步骤后我们就可以正常启动训练
```
!python /home/aistudio/work/PaddleOCR/tools/train.py -c /home/aistudio/work/PaddleOCR/configs/det/det_mv3_db.yml
```
其他命令:
```
!python /home/aistudio/work/PaddleOCR/tools/eval.py -c /home/aistudio/work/PaddleOCR/configs/det/det_mv3_db.yml
!python /home/aistudio/work/PaddleOCR/tools/infer_det.py -c /home/aistudio/work/PaddleOCR/configs/det/det_mv3_db.yml
```
模型推理
```
!python /home/aistudio/work/PaddleOCR/tools/infer/predict_det.py --image_dir="/home/aistudio/work/test_img/" --det_model_dir="/home/aistudio/work/PaddleOCR/output/infer"
```
## 5 总结
1.
分类+检测在一定程度上能够缩短用时,具体的模型选取要根据业务场景恰当选择。
2.
数据标注需要多次进行测试调整标注方法,一般进行检测模型微调,需要标注至少上百张。
3.
设置合理的batch_size以及resize大小,同时注意lr设置。
## References
1 https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR
2 https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleClas
3 https://blog.csdn.net/YY007H/article/details/124491217
编辑
预览
Markdown
is supported
0%
请重试
或
添加新附件
.
添加附件
取消
You are about to add
0
people
to the discussion. Proceed with caution.
先完成此消息的编辑!
取消
想要评论请
注册
或
登录