Merge branch 'develop' of https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/book into change_None
Showing
0.coding_guideline/README.MD
0 → 100644
1010.4 KB
220.2 KB
140.3 KB
631.8 KB
404.0 KB
240.7 KB
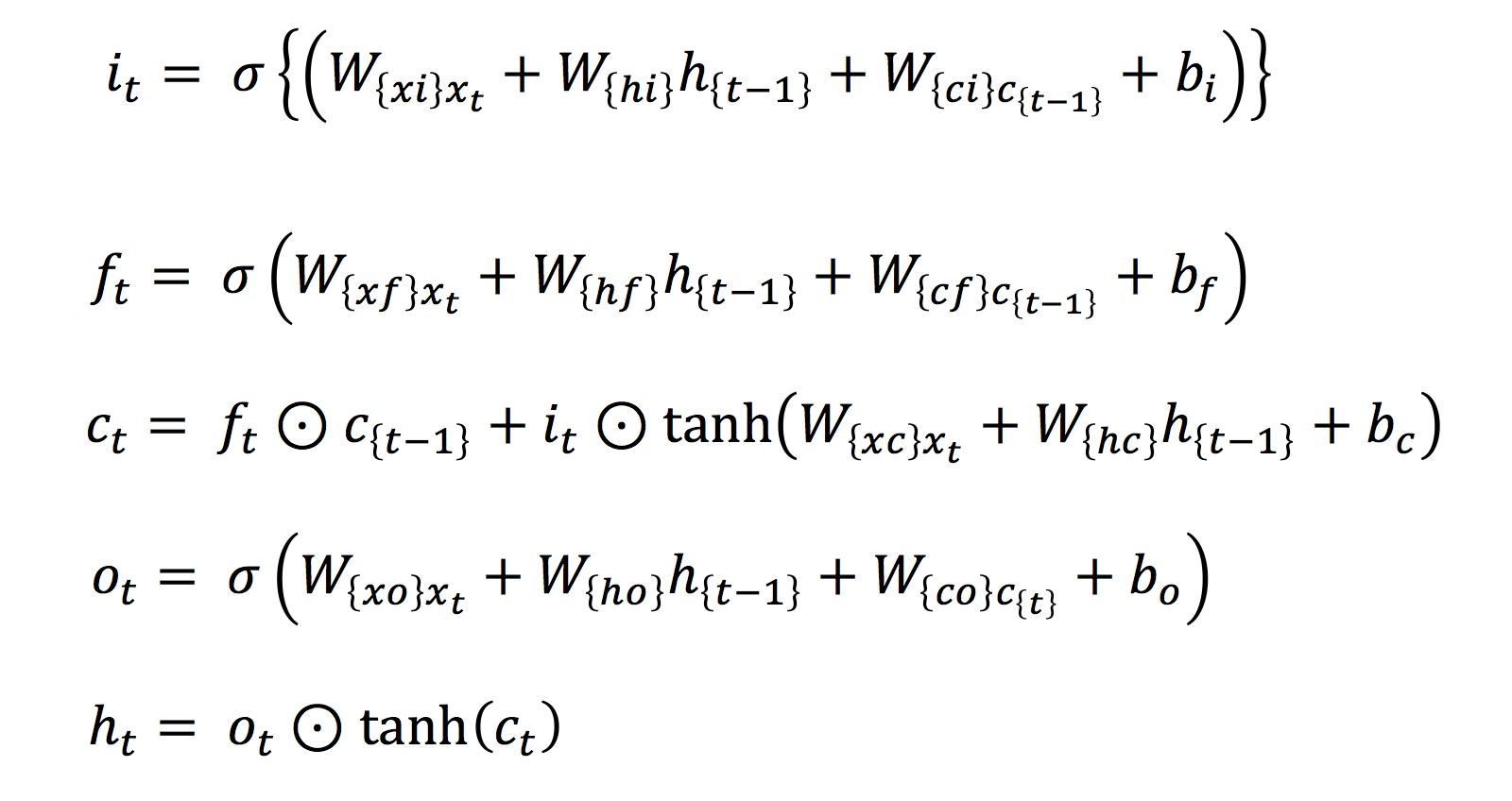
| W: | H:
| W: | H:
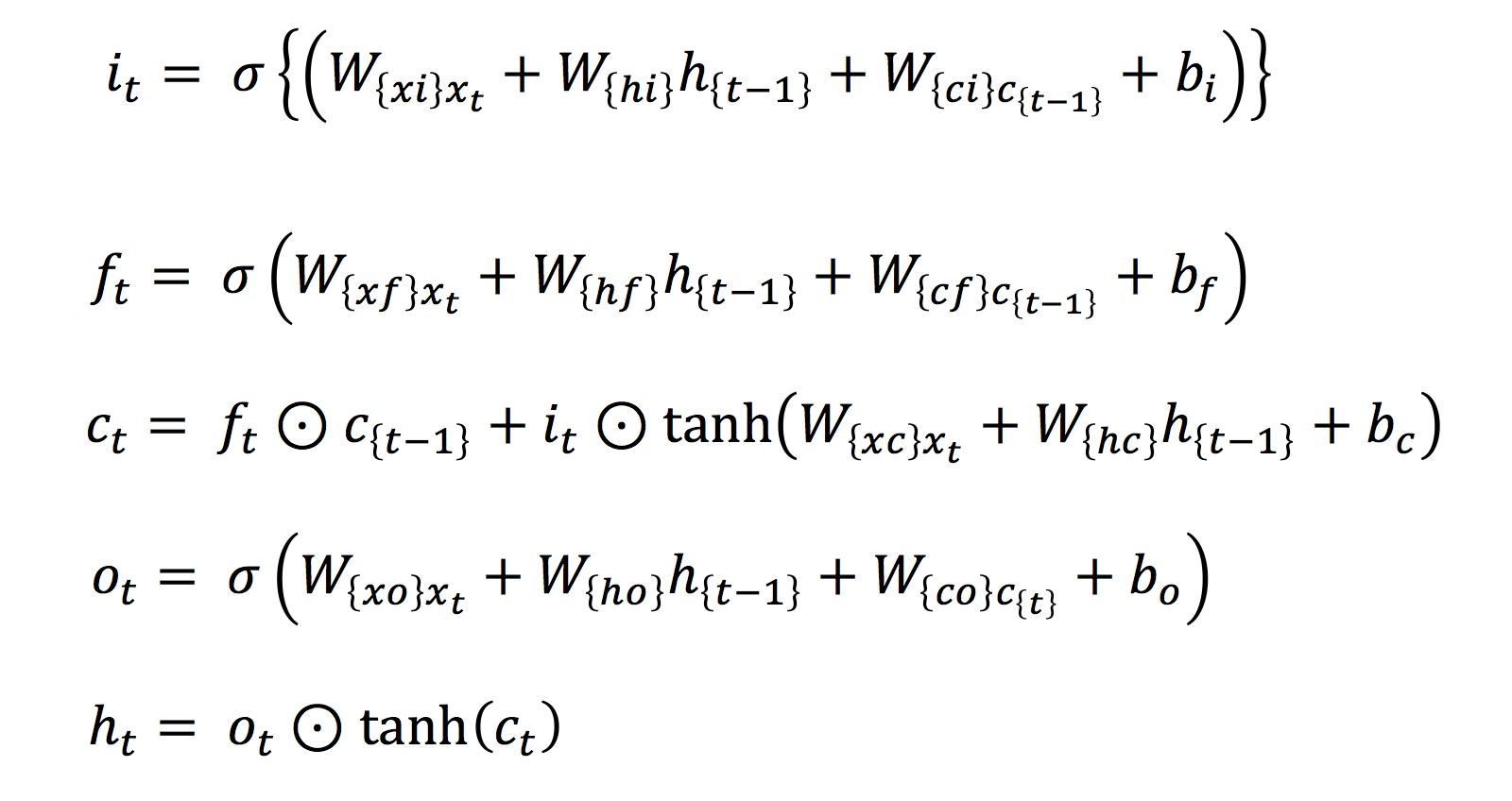
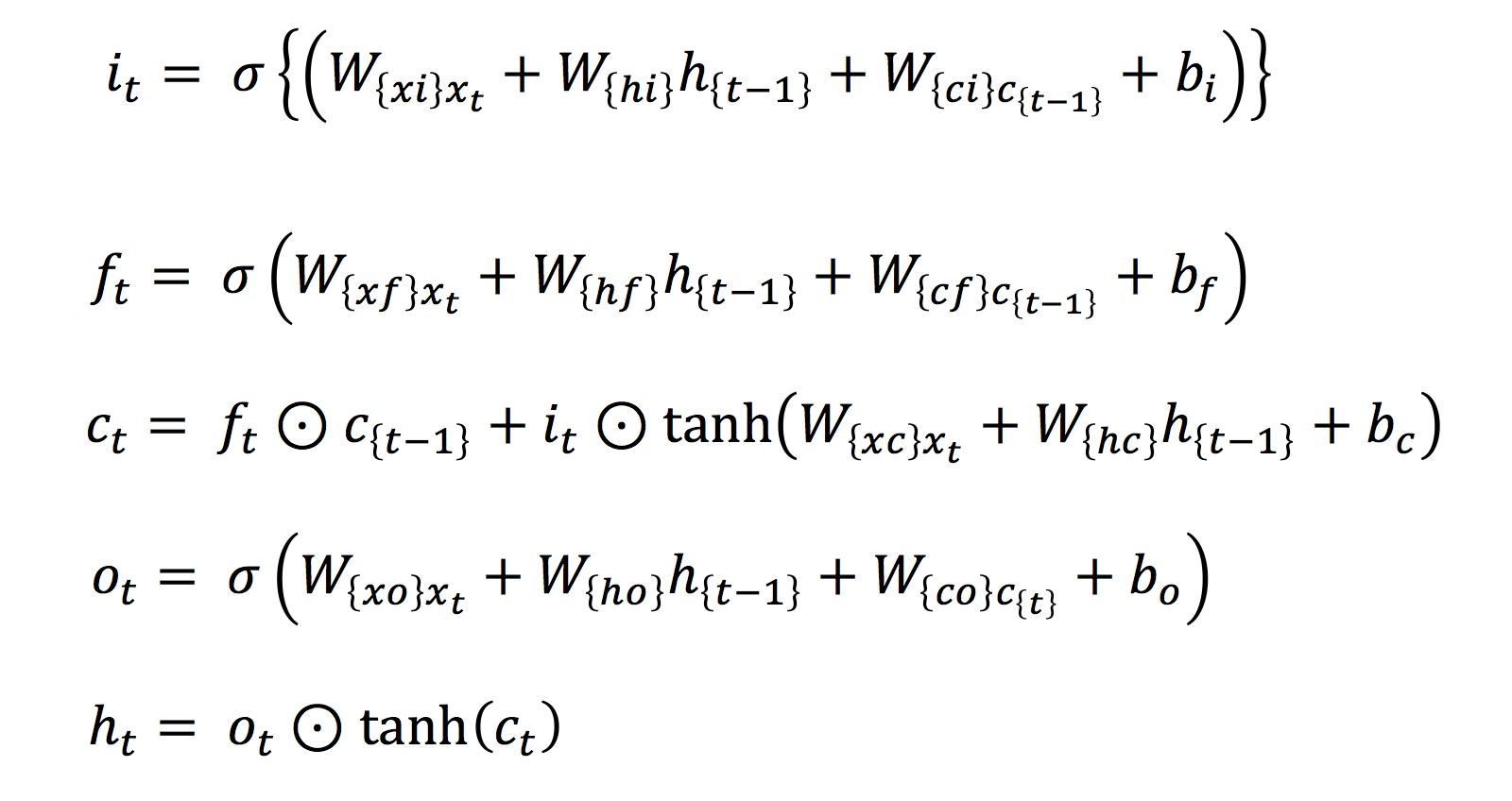
1010.4 KB
220.2 KB

140.3 KB
631.8 KB
404.0 KB

240.7 KB
120.8 KB | W: | H:
45.5 KB | W: | H: