Merge pull request #857 from sunshine-2015/patch-4
create ltr/README_en.md
Showing
ltr/README_en.md
0 → 100644
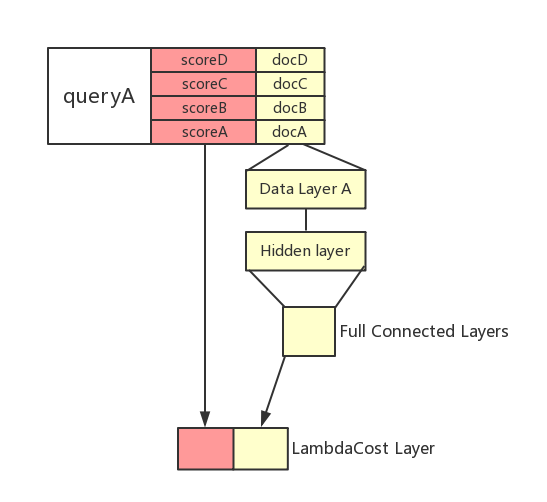
ltr/images/LambdaRank_EN.png
0 → 100644
24.1 KB
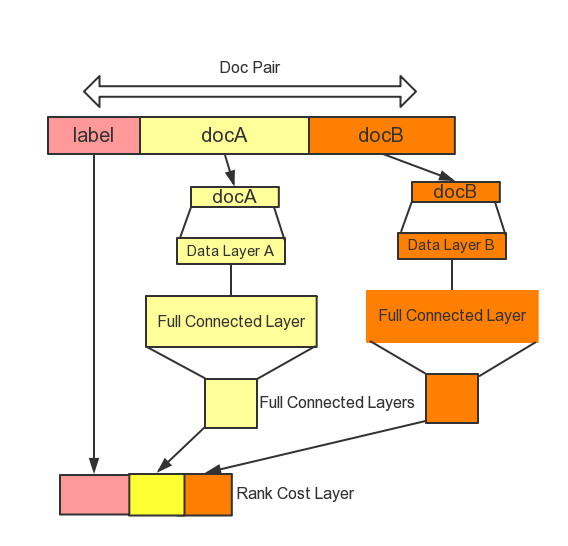
ltr/images/ranknet_en.png
0 → 100644
32.4 KB