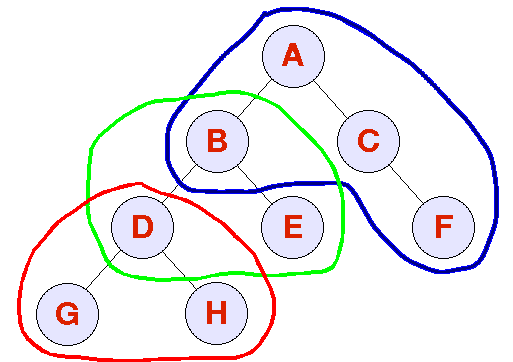
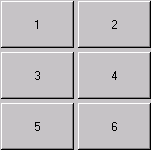
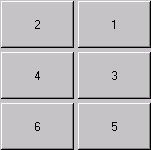
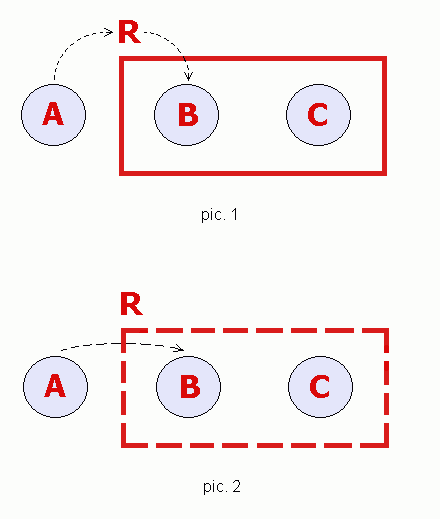
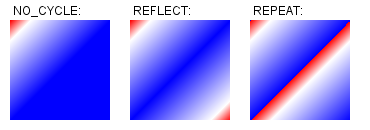
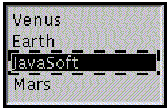
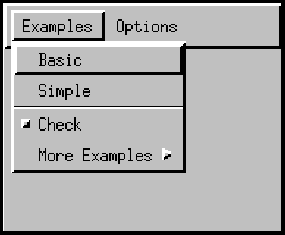
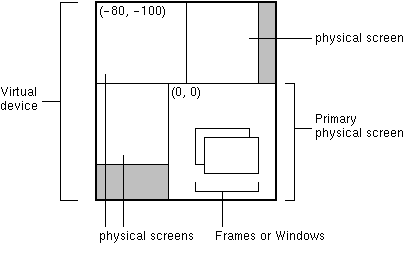
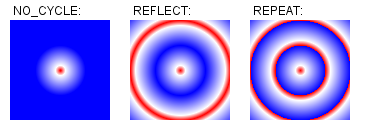
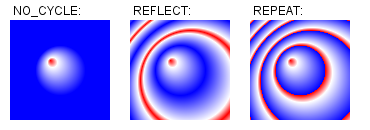
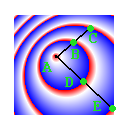
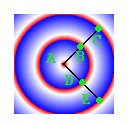
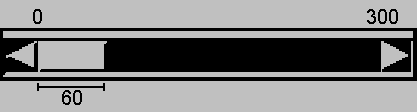
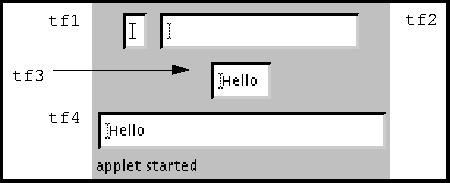
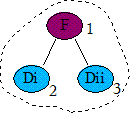
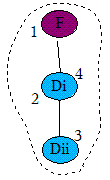
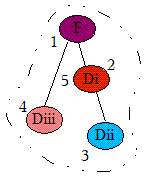
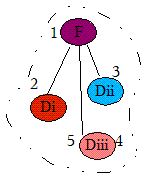
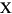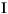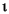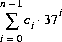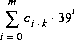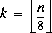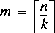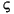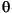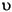fix:添加重写
Showing
2.7 KB
1.9 KB
2.3 KB
712 字节
486 字节
1.9 KB
6.8 KB
290 字节
2.5 KB
2.5 KB
1.7 KB
1.7 KB
819 字节
3.3 KB
4.1 KB
2.2 KB
3.1 KB
21.4 KB
24.9 KB
14.1 KB
968 字节
1.9 KB
2.2 KB
2.5 KB
2.1 KB
2.3 KB
2.8 KB
2.8 KB
144 字节
111 字节
131 字节
153 字节
140 字节
145 字节
112 字节
206 字节
220 字节
187 字节
191 字节
135 字节
144 字节
133 字节