Merge branch 'develop' of https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/models into...
Merge branch 'develop' of https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/models into add-transformer-BeamsearchDecoder-clean
Showing
deep_fm/README.cn.md
0 → 100644
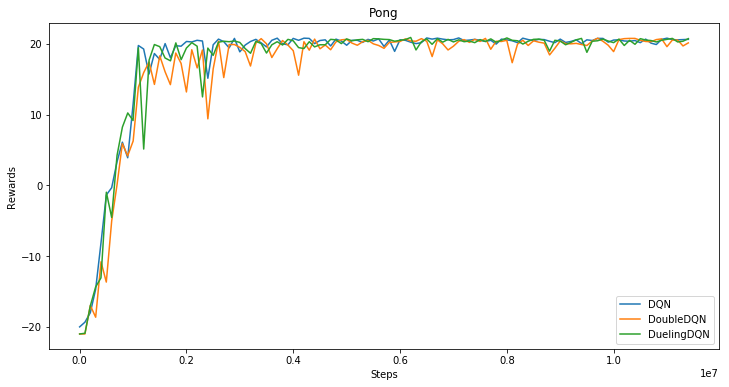
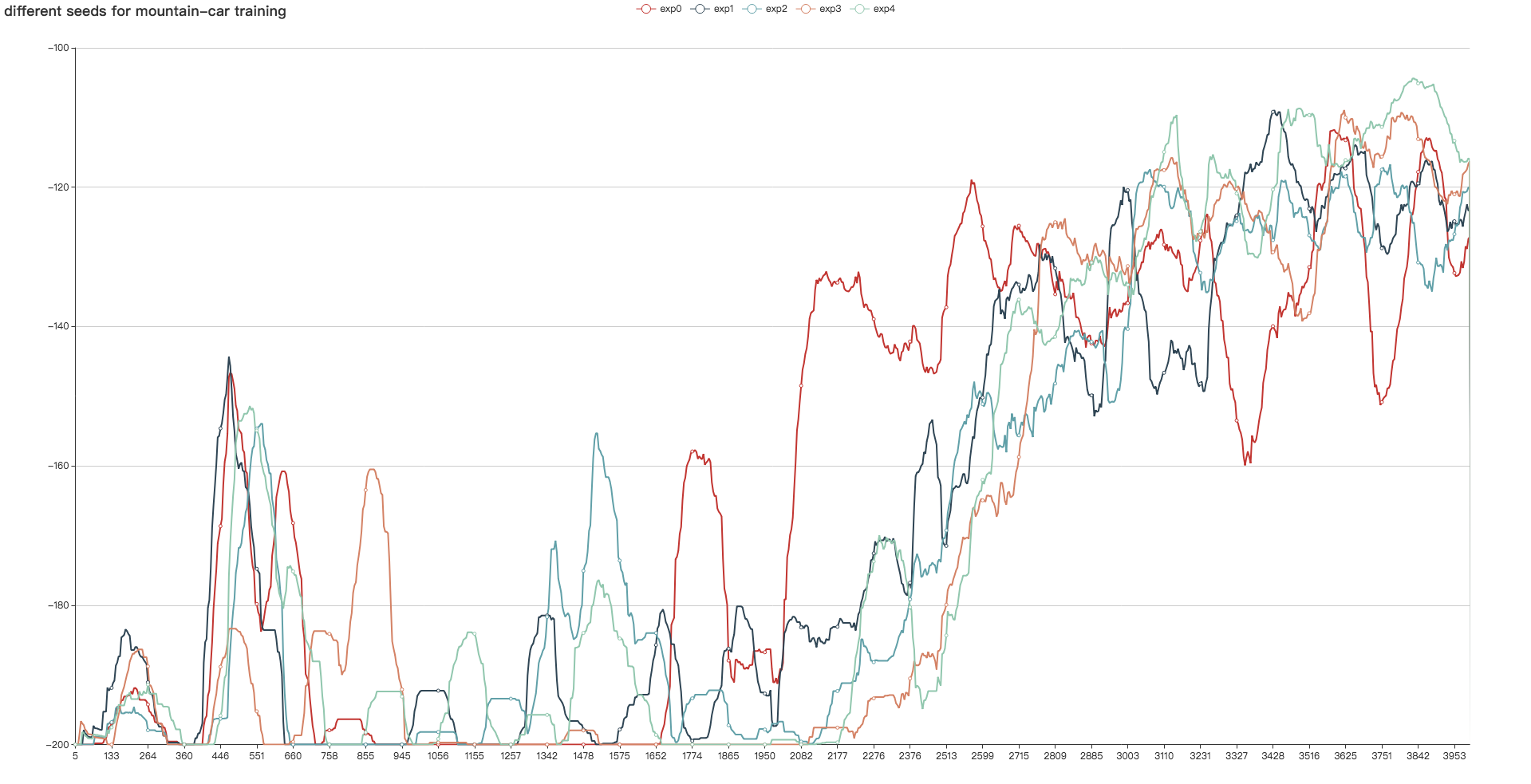
fluid/DeepQNetwork/DQN.py
已删除
100644 → 0
fluid/DeepQNetwork/DQN_agent.py
0 → 100644
fluid/DeepQNetwork/assets/dqn.png
0 → 100644
38.1 KB
fluid/DeepQNetwork/atari.py
0 → 100644
fluid/DeepQNetwork/curve.png
已删除
100644 → 0
442.3 KB
98.6 KB
fluid/DeepQNetwork/play.py
0 → 100644
文件已添加
文件已添加
fluid/DeepQNetwork/train.py
0 → 100644
fluid/DeepQNetwork/utils.py
0 → 100644
fluid/face_detection/.gitignore
0 → 100644
fluid/face_detection/infer.py
0 → 100644
fluid/face_detection/reader.py
0 → 100644
fluid/face_detection/train.py
0 → 100644
fluid/face_detection/utility.py
0 → 100644
fluid/icnet/README.md
0 → 100644
fluid/icnet/cityscape.py
0 → 100644
fluid/icnet/eval.py
0 → 100644
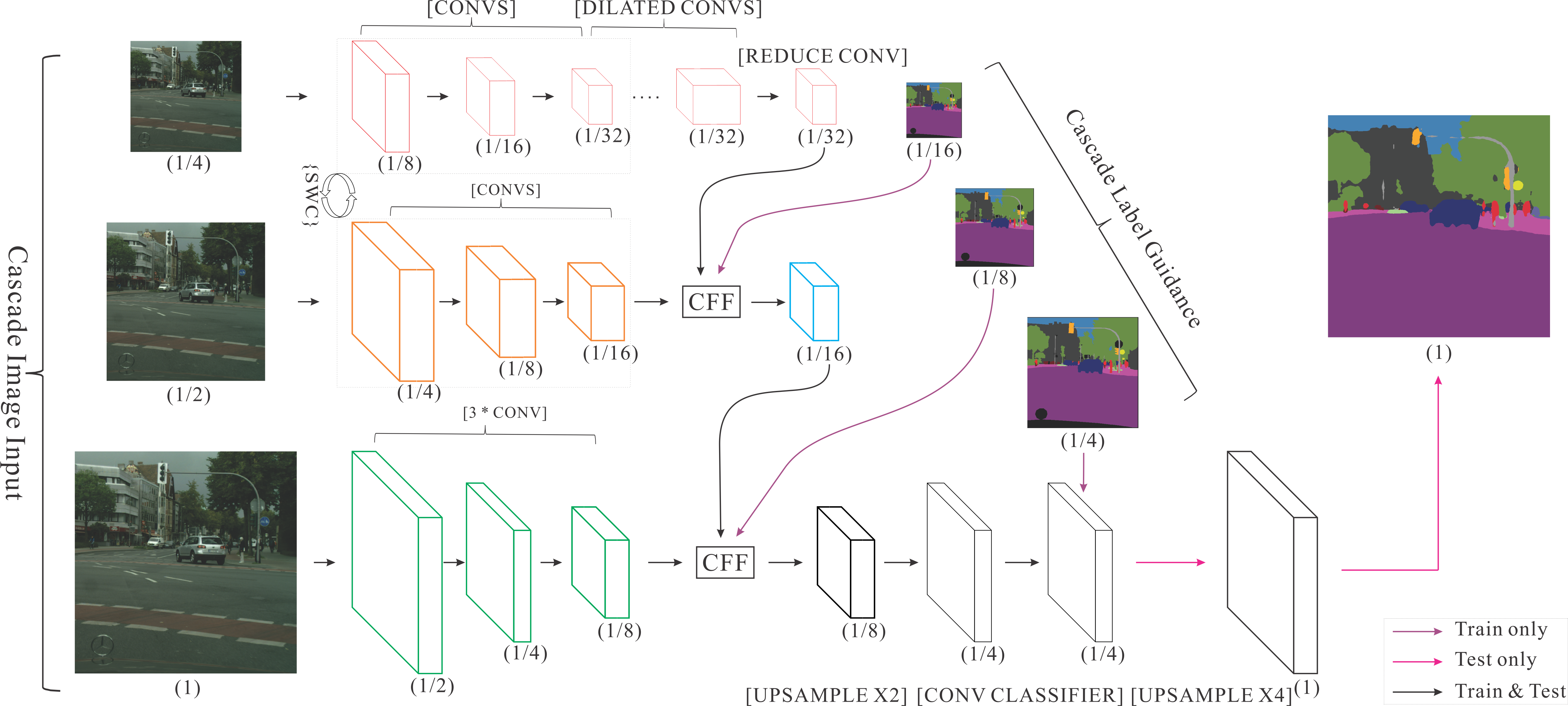
fluid/icnet/icnet.py
0 → 100644
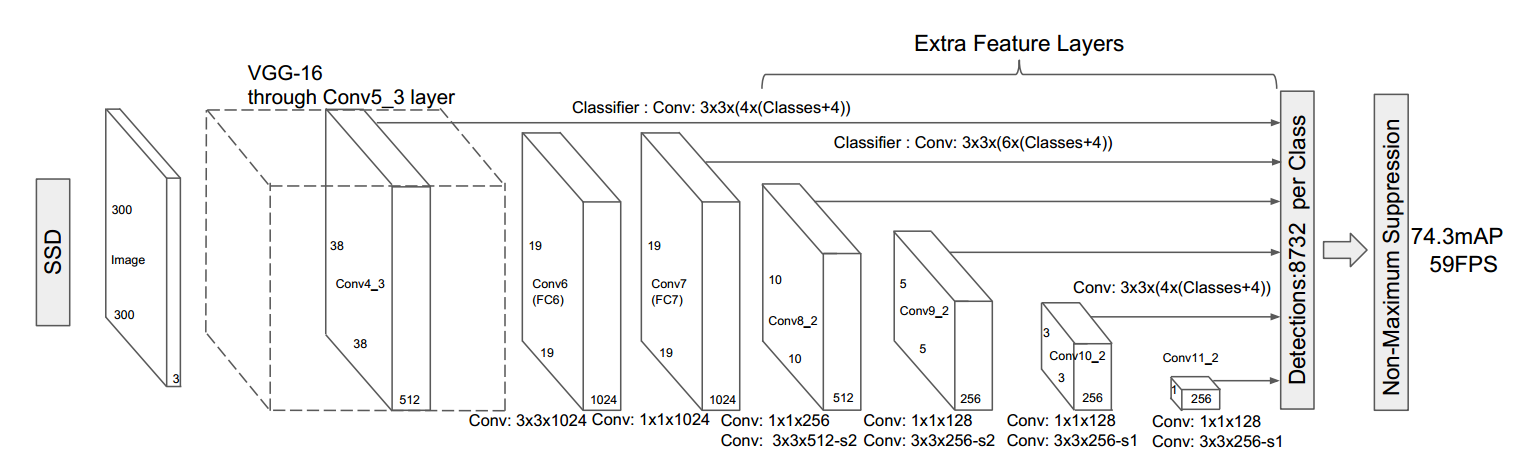
fluid/icnet/images/icnet.png
0 → 100644
2.0 MB
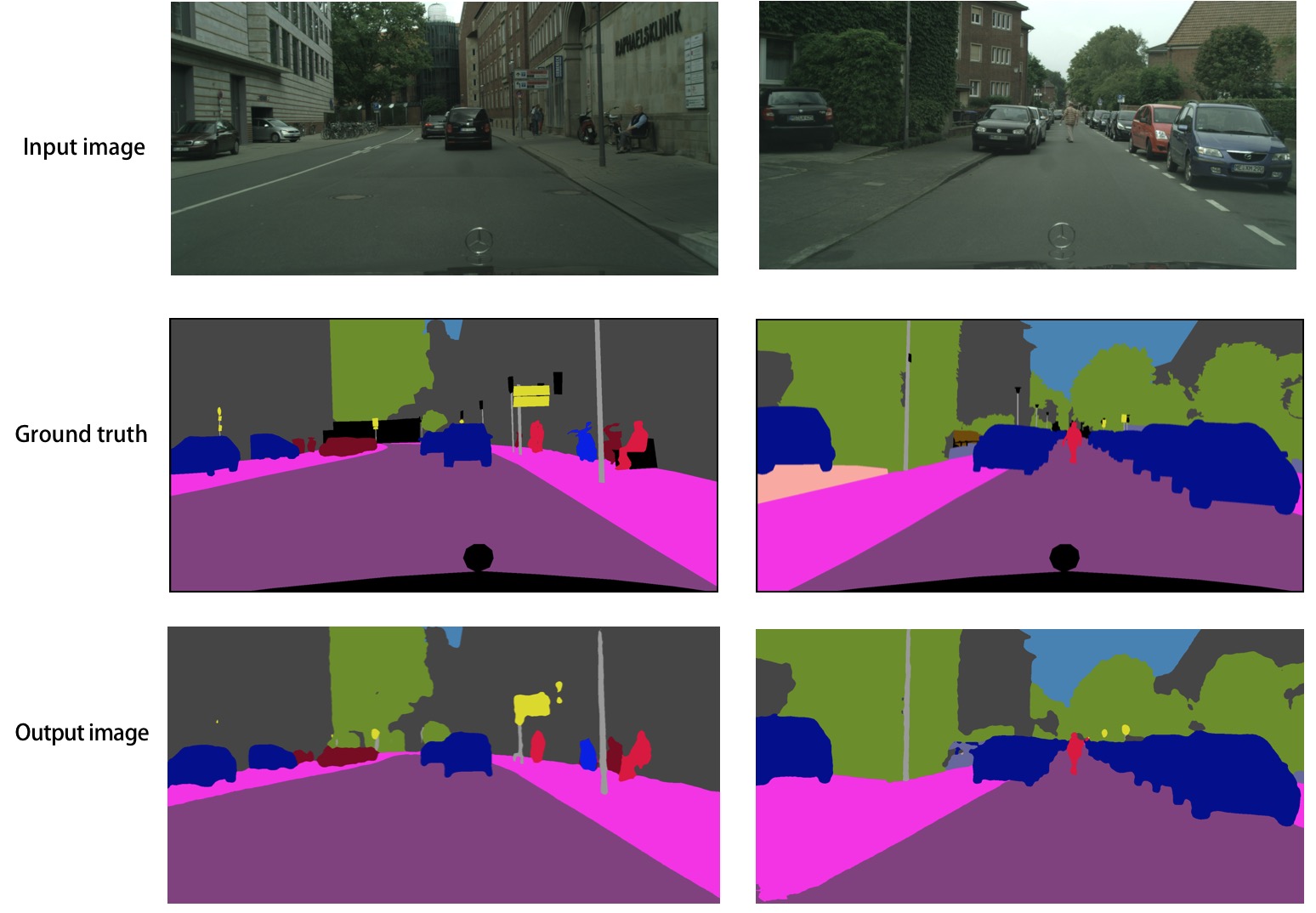
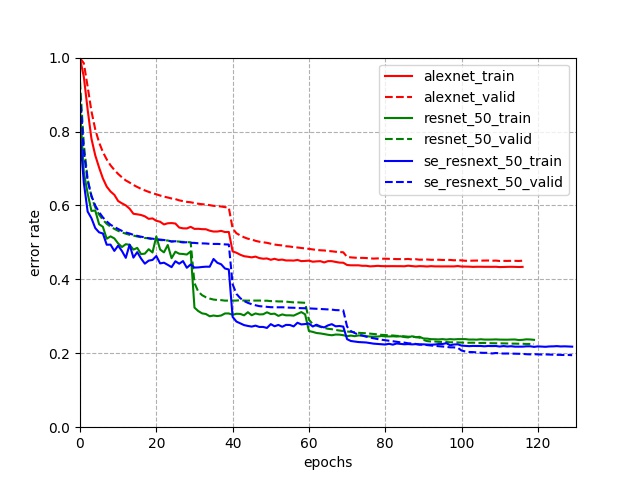
fluid/icnet/images/result.png
0 → 100644
207.7 KB
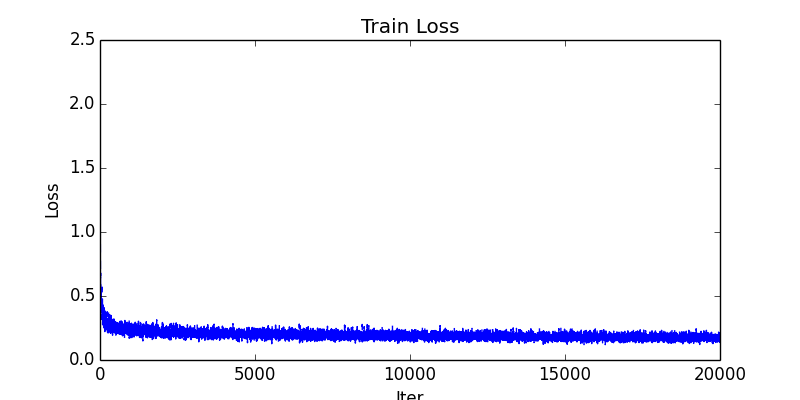
fluid/icnet/images/train_loss.png
0 → 100644
19.4 KB
fluid/icnet/infer.py
0 → 100644
fluid/icnet/train.py
0 → 100644
fluid/icnet/utils.py
0 → 100644
72.4 KB
24.1 KB
42.1 KB
32.7 KB
47.6 KB
126.0 KB

| W: | H:
| W: | H:



| W: | H:
| W: | H:


ltr/README_en.md
0 → 100644
ltr/images/LambdaRank_EN.png
0 → 100644
24.1 KB
ltr/images/ranknet_en.png
0 → 100644
32.4 KB
nested_sequence/README_en.md
0 → 100644
scheduled_sampling/README_en.md
0 → 100644