follow comments, except for the formula part
Showing
recognize_digits/.gitignore
0 → 100644
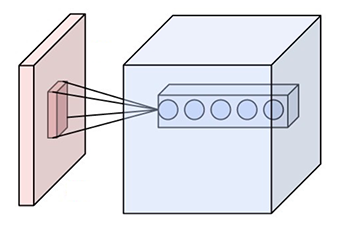
| W: | H:
| W: | H:


49.4 KB
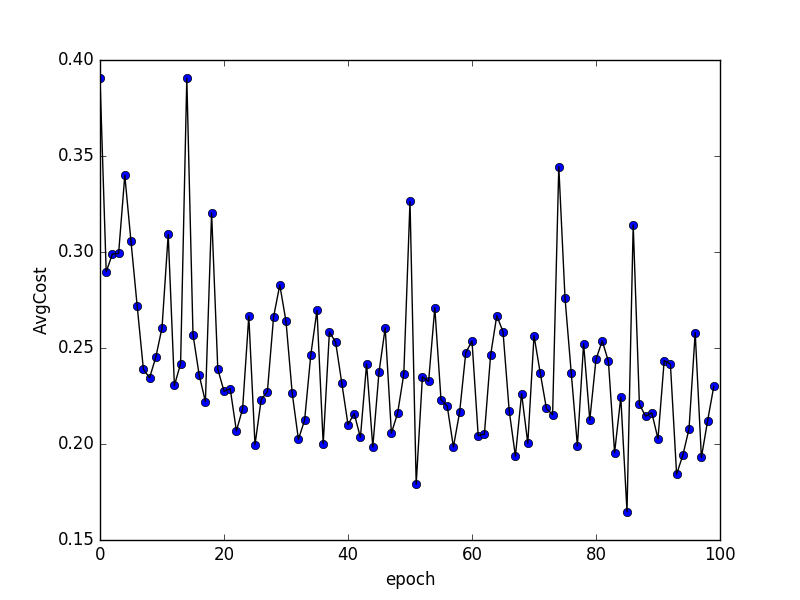
| W: | H:
| W: | H:


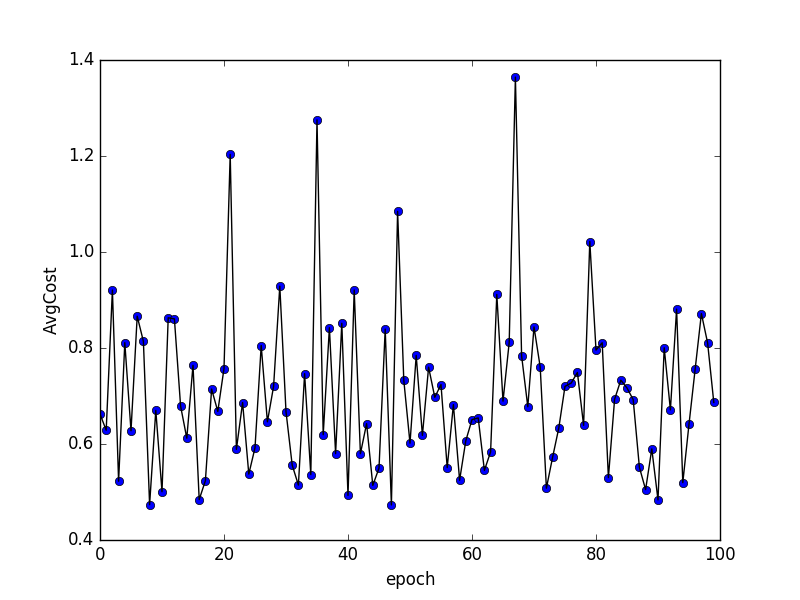
| W: | H:
| W: | H:



55.2 KB | W: | H:

147.3 KB | W: | H:





49.4 KB

57.2 KB | W: | H:

56.1 KB | W: | H:





57.8 KB | W: | H:

58.0 KB | W: | H:




