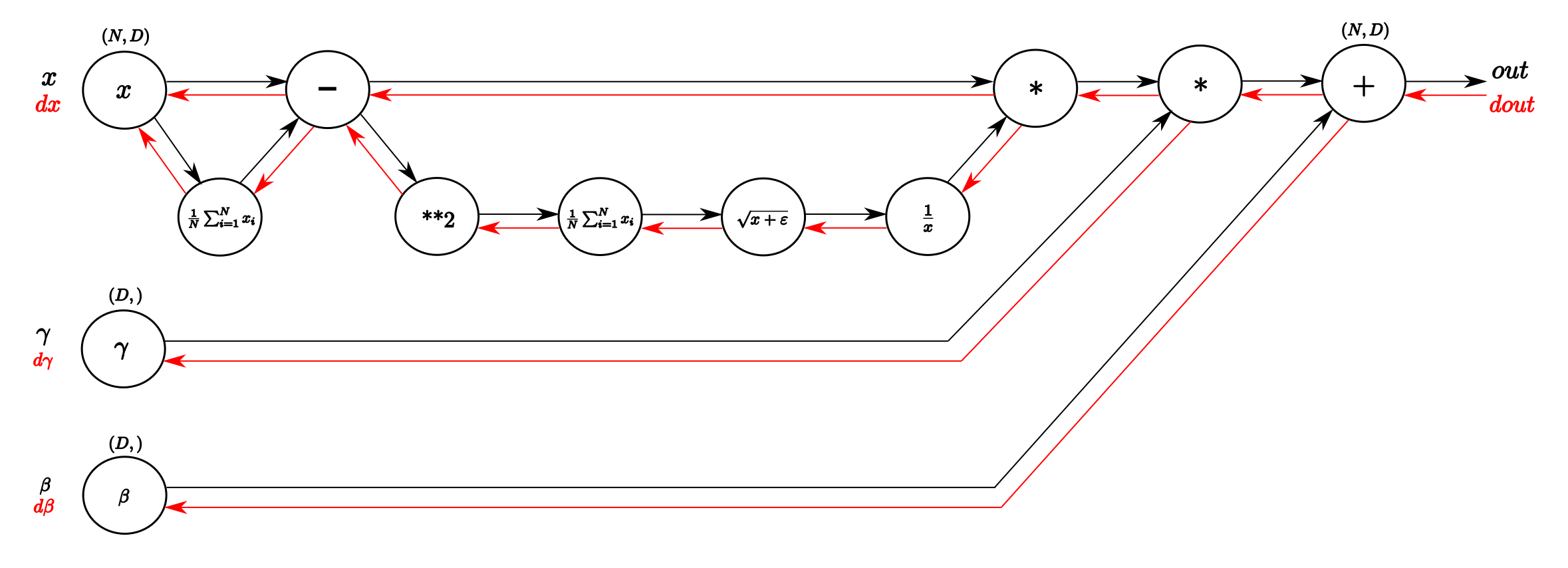
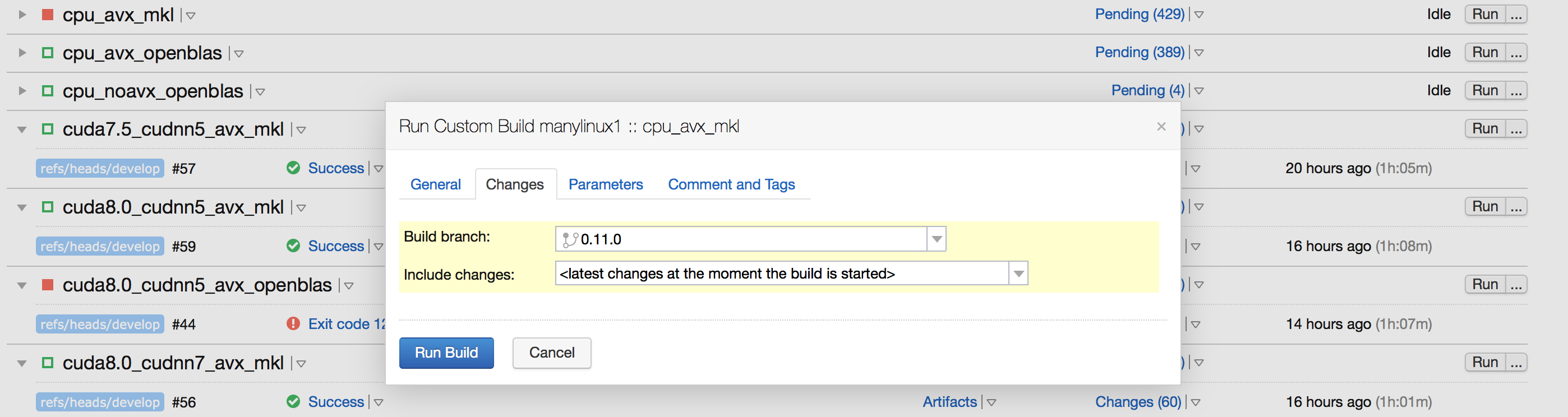
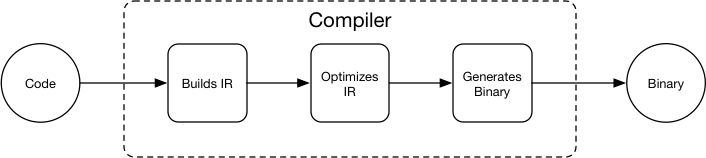
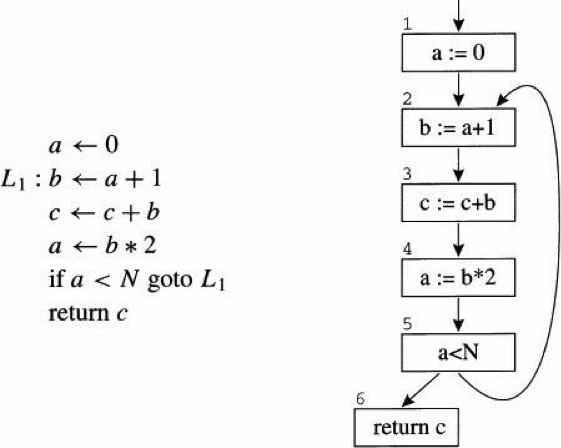
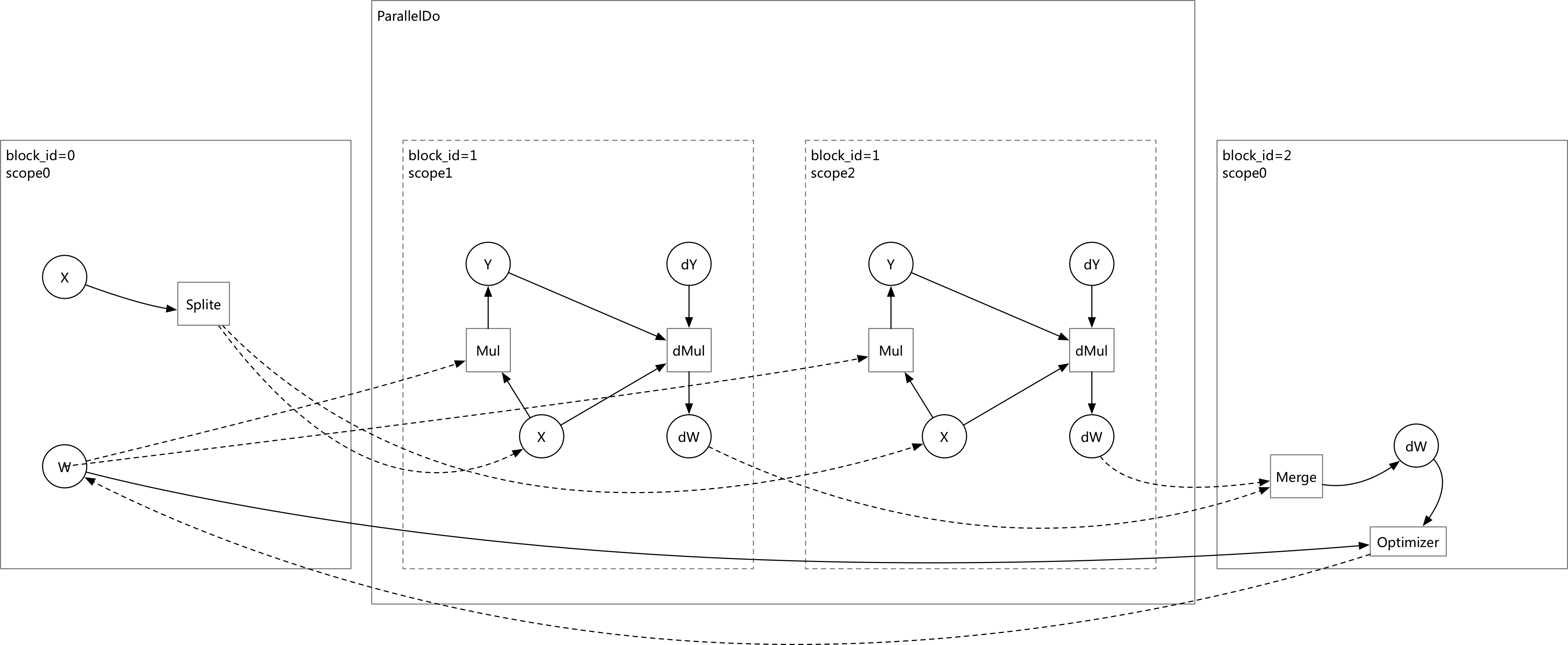
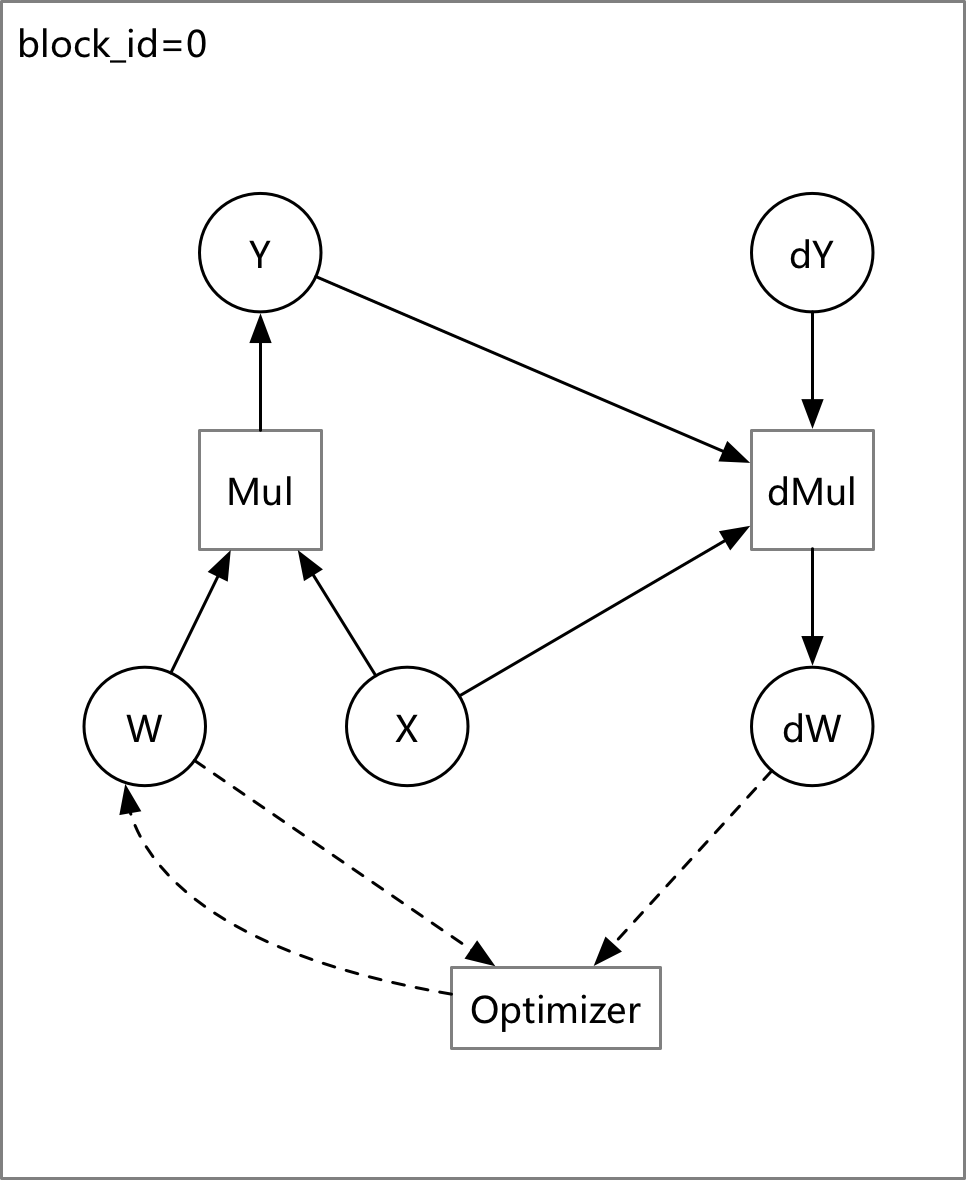
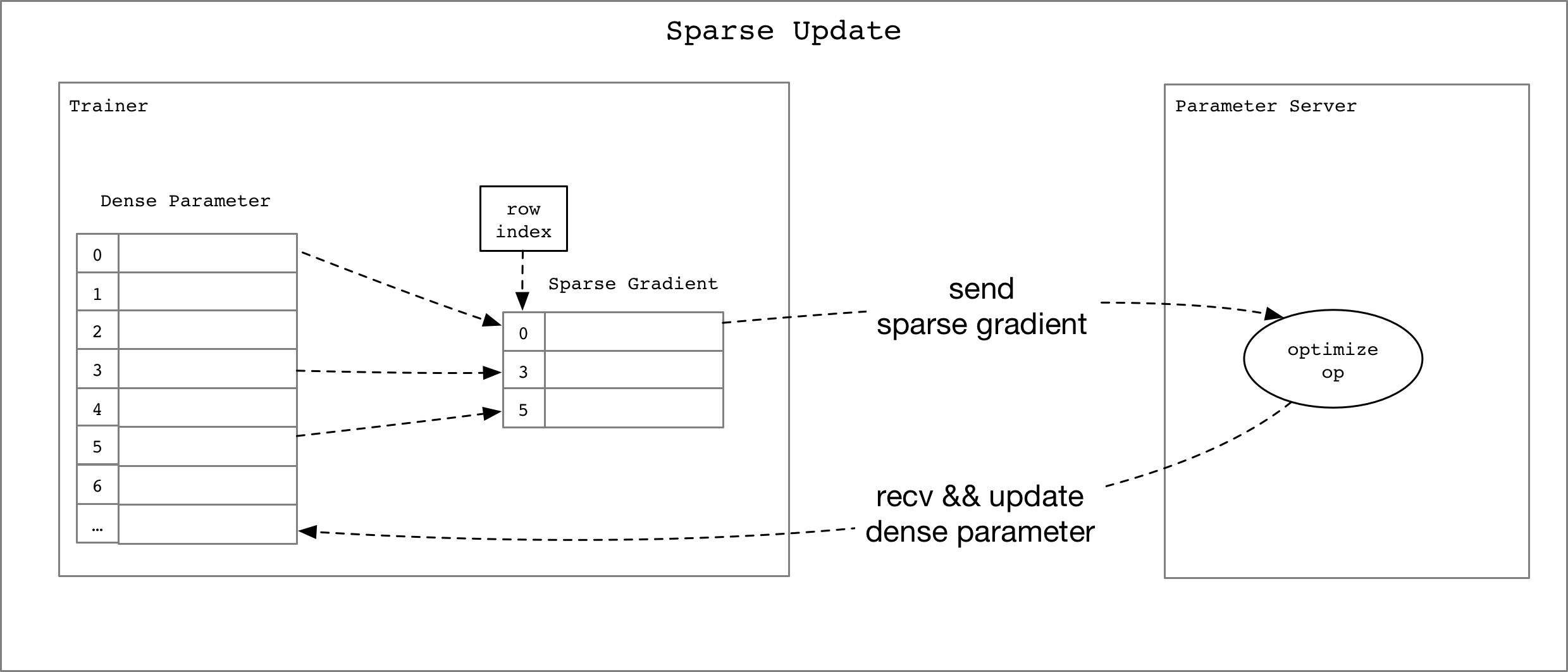
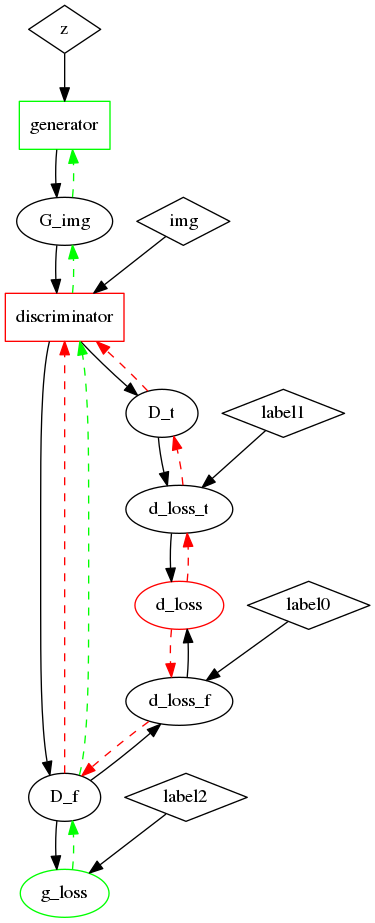
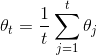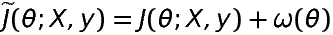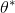Merge branch 'develop' into core_inference_prepare
Showing
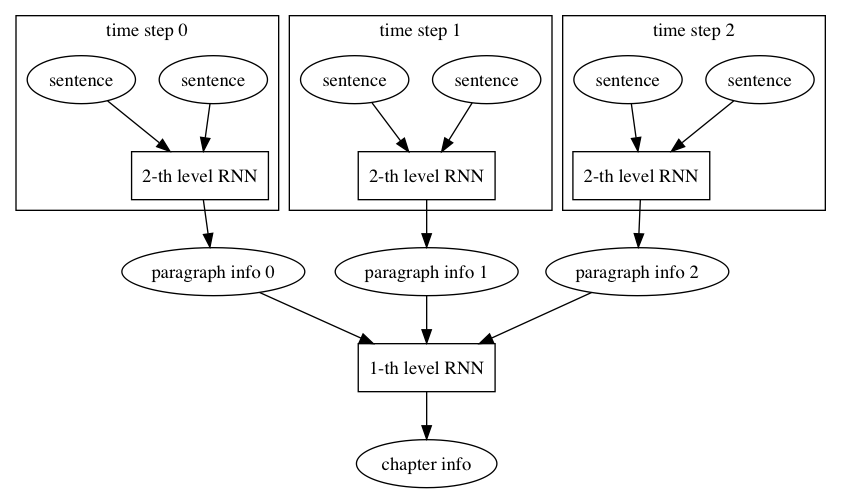
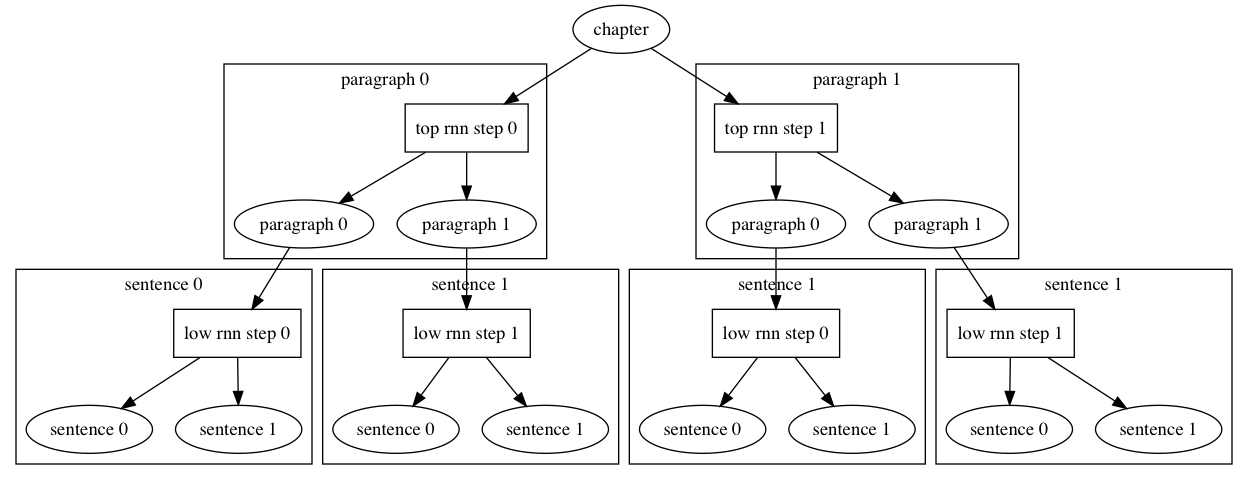
doc/fluid/images/2_level_rnn.dot
0 → 100644
doc/fluid/images/2_level_rnn.png
0 → 100644
51.4 KB
61.2 KB
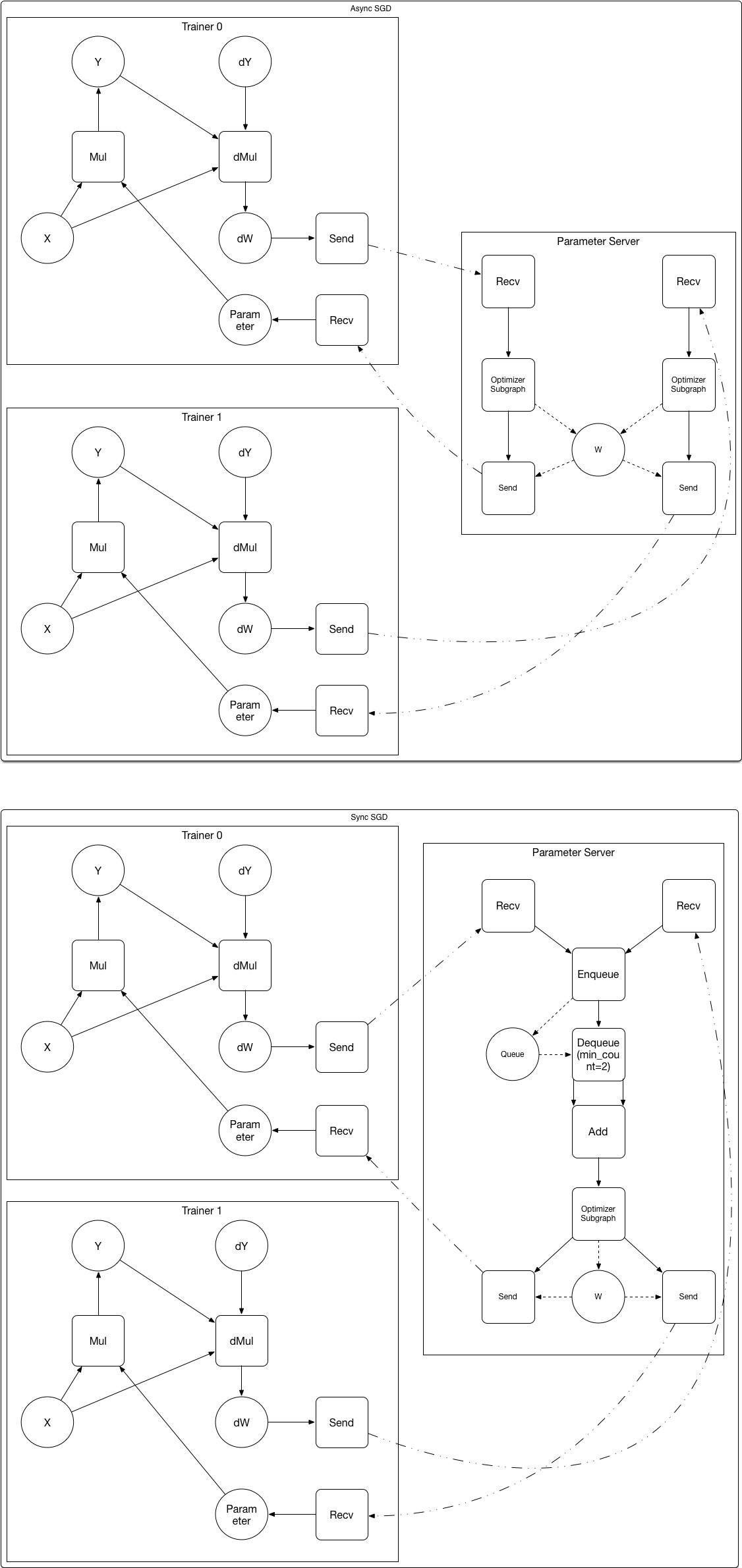
doc/fluid/images/asgd.gif
0 → 100644
620 字节
23.3 KB
161.3 KB
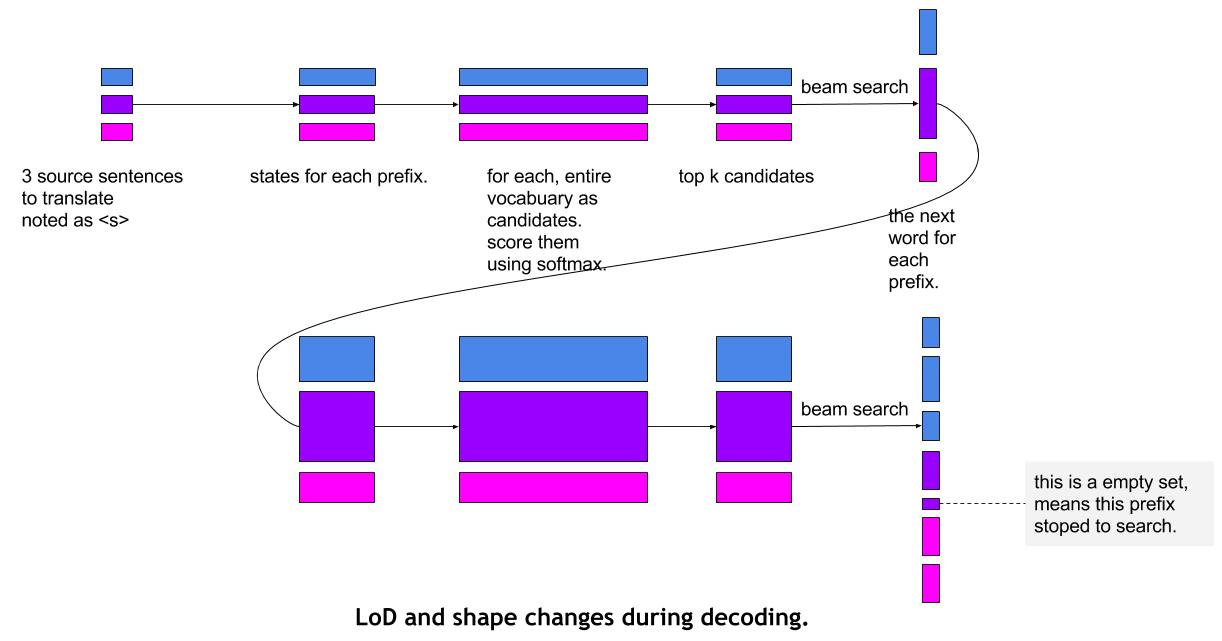
doc/fluid/images/beam_search.png
0 → 100644
463.6 KB
doc/fluid/images/ci_build_whl.png
0 → 100644
280.4 KB
doc/fluid/images/compiler.graffle
0 → 100644
文件已添加
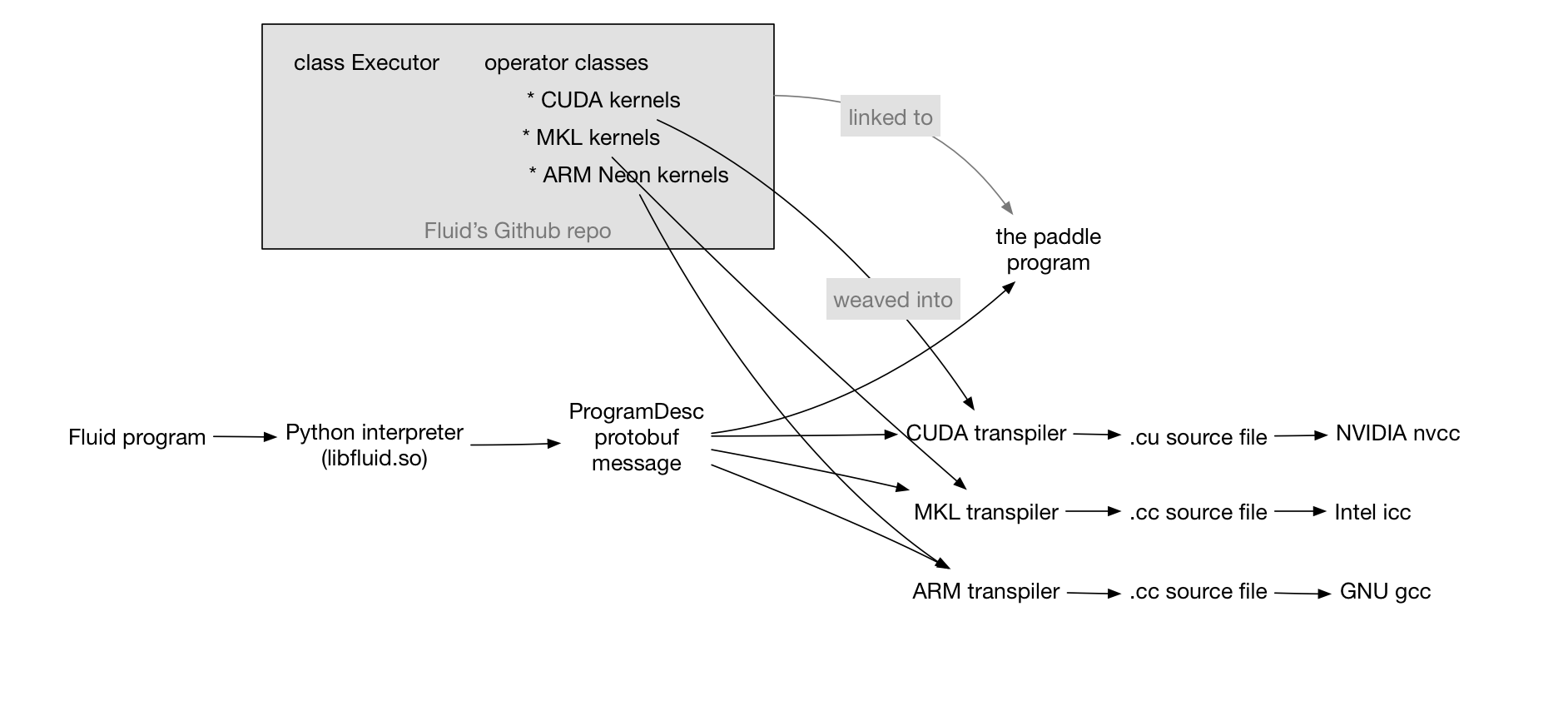
doc/fluid/images/compiler.png
0 → 100644
15.5 KB
83.3 KB
22.5 KB
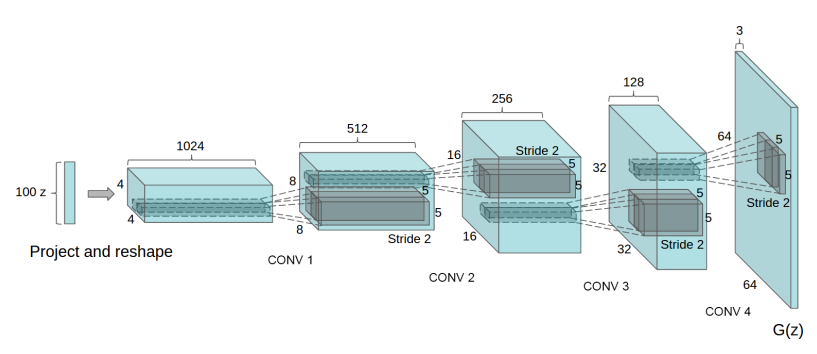
doc/fluid/images/dcgan.png
0 → 100644
56.6 KB
39.7 KB
文件已添加
doc/fluid/images/dist-graph.png
0 → 100644
222.2 KB
文件已添加
189.2 KB
doc/fluid/images/ds2_network.png
0 → 100644
113.8 KB
doc/fluid/images/feed_forward.png
0 → 100644
31.5 KB
45.0 KB
文件已添加
121.2 KB
56.2 KB
48.9 KB
30.1 KB
1.1 KB
989 字节
文件已添加
doc/fluid/images/local-graph.png
0 → 100644
27.9 KB
文件已添加
102.5 KB
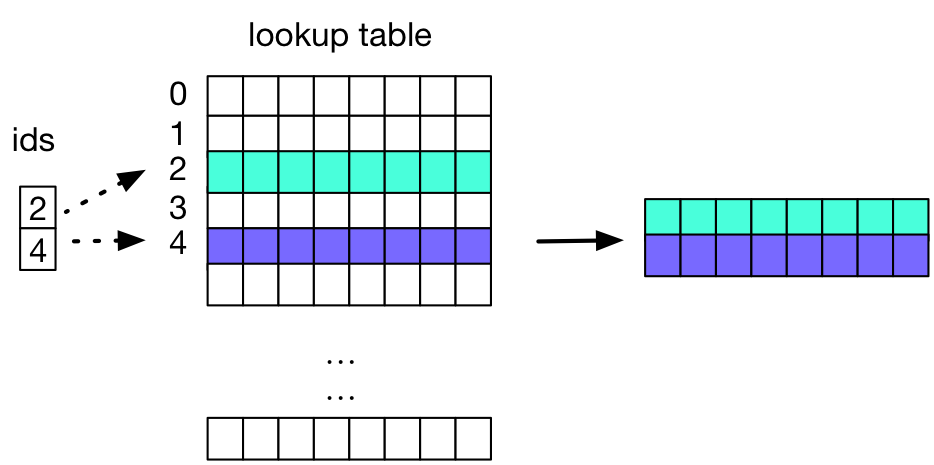
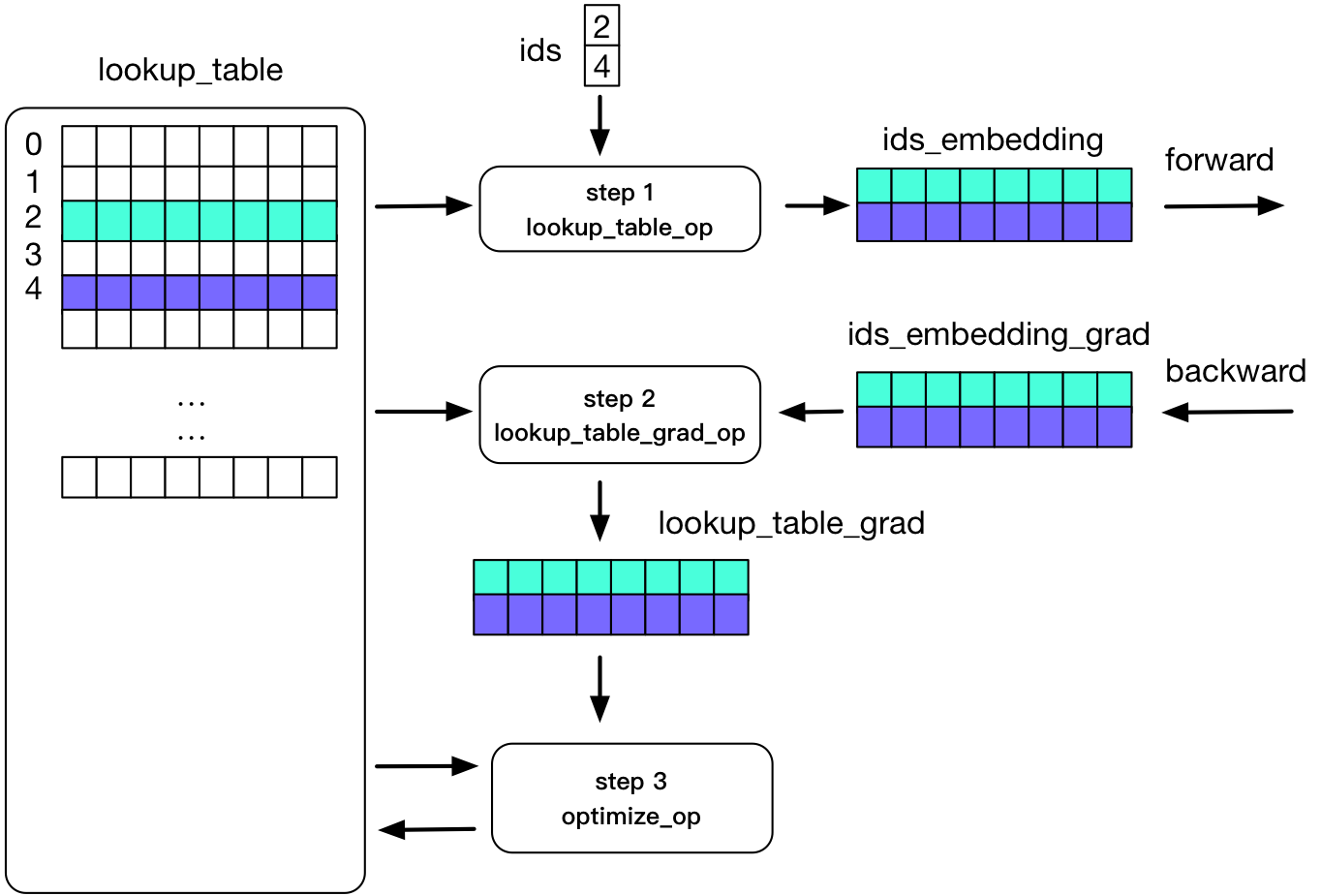
doc/fluid/images/lookup_table.png
0 → 100644
23.7 KB
88.3 KB
1.6 KB
文件已添加
350.4 KB
文件已添加
108.4 KB
文件已添加
32.8 KB
160.0 KB
文件已添加
19.7 KB
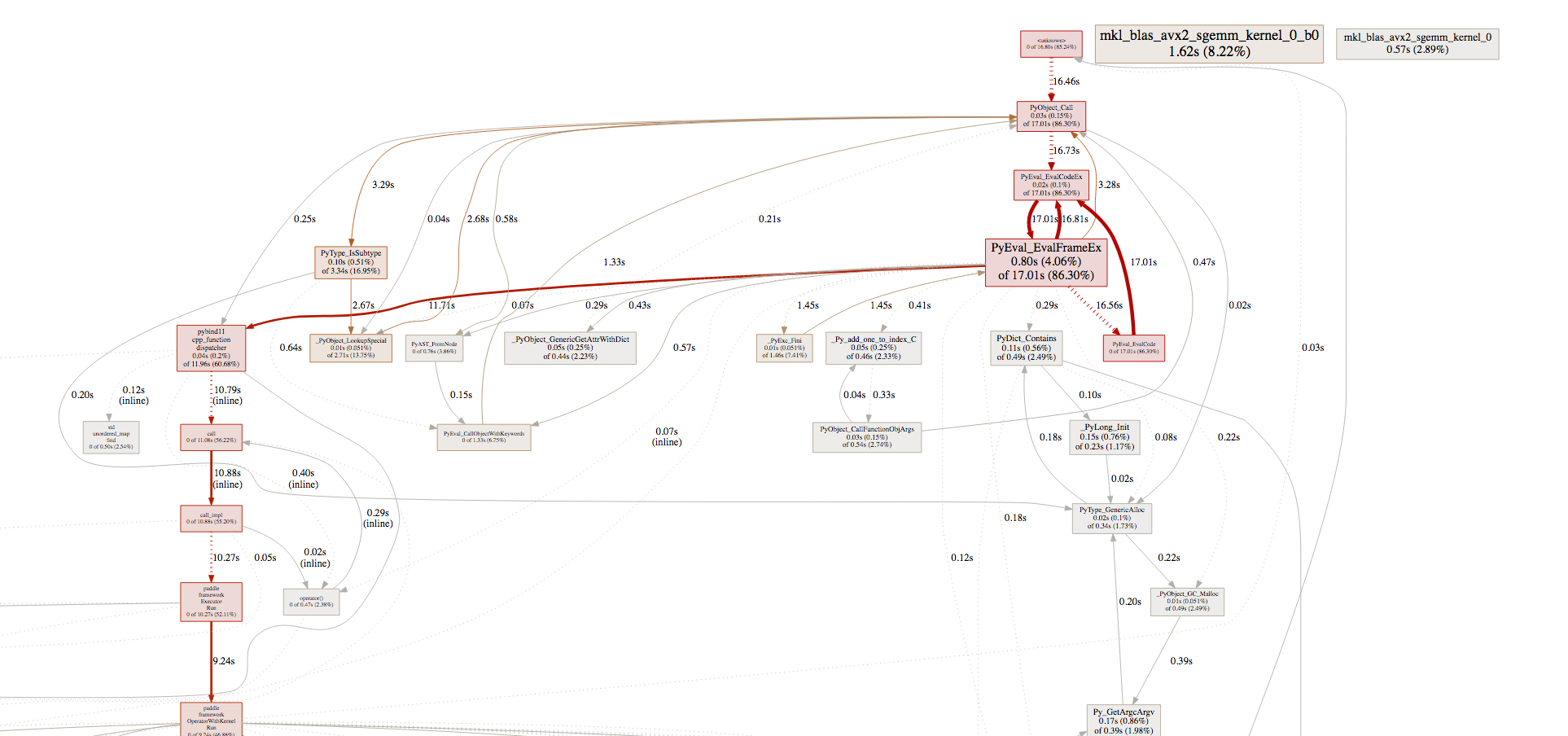
doc/fluid/images/pprof_1.png
0 → 100644
344.4 KB
doc/fluid/images/pprof_2.png
0 → 100644
189.5 KB
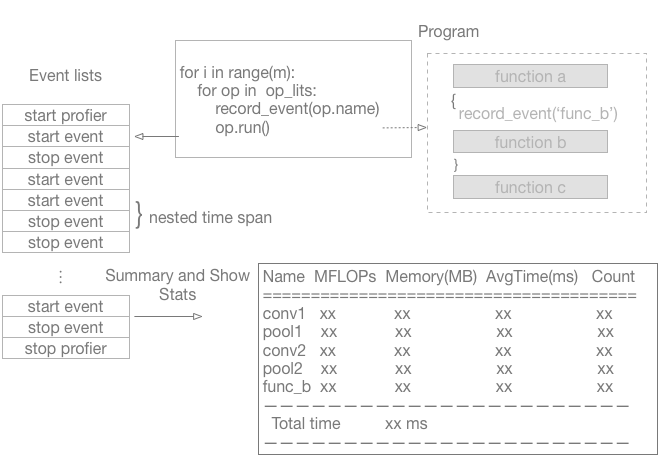
doc/fluid/images/profiler.png
0 → 100644
49.9 KB
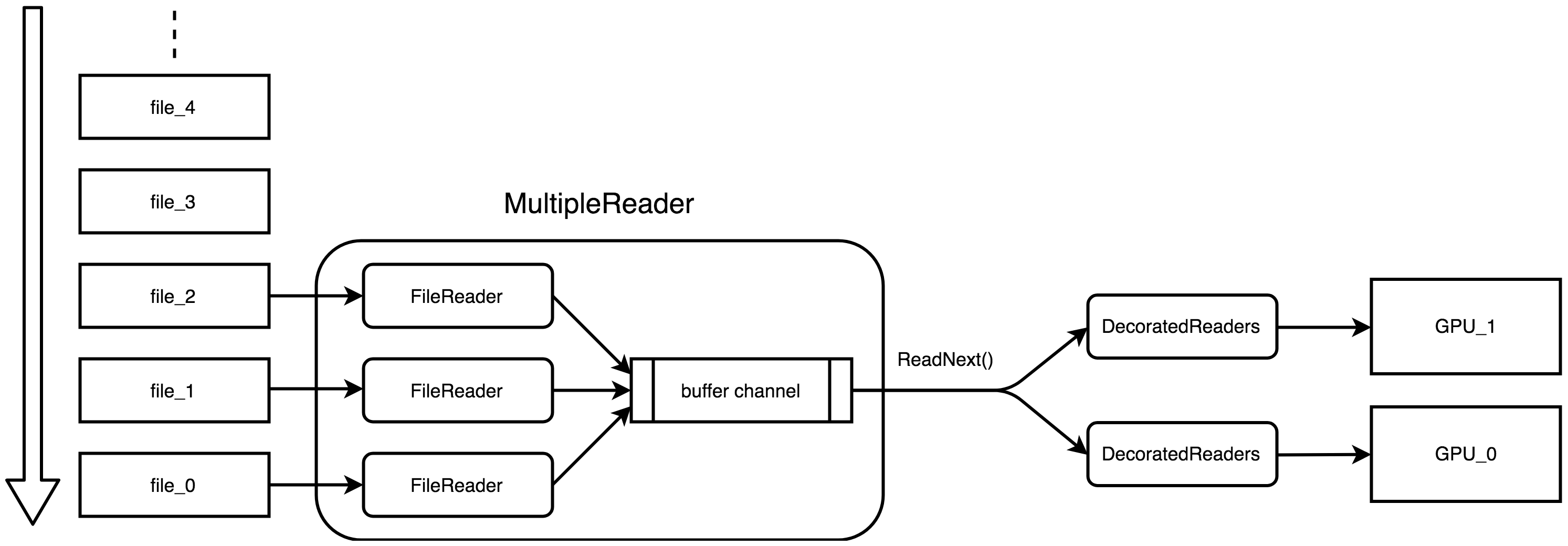
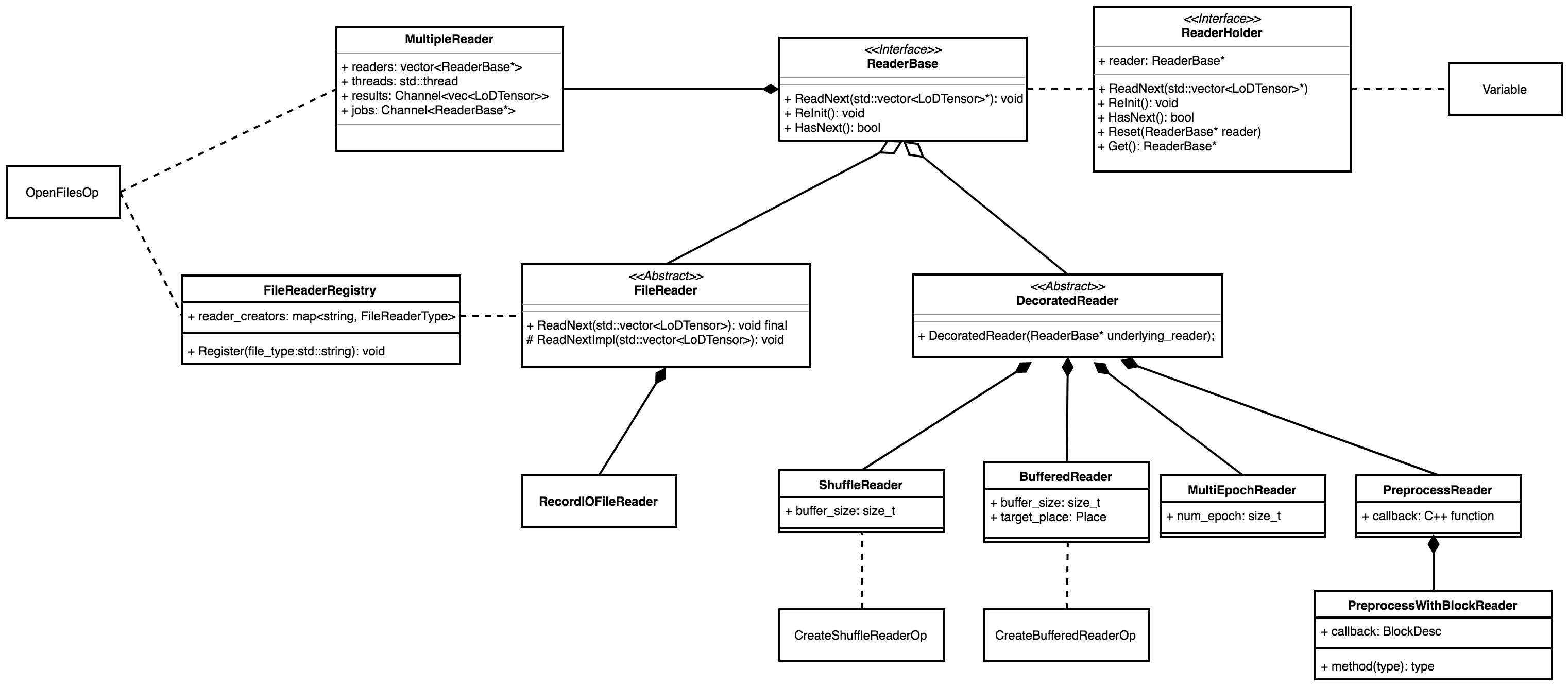
doc/fluid/images/readers.png
0 → 100644
347.4 KB
文件已添加
118.0 KB
doc/fluid/images/rnn.dot
0 → 100644
doc/fluid/images/rnn.jpg
0 → 100644
43.3 KB
doc/fluid/images/rnn.png
0 → 100644
180.8 KB
67.3 KB
76.3 KB
文件已添加
119.7 KB
doc/fluid/images/test.dot
0 → 100644
doc/fluid/images/test.dot.png
0 → 100644
57.6 KB
doc/fluid/images/theta_star.gif
0 → 100644
156 字节
doc/fluid/images/timeline.jpeg
0 → 100644
此差异已折叠。
doc/fluid/images/tracing.jpeg
0 → 100644
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
paddle/fluid/operators/fc_op.cc
0 → 100644
此差异已折叠。
paddle/fluid/operators/fc_op.h
0 → 100644
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。
此差异已折叠。