adapt to the new data provider
Showing
.travis/unittest.sh
0 → 100755
deep_speech_2/compute_mean_std.py
0 → 100644
deep_speech_2/data_utils/audio.py
0 → 100644
deep_speech_2/data_utils/data.py
0 → 100644
deep_speech_2/data_utils/utils.py
0 → 100644
deep_speech_2/datasets/run_all.sh
0 → 100644
deep_speech_2/decoder.py
100755 → 100644
deep_speech_2/error_rate.py
0 → 100644
deep_speech_2/utils.py
0 → 100644
image_classification/alexnet.py
0 → 100644
image_classification/googlenet.py
0 → 100644
image_classification/infer.py
0 → 100644
image_classification/resnet.py
0 → 100644
image_classification/train.py
100644 → 100755
language_model/config.py
0 → 100644
language_model/data/input.txt
0 → 100644
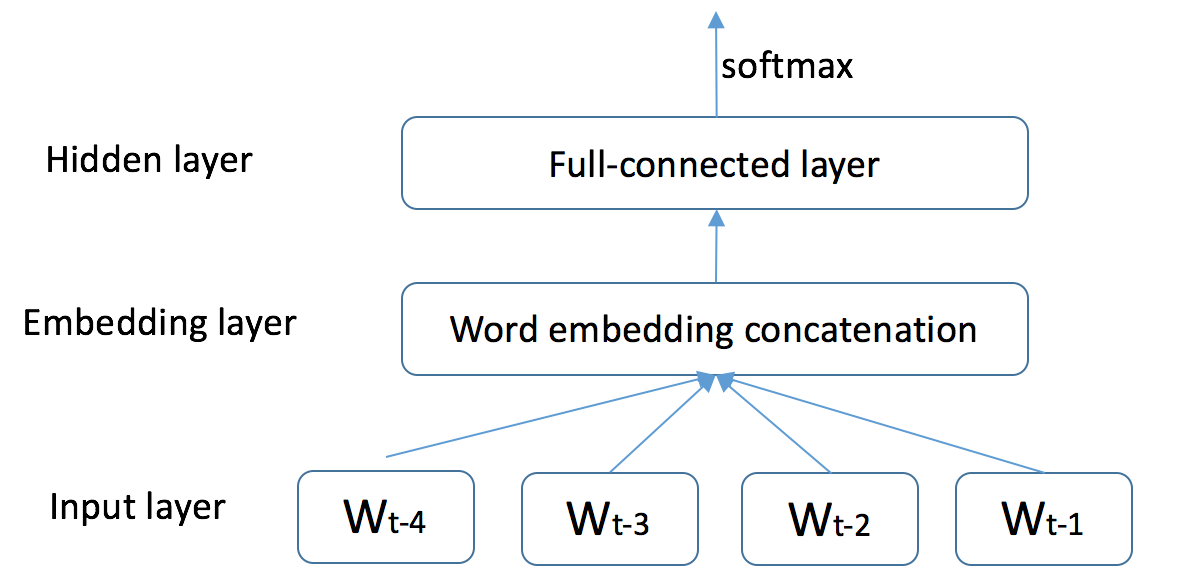
language_model/images/ngram.png
0 → 100644
67.1 KB
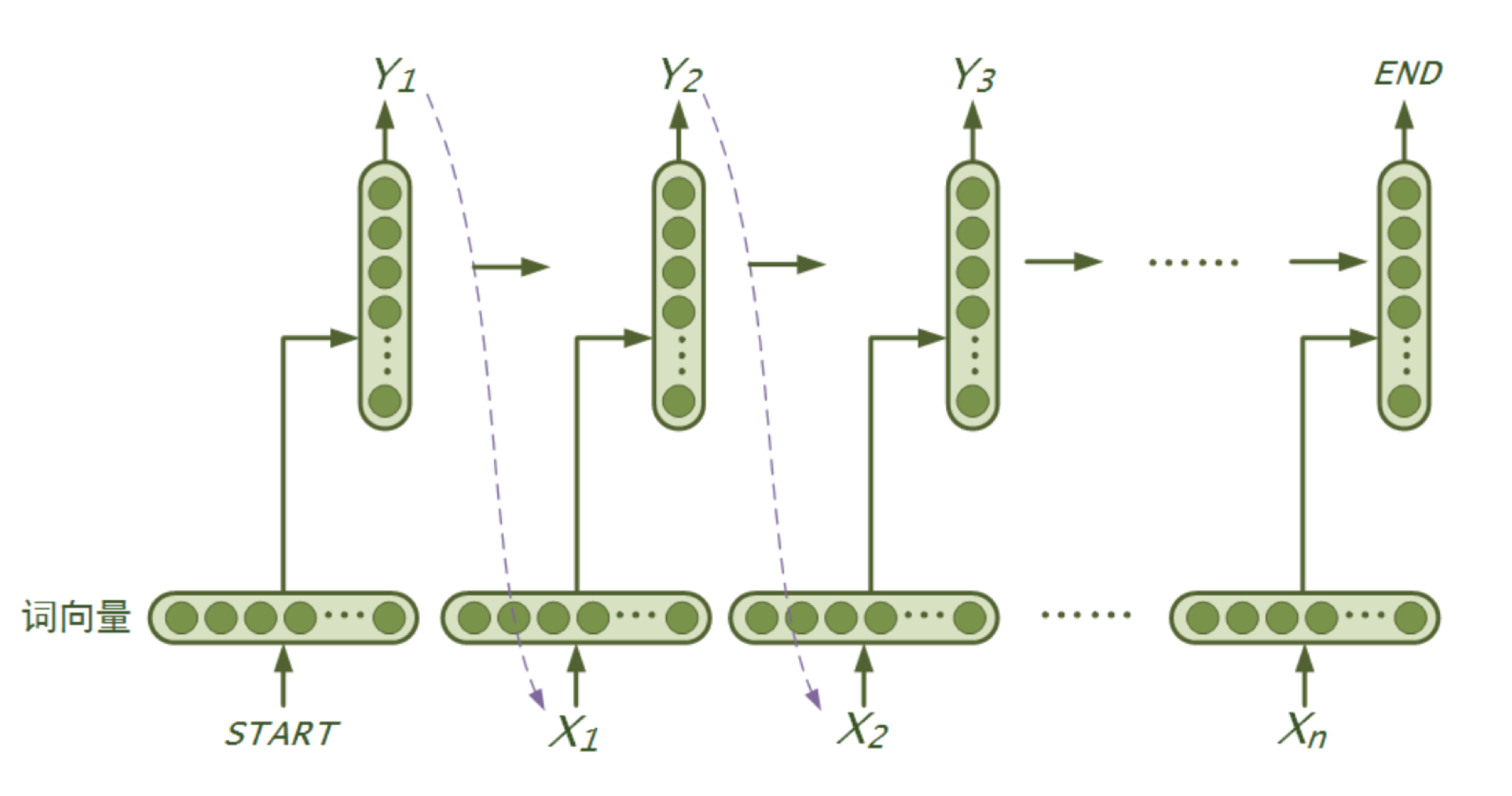
language_model/images/rnn.png
0 → 100644
335.3 KB
language_model/infer.py
0 → 100644
language_model/network_conf.py
0 → 100644
language_model/reader.py
0 → 100644
language_model/train.py
0 → 100644
language_model/utils.py
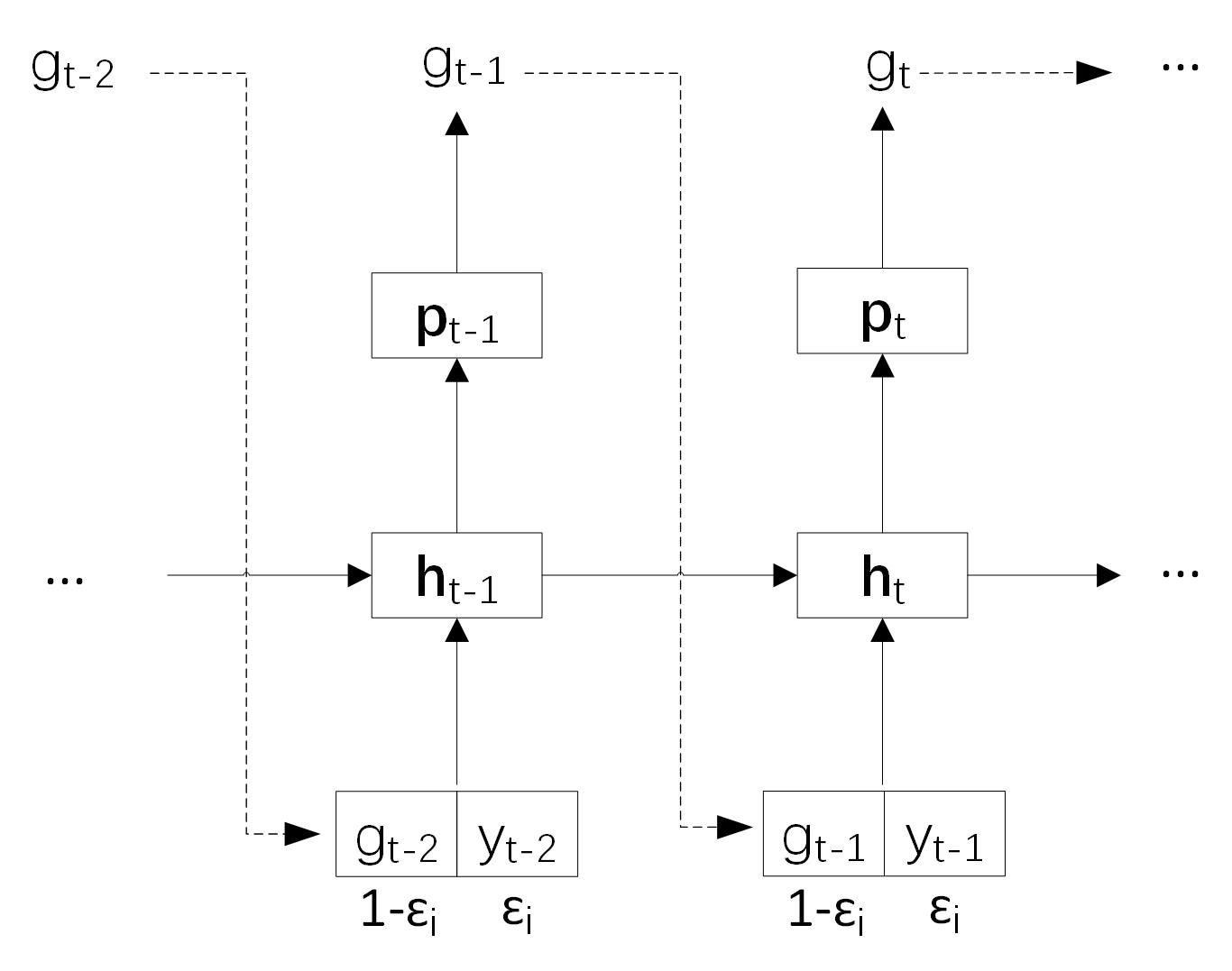
0 → 100644
59.2 KB
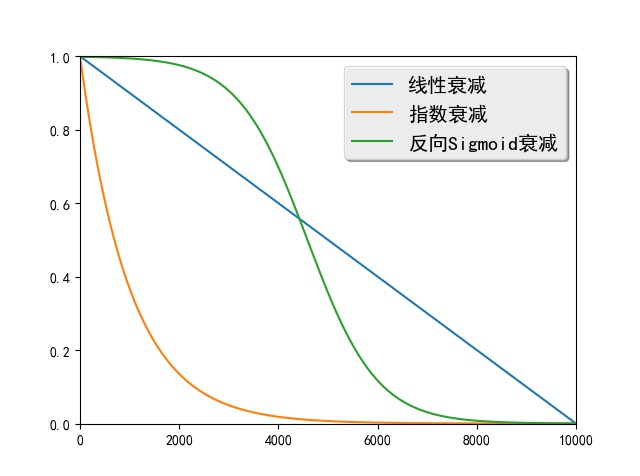
scheduled_sampling/img/decay.jpg
0 → 100644
44.6 KB
text_classification/.gitignore
0 → 100644
text_classification/infer.py
0 → 100644
text_classification/reader.py
0 → 100644
text_classification/run.sh
0 → 100644
text_classification/train.py
0 → 100644
text_classification/utils.py
0 → 100644