# Python Pipeline 核心功能
从设计上,Python Pipeline 框架实现轻量级的服务化部署,提供了丰富的核心功能,既能满足服务基本使用,又能满足特性需求。
- [安装与环境检查](#1)
- [服务启动与关闭](#2)
- [本地与远程推理](#3)
- [批量推理](#4)
- [4.1 客户端打包批量数据](#4.1)
- [4.2 服务端合并多个请求动态合并批量](#4.2)
- [4.3 Mini-Batch](#4.3)
- [单机多卡推理](#5)
- [多种计算芯片上推理](#6)
- [TensorRT 推理加速](#7)
- [MKLDNN 推理加速](#8)
- [低精度推理](#9)
- [9.1 CPU 低精度推理](#9.1)
- [9.2 GPU 和 TensorRT 低精度推理](#9.2)
- [9.3 性能测试](#9.3)
- [复杂图结构 DAG 跳过某个 Op 运行](#10)
## 安装与环境检查
在运行 Python Pipeline 服务前,确保当前环境下可部署且通过[安装指南](../Install_CN.md)已完成安装。其次,`v0.8.0`及以上版本提供了环境检查功能,检验环境是否安装正确。
输入以下命令,进入环境检查程序。
```python
python3 -m paddle_serving_server.serve check
```
在环境检验程序中输入多条指令来检查,例如 `check_pipeline`,`check_all`等,完整指令列表如下。
| 指令 | 描述|
|---------|----|
|check_all | 检查 Paddle Inference、Pipeline Serving、C++ Serving。只打印检测结果,不记录日志|
|check_pipeline | 检查 Pipeline Serving,只打印检测结果,不记录日志|
|check_cpp | 检查 C++ Serving,只打印检测结果,不记录日志|
|check_inference | 检查 Paddle Inference 是否安装正确,只打印检测结果,不记录日志|
|debug | 发生报错后,该命令将打印提示日志到屏幕,并记录详细日志文件|
|exit | 退出|
程序会分别运行 cpu 和 gpu 示例。运行成功则打印 `Pipeline cpu environment running success
` 和 `Pipeline gpu environment running success`。
```
/usr/local/lib/python3.7/runpy.py:125: RuntimeWarning: 'paddle_serving_server.serve' found in sys.modules after import of package 'paddle_serving_server', but prior to execution of 'paddle_serving_server.serve'; this may result in unpredictable behaviour
warn(RuntimeWarning(msg))
Welcome to the check env shell.Type help to list commands.
(Cmd) check_pipeline
Pipeline cpu environment running success
Pipeline gpu environment running success
```
运行失败时,错误信息会记录到当前目录下 `stderr.log` 文件 和 `Pipeline_test_cpu/PipelineServingLogs` 目录下。用户可根据错误信息调试。
```
(Cmd) check_all
PaddlePaddle inference environment running success
C++ cpu environment running success
C++ gpu environment running failure, if you need this environment, please refer to https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Serving/blob/develop/doc/Install_CN.md
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/usr/local/lib/python3.7/runpy.py", line 193, in _run_module_as_main
"__main__", mod_spec)
File "/usr/local/lib/python3.7/runpy.py", line 85, in _run_code
exec(code, run_globals)
File "/usr/local/lib/python3.7/site-packages/paddle_serving_server/serve.py", line 541, in
Check_Env_Shell().cmdloop()
File "/usr/local/lib/python3.7/cmd.py", line 138, in cmdloop
stop = self.onecmd(line)
File "/usr/local/lib/python3.7/cmd.py", line 217, in onecmd
return func(arg)
File "/usr/local/lib/python3.7/site-packages/paddle_serving_server/serve.py", line 501, in do_check_all
check_env("all")
File "/usr/local/lib/python3.7/site-packages/paddle_serving_server/env_check/run.py", line 94, in check_env
run_test_cases(pipeline_test_cases, "Pipeline", is_open_std)
File "/usr/local/lib/python3.7/site-packages/paddle_serving_server/env_check/run.py", line 66, in run_test_cases
mv_log_to_new_dir(new_dir_path)
File "/usr/local/lib/python3.7/site-packages/paddle_serving_server/env_check/run.py", line 48, in mv_log_to_new_dir
shutil.move(file_path, dir_path)
File "/usr/local/lib/python3.7/shutil.py", line 555, in move
raise Error("Destination path '%s' already exists" % real_dst)
shutil.Error: Destination path '/home/work/Pipeline_test_cpu/PipelineServingLogs' already exists
```
## 服务启动与关闭
服务启动需要三类文件,PYTHON 程序、模型文件和配置文件。以[Python Pipeline 快速部署案例](../Quick_Start_CN.md)为例,
```
.
├── config.yml
├── imgs
│ └── ggg.png
├── ocr_det_client
│ ├── serving_client_conf.prototxt
│ └── serving_client_conf.stream.prototxt
├── ocr_det_model
│ ├── inference.pdiparams
│ ├── inference.pdmodel
│ ├── serving_server_conf.prototxt
│ └── serving_server_conf.stream.prototxt
├── ocr_det.tar.gz
├── ocr_rec_client
│ ├── serving_client_conf.prototxt
│ └── serving_client_conf.stream.prototxt
├── ocr_rec_model
│ ├── inference.pdiparams
│ ├── inference.pdmodel
│ ├── serving_server_conf.prototxt
│ └── serving_server_conf.stream.prototxt
├── pipeline_http_client.py
├── pipeline_rpc_client.py
├── ppocr_keys_v1.txt
└── web_service.py
```
启动服务端程序运行 `web_service.py`,启动客户端程序运行 `pipeline_http_client.py` 或 `pipeline_rpc_client.py`。服务端启动的日志信息在 `PipelineServingLogs` 目录下可用于调试。
```
├── PipelineServingLogs
│ ├── pipeline.log
│ ├── pipeline.log.wf
│ └── pipeline.tracer
```
关闭程序可使用2种方式,
- 前台关闭程序:`Ctrl+C` 关停服务
- 后台关闭程序:
```python
python3 -m paddle_serving_server.serve stop # 触发 SIGINT 信号
python3 -m paddle_serving_server.serve kill # 触发 SIGKILL 信号,强制关闭
```
## 本地与远程推理
本地推理是指在服务所在机器环境下开启多进程推理,而远程推理是指本地服务请求远程 C++ Serving 推理服务。
本地推理的优势是实现简单,一般本地处理相比于远程推理耗时更低。而远程推理的优势是可实现 Python Pipeline 较难实现的功能,如部署加密模型,大模型推理。
Python Pipeline 的本地推理可参考如下配置,在 `uci` op 中 增加 `local_service_conf` 配置,并设置 `client_type: local_predictor`。
```
op:
uci:
#并发数,is_thread_op=True时,为线程并发;否则为进程并发
concurrency: 10
#当op配置没有server_endpoints时,从local_service_conf读取本地服务配置
local_service_conf:
#uci模型路径
model_config: uci_housing_model
#计算硬件类型: 空缺时由devices决定(CPU/GPU),0=cpu, 1=gpu, 2=tensorRT, 3=arm cpu, 4=kunlun xpu
device_type: 0
#计算硬件ID,优先由device_type决定硬件类型。devices为""或空缺时为CPU预测;当为"0", "0,1,2"时为GPU预测,表示使用的GPU卡
devices: "" # "0,1"
#client类型,包括brpc, grpc和local_predictor.local_predictor不启动Serving服务,进程内预测
client_type: local_predictor
#Fetch结果列表,以client_config中fetch_var的alias_name为准
fetch_list: ["price"]
```
Python Pipeline 的远程推理可参考如下配置,设置 `client_type: brpc`,`server_endpoints`,`timeout` 和本地 `client_config`。
```
op:
bow:
#并发数,is_thread_op=True时,为线程并发;否则为进程并发
concurrency: 1
#client连接类型,brpc
client_type: brpc
#Serving交互重试次数,默认不重试
retry: 1
#Serving交互超时时间, 单位ms
timeout: 3000
#Serving IPs
server_endpoints: ["127.0.0.1:9393"]
#bow模型client端配置
client_config: "imdb_bow_client_conf/serving_client_conf.prototxt"
#Fetch结果列表,以client_config中fetch_var的alias_name为准
fetch_list: ["prediction"]
```
## 批量推理
Pipeline 支持批量推理,通过增大 batch size 可以提高 GPU 利用率。Python Pipeline 支持3种 batch 形式以及适用的场景如下:
- 场景1:客户端打包批量数据(Client Batch)
- 场景2:服务端合并多个请求动态合并批量(Server auto-batching)
- 场景3:拆分一个大批量的推理请求为多个小批量推理请求(Server mini-batch)
**一.客户端打包批量数据**
当输入数据是 numpy 类型,如shape 为[4, 3, 512, 512]的 numpy 数据,即4张图片,可直接作为输入数据。
当输入数据的 shape 不同时,需要按最大的shape的尺寸 Padding 对齐后发送给服务端
**二.服务端合并多个请求动态合并批量**
有助于提升吞吐和计算资源的利用率,当多个请求的 shape 尺寸不相同时,不支持合并。当前有2种合并策略,分别是:
- 等待时间与最大批量结合(推荐):结合`batch_size`和`auto_batching_timeout`配合使用,实际请求的批量条数超过`batch_size`时会立即执行,不超过时会等待`auto_batching_timeout`时间再执行
```
op:
bow:
# 并发数,is_thread_op=True时,为线程并发;否则为进程并发
concurrency: 1
# client连接类型,brpc, grpc和local_predictor
client_type: brpc
# Serving IPs
server_endpoints: ["127.0.0.1:9393"]
# bow模型client端配置
client_config: "imdb_bow_client_conf/serving_client_conf.prototxt"
# 批量查询Serving的数量, 默认1。batch_size>1要设置auto_batching_timeout,否则不足batch_size时会阻塞
batch_size: 2
# 批量查询超时,与batch_size配合使用
auto_batching_timeout: 2000
```
- 阻塞式等待:仅设置`batch_size`,不设置`auto_batching_timeout`或`auto_batching_timeout=0`,会一直等待接受 `batch_size` 个请求后再推理。
```
op:
bow:
# 并发数,is_thread_op=True时,为线程并发;否则为进程并发
concurrency: 1
# client连接类型,brpc, grpc和local_predictor
client_type: brpc
# Serving IPs
server_endpoints: ["127.0.0.1:9393"]
# bow模型client端配置
client_config: "imdb_bow_client_conf/serving_client_conf.prototxt"
# 批量查询Serving的数量, 默认1。batch_size>1要设置auto_batching_timeout,否则不足batch_size时会阻塞
batch_size: 2
# 批量查询超时,与batch_size配合使用
auto_batching_timeout: 2000
```
**三.Mini-Batch**
拆分一个批量数据推理请求成为多个小块推理:会降低批量数据 Padding 对齐的大小,从而提升速度。可参考 [OCR 示例](),核心思路是拆分数据成多个小批量,放入 list 对象 feed_list 并返回
```
def preprocess(self, input_dicts, data_id, log_id):
(_, input_dict), = input_dicts.items()
raw_im = input_dict["image"]
data = np.frombuffer(raw_im, np.uint8)
im = cv2.imdecode(data, cv2.IMREAD_COLOR)
dt_boxes = input_dict["dt_boxes"]
dt_boxes = self.sorted_boxes(dt_boxes)
feed_list = []
img_list = []
max_wh_ratio = 0
## Many mini-batchs, the type of feed_data is list.
max_batch_size = len(dt_boxes)
# If max_batch_size is 0, skipping predict stage
if max_batch_size == 0:
return {}, True, None, ""
boxes_size = len(dt_boxes)
batch_size = boxes_size // max_batch_size
rem = boxes_size % max_batch_size
for bt_idx in range(0, batch_size + 1):
imgs = None
boxes_num_in_one_batch = 0
if bt_idx == batch_size:
if rem == 0:
continue
else:
boxes_num_in_one_batch = rem
elif bt_idx < batch_size:
boxes_num_in_one_batch = max_batch_size
else:
_LOGGER.error("batch_size error, bt_idx={}, batch_size={}".
format(bt_idx, batch_size))
break
start = bt_idx * max_batch_size
end = start + boxes_num_in_one_batch
img_list = []
for box_idx in range(start, end):
boximg = self.get_rotate_crop_image(im, dt_boxes[box_idx])
img_list.append(boximg)
h, w = boximg.shape[0:2]
wh_ratio = w * 1.0 / h
max_wh_ratio = max(max_wh_ratio, wh_ratio)
_, w, h = self.ocr_reader.resize_norm_img(img_list[0],
max_wh_ratio).shape
imgs = np.zeros((boxes_num_in_one_batch, 3, w, h)).astype('float32')
for id, img in enumerate(img_list):
norm_img = self.ocr_reader.resize_norm_img(img, max_wh_ratio)
imgs[id] = norm_img
feed = {"x": imgs.copy()}
feed_list.append(feed)
return feed_list, False, None, ""
```
## 单机多卡推理
单机多卡推理与 `config.yml` 中配置4个参数关系紧密,`is_thread_op`、`concurrency`、`device_type` 和 `devices`,必须在进程模型和 GPU 模式,每张卡上可分配多个进程,即 M 个 Op 进程与 N 个 GPU 卡绑定。
```
dag:
#op资源类型, True, 为线程模型;False,为进程模型
is_thread_op: False
op:
det:
#并发数,is_thread_op=True时,为线程并发;否则为进程并发
concurrency: 6
#当op配置没有server_endpoints时,从local_service_conf读取本地服务配置
local_service_conf:
client_type: local_predictor
# device_type, 0=cpu, 1=gpu, 2=tensorRT, 3=arm cpu, 4=kunlun xpu
device_type: 0
# 计算硬件 ID,当 devices 为""或不写时为 CPU 预测;当 devices 为"0", "0,1,2"时为 GPU 预测,表示使用的 GPU 卡
devices: "0,1,2"
```
以上述案例为例,`concurrency:6`,即启动6个进程,`devices:0,1,2`,根据轮询分配机制,得到如下绑定关系:
- 进程ID: 0 绑定 GPU 卡0
- 进程ID: 1 绑定 GPU 卡1
- 进程ID: 2 绑定 GPU 卡2
- 进程ID: 3 绑定 GPU 卡0
- 进程ID: 4 绑定 GPU 卡1
- 进程ID: 5 绑定 GPU 卡2
- 进程ID: 6 绑定 GPU 卡0
对于更灵活的进程与 GPU 卡绑定方式,会持续开发。
## 多种计算芯片上推理
除了支持 CPU、GPU 芯片推理之外,Python Pipeline 还支持在多种计算硬件上推理。根据 `config.yml` 中的 `device_type` 和 `devices`来设置推理硬件和加速库如下:
- CPU(Intel) : 0
- GPU(GPU / Jetson / 海光 DCU) : 1
- TensorRT : 2
- CPU(Arm) : 3
- XPU : 4
- Ascend310 : 5
- ascend910 : 6
当不设置`device_type`时,根据 `devices` 来设置,即当 `device_type` 为 "" 或空缺时为 CPU 推理;当有设定如"0,1,2"时,为 GPU 推理,并指定 GPU 卡。
以使用 XPU 的编号为0卡为例,配合 `ir_optim` 一同开启,`config.yml`详细配置如下:
```
# 计算硬件类型
device_type: 4
# 计算硬件ID,优先由device_type决定硬件类型
devices: "0"
# 开启ir优化
ir_optim: True
```
## TensorRT 推理加速
TensorRT 是一个高性能的深度学习推理优化器,在 Nvdia 的 GPU 硬件平台运行的推理框架,为深度学习应用提供低延迟、高吞吐率的部署推理。
通过设置`device_type`、`devices`和`ir_optim` 字段即可实现 TensorRT 高性能推理。必须同时设置 `ir_optim: True` 才能开启 TensorRT。
```
op:
imagenet:
#并发数,is_thread_op=True时,为线程并发;否则为进程并发
concurrency: 1
#当op配置没有server_endpoints时,从local_service_conf读取本地服务配置
local_service_conf:
#uci模型路径
model_config: serving_server/
#计算硬件类型: 空缺时由devices决定(CPU/GPU),0=cpu, 1=gpu, 2=tensorRT, 3=arm cpu, 4=kunlun xpu
device_type: 2
#计算硬件ID,当devices为""或不写时为CPU预测;当devices为"0", "0,1,2"时为GPU预测,表示使用的GPU卡
devices: "1" # "0,1"
#client类型,包括brpc, grpc和local_predictor.local_predictor不启动Serving服务,进程内预测
client_type: local_predictor
#Fetch结果列表,以client_config中fetch_var的alias_name为准
fetch_list: ["score"]
#开启 ir_optim
ir_optim: True
```
## MKL-DNN 推理加速
MKL-DNN 针对 Intel CPU 和 GPU 的数学核心库,对深度学习网络进行算子和指令集的性能优化,从而提升执行速度。Paddle 框架已集成了 MKL-DNN。
目前仅支持 Intel CPU 推理加速,通过设置`device_type` 和 `devices` 和 `use_mkldnn` 字段使用 MKL-DNN。
```
op:
imagenet:
#并发数,is_thread_op=True时,为线程并发;否则为进程并发
concurrency: 1
#当op配置没有server_endpoints时,从local_service_conf读取本地服务配置
local_service_conf:
#uci模型路径
model_config: serving_server/
#计算硬件类型: 空缺时由devices决定(CPU/GPU),0=cpu, 1=gpu, 2=tensorRT, 3=arm cpu, 4=kunlun xpu
device_type: 0
#计算硬件ID,当devices为""或不写时为CPU预测;当devices为"0", "0,1,2"时为GPU预测,表示使用的GPU卡
devices: ""
#client类型,包括brpc, grpc和local_predictor.local_predictor不启动Serving服务,进程内预测
client_type: local_predictor
#Fetch结果列表,以client_config中fetch_var的alias_name为准
fetch_list: ["score"]
#开启 MKLDNN
use_mkldnn: True
```
## 低精度推理
Pipeline Serving支持低精度推理,CPU、GPU和TensoRT支持的精度类型如下图所示:
低精度推理需要有量化模型,配合`config.yml`配置一起使用,以[低精度示例](../Low_Precision_CN.md) 为例
**一.CPU 低精度推理**
通过设置,`device_type` 和 `devices` 字段使用 CPU 推理,通过调整`precision`、`thread_num`和`use_mkldnn`参数选择低精度和性能调优。
```
op:
imagenet:
#并发数,is_thread_op=True时,为线程并发;否则为进程并发
concurrency: 1
#当op配置没有server_endpoints时,从local_service_conf读取本地服务配置
local_service_conf:
#uci模型路径
model_config: serving_server/
#计算硬件类型: 空缺时由devices决定(CPU/GPU),0=cpu, 1=gpu, 2=tensorRT, 3=arm cpu, 4=kunlun xpu
device_type: 0
#计算硬件ID,当devices为""或不写时为CPU预测;当devices为"0", "0,1,2"时为GPU预测,表示使用的GPU卡
devices: ""
#client类型,包括brpc, grpc和local_predictor.local_predictor不启动Serving服务,进程内预测
client_type: local_predictor
#Fetch结果列表,以client_config中fetch_var的alias_name为准
fetch_list: ["score"]
#精度,CPU 支持: "fp32"(default), "bf16"(mkldnn); 不支持: "int8"
precision: "bf16"
#CPU 算数计算线程数,默认4线程
thread_num: 10
#开启 MKLDNN
use_mkldnn: True
```
**二.GPU 和 TensorRT 低精度推理**
通过设置`device_type` 和 `devices` 字段使用原生 GPU 或 TensorRT 推理,通过调整`precision`、`ir_optim`和`use_calib`参数选择低精度和性能调优,如开启 TensorRT,必须一同开启`ir_optim`,`use_calib`仅配合 int8 使用。
```
op:
imagenet:
#并发数,is_thread_op=True时,为线程并发;否则为进程并发
concurrency: 1
#当op配置没有server_endpoints时,从local_service_conf读取本地服务配置
local_service_conf:
#uci模型路径
model_config: serving_server/
#计算硬件类型: 空缺时由devices决定(CPU/GPU),0=cpu, 1=gpu, 2=tensorRT, 3=arm cpu, 4=kunlun xpu
device_type: 2
#计算硬件ID,当devices为""或不写时为CPU预测;当devices为"0", "0,1,2"时为GPU预测,表示使用的GPU卡
devices: "1" # "0,1"
#client类型,包括brpc, grpc和local_predictor.local_predictor不启动Serving服务,进程内预测
client_type: local_predictor
#Fetch结果列表,以client_config中fetch_var的alias_name为准
fetch_list: ["score"]
#精度,GPU 支持: "fp32"(default), "fp16", "int8"
precision: "int8"
#开启 TensorRT int8 calibration
use_calib: True
#开启 ir_optim
ir_optim: True
```
**三.性能测试**
测试环境如下:
- GPU 型号: A100-40GB
- CPU 型号: Intel(R) Xeon(R) Gold 6148 CPU @ 2.40GHz * 160
- CUDA: CUDA Version: 11.2
- CuDNN: 8.0
测试方法:
- 模型: Resnet50 量化模型
- 部署方法: Python Pipeline 部署
- 计时方法: 刨除第一次运行初始化,运行100次计算平均值
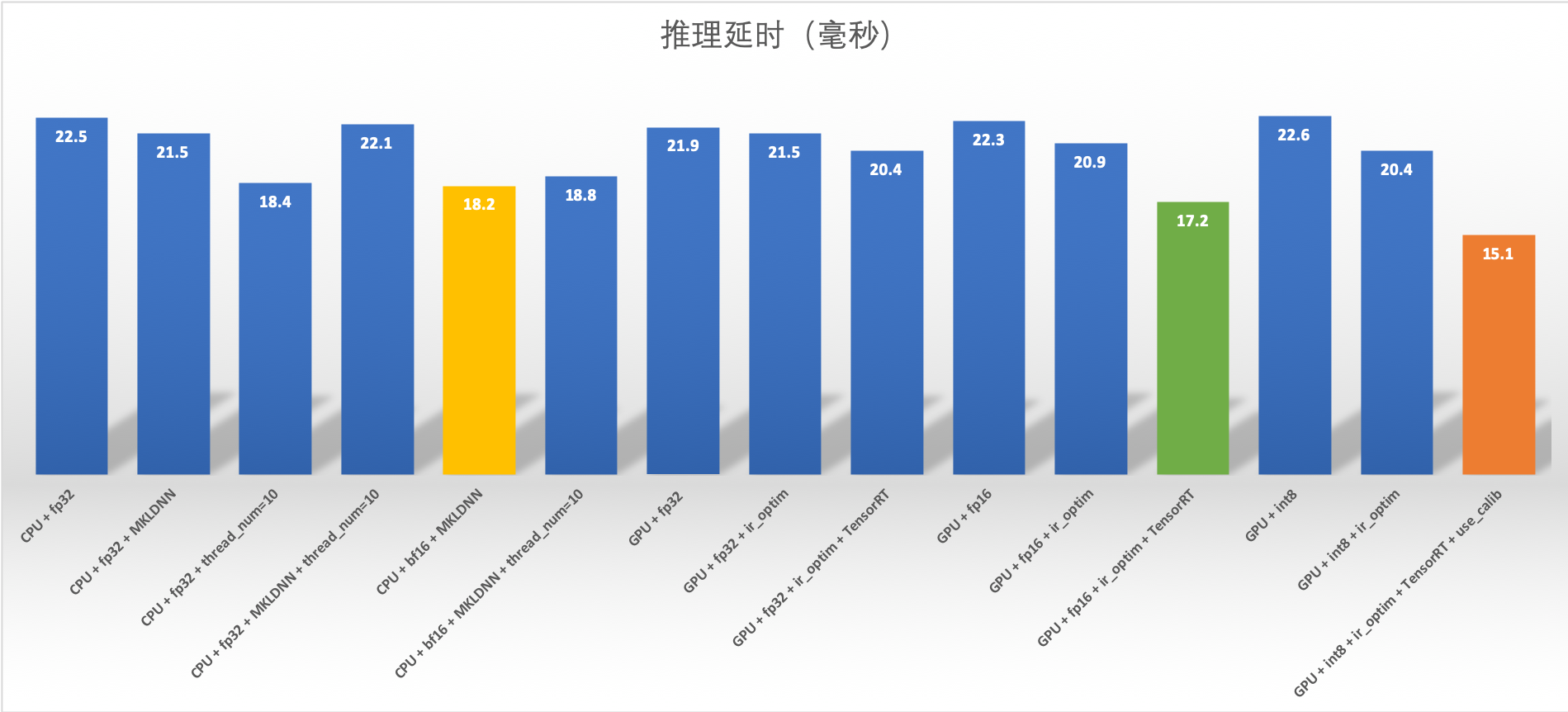
在此环境下测试不同精度推理结果,GPU 推理性能较好的配置是
- GPU + int8 + ir_optim + TensorRT + use_calib : 15.1 ms
- GPU + fp16 + ir_optim + TensorRT : 17.2 ms
CPU 推理性能较好的配置是
- CPU + bf16 + MKLDNN : 18.2 ms
- CPU + fp32 + thread_num=10 : 18.4 ms
完整性能指标如下:
## 复杂图结构 DAG 跳过某个 Op 运行
此应用场景一般在 Op 前后处理中有 if 条件判断时,不满足条件时,跳过后面处理。实际做法是在跳过此 Op 的 process 阶段,只要在 preprocess 做好判断,跳过 process 阶段,在和 postprocess 后直接返回即可。
preprocess 返回结果列表的第二个结果是 `is_skip_process=True` 表示是否跳过当前 Op 的 process 阶段,直接进入 postprocess 处理。
```python
## Op::preprocess() 函数实现
def preprocess(self, input_dicts, data_id, log_id):
"""
In preprocess stage, assembling data for process stage. users can
override this function for model feed features.
Args:
input_dicts: input data to be preprocessed
data_id: inner unique id
log_id: global unique id for RTT
Return:
input_dict: data for process stage
is_skip_process: skip process stage or not, False default
prod_errcode: None default, otherwise, product errores occured.
It is handled in the same way as exception.
prod_errinfo: "" default
"""
# multiple previous Op
if len(input_dicts) != 1:
_LOGGER.critical(
self._log(
"Failed to run preprocess: this Op has multiple previous "
"inputs. Please override this func."))
os._exit(-1)
(_, input_dict), = input_dicts.items()
return input_dict, False, None, ""
```
以下示例 Jump::preprocess() 重载了原函数,返回了 True 字段
```python
class JumpOp(Op):
## Overload func JumpOp::preprocess
def preprocess(self, input_dicts, data_id, log_id):
(_, input_dict), = input_dicts.items()
if input_dict.has_key("jump"):
return input_dict, True, None, ""
else
return input_dict, False, None, ""
```