From f5f9dee4e7f01aae639cb4290476963b9aca462d Mon Sep 17 00:00:00 2001
From: Steffy-zxf <48793257+Steffy-zxf@users.noreply.github.com>
Date: Fri, 11 Dec 2020 21:30:29 +0800
Subject: [PATCH] Add Sentence Transformer for text matching and Add readme
(#5004)
* update docs
* add sbert
* add readme
* update readme
* update codes
---
.../pretrained_models/README.md | 28 +-
.../pretrained_models/train.py | 4 +-
.../text_classification/rnn/README.md | 83 ++--
PaddleNLP/examples/text_matching/README.md | 30 +-
.../sentence_transformers/README.md | 207 ++++++++++
.../sentence_transformers/model.py | 71 ++++
.../sentence_transformers/predict.py | 227 +++++++++++
.../sentence_transformers/train.py | 370 ++++++++++++++++++
.../examples/text_matching/simnet/README.md | 168 ++++++++
.../examples/text_matching/simnet/predict.py | 2 +-
.../examples/text_matching/simnet/train.py | 8 +-
11 files changed, 1130 insertions(+), 68 deletions(-)
create mode 100644 PaddleNLP/examples/text_matching/sentence_transformers/README.md
create mode 100644 PaddleNLP/examples/text_matching/sentence_transformers/model.py
create mode 100644 PaddleNLP/examples/text_matching/sentence_transformers/predict.py
create mode 100644 PaddleNLP/examples/text_matching/sentence_transformers/train.py
create mode 100644 PaddleNLP/examples/text_matching/simnet/README.md
diff --git a/PaddleNLP/examples/text_classification/pretrained_models/README.md b/PaddleNLP/examples/text_classification/pretrained_models/README.md
index 3f75f6a2..efdb0f8f 100644
--- a/PaddleNLP/examples/text_classification/pretrained_models/README.md
+++ b/PaddleNLP/examples/text_classification/pretrained_models/README.md
@@ -11,9 +11,11 @@
本项目针对中文文本分类问题,开源了一系列模型,供用户可配置地使用:
+ BERT([Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers](https://arxiv.org/abs/1810.04805))中文模型,简写`bert-base-chinese`, 其由12层Transformer网络组成。
-+ ERNIE([Enhanced Representation through Knowledge Integration](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1904.09223)),支持ERNIE 1.0中文模型(简写`ernie`)和ERNIE Tiny中文模型(简写`ernie_tiny`)。
++ ERNIE([Enhanced Representation through Knowledge Integration](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1904.09223)),支持ERNIE 1.0中文模型(简写`ernie-1.0`)和ERNIE Tiny中文模型(简写`ernie_tiny`)。
其中`ernie`由12层Transformer网络组成,`ernie_tiny`由3层Transformer网络组成。
+ RoBERTa([A Robustly Optimized BERT Pretraining Approach](https://arxiv.org/abs/1907.11692)),支持24层Transformer网络的`roberta-wwm-ext-large`和12层Transformer网络的`roberta-wwm-ext`。
++ Electra([ELECTRA: Pre-training Text Encoders as Discriminators Rather Than Generators](https://arxiv.org/abs/2003.10555)), 支持hidden_size=256的`chinese-electra-discriminator-small`和
+ hidden_size=768的`chinese-electra-discriminator-base`
| 模型 | dev acc | test acc |
| ---- | ------- | -------- |
@@ -63,24 +65,24 @@ pretrained_models/
我们以中文情感分类公开数据集ChnSentiCorp为示例数据集,可以运行下面的命令,在训练集(train.tsv)上进行模型训练,并在开发集(dev.tsv)验证
```shell
# 设置使用的GPU卡号
-export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0
+CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0
python train.py --model_type ernie --model_name ernie_tiny --n_gpu 1 --save_dir ./checkpoints
```
可支持配置的参数:
-* model_type:必选,模型类型,可以选择bert,ernie,roberta。
-* model_name: 必选,具体的模型简称。如`model_type=ernie`,则model_name可以选择`ernie`和`ernie_tiny`。`model_type=bert`,则model_name可以选择`bert-base-chinese`。
+* `model_type`:必选,模型类型,可以选择bert,ernie,roberta。
+* `model_name`: 必选,具体的模型简称。如`model_type=ernie`,则model_name可以选择`ernie`和`ernie_tiny`。`model_type=bert`,则model_name可以选择`bert-base-chinese`。
`model_type=roberta`,则model_name可以选择`roberta-wwm-ext-large`和`roberta-wwm-ext`。
-* save_dir:必选,保存训练模型的目录。
-* max_seq_length:可选,ERNIE/BERT模型使用的最大序列长度,最大不能超过512, 若出现显存不足,请适当调低这一参数;默认为128。
-* batch_size:可选,批处理大小,请结合显存情况进行调整,若出现显存不足,请适当调低这一参数;默认为32。
-* learning_rate:可选,Fine-tune的最大学习率;默认为5e-5。
-* weight_decay:可选,控制正则项力度的参数,用于防止过拟合,默认为0.00。
-* warmup_proption:可选,学习率warmup策略的比例,如果0.1,则学习率会在前10%训练step的过程中从0慢慢增长到learning_rate, 而后再缓慢衰减,默认为0.1。
-* init_from_ckpt:可选,模型参数路径,热启动模型训练;默认为None。
-* seed:可选,随机种子,默认为1000.
-* n_gpu:可选,训练过程中使用GPU卡数量,默认为1。若n_gpu=0,则使用CPU训练。
+* `save_dir`:必选,保存训练模型的目录。
+* `max_seq_length`:可选,ERNIE/BERT模型使用的最大序列长度,最大不能超过512, 若出现显存不足,请适当调低这一参数;默认为128。
+* `batch_size`:可选,批处理大小,请结合显存情况进行调整,若出现显存不足,请适当调低这一参数;默认为32。
+* `learning_rate`:可选,Fine-tune的最大学习率;默认为5e-5。
+* `weight_decay`:可选,控制正则项力度的参数,用于防止过拟合,默认为0.00。
+* `warmup_proption`:可选,学习率warmup策略的比例,如果0.1,则学习率会在前10%训练step的过程中从0慢慢增长到learning_rate, 而后再缓慢衰减,默认为0.1。
+* `init_from_ckpt`:可选,模型参数路径,热启动模型训练;默认为None。
+* `seed`:可选,随机种子,默认为1000.
+* `n_gpu`:可选,训练过程中使用GPU卡数量,默认为1。若n_gpu=0,则使用CPU训练。
程序运行时将会自动进行训练,评估,测试。同时训练过程中会自动保存模型在指定的`save_dir`中。
diff --git a/PaddleNLP/examples/text_classification/pretrained_models/train.py b/PaddleNLP/examples/text_classification/pretrained_models/train.py
index 2a590b9a..33cf2211 100644
--- a/PaddleNLP/examples/text_classification/pretrained_models/train.py
+++ b/PaddleNLP/examples/text_classification/pretrained_models/train.py
@@ -94,7 +94,7 @@ def parse_args():
help="Total number of training epochs to perform.")
parser.add_argument(
"--warmup_proption",
- default=0.1,
+ default=0.0,
type=float,
help="Linear warmup proption over the training process.")
parser.add_argument(
@@ -304,7 +304,7 @@ def do_train(args):
])
criterion = paddle.nn.loss.CrossEntropyLoss()
- metric = paddle.metric.Accuracy(name='acc_accumulation')
+ metric = paddle.metric.Accuracy()
global_step = 0
tic_train = time.time()
diff --git a/PaddleNLP/examples/text_classification/rnn/README.md b/PaddleNLP/examples/text_classification/rnn/README.md
index b8fd860e..0eac7ee4 100644
--- a/PaddleNLP/examples/text_classification/rnn/README.md
+++ b/PaddleNLP/examples/text_classification/rnn/README.md
@@ -28,15 +28,6 @@
| Bi-LSTM Attention | 序列模型,在双向LSTM结构之上加入Attention机制,结合上下文更好地表征句子语义特征 |
| TextCNN | 序列模型,使用多种卷积核大小,提取局部区域地特征 |
-+ BOW(Bag Of Words)模型,是一个非序列模型,使用基本的全连接结构;
-+ RNN (Recurrent Neural Network),序列模型,能够有效地处理序列信息;
-+ GRU(Gated Recurrent Unit),序列模型,能够较好地解决序列文本中长距离依赖的问题;
-+ LSTM(Long Short Term Memory),序列模型,能够较好地解决序列文本中长距离依赖的问题;
-+ Bi-LSTM(Bidirectional Long Short Term Memory),序列模型,采用双向LSTM结构,更好地捕获句子中的语义特征;
-+ Bi-GRU(Bidirectional Gated Recurrent Unit),序列模型,采用双向GRU结构,更好地捕获句子中的语义特征;
-+ Bi-RNN(Bidirectional Recurrent Neural Network),序列模型,采用双向RNN结构,更好地捕获句子中的语义特征;
-+ Bi-LSTM Attention, 序列模型,在双向LSTM结构之上加入Attention机制,结合上下文更好地表征句子语义特征;
-+ TextCNN, 序列模型,使用多种卷积核大小,提取局部区域地特征;
| 模型 | dev acc | test acc |
| ---- | ------- | -------- |
@@ -73,11 +64,10 @@
```text
.
-├── config.py # 运行配置文件
├── data.py # 数据读取
-├── train.py # 训练模型主程序入口,包括训练、评估
├── predict.py # 模型预测
-├── model.py # 模型组网
+├── utils.py # 数据处理工具
+├── train.py # 训练模型主程序入口,包括训练、评估
└── README.md # 文档说明
```
@@ -86,9 +76,9 @@
#### 使用PaddleNLP内置数据集
```python
-train_dataset = ppnlp.datasets.ChnSentiCorp('train')
-dev_dataset = ppnlp.datasets.ChnSentiCorp('dev')
-test_dataset = ppnlp.datasets.ChnSentiCorp('test')
+from paddlenlp.datasets import ChnSentiCorp
+
+train_ds, dev_ds, test_ds = ChnSentiCorp.get_datasets(['train', 'dev', 'test'])
```
#### 自定义数据集
@@ -100,29 +90,33 @@ test_dataset = ppnlp.datasets.ChnSentiCorp('test')
在模型训练之前,需要先下载词汇表文件word_dict.txt,用于构造词-id映射关系。
```shell
-wget https://paddlenlp.bj.bcebos.com/data/word_dict.txt
+wget https://paddlenlp.bj.bcebos.com/data/senta_word_dict.txt
```
我们以中文情感分类公开数据集ChnSentiCorp为示例数据集,可以运行下面的命令,在训练集(train.tsv)上进行模型训练,并在开发集(dev.tsv)验证
+
+CPU 启动:
+
```shell
-# CPU启动
-python train.py --vocab_path='./word_dict.txt' --use_gpu=False --network_name=bilstm --lr=5e-4 --batch_size=64 --epochs=5 --save_dir='./checkpoints'
+python train.py --vocab_path='./senta_word_dict.txt' --use_gpu=False --network_name=bilstm --lr=5e-4 --batch_size=64 --epochs=5 --save_dir='./checkpoints'
+```
-# GPU启动
-# CUDA_VSIBLE_DEVICES指定想要利用的GPU卡号,可以是单卡,也可以多卡
-# CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1 python -m paddle.distributed.launch train.py --vocab_path='./word_dict.txt' --use_gpu=True --network_name=bilstm --lr=5e-4 --batch_size=64 --epochs=5 --save_dir='./checkpoints'
+GPU 启动:
+
+```shell
+# CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python train.py --vocab_path='./senta_word_dict.txt' --use_gpu=True --network_name=bilstm --lr=5e-4 --batch_size=64 --epochs=5 --save_dir='./checkpoints'
```
以上参数表示:
-* vocab_path: 词汇表文件路径。
-* use_gpu: 是否使用GPU进行训练, 默认为`False`。
-* network_name: 模型网络名称,默认为`bilstm_attn`, 可更换为bilstm, bigru, birnn,bow,lstm,rnn,gru,bilstm_attn,textcnn等。
-* lr: 学习率, 默认为5e-4。
-* batch_size: 运行一个batch大小,默认为64。
-* epochs: 训练轮次,默认为5。
-* save_dir: 训练保存模型的文件路径。
-* init_from_ckpt: 恢复模型训练的断点路径。
+* `vocab_path`: 词汇表文件路径。
+* `use_gpu`: 是否使用GPU进行训练, 默认为`False`。
+* `network_name`: 模型网络名称,默认为`bilstm_attn`, 可更换为bilstm, bigru, birnn,bow,lstm,rnn,gru,bilstm_attn,textcnn等。
+* `lr`: 学习率, 默认为5e-4。
+* `batch_size`: 运行一个batch大小,默认为64。
+* `epochs`: 训练轮次,默认为5。
+* `save_dir`: 训练保存模型的文件路径。
+* `init_from_ckpt`: 恢复模型训练的断点路径。
程序运行时将会自动进行训练,评估,测试。同时训练过程中会自动保存模型在指定的`save_dir`中。
@@ -142,21 +136,25 @@ checkpoints/
### 模型预测
启动预测:
+
+CPU启动:
+
```shell
-# CPU启动
-python predict.py --vocab_path='./word_dict.txt' --use_gpu=False --network_name=bilstm --params_path=checkpoints/final.pdparams
+python predict.py --vocab_path='./senta_word_dict.txt' --use_gpu=False --network_name=bilstm --params_path=checkpoints/final.pdparams
+```
+
+GPU启动:
-# GPU启动
-# CUDA_VSIBLE_DEVICES指定想要利用的GPU卡号,可以是单卡,也可以多卡
-# CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python predict.py --vocab_path='./word_dict.txt' --use_gpu=True --network_name=bilstm --params_path='./checkpoints/final.pdparams'
+```shell
+CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python predict.py --vocab_path='./senta_word_dict.txt' --use_gpu=True --network_name=bilstm --params_path='./checkpoints/final.pdparams'
```
将待预测数据分词完毕后,如以下示例:
```text
-这个 宾馆 比较 陈旧 了 , 特价 的 房间 也 很一般 。 总体来说 一般
-怀着 十分 激动 的 心情 放映 , 可是 看着 看着 发现 , 在 放映 完毕 后 , 出现 一集米 老鼠 的 动画片 !
-作为 老 的 四星酒店 , 房间 依然 很 整洁 , 相当 不错 。 机场 接机 服务 很好 , 可以 在 车上 办理 入住 手续 , 节省 时间 。
+这个宾馆比较陈旧了,特价的房间也很一般。总体来说一般
+怀着十分激动的心情放映,可是看着看着发现,在放映完毕后,出现一集米老鼠的动画片
+作为老的四星酒店,房间依然很整洁,相当不错。机场接机服务很好,可以在车上办理入住手续,节省时间。
```
处理成模型所需的`Tensor`,如可以直接调用`preprocess_prediction_data`函数既可处理完毕。之后传入`predict`函数即可输出预测结果。
@@ -164,12 +162,7 @@ python predict.py --vocab_path='./word_dict.txt' --use_gpu=False --network_name=
如
```text
-Data: 这个 宾馆 比较 陈旧 了 , 特价 的 房间 也 很一般 。 总体来说 一般 Lable: negative
-Data: 怀着 十分 激动 的 心情 放映 , 可是 看着 看着 发现 , 在 放映 完毕 后 , 出现 一集米 老鼠 的 动画片 ! Lable: negative
-Data: 作为 老 的 四星酒店 , 房间 依然 很 整洁 , 相当 不错 。 机场 接机 服务 很好 , 可以 在 车上 办理 入住 手续 , 节省 时间 。 Lable: positive
+Data: 这个宾馆比较陈旧了,特价的房间也很一般。总体来说一般 Lable: negative
+Data: 怀着十分激动的心情放映,可是看着看着发现,在放映完毕后,出现一集米老鼠的动画片 Lable: negative
+Data: 作为老的四星酒店,房间依然很整洁,相当不错。机场接机服务很好,可以在车上办理入住手续,节省时间。 Lable: positive
```
-
-## 其他
-
-1、如何进行多分类?
-本项目采用二分类数据集,如需进行多分类任务,修改类别数目及类别标签列表即可。
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/PaddleNLP/examples/text_matching/README.md b/PaddleNLP/examples/text_matching/README.md
index d83d18bc..a875dcbc 100644
--- a/PaddleNLP/examples/text_matching/README.md
+++ b/PaddleNLP/examples/text_matching/README.md
@@ -1,5 +1,29 @@
-# Text Matching
+# Pointwise文本匹配
-## SimNet
+**文本匹配一直是自然语言处理(NLP)领域一个基础且重要的方向,一般研究两段文本之间的关系。文本相似度计算、自然语言推理、问答系统、信息检索等,都可以看作针对不同数据和场景的文本匹配应用。这些自然语言处理任务在很大程度上都可以抽象成文本匹配问题,比如信息检索可以归结为搜索词和文档资源的匹配,问答系统可以归结为问题和候选答案的匹配,复述问题可以归结为两个同义句的匹配,对话系统可以归结为前一句对话和回复的匹配,机器翻译则可以归结为两种语言的匹配。**
-## Sentence-BERT
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+文本匹配任务可以分为pointwise和pairwise类型。
+
+pointwise,每一个样本通常由两个文本组成(query,title)。类别形式为0或1,0表示query与title不匹配; 1表示匹配。
+pairwise,每一个样本通常由三个文本组成(query,positive_title, negative_title)。positive_title比negative_title更加匹配query。
+根据本数据集示例,该匹配任务为pointwise类型。
+
+该项目展示了使用传统的[SimNet](./simnet) 和 [SentenceBert](./sentence_bert)两种方法完成pointwise本匹配任务。
+
+## Conventional Models
+
+[SimNet](./simnet) 展示了如何使用CNN、LSTM、GRU等网络完成pointwise文本匹配任务。
+
+## Pretrained Model (PTMs)
+
+[Sentence Transformers](./sentence_transformers) 展示了如何使用以ERNIE为代表的模型Fine-tune完成pointwise文本匹配任务。
diff --git a/PaddleNLP/examples/text_matching/sentence_transformers/README.md b/PaddleNLP/examples/text_matching/sentence_transformers/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..5670563c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/PaddleNLP/examples/text_matching/sentence_transformers/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,207 @@
+# 使用预训练模型Fine-tune完成pointwise中文文本匹配任务
+
+随着深度学习的发展,模型参数的数量飞速增长。为了训练这些参数,需要更大的数据集来避免过拟合。然而,对于大部分NLP任务来说,构建大规模的标注数据集非常困难(成本过高),特别是对于句法和语义相关的任务。相比之下,大规模的未标注语料库的构建则相对容易。为了利用这些数据,我们可以先从其中学习到一个好的表示,再将这些表示应用到其他任务中。最近的研究表明,基于大规模未标注语料库的预训练模型(Pretrained Models, PTM) 在NLP任务上取得了很好的表现。
+
+近年来,大量的研究表明基于大型语料库的预训练模型(Pretrained Models, PTM)可以学习通用的语言表示,有利于下游NLP任务,同时能够避免从零开始训练模型。随着计算能力的发展,深度模型的出现(即 Transformer)和训练技巧的增强使得 PTM 不断发展,由浅变深。
+
+百度的预训练模型ERNIE经过海量的数据训练后,其特征抽取的工作已经做的非常好。借鉴迁移学习的思想,我们可以利用其在海量数据中学习的语义信息辅助小数据集(如本示例中的医疗文本数据集)上的任务。
+
+  +
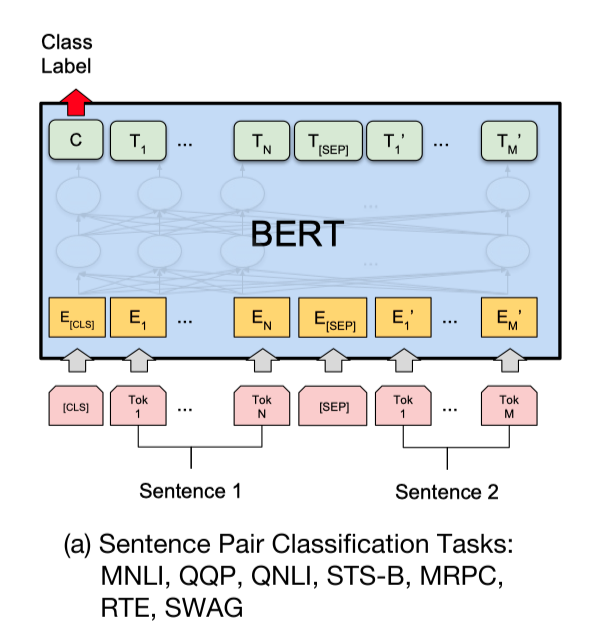
+使用预训练模型ERNIE完成pointwise文本匹配任务,大家可能会想到将query和title文本拼接,之后输入ERNIE中,取`CLS`特征(pooled_output),之后输出全连接层,进行二分类。如下图ERNIE用于句对分类任务的用法:
+
+
+
+使用预训练模型ERNIE完成pointwise文本匹配任务,大家可能会想到将query和title文本拼接,之后输入ERNIE中,取`CLS`特征(pooled_output),之后输出全连接层,进行二分类。如下图ERNIE用于句对分类任务的用法:
+
+
+
+
+
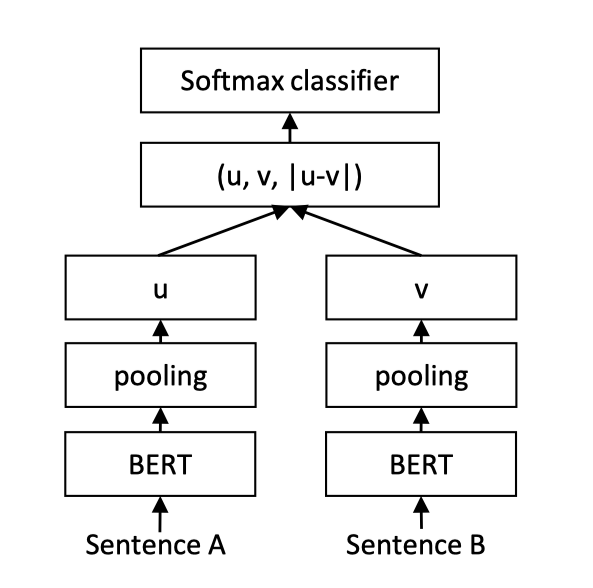
+然而,以上用法的问题在于,**ERNIE的模型参数非常庞大,导致计算量非常大,预测的速度也不够理想**。从而达不到线上业务的要求。针对该问题,可以使用PaddleNLP工具搭建Sentence Transformer网络。
+
+
+
+
+
+Sentence Transformer采用了双塔(Siamese)的网络结构。Query和Title分别输入ERNIE,共享一个ERNIE参数,得到各自的token embedding特征。之后对token embedding进行pooling(此处教程使用mean pooling操作),之后输出分别记作u,v。之后将三个表征(u,v,|u-v|)拼接起来,进行二分类。网络结构如上图所示。
+
+更多关于Sentence Transformer的信息可以参考论文:https://arxiv.org/abs/1908.10084
+
+**同时,不仅可以使用ERNIR作为文本语义特征提取器,可以利用BERT/RoBerta/Electra等模型作为文本语义特征提取器**
+
+**那么Sentence Transformer采用Siamese的网路结构,是如何提升预测速度呢?**
+
+**Siamese的网络结构好处在于query和title分别输入同一套网络。如在信息搜索任务中,此时就可以将数据库中的title文本提前计算好对应sequence_output特征,保存在数据库中。当用户搜索query时,只需计算query的sequence_output特征与保存在数据库中的title sequence_output特征,通过一个简单的mean_pooling和全连接层进行二分类即可。从而大幅提升预测效率,同时也保障了模型性能。**
+
+关于匹配任务常用的Siamese网络结构可以参考:https://blog.csdn.net/thriving_fcl/article/details/73730552
+
+PaddleNLP提供了丰富的预训练模型,并且可以便捷地获取PaddlePaddle生态下的所有预训练模型。下面展示如何使用PaddleNLP一键加载ERNIE,优化文本匹配任务。
+
+## 模型简介
+
+本项目针对中文文本匹配问题,开源了一系列模型,供用户可配置地使用:
+
++ BERT([Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers](https://arxiv.org/abs/1810.04805))中文模型,简写`bert-base-chinese`, 其由12层Transformer网络组成。
++ ERNIE([Enhanced Representation through Knowledge Integration](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1904.09223)),支持ERNIE 1.0中文模型(简写`ernie-1.0`)和ERNIE Tiny中文模型(简写`ernie_tiny`)。
+ 其中`ernie`由12层Transformer网络组成,`ernie_tiny`由3层Transformer网络组成。
++ RoBERTa([A Robustly Optimized BERT Pretraining Approach](https://arxiv.org/abs/1907.11692)),支持24层Transformer网络的`roberta-wwm-ext-large`和12层Transformer网络的`roberta-wwm-ext`。
++ Electra([ELECTRA: Pre-training Text Encoders as Discriminators Rather Than Generators](https://arxiv.org/abs/2003.10555)), 支持hidden_size=256的`chinese-electra-discriminator-small`和
+ hidden_size=768的`chinese-electra-discriminator-base`
+
+## TODO 增加模型效果
+| 模型 | dev acc | test acc |
+| ---- | ------- | -------- |
+| bert-base-chinese | | |
+| bert-wwm-chinese | | |
+| bert-wwm-ext-chinese | | |
+| ernie | | |
+| ernie-tiny | | |
+| roberta-wwm-ext | | |
+| roberta-wwm-ext-large | | |
+| rbt3 | | |
+| rbtl3 | | |
+| chinese-electra-discriminator-base | | |
+| chinese-electra-discriminator-small | | |
+
+## 快速开始
+
+### 安装说明
+
+* PaddlePaddle 安装
+
+ 本项目依赖于 PaddlePaddle 2.0 及以上版本,请参考 [安装指南](http://www.paddlepaddle.org/#quick-start) 进行安装
+
+* PaddleNLP 安装
+
+ ```shell
+ pip install paddlenlp
+ ```
+
+* 环境依赖
+
+ Python的版本要求 3.6+,其它环境请参考 PaddlePaddle [安装说明](https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/documentation/docs/zh/1.5/beginners_guide/install/index_cn.html) 部分的内容
+
+### 代码结构说明
+
+以下是本项目主要代码结构及说明:
+
+```text
+sentence_transformers/
+├── checkpoint
+│ ├── model_100
+│ │ ├── model_state.pdparams
+│ │ ├── tokenizer_config.json
+│ │ └── vocab.txt
+│ ├── ...
+│
+├── model.py # Sentence Transfomer 组网文件
+├── README.md # 文本说明
+└── train.py # 模型训练评估
+```
+
+### 模型训练
+
+我们以中文文本匹配公开数据集LCQMC为示例数据集,可以运行下面的命令,在训练集(train.tsv)上进行模型训练,并在开发集(dev.tsv)验证
+```shell
+# 设置使用的GPU卡号
+CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0
+python train.py --model_type ernie --model_name ernie-1.0 --n_gpu 1 --save_dir ./checkpoints
+```
+
+可支持配置的参数:
+
+* `model_type`:必选,模型类型,可以选择bert,ernie,roberta。
+* `model_name`: 必选,具体的模型简称。如`model_type=ernie`,则model_name可以选择`ernie`和`ernie_tiny`。`model_type=bert`,则model_name可以选择`bert-base-chinese`。
+ `model_type=roberta`,则model_name可以选择`roberta-wwm-ext-large`和`roberta-wwm-ext`。
+* `save_dir`:必选,保存训练模型的目录。
+* `max_seq_length`:可选,ERNIE/BERT模型使用的最大序列长度,最大不能超过512, 若出现显存不足,请适当调低这一参数;默认为128。
+* `batch_size`:可选,批处理大小,请结合显存情况进行调整,若出现显存不足,请适当调低这一参数;默认为32。
+* `learning_rate`:可选,Fine-tune的最大学习率;默认为5e-5。
+* `weight_decay`:可选,控制正则项力度的参数,用于防止过拟合,默认为0.00。
+* `warmup_proption`:可选,学习率warmup策略的比例,如果0.1,则学习率会在前10%训练step的过程中从0慢慢增长到learning_rate, 而后再缓慢衰减,默认为0.1。
+* `init_from_ckpt`:可选,模型参数路径,热启动模型训练;默认为None。
+* `seed`:可选,随机种子,默认为1000.
+* `n_gpu`:可选,训练过程中使用GPU卡数量,默认为1。若n_gpu=0,则使用CPU训练。
+
+
+程序运行时将会自动进行训练,评估,测试。同时训练过程中会自动保存模型在指定的`save_dir`中。
+如:
+```text
+checkpoints/
+├── model_100
+│ ├── model_config.json
+│ ├── model_state.pdparams
+│ ├── tokenizer_config.json
+│ └── vocab.txt
+└── ...
+```
+
+**NOTE:**
+* 如需恢复模型训练,则可以设置`init_from_ckpt`, 如`init_from_ckpt=checkpoints/model_100/model_state.pdparams`。
+* 如需使用ernie_tiny模型,则需要提前先安装sentencepiece依赖,如`pip install sentencepiece`
+
+### 模型预测
+
+启动预测:
+```shell
+CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0
+python predict.py --model_type ernie --model_name ernie_tiny --params_path checkpoints/model_400/model_state.pdparams
+```
+
+将待预测数据如以下示例:
+
+```text
+世界上什么东西最小 世界上什么东西最小?
+光眼睛大就好看吗 眼睛好看吗?
+小蝌蚪找妈妈怎么样 小蝌蚪找妈妈是谁画的
+```
+
+可以直接调用`predict`函数即可输出预测结果。
+
+如
+
+```text
+Data: ['世界上什么东西最小', '世界上什么东西最小?'] Label: similar
+Data: ['光眼睛大就好看吗', '眼睛好看吗?'] Label: dissimilar
+Data: ['小蝌蚪找妈妈怎么样', '小蝌蚪找妈妈是谁画的'] Label: dissimilar
+```
+
+
+## 引用
+
+关于Sentence Transformer更多信息参考[www.SBERT.net](https://www.sbert.net)以及论文:
+- [Sentence-BERT: Sentence Embeddings using Siamese BERT-Networks](https://arxiv.org/abs/1908.10084) (EMNLP 2019)
+- [Making Monolingual Sentence Embeddings Multilingual using Knowledge Distillation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.09813) (EMNLP 2020)
+- [Augmented SBERT: Data Augmentation Method for Improving Bi-Encoders for Pairwise Sentence Scoring Tasks](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.08240) (arXiv 2020)
+
+```
+@inproceedings{reimers-2019-sentence-bert,
+ title = "Sentence-BERT: Sentence Embeddings using Siamese BERT-Networks",
+ author = "Reimers, Nils and Gurevych, Iryna",
+ booktitle = "Proceedings of the 2019 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing",
+ month = "11",
+ year = "2019",
+ publisher = "Association for Computational Linguistics",
+ url = "https://arxiv.org/abs/1908.10084",
+}
+```
+
+```
+@inproceedings{reimers-2020-multilingual-sentence-bert,
+ title = "Making Monolingual Sentence Embeddings Multilingual using Knowledge Distillation",
+ author = "Reimers, Nils and Gurevych, Iryna",
+ booktitle = "Proceedings of the 2020 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing",
+ month = "11",
+ year = "2020",
+ publisher = "Association for Computational Linguistics",
+ url = "https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.09813",
+}
+```
+
+```
+@article{thakur-2020-AugSBERT,
+ title = "Augmented SBERT: Data Augmentation Method for Improving Bi-Encoders for Pairwise Sentence Scoring Tasks",
+ author = "Thakur, Nandan and Reimers, Nils and Daxenberger, Johannes and Gurevych, Iryna",
+ journal= "arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.08240",
+ month = "10",
+ year = "2020",
+ url = "https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.08240",
+}
+```
diff --git a/PaddleNLP/examples/text_matching/sentence_transformers/model.py b/PaddleNLP/examples/text_matching/sentence_transformers/model.py
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..44c178f6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/PaddleNLP/examples/text_matching/sentence_transformers/model.py
@@ -0,0 +1,71 @@
+# Copyright (c) 2020 PaddlePaddle Authors. All Rights Reserved.
+#
+# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"
+# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
+# You may obtain a copy of the License at
+#
+# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
+#
+# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
+# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
+# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
+# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
+# limitations under the License.
+
+import paddle
+import paddle.nn as nn
+import paddle.nn.functional as F
+
+
+class SentenceTransformer(nn.Layer):
+ def __init__(self, pretrained_model, dropout=None):
+ super().__init__()
+ self.ptm = pretrained_model
+ self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout if dropout is not None else 0.1)
+ # num_labels = 2 (similar or dissimilar)
+ self.classifier = nn.Linear(self.ptm.config["hidden_size"] * 3, 2)
+
+ def forward(self,
+ query_input_ids,
+ title_input_ids,
+ query_token_type_ids=None,
+ query_position_ids=None,
+ query_attention_mask=None,
+ title_token_type_ids=None,
+ title_position_ids=None,
+ title_attention_mask=None):
+ query_token_embedding, _ = self.ptm(
+ query_input_ids, query_token_type_ids, query_position_ids,
+ query_attention_mask)
+ query_token_embedding = self.dropout(query_token_embedding)
+ query_attention_mask = paddle.unsqueeze(
+ (query_input_ids != self.ptm.pad_token_id
+ ).astype(self.ptm.pooler.dense.weight.dtype),
+ axis=2)
+ # Set token embeddings to 0 for padding tokens
+ query_token_embedding = query_token_embedding * query_attention_mask
+ query_sum_embedding = paddle.sum(query_token_embedding, axis=1)
+ query_sum_mask = paddle.sum(query_attention_mask, axis=1)
+ query_mean = query_sum_embedding / query_sum_mask
+
+ title_token_embedding, _ = self.ptm(
+ title_input_ids, title_token_type_ids, title_position_ids,
+ title_attention_mask)
+ title_token_embedding = self.dropout(title_token_embedding)
+ title_attention_mask = paddle.unsqueeze(
+ (title_input_ids != self.ptm.pad_token_id
+ ).astype(self.ptm.pooler.dense.weight.dtype),
+ axis=2)
+ # Set token embeddings to 0 for padding tokens
+ title_token_embedding = title_token_embedding * title_attention_mask
+ title_sum_embedding = paddle.sum(title_token_embedding, axis=1)
+ title_sum_mask = paddle.sum(title_attention_mask, axis=1)
+ title_mean = title_sum_embedding / title_sum_mask
+
+ sub = paddle.abs(paddle.subtract(query_mean, title_mean))
+ projection = paddle.concat([query_mean, title_mean, sub], axis=-1)
+
+ logits = self.classifier(projection)
+ probs = F.softmax(logits)
+
+ return probs
diff --git a/PaddleNLP/examples/text_matching/sentence_transformers/predict.py b/PaddleNLP/examples/text_matching/sentence_transformers/predict.py
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..6d90dc9a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/PaddleNLP/examples/text_matching/sentence_transformers/predict.py
@@ -0,0 +1,227 @@
+# Copyright (c) 2020 PaddlePaddle Authors. All Rights Reserved.
+#
+# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
+# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
+# You may obtain a copy of the License at
+#
+# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
+#
+# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
+# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
+# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
+# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
+# limitations under the License.
+
+from functools import partial
+import argparse
+import os
+import random
+import time
+
+import numpy as np
+import paddle
+import paddle.nn.functional as F
+import paddlenlp as ppnlp
+from paddlenlp.data import Stack, Tuple, Pad
+
+from model import SentenceTransformer
+
+MODEL_CLASSES = {
+ "bert": (ppnlp.transformers.BertModel, ppnlp.transformers.BertTokenizer),
+ 'ernie': (ppnlp.transformers.ErnieModel, ppnlp.transformers.ErnieTokenizer),
+ 'roberta': (ppnlp.transformers.RobertaModel,
+ ppnlp.transformers.RobertaTokenizer),
+ # 'electra': (ppnlp.transformers.Electra,
+ # ppnlp.transformers.ElectraTokenizer)
+}
+
+
+# yapf: disable
+def parse_args():
+ parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
+ # Required parameters
+ parser.add_argument("--model_type", default='ernie', type=str, help="Model type selected in the list: " +", ".join(MODEL_CLASSES.keys()))
+ parser.add_argument("--model_name", default='ernie-1.0', type=str, help="Path to pre-trained model or shortcut name selected in the list: " +
+ ", ".join(sum([list(classes[-1].pretrained_init_configuration.keys()) for classes in MODEL_CLASSES.values()], [])))
+ parser.add_argument("--params_path", type=str, default='./checkpoint/model_4900/model_state.pdparams', help="The path to model parameters to be loaded.")
+
+ parser.add_argument("--max_seq_length", default=50, type=int, help="The maximum total input sequence length after tokenization. "
+ "Sequences longer than this will be truncated, sequences shorter will be padded.")
+ parser.add_argument("--batch_size", default=32, type=int, help="Batch size per GPU/CPU for training.")
+ parser.add_argument("--n_gpu", type=int, default=0, help="Number of GPUs to use, 0 for CPU.")
+ args = parser.parse_args()
+ return args
+# yapf: enable
+
+
+def convert_example(example,
+ tokenizer,
+ label_list,
+ max_seq_length=512,
+ is_test=False):
+ """
+ Builds model inputs from a sequence or a pair of sequence for sequence classification tasks
+ by concatenating and adding special tokens. And creates a mask from the two sequences passed
+ to be used in a sequence-pair classification task.
+
+ A BERT sequence has the following format:
+
+ - single sequence: ``[CLS] X [SEP]``
+ - pair of sequences: ``[CLS] A [SEP] B [SEP]``
+
+ A BERT sequence pair mask has the following format:
+ ::
+ 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
+ | first sequence | second sequence |
+
+ If only one sequence, only returns the first portion of the mask (0's).
+
+
+ Args:
+ example(obj:`list[str]`): List of input data, containing query, title and label if it have label.
+ tokenizer(obj:`PretrainedTokenizer`): This tokenizer inherits from :class:`~paddlenlp.transformers.PretrainedTokenizer`
+ which contains most of the methods. Users should refer to the superclass for more information regarding methods.
+ label_list(obj:`list[str]`): All the labels that the data has.
+ max_seq_len(obj:`int`): The maximum total input sequence length after tokenization.
+ Sequences longer than this will be truncated, sequences shorter will be padded.
+ is_test(obj:`False`, defaults to `False`): Whether the example contains label or not.
+
+ Returns:
+ query_input_ids(obj:`list[int]`): The list of query token ids.
+ query_segment_ids(obj: `list[int]`): List of query sequence pair mask.
+ title_input_ids(obj:`list[int]`): The list of title token ids.
+ title_segment_ids(obj: `list[int]`): List of title sequence pair mask.
+ label(obj:`numpy.array`, data type of int64, optional): The input label if not is_test.
+ """
+ print(example)
+ query, title = example[0], example[1]
+
+ query_encoded_inputs = tokenizer.encode(
+ text=query, max_seq_len=max_seq_length)
+ query_input_ids = query_encoded_inputs["input_ids"]
+ query_segment_ids = query_encoded_inputs["segment_ids"]
+
+ title_encoded_inputs = tokenizer.encode(
+ text=title, max_seq_len=max_seq_length)
+ title_input_ids = title_encoded_inputs["input_ids"]
+ title_segment_ids = title_encoded_inputs["segment_ids"]
+
+ if not is_test:
+ # create label maps if classification task
+ label = example[-1]
+ label_map = {}
+ for (i, l) in enumerate(label_list):
+ label_map[l] = i
+ label = label_map[label]
+ label = np.array([label], dtype="int64")
+ return query_input_ids, query_segment_ids, title_input_ids, title_segment_ids, label
+ else:
+ return query_input_ids, query_segment_ids, title_input_ids, title_segment_ids
+
+
+def predict(model, data, tokenizer, label_map, batch_size=1):
+ """
+ Predicts the data labels.
+
+ Args:
+ model (obj:`paddle.nn.Layer`): A model to classify texts.
+ data (obj:`List(Example)`): The processed data whose each element is a Example (numedtuple) object.
+ A Example object contains `text`(word_ids) and `se_len`(sequence length).
+ tokenizer(obj:`PretrainedTokenizer`): This tokenizer inherits from :class:`~paddlenlp.transformers.PretrainedTokenizer`
+ which contains most of the methods. Users should refer to the superclass for more information regarding methods.
+ label_map(obj:`dict`): The label id (key) to label str (value) map.
+ batch_size(obj:`int`, defaults to 1): The number of batch.
+
+ Returns:
+ results(obj:`dict`): All the predictions labels.
+ """
+ examples = []
+ for text_pair in data:
+ query_input_ids, query_segment_ids, title_input_ids, title_segment_ids = convert_example(
+ text_pair,
+ tokenizer,
+ label_list=label_map.values(),
+ max_seq_length=args.max_seq_length,
+ is_test=True)
+ examples.append((query_input_ids, query_segment_ids, title_input_ids,
+ title_segment_ids))
+
+ batchify_fn = lambda samples, fn=Tuple(
+ Pad(axis=0, pad_val=tokenizer.pad_token_id), # query_input
+ Pad(axis=0, pad_val=tokenizer.pad_token_id), # query_segment
+ Pad(axis=0, pad_val=tokenizer.pad_token_id), # title_input
+ Pad(axis=0, pad_val=tokenizer.pad_token_id), # tilte_segment
+ ): [data for data in fn(samples)]
+
+ # Seperates data into some batches.
+ batches = []
+ one_batch = []
+ for example in examples:
+ one_batch.append(example)
+ if len(one_batch) == batch_size:
+ batches.append(one_batch)
+ one_batch = []
+ if one_batch:
+ # The last batch whose size is less than the config batch_size setting.
+ batches.append(one_batch)
+
+ results = []
+ model.eval()
+ for batch in batches:
+ query_input_ids, query_segment_ids, title_input_ids, title_segment_ids = batchify_fn(
+ batch)
+
+ query_input_ids = paddle.to_tensor(query_input_ids)
+ query_segment_ids = paddle.to_tensor(query_segment_ids)
+ title_input_ids = paddle.to_tensor(title_input_ids)
+ title_segment_ids = paddle.to_tensor(title_segment_ids)
+
+ print(query_input_ids)
+ print(query_segment_ids)
+ print(title_segment_ids)
+
+ probs = model(
+ query_input_ids,
+ title_input_ids,
+ query_token_type_ids=query_segment_ids,
+ title_token_type_ids=title_segment_ids)
+ idx = paddle.argmax(probs, axis=1).numpy()
+ idx = idx.tolist()
+ labels = [label_map[i] for i in idx]
+ results.extend(labels)
+ return results
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ args = parse_args()
+ paddle.set_device("gpu" if args.n_gpu else "cpu")
+
+ args.model_type = args.model_type.lower()
+ model_class, tokenizer_class = MODEL_CLASSES[args.model_type]
+
+ if args.model_name == 'ernie_tiny':
+ # ErnieTinyTokenizer is special for ernie_tiny pretained model.
+ tokenizer = ppnlp.transformers.ErnieTinyTokenizer.from_pretrained(
+ args.model_name)
+ else:
+ tokenizer = tokenizer_class.from_pretrained(args.model_name)
+
+ data = [
+ ['世界上什么东西最小', '世界上什么东西最小?'],
+ ['光眼睛大就好看吗', '眼睛好看吗?'],
+ ['小蝌蚪找妈妈怎么样', '小蝌蚪找妈妈是谁画的'],
+ ]
+ label_map = {0: 'dissimilar', 1: 'similar'}
+
+ pretrained_model = model_class.from_pretrained(args.model_name)
+ model = SentenceTransformer(pretrained_model)
+
+ if args.params_path and os.path.isfile(args.params_path):
+ state_dict = paddle.load(args.params_path)
+ model.set_dict(state_dict)
+ print("Loaded parameters from %s" % args.params_path)
+
+ results = predict(
+ model, data, tokenizer, label_map, batch_size=args.batch_size)
+ for idx, text in enumerate(data):
+ print('Data: {} \t Lable: {}'.format(text, results[idx]))
diff --git a/PaddleNLP/examples/text_matching/sentence_transformers/train.py b/PaddleNLP/examples/text_matching/sentence_transformers/train.py
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..bb9673ab
--- /dev/null
+++ b/PaddleNLP/examples/text_matching/sentence_transformers/train.py
@@ -0,0 +1,370 @@
+# Copyright (c) 2020 PaddlePaddle Authors. All Rights Reserved.
+#
+# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
+# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
+# You may obtain a copy of the License at
+#
+# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
+#
+# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
+# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
+# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
+# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
+# limitations under the License.
+
+from functools import partial
+import argparse
+import os
+import random
+import time
+
+import numpy as np
+import paddle
+import paddle.nn.functional as F
+
+from paddlenlp.data import Stack, Tuple, Pad
+import paddlenlp as ppnlp
+
+from model import SentenceTransformer
+
+MODEL_CLASSES = {
+ "bert": (ppnlp.transformers.BertModel, ppnlp.transformers.BertTokenizer),
+ 'ernie': (ppnlp.transformers.ErnieModel, ppnlp.transformers.ErnieTokenizer),
+ 'roberta': (ppnlp.transformers.RobertaModel,
+ ppnlp.transformers.RobertaTokenizer),
+ # 'electra': (ppnlp.transformers.Electra,
+ # ppnlp.transformers.ElectraTokenizer)
+}
+
+
+def parse_args():
+ parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
+ # Required parameters
+ parser.add_argument(
+ "--model_type",
+ default='ernie',
+ required=True,
+ type=str,
+ help="Model type selected in the list: " +
+ ", ".join(MODEL_CLASSES.keys()))
+ parser.add_argument(
+ "--model_name",
+ default='ernie-1.0',
+ required=True,
+ type=str,
+ help="Path to pre-trained model or shortcut name selected in the list: "
+ + ", ".join(
+ sum([
+ list(classes[-1].pretrained_init_configuration.keys())
+ for classes in MODEL_CLASSES.values()
+ ], [])))
+ parser.add_argument(
+ "--save_dir",
+ default='./checkpoint',
+ required=True,
+ type=str,
+ help="The output directory where the model checkpoints will be written.")
+
+ parser.add_argument(
+ "--max_seq_length",
+ default=128,
+ type=int,
+ help="The maximum total input sequence length after tokenization. "
+ "Sequences longer than this will be truncated, sequences shorter will be padded."
+ )
+ parser.add_argument(
+ "--batch_size",
+ default=32,
+ type=int,
+ help="Batch size per GPU/CPU for training.")
+ parser.add_argument(
+ "--learning_rate",
+ default=5e-5,
+ type=float,
+ help="The initial learning rate for Adam.")
+ parser.add_argument(
+ "--weight_decay",
+ default=0.0,
+ type=float,
+ help="Weight decay if we apply some.")
+ parser.add_argument(
+ "--epochs",
+ default=3,
+ type=int,
+ help="Total number of training epochs to perform.")
+ parser.add_argument(
+ "--warmup_proption",
+ default=0.0,
+ type=float,
+ help="Linear warmup proption over the training process.")
+ parser.add_argument(
+ "--init_from_ckpt",
+ type=str,
+ default=None,
+ help="The path of checkpoint to be loaded.")
+ parser.add_argument(
+ "--seed", type=int, default=1000, help="random seed for initialization")
+ parser.add_argument(
+ "--n_gpu",
+ type=int,
+ default=1,
+ help="Number of GPUs to use, 0 for CPU.")
+ args = parser.parse_args()
+ return args
+
+
+def set_seed(args):
+ """sets random seed"""
+ random.seed(args.seed)
+ np.random.seed(args.seed)
+ paddle.seed(args.seed)
+
+
+@paddle.no_grad()
+def evaluate(model, criterion, metric, data_loader):
+ """
+ Given a dataset, it evals model and computes the metric.
+
+ Args:
+ model(obj:`paddle.nn.Layer`): A model to classify texts.
+ data_loader(obj:`paddle.io.DataLoader`): The dataset loader which generates batches.
+ criterion(obj:`paddle.nn.Layer`): It can compute the loss.
+ metric(obj:`paddle.metric.Metric`): The evaluation metric.
+ """
+ model.eval()
+ metric.reset()
+ losses = []
+ for batch in data_loader:
+ query_input_ids, query_segment_ids, title_input_ids, title_segment_ids, labels = batch
+ probs = model(
+ query_input_ids,
+ title_input_ids,
+ query_token_type_ids=query_segment_ids,
+ title_token_type_ids=title_segment_ids)
+ loss = criterion(probs, labels)
+ losses.append(loss.numpy())
+ correct = metric.compute(probs, labels)
+ metric.update(correct)
+ accu = metric.accumulate()
+ print("eval loss: %.5f, accu: %.5f" % (np.mean(losses), accu))
+ model.train()
+ metric.reset()
+
+
+def convert_example(example,
+ tokenizer,
+ label_list,
+ max_seq_length=512,
+ is_test=False):
+ """
+ Builds model inputs from a sequence or a pair of sequence for sequence classification tasks
+ by concatenating and adding special tokens. And creates a mask from the two sequences passed
+ to be used in a sequence-pair classification task.
+
+ A BERT sequence has the following format:
+
+ - single sequence: ``[CLS] X [SEP]``
+ - pair of sequences: ``[CLS] A [SEP] B [SEP]``
+
+ A BERT sequence pair mask has the following format:
+ ::
+ 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
+ | first sequence | second sequence |
+
+ If only one sequence, only returns the first portion of the mask (0's).
+
+
+ Args:
+ example(obj:`list[str]`): List of input data, containing query, title and label if it have label.
+ tokenizer(obj:`PretrainedTokenizer`): This tokenizer inherits from :class:`~paddlenlp.transformers.PretrainedTokenizer`
+ which contains most of the methods. Users should refer to the superclass for more information regarding methods.
+ label_list(obj:`list[str]`): All the labels that the data has.
+ max_seq_len(obj:`int`): The maximum total input sequence length after tokenization.
+ Sequences longer than this will be truncated, sequences shorter will be padded.
+ is_test(obj:`False`, defaults to `False`): Whether the example contains label or not.
+
+ Returns:
+ query_input_ids(obj:`list[int]`): The list of query token ids.
+ query_segment_ids(obj: `list[int]`): List of query sequence pair mask.
+ title_input_ids(obj:`list[int]`): The list of title token ids.
+ title_segment_ids(obj: `list[int]`): List of title sequence pair mask.
+ label(obj:`numpy.array`, data type of int64, optional): The input label if not is_test.
+ """
+ query, title = example[0], example[1]
+
+ query_encoded_inputs = tokenizer.encode(
+ text=query, max_seq_len=max_seq_length)
+ query_input_ids = query_encoded_inputs["input_ids"]
+ query_segment_ids = query_encoded_inputs["segment_ids"]
+
+ title_encoded_inputs = tokenizer.encode(
+ text=title, max_seq_len=max_seq_length)
+ title_input_ids = title_encoded_inputs["input_ids"]
+ title_segment_ids = title_encoded_inputs["segment_ids"]
+
+ if not is_test:
+ # create label maps if classification task
+ label = example[-1]
+ label_map = {}
+ for (i, l) in enumerate(label_list):
+ label_map[l] = i
+ label = label_map[label]
+ label = np.array([label], dtype="int64")
+ return query_input_ids, query_segment_ids, title_input_ids, title_segment_ids, label
+ else:
+ return query_input_ids, query_segment_ids, title_input_ids, title_segment_ids
+
+
+def create_dataloader(dataset,
+ mode='train',
+ batch_size=1,
+ batchify_fn=None,
+ trans_fn=None):
+ if trans_fn:
+ dataset = dataset.apply(trans_fn, lazy=True)
+
+ shuffle = True if mode == 'train' else False
+ if mode == 'train':
+ batch_sampler = paddle.io.DistributedBatchSampler(
+ dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=shuffle)
+ else:
+ batch_sampler = paddle.io.BatchSampler(
+ dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=shuffle)
+
+ return paddle.io.DataLoader(
+ dataset=dataset,
+ batch_sampler=batch_sampler,
+ collate_fn=batchify_fn,
+ return_list=True)
+
+
+def do_train(args):
+ set_seed(args)
+ paddle.set_device("gpu" if args.n_gpu else "cpu")
+ world_size = paddle.distributed.get_world_size()
+ if world_size > 1:
+ paddle.distributed.init_parallel_env()
+
+ args.model_type = args.model_type.lower()
+ model_class, tokenizer_class = MODEL_CLASSES[args.model_type]
+
+ train_dataset, dev_dataset, test_dataset = ppnlp.datasets.LCQMC.get_datasets(
+ ['train', 'dev', 'test'])
+ if args.model_name == 'ernie_tiny':
+ # ErnieTinyTokenizer is special for ernie_tiny pretained model.
+ tokenizer = ppnlp.transformers.ErnieTinyTokenizer.from_pretrained(
+ args.model_name)
+ else:
+ tokenizer = tokenizer_class.from_pretrained(args.model_name)
+
+ trans_func = partial(
+ convert_example,
+ tokenizer=tokenizer,
+ label_list=train_dataset.get_labels(),
+ max_seq_length=args.max_seq_length)
+ batchify_fn = lambda samples, fn=Tuple(
+ Pad(axis=0, pad_val=tokenizer.pad_token_id), # query_input
+ Pad(axis=0, pad_val=tokenizer.pad_token_id), # query_segment
+ Pad(axis=0, pad_val=tokenizer.pad_token_id), # title_input
+ Pad(axis=0, pad_val=tokenizer.pad_token_id), # tilte_segment
+ Stack(dtype="int64") # label
+ ): [data for data in fn(samples)]
+ train_data_loader = create_dataloader(
+ train_dataset,
+ mode='train',
+ batch_size=args.batch_size,
+ batchify_fn=batchify_fn,
+ trans_fn=trans_func)
+ dev_data_loader = create_dataloader(
+ dev_dataset,
+ mode='dev',
+ batch_size=args.batch_size,
+ batchify_fn=batchify_fn,
+ trans_fn=trans_func)
+ test_data_loader = create_dataloader(
+ test_dataset,
+ mode='test',
+ batch_size=args.batch_size,
+ batchify_fn=batchify_fn,
+ trans_fn=trans_func)
+
+ pretrained_model = model_class.from_pretrained(args.model_name)
+ model = SentenceTransformer(pretrained_model)
+
+ if args.init_from_ckpt and os.path.isfile(args.init_from_ckpt):
+ state_dict = paddle.load(args.init_from_ckpt)
+ model.set_dict(state_dict)
+ model = paddle.DataParallel(model)
+
+ num_training_steps = len(train_data_loader) * args.epochs
+ num_warmup_steps = int(args.warmup_proption * num_training_steps)
+
+ def get_lr_factor(current_step):
+ if current_step < num_warmup_steps:
+ return float(current_step) / float(max(1, num_warmup_steps))
+ else:
+ return max(0.0,
+ float(num_training_steps - current_step) /
+ float(max(1, num_training_steps - num_warmup_steps)))
+
+ lr_scheduler = paddle.optimizer.lr.LambdaDecay(
+ args.learning_rate,
+ lr_lambda=lambda current_step: get_lr_factor(current_step))
+ optimizer = paddle.optimizer.AdamW(
+ learning_rate=lr_scheduler,
+ parameters=model.parameters(),
+ weight_decay=args.weight_decay,
+ apply_decay_param_fun=lambda x: x in [
+ p.name for n, p in model.named_parameters()
+ if not any(nd in n for nd in ["bias", "norm"])
+ ])
+
+ criterion = paddle.nn.loss.CrossEntropyLoss()
+ metric = paddle.metric.Accuracy()
+
+ global_step = 0
+ tic_train = time.time()
+ for epoch in range(1, args.epochs + 1):
+ for step, batch in enumerate(train_data_loader, start=1):
+ query_input_ids, query_segment_ids, title_input_ids, title_segment_ids, labels = batch
+ probs = model(
+ query_input_ids,
+ title_input_ids,
+ query_token_type_ids=query_segment_ids,
+ title_token_type_ids=title_segment_ids)
+ loss = criterion(probs, labels)
+ correct = metric.compute(probs, labels)
+ metric.update(correct)
+ acc = metric.accumulate()
+
+ global_step += 1
+ if global_step % 10 == 0 and paddle.distributed.get_rank() == 0:
+ print(
+ "global step %d, epoch: %d, batch: %d, loss: %.5f, accu: %.5f, speed: %.2f step/s"
+ % (global_step, epoch, step, loss, acc,
+ 10 / (time.time() - tic_train)))
+ tic_train = time.time()
+ loss.backward()
+ optimizer.step()
+ lr_scheduler.step()
+ optimizer.clear_gradients()
+ if global_step % 100 == 0 and paddle.distributed.get_rank() == 0:
+ save_dir = os.path.join(args.save_dir, "model_%d" % global_step)
+ if not os.path.exists(save_dir):
+ os.makedirs(save_dir)
+ evaluate(model, criterion, metric, dev_data_loader)
+ save_param_path = os.path.join(save_dir, 'model_state.pdparams')
+ paddle.save(model.state_dict(), save_param_path)
+ tokenizer.save_pretrained(save_dir)
+
+ if paddle.distributed.get_rank() == 0:
+ print('Evaluating on test data.')
+ evaluate(model, criterion, metric, test_data_loader)
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ args = parse_args()
+ if args.n_gpu > 1:
+ paddle.distributed.spawn(do_train, args=(args, ), nprocs=args.n_gpu)
+ else:
+ do_train(args)
diff --git a/PaddleNLP/examples/text_matching/simnet/README.md b/PaddleNLP/examples/text_matching/simnet/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..111f836e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/PaddleNLP/examples/text_matching/simnet/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,168 @@
+# 使用SimNet完成pointwise文本匹配任务
+
+短文本语义匹配(SimilarityNet, SimNet)是一个计算短文本相似度的框架,可以根据用户输入的两个文本,计算出相似度得分。
+SimNet框架在百度各产品上广泛应用,主要包括BOW、CNN、RNN、MMDNN等核心网络结构形式,提供语义相似度计算训练和预测框架,
+适用于信息检索、新闻推荐、智能客服等多个应用场景,帮助企业解决语义匹配问题。
+可通过[AI开放平台-短文本相似度](https://ai.baidu.com/tech/nlp_basic/simnet)线上体验。
+
+## 模型简介
+
+
+本项目通过调用[Seq2Vec](../../../paddlenlp/seq2vec/)中内置的模型进行序列建模,完成句子的向量表示。包含最简单的词袋模型和一系列经典的RNN类模型。
+
+| 模型 | 模型介绍 |
+| ------------------------------------------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------ |
+| BOW(Bag Of Words) | 非序列模型,将句子表示为其所包含词的向量的加和 |
+| RNN (Recurrent Neural Network) | 序列模型,能够有效地处理序列信息 |
+| GRU(Gated Recurrent Unit) | 序列模型,能够较好地解决序列文本中长距离依赖的问题 |
+| LSTM(Long Short Term Memory) | 序列模型,能够较好地解决序列文本中长距离依赖的问题 |
+
+
+## TBD 增加模型效果
+| 模型 | dev acc | test acc |
+| ---- | ------- | -------- |
+| BoW | | |
+| CNN | | |
+| GRU | | |
+| LSTM | | |
+
+
+
+## 快速开始
+
+### 安装说明
+
+* PaddlePaddle 安装
+
+ 本项目依赖于 PaddlePaddle 2.0 及以上版本,请参考 [安装指南](http://www.paddlepaddle.org/#quick-start) 进行安装
+
+* PaddleNLP 安装
+
+ ```shell
+ pip install paddlenlp
+ ```
+
+* 环境依赖
+
+ 本项目依赖于jieba分词,请在运行本项目之前,安装jieba,如`pip install -U jieba`
+
+ Python的版本要求 3.6+,其它环境请参考 PaddlePaddle [安装说明](https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/install/quick/zh/2.0rc-linux-docker) 部分的内容
+
+### 代码结构说明
+
+以下是本项目主要代码结构及说明:
+
+```text
+.
+├── data.py # 数据读取
+├── predict.py # 模型预测
+├── utils.py # 数据处理工具
+├── train.py # 训练模型主程序入口,包括训练、评估
+└── README.md # 文档说明
+```
+
+### 数据准备
+
+#### 使用PaddleNLP内置数据集
+
+```python
+from paddlenlp.datasets import LCQMC
+
+train_ds, dev_dataset, test_ds = LCQMC.get_datasets(['train', 'dev', 'test'])
+```
+
+部分样例数据如下:
+
+```text
+query title label
+最近有什么好看的电视剧,推荐一下 近期有什么好看的电视剧,求推荐? 1
+大学生验证仅针对在读学生,已毕业学生不能申请的哦。 通过了大学生验证的用户,可以在支付宝的合作商户,享受学生优惠 0
+如何在网上查户口 如何网上查户口 1
+关于故事的成语 来自故事的成语 1
+ 湖北农村信用社手机银行客户端下载 湖北长阳农村商业银行手机银行客户端下载 0
+草泥马是什么动物 草泥马是一种什么动物 1
+```
+
+### 模型训练
+
+在模型训练之前,需要先下载词汇表文件term2id.dict,用于构造词-id映射关系。
+
+```shell
+wget https://paddlenlp.bj.bcebos.com/data/simnet_word_dict.txt
+```
+
+我们以中文pointwise文本匹配数据集LCQMC为示例数据集,可以运行下面的命令,在训练集(train.tsv)上进行模型训练,并在开发集(dev.tsv)验证
+
+CPU启动:
+
+```shell
+CPU启动
+python train.py --vocab_path='./simnet_word_dict.txt' --use_gpu=False --network=lstm --lr=5e-4 --batch_size=64 --epochs=5 --save_dir='./checkpoints'
+```
+
+GPU启动:
+
+```shell
+CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0
+python train.py --vocab_path='./simnet_word_dict.txt' --use_gpu=True --network=lstm --lr=5e-4 --batch_size=64 --epochs=5 --save_dir='./checkpoints'
+```
+
+以上参数表示:
+
+* `vocab_path`: 词汇表文件路径。
+* `use_gpu`: 是否使用GPU进行训练, 默认为`False`。
+* `network`: 模型网络名称,默认为`lstm`, 可更换为lstm, gru, rnn,bow,cnn等。
+* `lr`: 学习率, 默认为5e-4。
+* `batch_size`: 运行一个batch大小,默认为64。
+* `epochs`: 训练轮次,默认为5。
+* `save_dir`: 训练保存模型的文件路径。
+* `init_from_ckpt`: 恢复模型训练的断点路径。
+
+
+程序运行时将会自动进行训练,评估,测试。同时训练过程中会自动保存模型在指定的`save_dir`中。
+如:
+```text
+checkpoints/
+├── 0.pdopt
+├── 0.pdparams
+├── 1.pdopt
+├── 1.pdparams
+├── ...
+└── final.pdparams
+```
+
+**NOTE:** 如需恢复模型训练,则init_from_ckpt只需指定到文件名即可,不需要添加文件尾缀。如`--init_from_ckpt=checkpoints/0`即可,程序会自动加载模型参数`checkpoints/0.pdparams`,也会自动加载优化器状态`checkpoints/0.pdopt`。
+
+### 模型预测
+
+启动预测
+
+CPU启动:
+
+```shell
+python predict.py --vocab_path='./simnet_word_dict.txt' --use_gpu=False --network=lstm --params_path=checkpoints/final.pdparams
+```
+
+GPU启动:
+
+```shell
+CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python predict.py --vocab_path='./simnet_word_dict.txt' --use_gpu=True --network=lstm --params_path='./checkpoints/final.pdparams'
+```
+
+将待预测数据分词完毕后,如以下示例:
+
+```text
+世界上什么东西最小 世界上什么东西最小?
+光眼睛大就好看吗 眼睛好看吗?
+小蝌蚪找妈妈怎么样 小蝌蚪找妈妈是谁画的
+```
+
+处理成模型所需的`Tensor`,如可以直接调用`preprocess_prediction_data`函数既可处理完毕。之后传入`predict`函数即可输出预测结果。
+
+如
+
+```text
+Data: ['世界上什么东西最小', '世界上什么东西最小?'] Label: similar
+Data: ['光眼睛大就好看吗', '眼睛好看吗?'] Label: dissimilar
+Data: ['小蝌蚪找妈妈怎么样', '小蝌蚪找妈妈是谁画的'] Label: dissimilar
+```
diff --git a/PaddleNLP/examples/text_matching/simnet/predict.py b/PaddleNLP/examples/text_matching/simnet/predict.py
index 0a82fa68..07e252aa 100644
--- a/PaddleNLP/examples/text_matching/simnet/predict.py
+++ b/PaddleNLP/examples/text_matching/simnet/predict.py
@@ -25,7 +25,7 @@ parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(__doc__)
parser.add_argument("--use_gpu", type=eval, default=False, help="Whether use GPU for training, input should be True or False")
parser.add_argument("--batch_size", type=int, default=64, help="Total examples' number of a batch for training.")
parser.add_argument("--vocab_path", type=str, default="./data/term2id.dict", help="The path to vocabulary.")
-parser.add_argument('--network_name', type=str, default="lstm", help="Which network you would like to choose bow, lstm, bilstm, gru, bigru, rnn, birnn, bilstm_attn, cnn and textcnn?")
+parser.add_argument('--network_name', type=str, default="lstm", help="Which network you would like to choose bow, cnn, lstm or gru ?")
parser.add_argument("--params_path", type=str, default='./chekpoints/final.pdparams', help="The path of model parameter to be loaded.")
args = parser.parse_args()
# yapf: enable
diff --git a/PaddleNLP/examples/text_matching/simnet/train.py b/PaddleNLP/examples/text_matching/simnet/train.py
index a17e1df0..df308ab8 100644
--- a/PaddleNLP/examples/text_matching/simnet/train.py
+++ b/PaddleNLP/examples/text_matching/simnet/train.py
@@ -26,13 +26,13 @@ from utils import load_vocab, generate_batch, convert_example
# yapf: disable
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(__doc__)
-parser.add_argument("--epochs", type=int, default=3, help="Number of epoches for training.")
-parser.add_argument('--use_gpu', type=eval, default=True, help="Whether use GPU for training, input should be True or False")
+parser.add_argument("--epochs", type=int, default=10, help="Number of epoches for training.")
+parser.add_argument('--use_gpu', type=eval, default=False, help="Whether use GPU for training, input should be True or False")
parser.add_argument("--lr", type=float, default=5e-4, help="Learning rate used to train.")
parser.add_argument("--save_dir", type=str, default='chekpoints/', help="Directory to save model checkpoint")
parser.add_argument("--batch_size", type=int, default=64, help="Total examples' number of a batch for training.")
-parser.add_argument("--vocab_path", type=str, default="./data/term2id.dict", help="The directory to dataset.")
-parser.add_argument('--network', type=str, default="cnn", help="Which network you would like to choose bow, lstm, bilstm, gru, bigru, rnn, birnn, bilstm_attn and textcnn?")
+parser.add_argument("--vocab_path", type=str, default="./simnet_word_dict.txt", help="The directory to dataset.")
+parser.add_argument('--network', type=str, default="lstm", help="Which network you would like to choose bow, cnn, lstm or gru ?")
parser.add_argument("--init_from_ckpt", type=str, default=None, help="The path of checkpoint to be loaded.")
args = parser.parse_args()
# yapf: enable
--
GitLab





