Merge branch 'develop' of https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/models into caffe2fluid
support lenet and resnet conertion
Showing
fluid/DeepASR/data_utils/util.py
0 → 100644
fluid/DeepASR/infer.py
0 → 100644
fluid/DeepASR/tools/profile.py
0 → 100644
fluid/DeepASR/train.py
0 → 100644
fluid/transformer/.gitignore
0 → 100644
fluid/transformer/README.md
0 → 100644
fluid/transformer/config.py
0 → 100644
fluid/transformer/model.py
0 → 100644
fluid/transformer/optim.py
0 → 100644
fluid/transformer/train.py
0 → 100644
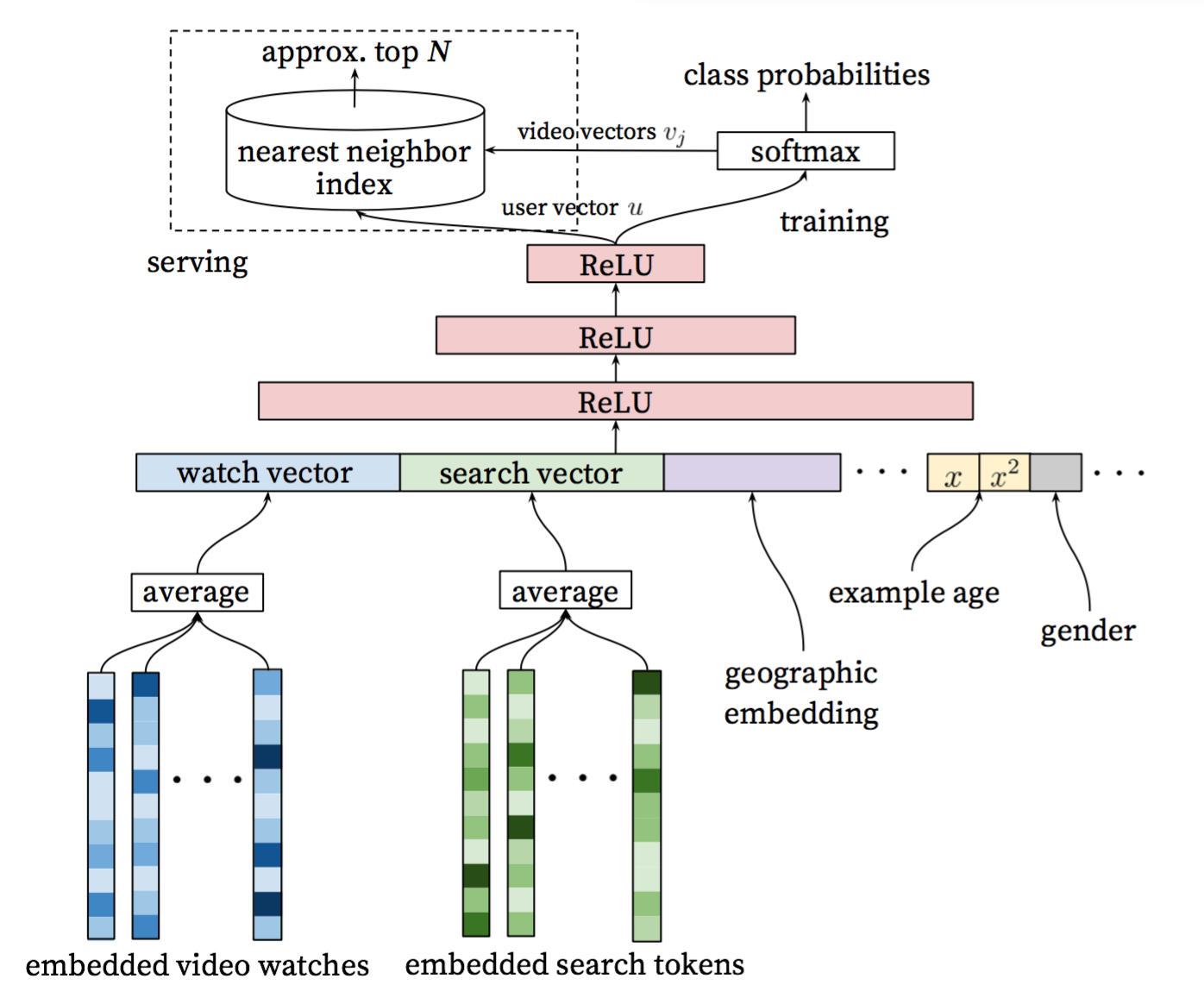
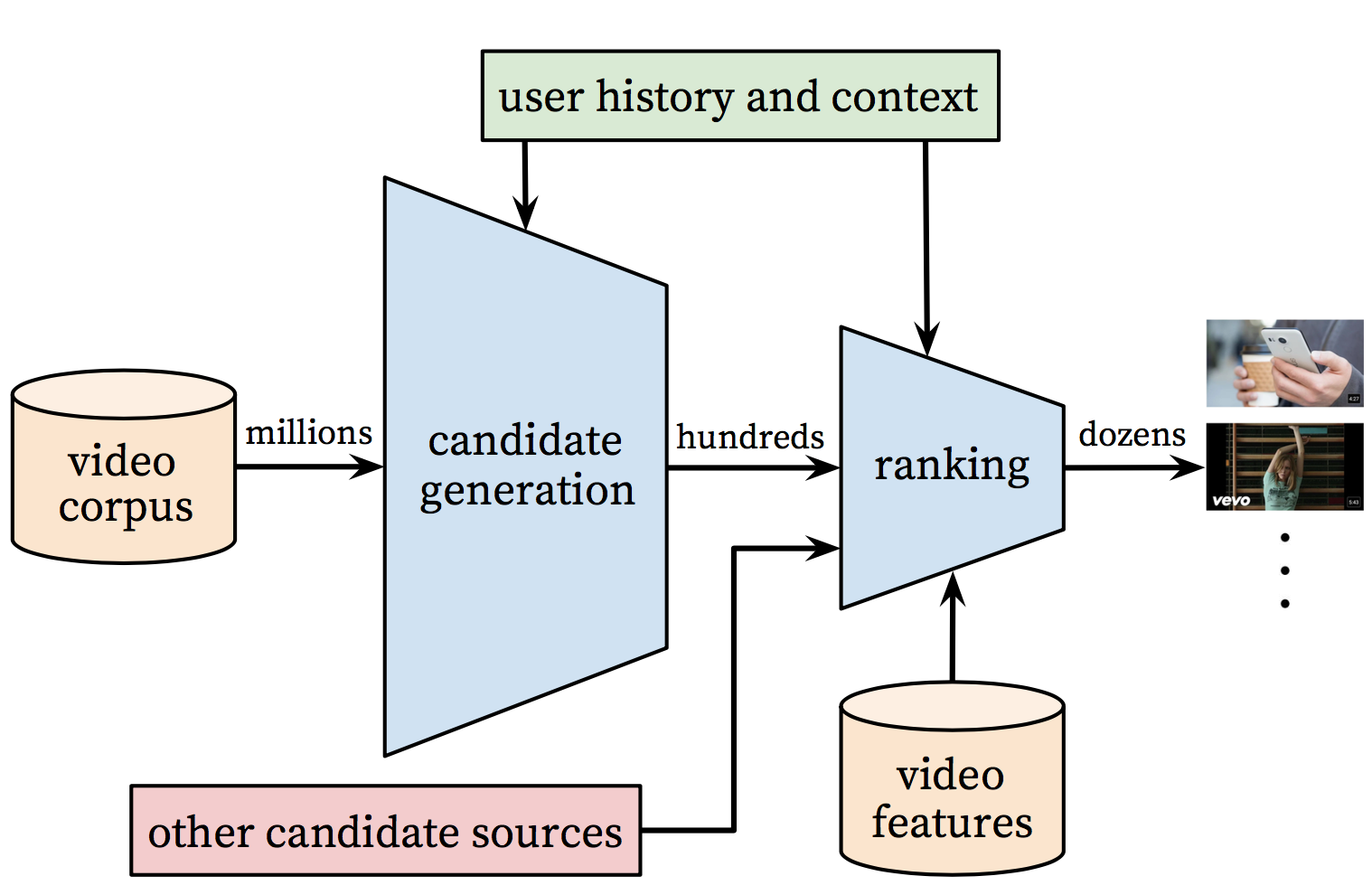
youtube_recall/README.cn.md
0 → 100644
youtube_recall/README.md
0 → 100644
youtube_recall/data/data.tar
0 → 100644
文件已添加
youtube_recall/data_processor.py
0 → 100644
241.5 KB
182.1 KB
youtube_recall/infer.py
0 → 100644
youtube_recall/infer_user.py
0 → 100644
youtube_recall/item_vector.py
0 → 100644
youtube_recall/network_conf.py
0 → 100644
youtube_recall/reader.py
0 → 100644
youtube_recall/train.py
0 → 100644
youtube_recall/user_vector.py
0 → 100644
youtube_recall/utils.py
0 → 100644