Merge branch 'develop' of https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/models into ctc_decoder_deploy
Showing
ctr/infer.py
0 → 100644
ctr/network_conf.py
0 → 100644
ctr/reader.py
0 → 100644
ctr/utils.py
0 → 100644
deep_speech_2/.gitignore
0 → 100644
deep_speech_2/README.md
100644 → 100755
deep_speech_2/cloud/README.md
0 → 100755
deep_speech_2/cloud/split_data.py
0 → 100644
文件模式从 100755 更改为 100644
deep_speech_2/data_utils/augmentor/resample.py
100755 → 100644
文件模式从 100755 更改为 100644
deep_speech_2/demo_client.py
0 → 100644
deep_speech_2/demo_server.py
0 → 100644
deep_speech_2/layer.py
0 → 100644
deep_speech_2/requirements.txt
100755 → 100644
deep_speech_2/tests/test_setup.py
0 → 100644
dssm/README.md
0 → 100644
dssm/data/classification/test.txt
0 → 100644
dssm/data/rank/test.txt
0 → 100644
dssm/data/rank/train.txt
0 → 100644
dssm/data/vocab.txt
0 → 100644
dssm/images/dssm.jpg
0 → 100644
33.0 KB
dssm/images/dssm.png
0 → 100644
210.2 KB
dssm/images/dssm2.jpg
0 → 100644
45.2 KB
dssm/images/dssm2.png
0 → 100644
80.9 KB
dssm/images/dssm3.jpg
0 → 100644
43.6 KB
dssm/infer.py
0 → 100644
dssm/network_conf.py
0 → 100644
dssm/reader.py
0 → 100644
dssm/train.py
0 → 100644
dssm/utils.py
0 → 100644
ltr/run_lambdarank.sh
0 → 100644
ltr/run_ranknet.sh
0 → 100644
ssd/README.md
0 → 100644
ssd/config/__init__.py
0 → 100644
ssd/config/pascal_voc_conf.py
0 → 100644
ssd/data/label_list
0 → 100644
ssd/data/prepare_voc_data.py
0 → 100644
ssd/data_provider.py
0 → 100644
ssd/eval.py
0 → 100644
ssd/image_util.py
0 → 100644
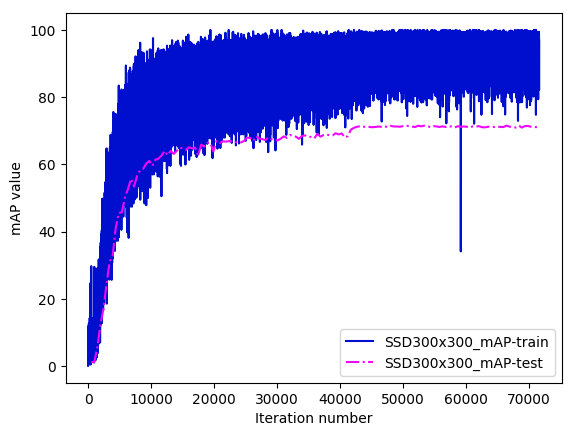
ssd/images/SSD300x300_map.png
0 → 100644
34.7 KB
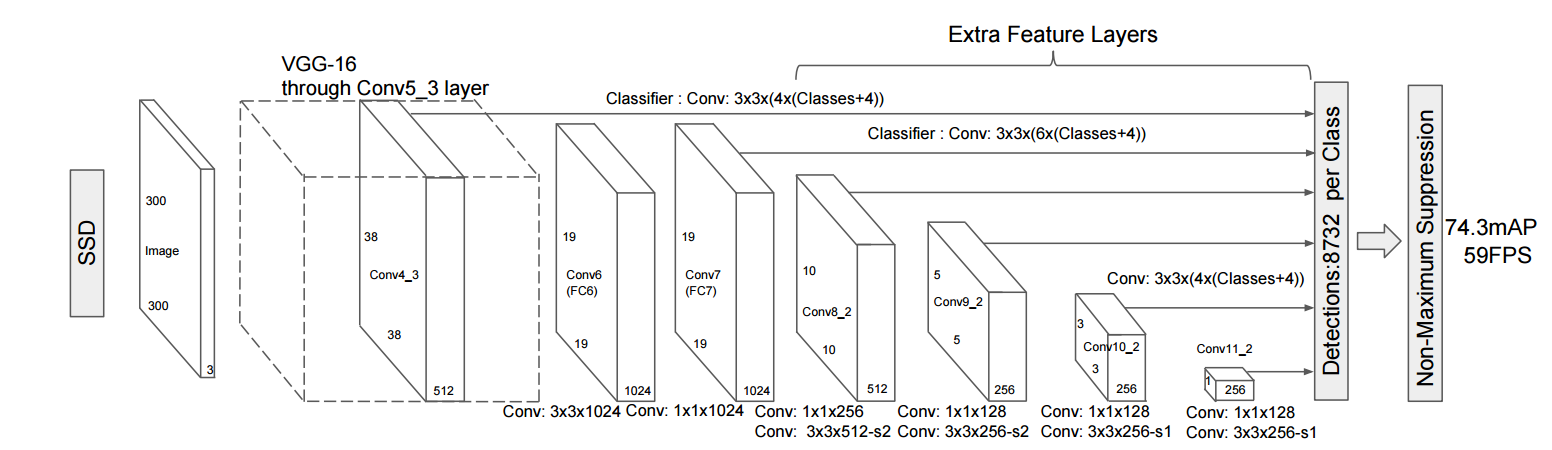
ssd/images/ssd_network.png
0 → 100644
151.0 KB
ssd/images/vis_1.jpg
0 → 100644
94.4 KB
ssd/images/vis_2.jpg
0 → 100644
82.6 KB
ssd/images/vis_3.jpg
0 → 100644
111.2 KB
ssd/images/vis_4.jpg
0 → 100644
73.2 KB
ssd/index.html
0 → 100644
ssd/infer.py
0 → 100644
ssd/train.py
0 → 100644
ssd/vgg_ssd_net.py
0 → 100644
ssd/visual.py
0 → 100644