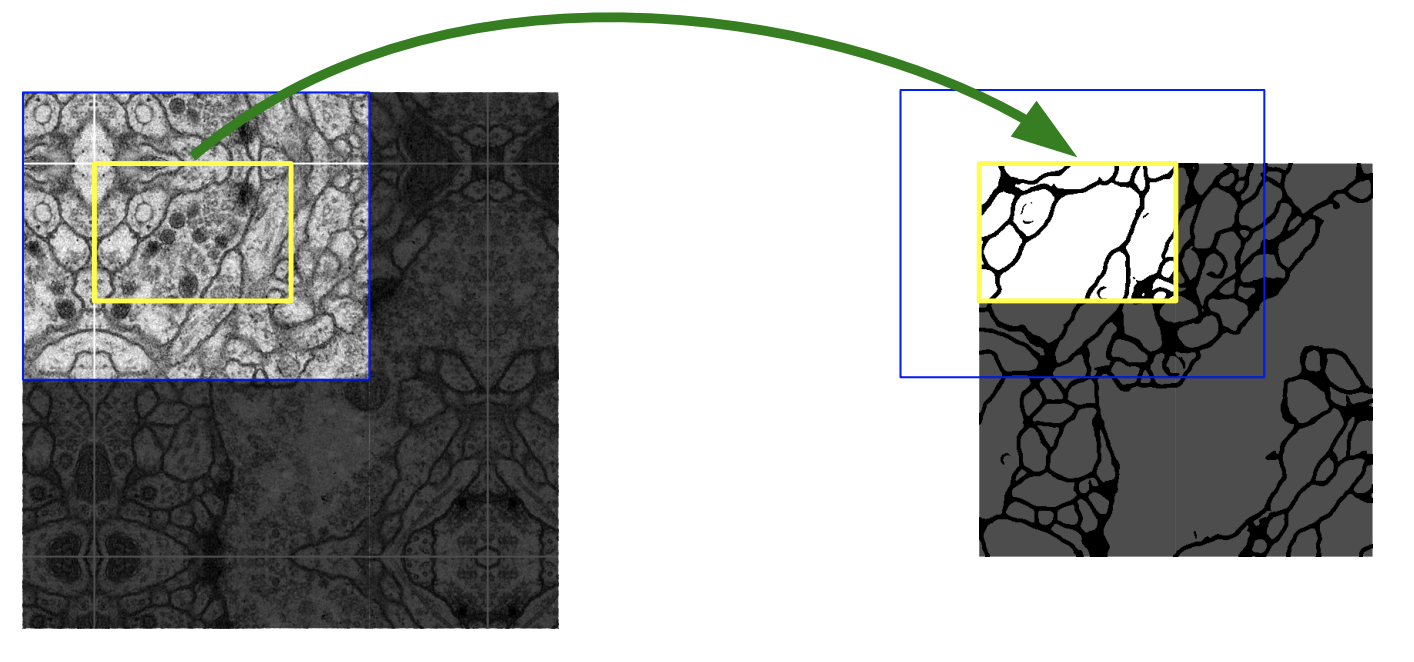
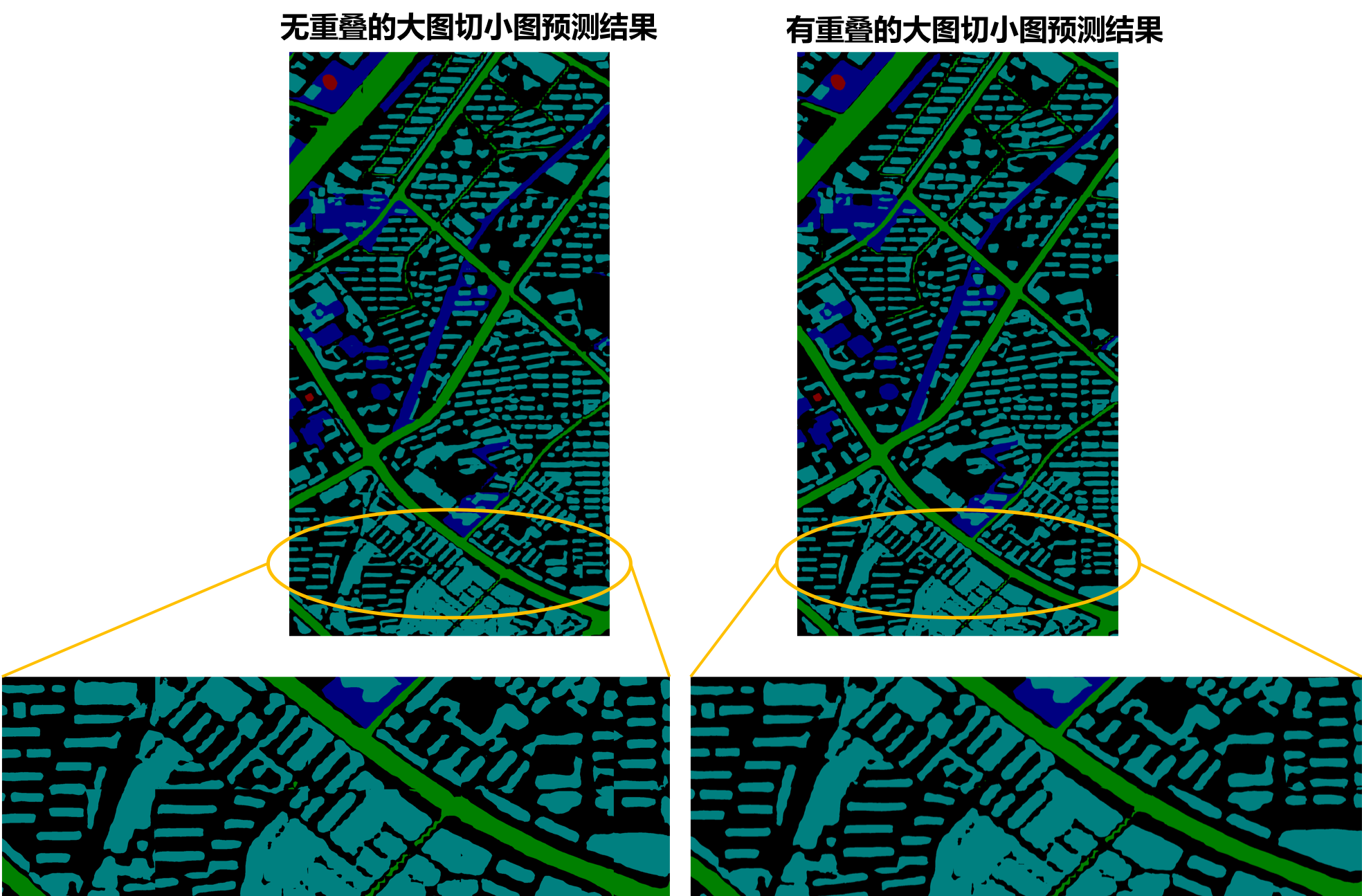
add remote_sensing
Showing
docs/examples/remote_sensing.md
0 → 100644
examples/remote_sensing/README.md
0 → 100644
examples/remote_sensing/eval.py
0 → 100644
432.6 KB
932.7 KB
examples/remote_sensing/train.py
0 → 100644