
-表1: 不同类型操作的开销对比 -
-
-表1: 不同类型操作的开销对比
-
-
-表2:模型量化前后精度对比
-
-
-图1:基于模拟量化训练的前向过程
-
-
-图2:基于模拟量化训练前向过程的等价工作流
-
-
-图3:基于模拟量化训练的反向传播和权重更新过程
-

-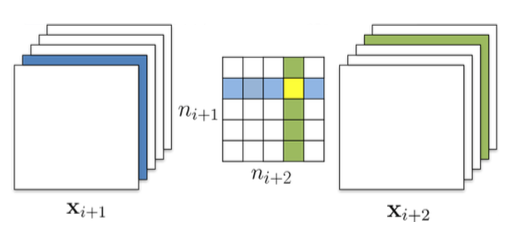
-图5
-
-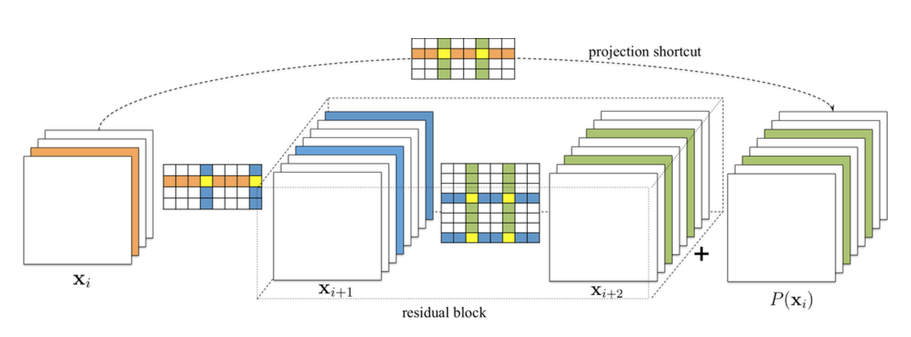
-图6
-
-
-图7
-
-
-图8
-
-
-图9
-
-
-图10
-
| Quantization | +Pruning | +NAS | +Distilling | +
|---|---|---|---|
+
|
+
+
|
+
+
|
+
+
+
|
+
+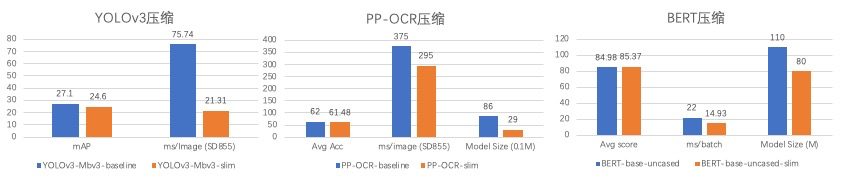
+表1: 部分模型压缩加速情况
+
-
-整体流程图
-
-
-整体流程图
-
 -
- -
- -
- -
-