fix
Showing
fluid/faster_rcnn/README.md
0 → 100644
fluid/faster_rcnn/README_cn.md
0 → 100644
40.6 KB
84.6 KB
104.2 KB
45.9 KB
27.1 KB
fluid/faster_rcnn/image/mAP.jpg
0 → 100644
80.0 KB
42.4 KB

40.6 KB

84.6 KB
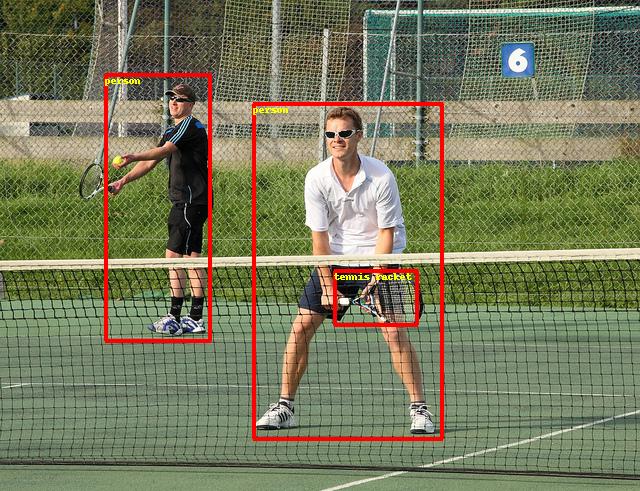
104.2 KB

45.9 KB
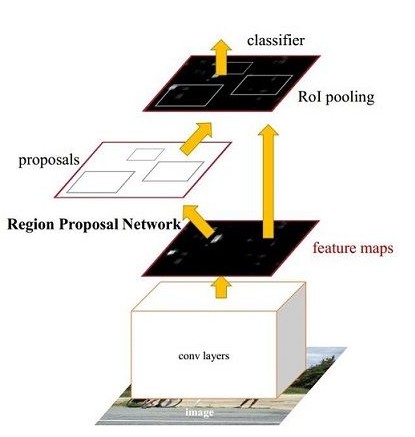
27.1 KB
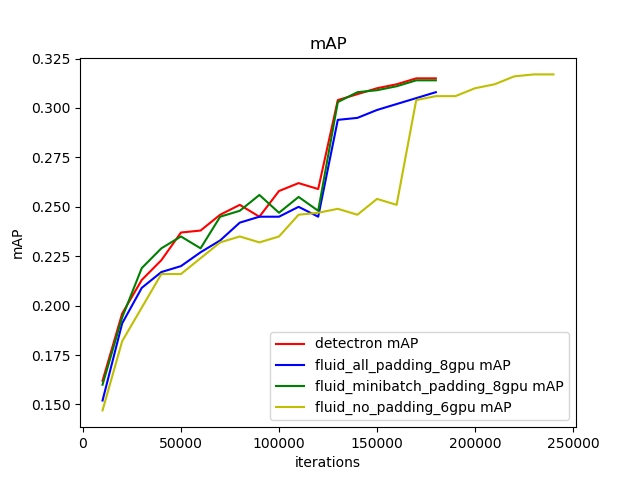
80.0 KB

42.4 KB
