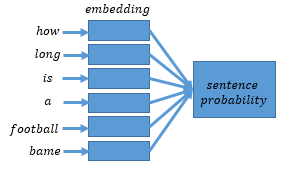
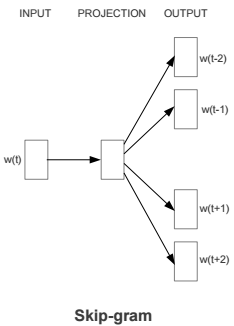
Merge https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/book into recommender_sys
Showing
word2vec/.gitignore
0 → 100644
此差异已折叠。
word2vec/calculate_dis.py
0 → 100755
word2vec/data/getdata.sh
0 → 100755
word2vec/dataprovider.py
0 → 100644
word2vec/format_convert.py
0 → 100755
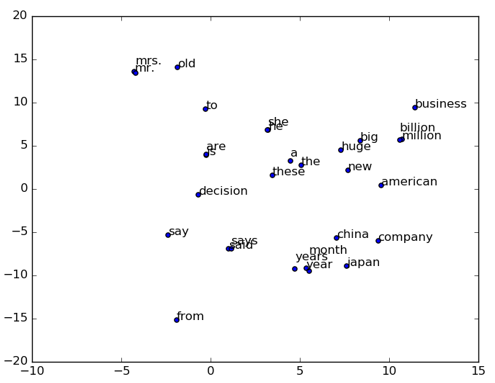
word2vec/image/2d_similarity.png
0 → 100644
23.6 KB
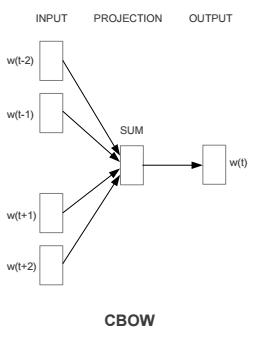
word2vec/image/cbow.png
0 → 100644
11.0 KB
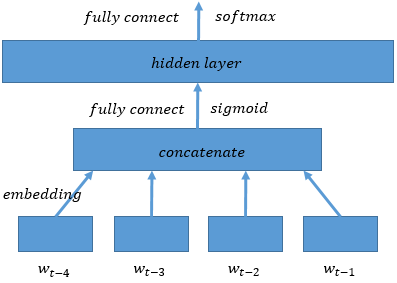
word2vec/image/ngram.png
0 → 100644
9.1 KB
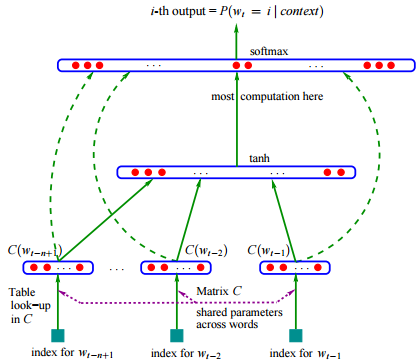
word2vec/image/nnlm.png
0 → 100644
33.1 KB
word2vec/image/sentence_emb.png
0 → 100644
6.6 KB
word2vec/image/skipgram.png
0 → 100644
10.6 KB
word2vec/ngram.py
0 → 100644
word2vec/train.sh
0 → 100755