diff --git a/PPOCRLabel/PPOCRLabel.py b/PPOCRLabel/PPOCRLabel.py
index d0d2bb721be41fe2c4042fbea1b55e4e76bdd664..0a3ae1cb3b8fc004aa7c48dc86b6546a80e17a0f 100644
--- a/PPOCRLabel/PPOCRLabel.py
+++ b/PPOCRLabel/PPOCRLabel.py
@@ -2449,13 +2449,6 @@ class MainWindow(QMainWindow):
export PPLabel and CSV to JSON (PubTabNet)
'''
import pandas as pd
- from libs.dataPartitionDialog import DataPartitionDialog
-
- # data partition user input
- partitionDialog = DataPartitionDialog(parent=self)
- partitionDialog.exec()
- if partitionDialog.getStatus() == False:
- return
# automatically save annotations
self.saveFilestate()
@@ -2478,28 +2471,19 @@ class MainWindow(QMainWindow):
labeldict[file] = eval(label)
else:
labeldict[file] = []
+
+ # read table recognition output
+ TableRec_excel_dir = os.path.join(
+ self.lastOpenDir, 'tableRec_excel_output')
- train_split, val_split, test_split = partitionDialog.getDataPartition()
- # check validate
- if train_split + val_split + test_split > 100:
- msg = "The sum of training, validation and testing data should be less than 100%"
- QMessageBox.information(self, "Information", msg)
- return
- print(train_split, val_split, test_split)
- train_split, val_split, test_split = float(train_split) / 100., float(val_split) / 100., float(test_split) / 100.
- train_id = int(len(labeldict) * train_split)
- val_id = int(len(labeldict) * (train_split + val_split))
- print('Data partition: train:', train_id,
- 'validation:', val_id - train_id,
- 'test:', len(labeldict) - val_id)
-
- TableRec_excel_dir = os.path.join(self.lastOpenDir, 'tableRec_excel_output')
- json_results = []
- imgid = 0
+ # save txt
+ fid = open(
+ "{}/gt.txt".format(self.lastOpenDir), "w", encoding='utf-8')
for image_path in labeldict.keys():
# load csv annotations
filename, _ = os.path.splitext(os.path.basename(image_path))
- csv_path = os.path.join(TableRec_excel_dir, filename + '.xlsx')
+ csv_path = os.path.join(
+ TableRec_excel_dir, filename + '.xlsx')
if not os.path.exists(csv_path):
continue
@@ -2518,28 +2502,31 @@ class MainWindow(QMainWindow):
cells = []
for anno in labeldict[image_path]:
tokens = list(anno['transcription'])
- obb = anno['points']
- hbb = OBB2HBB(np.array(obb)).tolist()
- cells.append({'tokens': tokens, 'bbox': hbb})
-
- # data split
- if imgid < train_id:
- split = 'train'
- elif imgid < val_id:
- split = 'val'
- else:
- split = 'test'
-
- # save dict
- html = {'structure': {'tokens': token_list}, 'cells': cells}
- json_results.append({'filename': os.path.basename(image_path), 'split': split, 'imgid': imgid, 'html': html})
- imgid += 1
-
- # save json
- with open("{}/annotation.json".format(self.lastOpenDir), "w", encoding='utf-8') as fid:
- fid.write(json.dumps(json_results, ensure_ascii=False))
-
- msg = 'JSON sucessfully saved in {}/annotation.json'.format(self.lastOpenDir)
+ cells.append({
+ 'tokens': tokens,
+ 'bbox': anno['points']
+ })
+
+ # 构造标注信息
+ html = {
+ 'structure': {
+ 'tokens': token_list
+ },
+ 'cells': cells
+ }
+ d = {
+ 'filename': os.path.basename(image_path),
+ 'html': html
+ }
+ # 重构HTML
+ d['gt'] = rebuild_html_from_ppstructure_label(d)
+ fid.write('{}\n'.format(
+ json.dumps(
+ d, ensure_ascii=False)))
+
+ # convert to PP-Structure label format
+ fid.close()
+ msg = 'JSON sucessfully saved in {}/gt.txt'.format(self.lastOpenDir)
QMessageBox.information(self, "Information", msg)
def autolcm(self):
@@ -2728,6 +2715,9 @@ class MainWindow(QMainWindow):
self._update_shape_color(shape)
self.keyDialog.addLabelHistory(key_text)
+
+ # save changed shape
+ self.setDirty()
def undoShapeEdit(self):
self.canvas.restoreShape()
diff --git a/PPOCRLabel/README.md b/PPOCRLabel/README.md
index 089a63fd55bb8c127104e7c404852ba52c3ac88c..9c483e1feff5a07467f7aa90343391888004bce7 100644
--- a/PPOCRLabel/README.md
+++ b/PPOCRLabel/README.md
@@ -105,9 +105,9 @@ python PPOCRLabel.py --kie True # [KIE mode] for [detection + recognition + keyw
#### 1.2.3 Build and Install the Whl Package Locally
Compile and install a new whl package, where 1.0.2 is the version number, you can specify the new version in 'setup.py'.
```bash
-cd PaddleOCR/PPOCRLabel
+cd ./PPOCRLabel
python3 setup.py bdist_wheel
-pip3 install dist/PPOCRLabel-1.0.2-py2.py3-none-any.whl
+pip3 install dist/PPOCRLabel-2.1.2-py2.py3-none-any.whl
```
diff --git a/PPOCRLabel/README_ch.md b/PPOCRLabel/README_ch.md
index 3ea684a3f09a6084403fa0b91e2511b7fd790f4b..784ab0985c4f83dcf5e03b0f5752d9825dd3a031 100644
--- a/PPOCRLabel/README_ch.md
+++ b/PPOCRLabel/README_ch.md
@@ -104,9 +104,9 @@ python PPOCRLabel.py --lang ch
编译与安装新的whl包,其中1.0.2为版本号,可在 `setup.py` 中指定新版本。
```bash
-cd PaddleOCR/PPOCRLabel
+cd ./PPOCRLabel
python3 setup.py bdist_wheel
-pip3 install dist/PPOCRLabel-1.0.2-py2.py3-none-any.whl -i https://mirror.baidu.com/pypi/simple
+pip3 install dist/PPOCRLabel-2.1.2-py2.py3-none-any.whl -i https://mirror.baidu.com/pypi/simple
```
diff --git a/PPOCRLabel/libs/canvas.py b/PPOCRLabel/libs/canvas.py
index 81f37995126140b03650f5ddea37ea282d5ceb09..44d899cbc9f21793f89c498cf844c95e418b08a1 100644
--- a/PPOCRLabel/libs/canvas.py
+++ b/PPOCRLabel/libs/canvas.py
@@ -611,8 +611,8 @@ class Canvas(QWidget):
if self.drawing() and not self.prevPoint.isNull() and not self.outOfPixmap(self.prevPoint):
p.setPen(QColor(0, 0, 0))
- p.drawLine(self.prevPoint.x(), 0, self.prevPoint.x(), self.pixmap.height())
- p.drawLine(0, self.prevPoint.y(), self.pixmap.width(), self.prevPoint.y())
+ p.drawLine(int(self.prevPoint.x()), 0, int(self.prevPoint.x()), self.pixmap.height())
+ p.drawLine(0, int(self.prevPoint.y()), self.pixmap.width(), int(self.prevPoint.y()))
self.setAutoFillBackground(True)
if self.verified:
@@ -909,4 +909,4 @@ class Canvas(QWidget):
def updateShapeIndex(self):
for i in range(len(self.shapes)):
self.shapes[i].idx = i
- self.update()
\ No newline at end of file
+ self.update()
diff --git a/PPOCRLabel/libs/dataPartitionDialog.py b/PPOCRLabel/libs/dataPartitionDialog.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 33bd491552fe773bd07020d82f7ea9bab76e7557..0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
--- a/PPOCRLabel/libs/dataPartitionDialog.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,113 +0,0 @@
-try:
- from PyQt5.QtGui import *
- from PyQt5.QtCore import *
- from PyQt5.QtWidgets import *
-except ImportError:
- from PyQt4.QtGui import *
- from PyQt4.QtCore import *
-
-from libs.utils import newIcon
-
-import time
-import datetime
-import json
-import cv2
-import numpy as np
-
-
-BB = QDialogButtonBox
-
-class DataPartitionDialog(QDialog):
- def __init__(self, parent=None):
- super().__init__()
- self.parnet = parent
- self.title = 'DATA PARTITION'
-
- self.train_ratio = 70
- self.val_ratio = 15
- self.test_ratio = 15
-
- self.initUI()
-
- def initUI(self):
- self.setWindowTitle(self.title)
- self.setWindowModality(Qt.ApplicationModal)
-
- self.flag_accept = True
-
- if self.parnet.lang == 'ch':
- msg = "导出JSON前请保存所有图像的标注且关闭EXCEL!"
- else:
- msg = "Please save all the annotations and close the EXCEL before exporting JSON!"
-
- info_msg = QLabel(msg, self)
- info_msg.setWordWrap(True)
- info_msg.setStyleSheet("color: red")
- info_msg.setFont(QFont('Arial', 12))
-
- train_lbl = QLabel('Train split: ', self)
- train_lbl.setFont(QFont('Arial', 15))
- val_lbl = QLabel('Valid split: ', self)
- val_lbl.setFont(QFont('Arial', 15))
- test_lbl = QLabel('Test split: ', self)
- test_lbl.setFont(QFont('Arial', 15))
-
- self.train_input = QLineEdit(self)
- self.train_input.setFont(QFont('Arial', 15))
- self.val_input = QLineEdit(self)
- self.val_input.setFont(QFont('Arial', 15))
- self.test_input = QLineEdit(self)
- self.test_input.setFont(QFont('Arial', 15))
-
- self.train_input.setText(str(self.train_ratio))
- self.val_input.setText(str(self.val_ratio))
- self.test_input.setText(str(self.test_ratio))
-
- validator = QIntValidator(0, 100)
- self.train_input.setValidator(validator)
- self.val_input.setValidator(validator)
- self.test_input.setValidator(validator)
-
- gridlayout = QGridLayout()
- gridlayout.addWidget(info_msg, 0, 0, 1, 2)
- gridlayout.addWidget(train_lbl, 1, 0)
- gridlayout.addWidget(val_lbl, 2, 0)
- gridlayout.addWidget(test_lbl, 3, 0)
- gridlayout.addWidget(self.train_input, 1, 1)
- gridlayout.addWidget(self.val_input, 2, 1)
- gridlayout.addWidget(self.test_input, 3, 1)
-
- bb = BB(BB.Ok | BB.Cancel, Qt.Horizontal, self)
- bb.button(BB.Ok).setIcon(newIcon('done'))
- bb.button(BB.Cancel).setIcon(newIcon('undo'))
- bb.accepted.connect(self.validate)
- bb.rejected.connect(self.cancel)
- gridlayout.addWidget(bb, 4, 0, 1, 2)
-
- self.setLayout(gridlayout)
-
- self.show()
-
- def validate(self):
- self.flag_accept = True
- self.accept()
-
- def cancel(self):
- self.flag_accept = False
- self.reject()
-
- def getStatus(self):
- return self.flag_accept
-
- def getDataPartition(self):
- self.train_ratio = int(self.train_input.text())
- self.val_ratio = int(self.val_input.text())
- self.test_ratio = int(self.test_input.text())
-
- return self.train_ratio, self.val_ratio, self.test_ratio
-
- def closeEvent(self, event):
- self.flag_accept = False
- self.reject()
-
-
diff --git a/PPOCRLabel/libs/utils.py b/PPOCRLabel/libs/utils.py
index e397f139e0cf34de4fd517f920dd3fef12cc2cd7..1bd46ab4dac65f4e63e4ac4b2af5a8d295d89671 100644
--- a/PPOCRLabel/libs/utils.py
+++ b/PPOCRLabel/libs/utils.py
@@ -176,18 +176,6 @@ def boxPad(box, imgShape, pad : int) -> np.array:
return box
-def OBB2HBB(obb) -> np.array:
- """
- Convert Oriented Bounding Box to Horizontal Bounding Box.
- """
- hbb = np.zeros(4, dtype=np.int32)
- hbb[0] = min(obb[:, 0])
- hbb[1] = min(obb[:, 1])
- hbb[2] = max(obb[:, 0])
- hbb[3] = max(obb[:, 1])
- return hbb
-
-
def expand_list(merged, html_list):
'''
Fill blanks according to merged cells
@@ -232,6 +220,26 @@ def convert_token(html_list):
return token_list
+def rebuild_html_from_ppstructure_label(label_info):
+ from html import escape
+ html_code = label_info['html']['structure']['tokens'].copy()
+ to_insert = [
+ i for i, tag in enumerate(html_code) if tag in ('| ', '>')
+ ]
+ for i, cell in zip(to_insert[::-1], label_info['html']['cells'][::-1]):
+ if cell['tokens']:
+ cell = [
+ escape(token) if len(token) == 1 else token
+ for token in cell['tokens']
+ ]
+ cell = ''.join(cell)
+ html_code.insert(i + 1, cell)
+ html_code = ''.join(html_code)
+ html_code = ''.format(
+ html_code)
+ return html_code
+
+
def stepsInfo(lang='en'):
if lang == 'ch':
msg = "1. 安装与运行:使用上述命令安装与运行程序。\n" \
diff --git a/PPOCRLabel/resources/strings/strings-en.properties b/PPOCRLabel/resources/strings/strings-en.properties
index 1b628016c079ad1c5eb5514c7d6eb2cba842b7e3..3dfc34e001ad098ffcf1f4528218befd692281b9 100644
--- a/PPOCRLabel/resources/strings/strings-en.properties
+++ b/PPOCRLabel/resources/strings/strings-en.properties
@@ -113,4 +113,4 @@ keyDialogTip=Enter object label
keyChange=Change Box Key
TableRecognition=Table Recognition
cellreRecognition=Cell Re-Recognition
-exportJSON=Export Excel Label(PubTabNet)
+exportJSON=Export Table Label
diff --git a/PPOCRLabel/resources/strings/strings-zh-CN.properties b/PPOCRLabel/resources/strings/strings-zh-CN.properties
index 0758729a8ca0cae862a4bf5bcf2e5b24f2d95822..00dfd31da2ce7a5b922fb5e4b15a84d657be0db6 100644
--- a/PPOCRLabel/resources/strings/strings-zh-CN.properties
+++ b/PPOCRLabel/resources/strings/strings-zh-CN.properties
@@ -113,4 +113,4 @@ keyDialogTip=请输入类型名称
keyChange=更改Box关键字类别
TableRecognition=表格识别
cellreRecognition=单元格重识别
-exportJSON=导出表格JSON标注
\ No newline at end of file
+exportJSON=导出表格标注
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/PPOCRLabel/setup.py b/PPOCRLabel/setup.py
index 1750f84b8259a237fb6bb1b5eb9dc33e29441bc1..a112df544ee385ba3dc87ffac3e15a9dc390c4db 100644
--- a/PPOCRLabel/setup.py
+++ b/PPOCRLabel/setup.py
@@ -33,7 +33,7 @@ setup(
package_dir={'PPOCRLabel': ''},
include_package_data=True,
entry_points={"console_scripts": ["PPOCRLabel= PPOCRLabel.PPOCRLabel:main"]},
- version='2.1.1',
+ version='2.1.2',
install_requires=requirements,
license='Apache License 2.0',
description='PPOCRLabel is a semi-automatic graphic annotation tool suitable for OCR field, with built-in PPOCR model to automatically detect and re-recognize data. It is written in python3 and pyqt5, supporting rectangular box annotation and four-point annotation modes. Annotations can be directly used for the training of PPOCR detection and recognition models',
diff --git "a/applications/\344\270\255\346\226\207\350\241\250\346\240\274\350\257\206\345\210\253.md" "b/applications/\344\270\255\346\226\207\350\241\250\346\240\274\350\257\206\345\210\253.md"
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..af7cc96b70410c614ef39e91c229d705c8bd400a
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/applications/\344\270\255\346\226\207\350\241\250\346\240\274\350\257\206\345\210\253.md"
@@ -0,0 +1,472 @@
+# 智能运营:通用中文表格识别
+
+- [1. 背景介绍](#1-背景介绍)
+- [2. 中文表格识别](#2-中文表格识别)
+- [2.1 环境准备](#21-环境准备)
+- [2.2 准备数据集](#22-准备数据集)
+ - [2.2.1 划分训练测试集](#221-划分训练测试集)
+ - [2.2.2 查看数据集](#222-查看数据集)
+- [2.3 训练](#23-训练)
+- [2.4 验证](#24-验证)
+- [2.5 训练引擎推理](#25-训练引擎推理)
+- [2.6 模型导出](#26-模型导出)
+- [2.7 预测引擎推理](#27-预测引擎推理)
+- [2.8 表格识别](#28-表格识别)
+- [3. 表格属性识别](#3-表格属性识别)
+- [3.1 代码、环境、数据准备](#31-代码环境数据准备)
+ - [3.1.1 代码准备](#311-代码准备)
+ - [3.1.2 环境准备](#312-环境准备)
+ - [3.1.3 数据准备](#313-数据准备)
+- [3.2 表格属性识别训练](#32-表格属性识别训练)
+- [3.3 表格属性识别推理和部署](#33-表格属性识别推理和部署)
+ - [3.3.1 模型转换](#331-模型转换)
+ - [3.3.2 模型推理](#332-模型推理)
+
+## 1. 背景介绍
+
+中文表格识别在金融行业有着广泛的应用,如保险理赔、财报分析和信息录入等领域。当前,金融行业的表格识别主要以手动录入为主,开发一种自动表格识别成为丞待解决的问题。
+
+
+
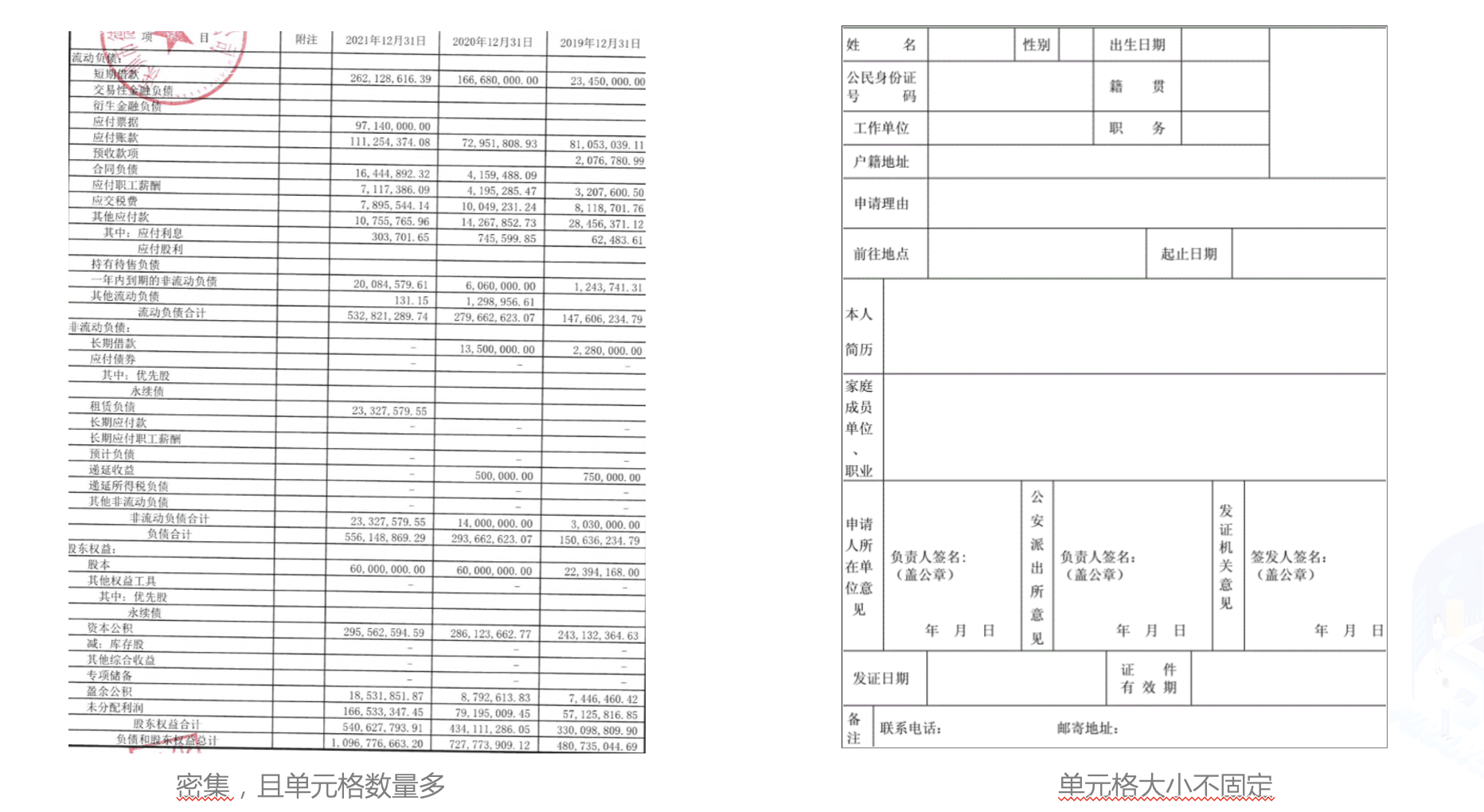
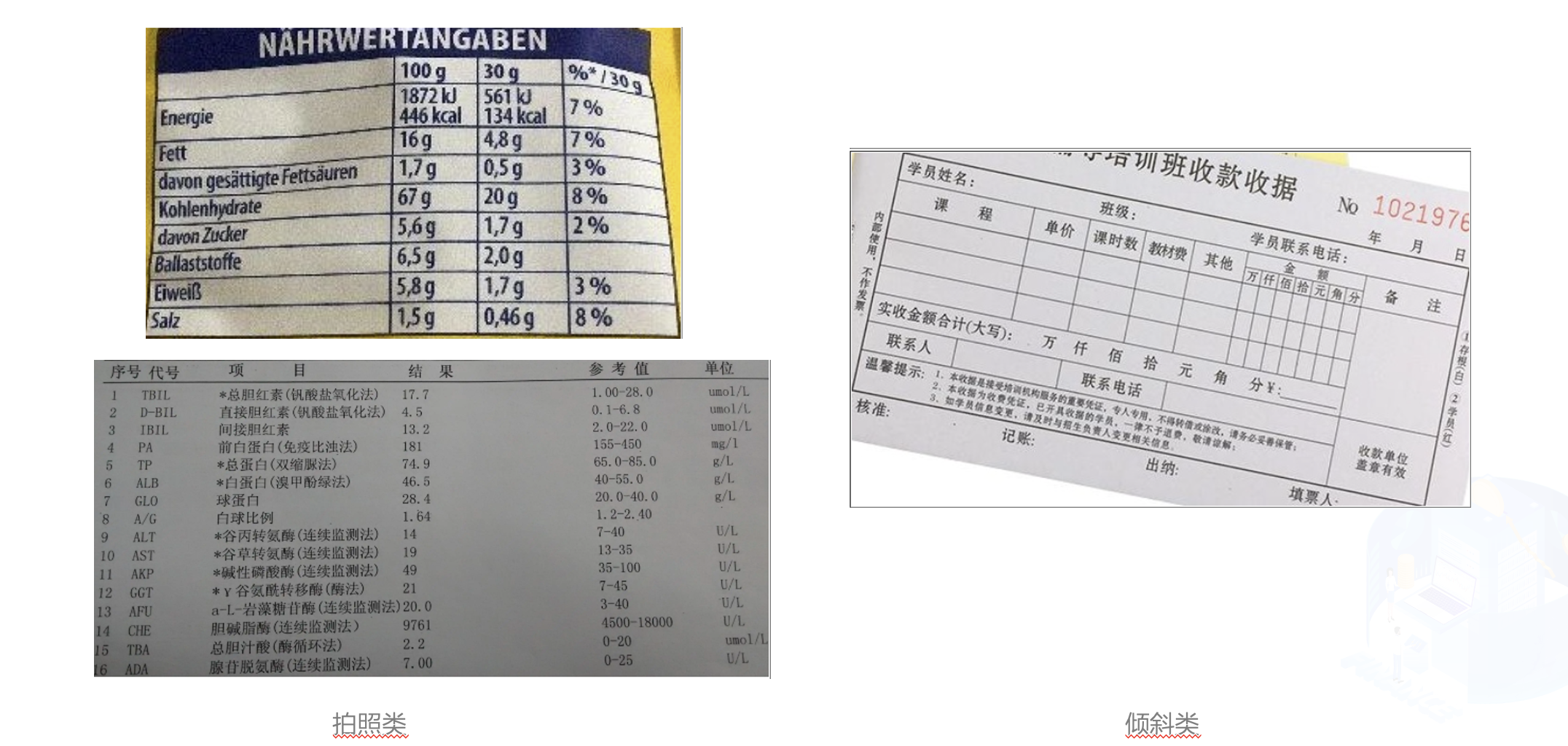
+在金融行业中,表格图像主要有清单类的单元格密集型表格,申请表类的大单元格表格,拍照表格和倾斜表格四种主要形式。
+
+
+
+
+
+当前的表格识别算法不能很好的处理这些场景下的表格图像。在本例中,我们使用PP-Structurev2最新发布的表格识别模型SLANet来演示如何进行中文表格是识别。同时,为了方便作业流程,我们使用表格属性识别模型对表格图像的属性进行识别,对表格的难易程度进行判断,加快人工进行校对速度。
+
+本项目AI Studio链接:https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/projectdetail/4588067
+
+## 2. 中文表格识别
+### 2.1 环境准备
+
+
+```python
+# 下载PaddleOCR代码
+! git clone -b dygraph https://gitee.com/paddlepaddle/PaddleOCR
+```
+
+
+```python
+# 安装PaddleOCR环境
+! pip install -r PaddleOCR/requirements.txt --force-reinstall
+! pip install protobuf==3.19
+```
+
+### 2.2 准备数据集
+
+本例中使用的数据集采用表格[生成工具](https://github.com/WenmuZhou/TableGeneration)制作。
+
+使用如下命令对数据集进行解压,并查看数据集大小
+
+
+```python
+! cd data/data165849 && tar -xf table_gen_dataset.tar && cd -
+! wc -l data/data165849/table_gen_dataset/gt.txt
+```
+
+#### 2.2.1 划分训练测试集
+
+使用下述命令将数据集划分为训练集和测试集, 这里将90%划分为训练集,10%划分为测试集
+
+
+```python
+import random
+with open('/home/aistudio/data/data165849/table_gen_dataset/gt.txt') as f:
+ lines = f.readlines()
+random.shuffle(lines)
+train_len = int(len(lines)*0.9)
+train_list = lines[:train_len]
+val_list = lines[train_len:]
+
+# 保存结果
+with open('/home/aistudio/train.txt','w',encoding='utf-8') as f:
+ f.writelines(train_list)
+with open('/home/aistudio/val.txt','w',encoding='utf-8') as f:
+ f.writelines(val_list)
+```
+
+划分完成后,数据集信息如下
+
+|类型|数量|图片地址|标注文件路径|
+|---|---|---|---|
+|训练集|18000|/home/aistudio/data/data165849/table_gen_dataset|/home/aistudio/train.txt|
+|测试集|2000|/home/aistudio/data/data165849/table_gen_dataset|/home/aistudio/val.txt|
+
+#### 2.2.2 查看数据集
+
+
+```python
+import cv2
+import os, json
+import numpy as np
+from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
+%matplotlib inline
+
+def parse_line(data_dir, line):
+ data_line = line.strip("\n")
+ info = json.loads(data_line)
+ file_name = info['filename']
+ cells = info['html']['cells'].copy()
+ structure = info['html']['structure']['tokens'].copy()
+
+ img_path = os.path.join(data_dir, file_name)
+ if not os.path.exists(img_path):
+ print(img_path)
+ return None
+ data = {
+ 'img_path': img_path,
+ 'cells': cells,
+ 'structure': structure,
+ 'file_name': file_name
+ }
+ return data
+
+def draw_bbox(img_path, points, color=(255, 0, 0), thickness=2):
+ if isinstance(img_path, str):
+ img_path = cv2.imread(img_path)
+ img_path = img_path.copy()
+ for point in points:
+ cv2.polylines(img_path, [point.astype(int)], True, color, thickness)
+ return img_path
+
+
+def rebuild_html(data):
+ html_code = data['structure']
+ cells = data['cells']
+ to_insert = [i for i, tag in enumerate(html_code) if tag in (' | ', '>')]
+
+ for i, cell in zip(to_insert[::-1], cells[::-1]):
+ if cell['tokens']:
+ text = ''.join(cell['tokens'])
+ # skip empty text
+ sp_char_list = ['', '', '\u2028', ' ', '', '']
+ text_remove_style = skip_char(text, sp_char_list)
+ if len(text_remove_style) == 0:
+ continue
+ html_code.insert(i + 1, text)
+
+ html_code = ''.join(html_code)
+ return html_code
+
+
+def skip_char(text, sp_char_list):
+ """
+ skip empty cell
+ @param text: text in cell
+ @param sp_char_list: style char and special code
+ @return:
+ """
+ for sp_char in sp_char_list:
+ text = text.replace(sp_char, '')
+ return text
+
+save_dir = '/home/aistudio/vis'
+os.makedirs(save_dir, exist_ok=True)
+image_dir = '/home/aistudio/data/data165849/'
+html_str = ''
+
+# 解析标注信息并还原html表格
+data = parse_line(image_dir, val_list[0])
+
+img = cv2.imread(data['img_path'])
+img_name = ''.join(os.path.basename(data['file_name']).split('.')[:-1])
+img_save_name = os.path.join(save_dir, img_name)
+boxes = [np.array(x['bbox']) for x in data['cells']]
+show_img = draw_bbox(data['img_path'], boxes)
+cv2.imwrite(img_save_name + '_show.jpg', show_img)
+
+html = rebuild_html(data)
+html_str += html
+html_str += ' '
+
+# 显示标注的html字符串
+from IPython.core.display import display, HTML
+display(HTML(html_str))
+# 显示单元格坐标
+plt.figure(figsize=(15,15))
+plt.imshow(show_img)
+plt.show()
+```
+
+### 2.3 训练
+
+这里选用PP-Structurev2中的表格识别模型[SLANet](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR/blob/dygraph/configs/table/SLANet.yml)
+
+SLANet是PP-Structurev2全新推出的表格识别模型,相比PP-Structurev1中TableRec-RARE,在速度不变的情况下精度提升4.7%。TEDS提升2%
+
+
+|算法|Acc|[TEDS(Tree-Edit-Distance-based Similarity)](https://github.com/ibm-aur-nlp/PubTabNet/tree/master/src)|Speed|
+| --- | --- | --- | ---|
+| EDD[2] |x| 88.3% |x|
+| TableRec-RARE(ours) | 71.73%| 93.88% |779ms|
+| SLANet(ours) | 76.31%| 95.89%|766ms|
+
+进行训练之前先使用如下命令下载预训练模型
+
+
+```python
+# 进入PaddleOCR工作目录
+os.chdir('/home/aistudio/PaddleOCR')
+# 下载英文预训练模型
+! wget -nc -P ./pretrain_models/ https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/ppstructure/models/slanet/en_ppstructure_mobile_v2.0_SLANet_train.tar --no-check-certificate
+! cd ./pretrain_models/ && tar xf en_ppstructure_mobile_v2.0_SLANet_train.tar && cd ../
+```
+
+使用如下命令即可启动训练,需要修改的配置有
+
+|字段|修改值|含义|
+|---|---|---|
+|Global.pretrained_model|./pretrain_models/en_ppstructure_mobile_v2.0_SLANet_train/best_accuracy.pdparams|指向英文表格预训练模型地址|
+|Global.eval_batch_step|562|模型多少step评估一次,一般设置为一个epoch总的step数|
+|Optimizer.lr.name|Const|学习率衰减器 |
+|Optimizer.lr.learning_rate|0.0005|学习率设为之前的0.05倍 |
+|Train.dataset.data_dir|/home/aistudio/data/data165849|指向训练集图片存放目录 |
+|Train.dataset.label_file_list|/home/aistudio/data/data165849/table_gen_dataset/train.txt|指向训练集标注文件 |
+|Train.loader.batch_size_per_card|32|训练时每张卡的batch_size |
+|Train.loader.num_workers|1|训练集多进程数据读取的进程数,在aistudio中需要设为1 |
+|Eval.dataset.data_dir|/home/aistudio/data/data165849|指向测试集图片存放目录 |
+|Eval.dataset.label_file_list|/home/aistudio/data/data165849/table_gen_dataset/val.txt|指向测试集标注文件 |
+|Eval.loader.batch_size_per_card|32|测试时每张卡的batch_size |
+|Eval.loader.num_workers|1|测试集多进程数据读取的进程数,在aistudio中需要设为1 |
+
+
+已经修改好的配置存储在 `/home/aistudio/SLANet_ch.yml`
+
+
+```python
+import os
+os.chdir('/home/aistudio/PaddleOCR')
+! python3 tools/train.py -c /home/aistudio/SLANet_ch.yml
+```
+
+大约在7个epoch后达到最高精度 97.49%
+
+### 2.4 验证
+
+训练完成后,可使用如下命令在测试集上评估最优模型的精度
+
+
+```python
+! python3 tools/eval.py -c /home/aistudio/SLANet_ch.yml -o Global.checkpoints=/home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/output/SLANet_ch/best_accuracy.pdparams
+```
+
+### 2.5 训练引擎推理
+使用如下命令可使用训练引擎对单张图片进行推理
+
+
+```python
+import os;os.chdir('/home/aistudio/PaddleOCR')
+! python3 tools/infer_table.py -c /home/aistudio/SLANet_ch.yml -o Global.checkpoints=/home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/output/SLANet_ch/best_accuracy.pdparams Global.infer_img=/home/aistudio/data/data165849/table_gen_dataset/img/no_border_18298_G7XZH93DDCMATGJQ8RW2.jpg
+```
+
+
+```python
+import cv2
+from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
+%matplotlib inline
+
+# 显示原图
+show_img = cv2.imread('/home/aistudio/data/data165849/table_gen_dataset/img/no_border_18298_G7XZH93DDCMATGJQ8RW2.jpg')
+plt.figure(figsize=(15,15))
+plt.imshow(show_img)
+plt.show()
+
+# 显示预测的单元格
+show_img = cv2.imread('/home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/output/infer/no_border_18298_G7XZH93DDCMATGJQ8RW2.jpg')
+plt.figure(figsize=(15,15))
+plt.imshow(show_img)
+plt.show()
+```
+
+### 2.6 模型导出
+
+使用如下命令可将模型导出为inference模型
+
+
+```python
+! python3 tools/export_model.py -c /home/aistudio/SLANet_ch.yml -o Global.checkpoints=/home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/output/SLANet_ch/best_accuracy.pdparams Global.save_inference_dir=/home/aistudio/SLANet_ch/infer
+```
+
+### 2.7 预测引擎推理
+使用如下命令可使用预测引擎对单张图片进行推理
+
+
+
+```python
+os.chdir('/home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/ppstructure')
+! python3 table/predict_structure.py \
+ --table_model_dir=/home/aistudio/SLANet_ch/infer \
+ --table_char_dict_path=../ppocr/utils/dict/table_structure_dict.txt \
+ --image_dir=/home/aistudio/data/data165849/table_gen_dataset/img/no_border_18298_G7XZH93DDCMATGJQ8RW2.jpg \
+ --output=../output/inference
+```
+
+
+```python
+# 显示原图
+show_img = cv2.imread('/home/aistudio/data/data165849/table_gen_dataset/img/no_border_18298_G7XZH93DDCMATGJQ8RW2.jpg')
+plt.figure(figsize=(15,15))
+plt.imshow(show_img)
+plt.show()
+
+# 显示预测的单元格
+show_img = cv2.imread('/home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/output/inference/no_border_18298_G7XZH93DDCMATGJQ8RW2.jpg')
+plt.figure(figsize=(15,15))
+plt.imshow(show_img)
+plt.show()
+```
+
+### 2.8 表格识别
+
+在表格结构模型训练完成后,可结合OCR检测识别模型,对表格内容进行识别。
+
+首先下载PP-OCRv3文字检测识别模型
+
+
+```python
+# 下载PP-OCRv3文本检测识别模型并解压
+! wget -nc -P ./inference/ https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_slim_infer.tar --no-check-certificate
+! wget -nc -P ./inference/ https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_slim_infer.tar --no-check-certificate
+! cd ./inference/ && tar xf ch_PP-OCRv3_det_slim_infer.tar && tar xf ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_slim_infer.tar && cd ../
+```
+
+模型下载完成后,使用如下命令进行表格识别
+
+
+```python
+import os;os.chdir('/home/aistudio/PaddleOCR/ppstructure')
+! python3 table/predict_table.py \
+ --det_model_dir=inference/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_slim_infer \
+ --rec_model_dir=inference/ch_PP-OCRv3_rec_slim_infer \
+ --table_model_dir=/home/aistudio/SLANet_ch/infer \
+ --rec_char_dict_path=../ppocr/utils/ppocr_keys_v1.txt \
+ --table_char_dict_path=../ppocr/utils/dict/table_structure_dict.txt \
+ --image_dir=/home/aistudio/data/data165849/table_gen_dataset/img/no_border_18298_G7XZH93DDCMATGJQ8RW2.jpg \
+ --output=../output/table
+```
+
+
+```python
+# 显示原图
+show_img = cv2.imread('/home/aistudio/data/data165849/table_gen_dataset/img/no_border_18298_G7XZH93DDCMATGJQ8RW2.jpg')
+plt.figure(figsize=(15,15))
+plt.imshow(show_img)
+plt.show()
+
+# 显示预测结果
+from IPython.core.display import display, HTML
+display(HTML('| alleadersh | 不贰过,推 | 从自己参与浙江数 | 。另一方 | | AnSha | 自己越 | 共商共建工作协商 | w.east | 抓好改革试点任务 | | Edime | ImisesElec | 怀天下”。 | | 22.26 | 31.61 | 4.30 | 794.94 | | ip | Profundi | :2019年12月1 | Horspro | 444.48 | 2.41 | 87 | 679.98 | | iehaiTrain | 组长蒋蕊 | Toafterdec | 203.43 | 23.54 | 4 | 4266.62 | | Tyint | roudlyRol | 谢您的好意,我知道 | ErChows | | 48.90 | 1031 | 6 | | NaFlint | | 一辈的 | aterreclam | 7823.86 | 9829.23 | 7.96 | 3068 | | 家上下游企业,5 | Tr | 景象。当地球上的我们 | Urelaw | 799.62 | 354.96 | 12.98 | 33 | | 赛事( | uestCh | 复制的业务模式并 | Listicjust | 9.23 | | 92 | 53.22 | | Ca | Iskole | 扶贫"之名引导 | Papua | 7191.90 | 1.65 | 3.62 | 48 | | 避讳 | ir | 但由于 | Fficeof | 0.22 | 6.37 | 7.17 | 3397.75 | | ndaTurk | 百处遗址 | gMa | 1288.34 | 2053.66 | 2.29 | 885.45 |
'))
+```
+
+## 3. 表格属性识别
+### 3.1 代码、环境、数据准备
+#### 3.1.1 代码准备
+首先,我们需要准备训练表格属性的代码,PaddleClas集成了PULC方案,该方案可以快速获得一个在CPU上用时2ms的属性识别模型。PaddleClas代码可以clone下载得到。获取方式如下:
+
+
+
+```python
+! git clone -b develop https://gitee.com/paddlepaddle/PaddleClas
+```
+
+#### 3.1.2 环境准备
+其次,我们需要安装训练PaddleClas相关的依赖包
+
+
+```python
+! pip install -r PaddleClas/requirements.txt --force-reinstall
+! pip install protobuf==3.20.0
+```
+
+
+#### 3.1.3 数据准备
+
+最后,准备训练数据。在这里,我们一共定义了表格的6个属性,分别是表格来源、表格数量、表格颜色、表格清晰度、表格有无干扰、表格角度。其可视化如下:
+
+
+
+这里,我们提供了一个表格属性的demo子集,可以快速迭代体验。下载方式如下:
+
+
+```python
+%cd PaddleClas/dataset
+!wget https://paddleclas.bj.bcebos.com/data/PULC/table_attribute.tar
+!tar -xf table_attribute.tar
+%cd ../PaddleClas/dataset
+%cd ../
+```
+
+### 3.2 表格属性识别训练
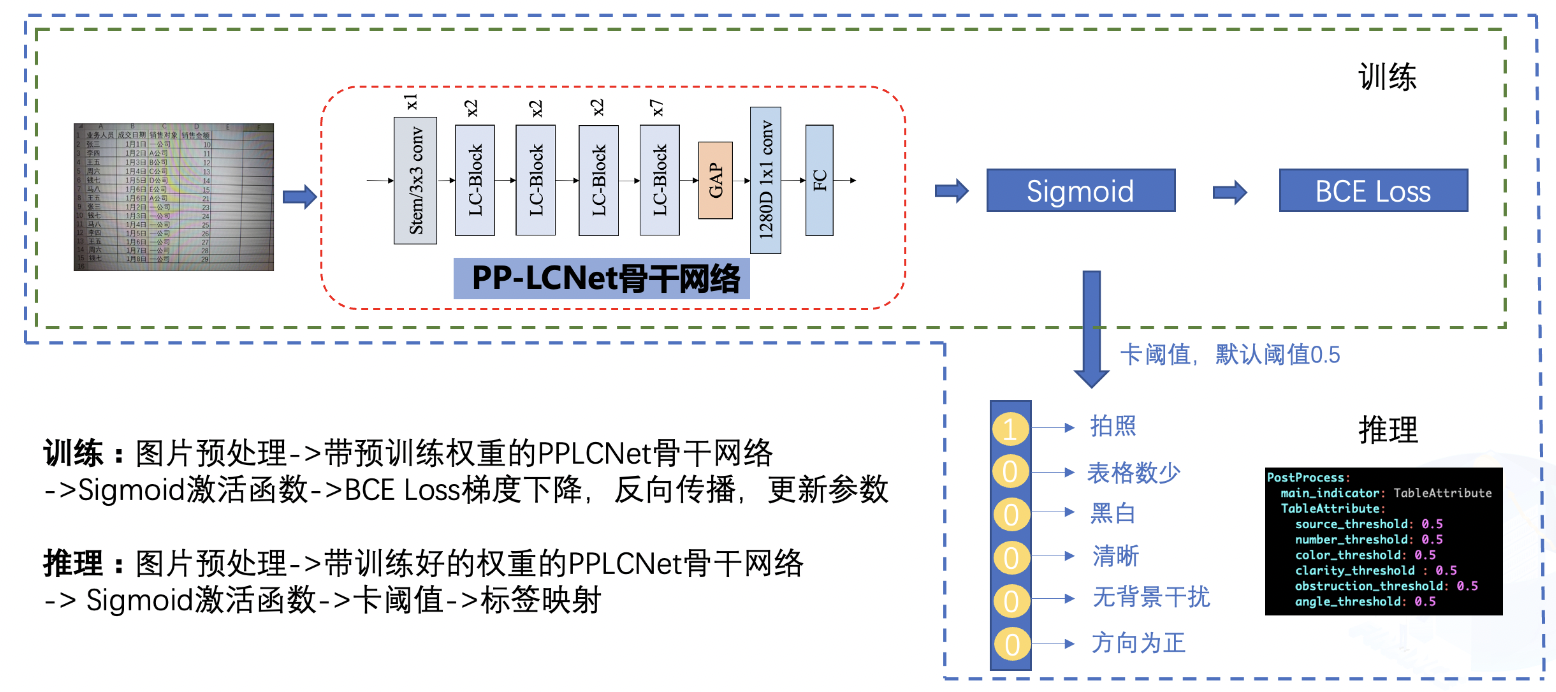
+表格属性训练整体pipelinie如下:
+
+
+
+1.训练过程中,图片经过预处理之后,送入到骨干网络之中,骨干网络将抽取表格图片的特征,最终该特征连接输出的FC层,FC层经过Sigmoid激活函数后和真实标签做交叉熵损失函数,优化器通过对该损失函数做梯度下降来更新骨干网络的参数,经过多轮训练后,骨干网络的参数可以对为止图片做很好的预测;
+
+2.推理过程中,图片经过预处理之后,送入到骨干网络之中,骨干网络加载学习好的权重后对该表格图片做出预测,预测的结果为一个6维向量,该向量中的每个元素反映了每个属性对应的概率值,通过对该值进一步卡阈值之后,得到最终的输出,最终的输出描述了该表格的6个属性。
+
+当准备好相关的数据之后,可以一键启动表格属性的训练,训练代码如下:
+
+
+```python
+
+!python tools/train.py -c ./ppcls/configs/PULC/table_attribute/PPLCNet_x1_0.yaml -o Global.device=cpu -o Global.epochs=10
+```
+
+### 3.3 表格属性识别推理和部署
+#### 3.3.1 模型转换
+当训练好模型之后,需要将模型转换为推理模型进行部署。转换脚本如下:
+
+
+```python
+!python tools/export_model.py -c ppcls/configs/PULC/table_attribute/PPLCNet_x1_0.yaml -o Global.pretrained_model=output/PPLCNet_x1_0/best_model
+```
+
+执行以上命令之后,会在当前目录上生成`inference`文件夹,该文件夹中保存了当前精度最高的推理模型。
+
+#### 3.3.2 模型推理
+安装推理需要的paddleclas包, 此时需要通过下载安装paddleclas的develop的whl包
+
+
+
+```python
+!pip install https://paddleclas.bj.bcebos.com/whl/paddleclas-0.0.0-py3-none-any.whl
+```
+
+进入`deploy`目录下即可对模型进行推理
+
+
+```python
+%cd deploy/
+```
+
+推理命令如下:
+
+
+```python
+!python python/predict_cls.py -c configs/PULC/table_attribute/inference_table_attribute.yaml -o Global.inference_model_dir="../inference" -o Global.infer_imgs="../dataset/table_attribute/Table_val/val_9.jpg"
+!python python/predict_cls.py -c configs/PULC/table_attribute/inference_table_attribute.yaml -o Global.inference_model_dir="../inference" -o Global.infer_imgs="../dataset/table_attribute/Table_val/val_3253.jpg"
+```
+
+推理的表格图片:
+
+
+
+预测结果如下:
+```
+val_9.jpg: {'attributes': ['Scanned', 'Little', 'Black-and-White', 'Clear', 'Without-Obstacles', 'Horizontal'], 'output': [1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]}
+```
+
+
+推理的表格图片:
+
+
+
+预测结果如下:
+```
+val_3253.jpg: {'attributes': ['Photo', 'Little', 'Black-and-White', 'Blurry', 'Without-Obstacles', 'Tilted'], 'output': [0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0]}
+```
+
+对比两张图片可以发现,第一张图片比较清晰,表格属性的结果也偏向于比较容易识别,我们可以更相信表格识别的结果,第二张图片比较模糊,且存在倾斜现象,表格识别可能存在错误,需要我们人工进一步校验。通过表格的属性识别能力,可以进一步将“人工”和“智能”很好的结合起来,为表格识别能力的落地的精度提供保障。
diff --git "a/applications/\345\215\260\347\253\240\345\274\257\346\233\262\346\226\207\345\255\227\350\257\206\345\210\253.md" "b/applications/\345\215\260\347\253\240\345\274\257\346\233\262\346\226\207\345\255\227\350\257\206\345\210\253.md"
index b97b2d09a0df4e68ce3364a9e7071b40923e9f4e..fce9ea772eed6575de10f50c0ff447aa1aee928b 100644
--- "a/applications/\345\215\260\347\253\240\345\274\257\346\233\262\346\226\207\345\255\227\350\257\206\345\210\253.md"
+++ "b/applications/\345\215\260\347\253\240\345\274\257\346\233\262\346\226\207\345\255\227\350\257\206\345\210\253.md"
@@ -34,6 +34,8 @@
| 印章文字识别-端对端OCR方法 | 700 | 47% |
| 印章文字识别-两阶段OCR方法 | 700 | 55% |
+点击进入 [AI Studio 项目](https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/projectdetail/4586113)
+
# 2. 环境搭建
本项目需要准备PaddleDetection和PaddleOCR的项目运行环境,其中PaddleDetection用于实现印章检测任务,PaddleOCR用于实现文字识别任务
diff --git "a/applications/\345\277\253\351\200\237\346\236\204\345\273\272\345\215\241\350\257\201\347\261\273OCR.md" "b/applications/\345\277\253\351\200\237\346\236\204\345\273\272\345\215\241\350\257\201\347\261\273OCR.md"
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..ab9ddf1bbd20e538f0b1e3d43e9a5af5383487b4
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/applications/\345\277\253\351\200\237\346\236\204\345\273\272\345\215\241\350\257\201\347\261\273OCR.md"
@@ -0,0 +1,782 @@
+# 快速构建卡证类OCR
+
+
+- [快速构建卡证类OCR](#快速构建卡证类ocr)
+ - [1. 金融行业卡证识别应用](#1-金融行业卡证识别应用)
+ - [1.1 金融行业中的OCR相关技术](#11-金融行业中的ocr相关技术)
+ - [1.2 金融行业中的卡证识别场景介绍](#12-金融行业中的卡证识别场景介绍)
+ - [1.3 OCR落地挑战](#13-ocr落地挑战)
+ - [2. 卡证识别技术解析](#2-卡证识别技术解析)
+ - [2.1 卡证分类模型](#21-卡证分类模型)
+ - [2.2 卡证识别模型](#22-卡证识别模型)
+ - [3. OCR技术拆解](#3-ocr技术拆解)
+ - [3.1技术流程](#31技术流程)
+ - [3.2 OCR技术拆解---卡证分类](#32-ocr技术拆解---卡证分类)
+ - [卡证分类:数据、模型准备](#卡证分类数据模型准备)
+ - [卡证分类---修改配置文件](#卡证分类---修改配置文件)
+ - [卡证分类---训练](#卡证分类---训练)
+ - [3.2 OCR技术拆解---卡证识别](#32-ocr技术拆解---卡证识别)
+ - [身份证识别:检测+分类](#身份证识别检测分类)
+ - [数据标注](#数据标注)
+ - [4 . 项目实践](#4--项目实践)
+ - [4.1 环境准备](#41-环境准备)
+ - [4.2 配置文件修改](#42-配置文件修改)
+ - [4.3 代码修改](#43-代码修改)
+ - [4.3.1 数据读取](#431-数据读取)
+ - [4.3.2 head修改](#432--head修改)
+ - [4.3.3 修改loss](#433-修改loss)
+ - [4.3.4 后处理](#434-后处理)
+ - [4.4. 模型启动](#44-模型启动)
+ - [5 总结](#5-总结)
+ - [References](#references)
+
+## 1. 金融行业卡证识别应用
+
+### 1.1 金融行业中的OCR相关技术
+
+* 《“十四五”数字经济发展规划》指出,2020年我国数字经济核心产业增加值占GDP比重达7.8%,随着数字经济迈向全面扩展,到2025年该比例将提升至10%。
+
+* 在过去数年的跨越发展与积累沉淀中,数字金融、金融科技已在对金融业的重塑与再造中充分印证了其自身价值。
+
+* 以智能为目标,提升金融数字化水平,实现业务流程自动化,降低人力成本。
+
+
+
+
+
+
+### 1.2 金融行业中的卡证识别场景介绍
+
+应用场景:身份证、银行卡、营业执照、驾驶证等。
+
+应用难点:由于数据的采集来源多样,以及实际采集数据各种噪声:反光、褶皱、模糊、倾斜等各种问题干扰。
+
+
+
+
+
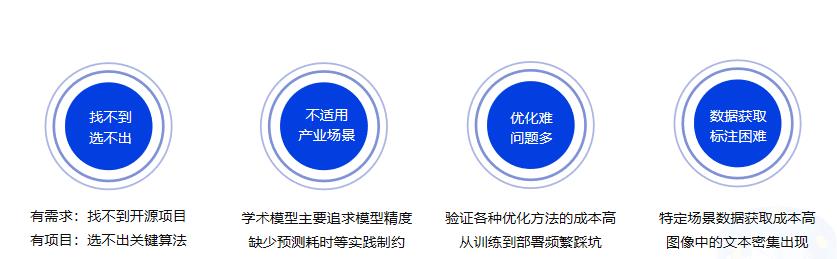
+### 1.3 OCR落地挑战
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
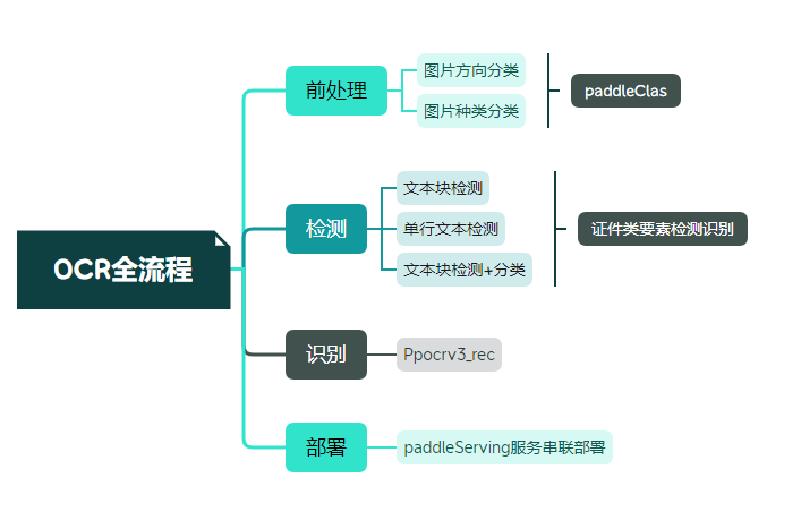
+## 2. 卡证识别技术解析
+
+
+
+
+
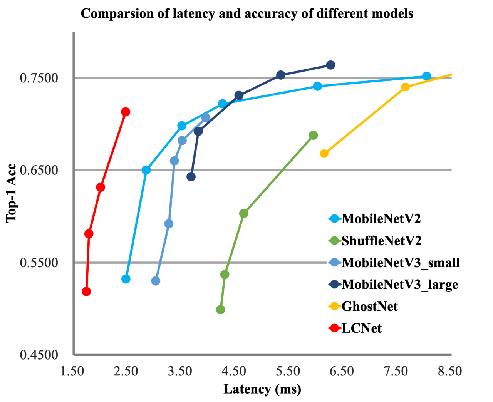
+### 2.1 卡证分类模型
+
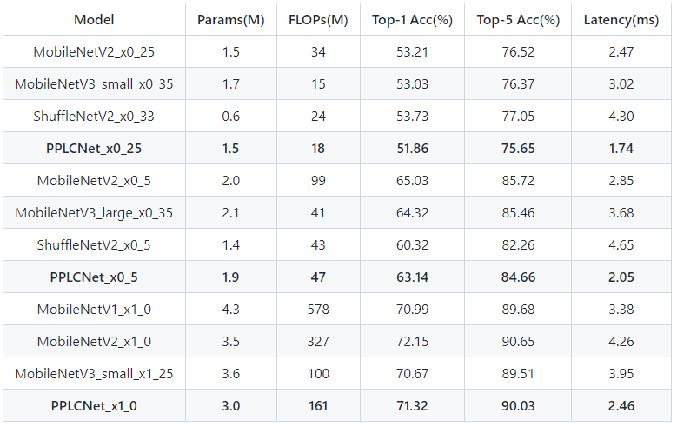
+卡证分类:基于PPLCNet
+
+与其他轻量级模型相比在CPU环境下ImageNet数据集上的表现
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+* 模型来自模型库PaddleClas,它是一个图像识别和图像分类任务的工具集,助力使用者训练出更好的视觉模型和应用落地。
+
+
+
+
+
+
+### 2.2 卡证识别模型
+
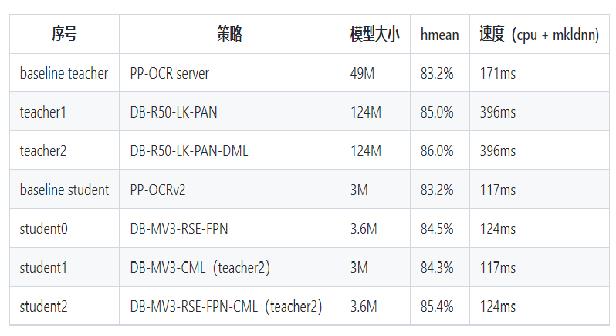
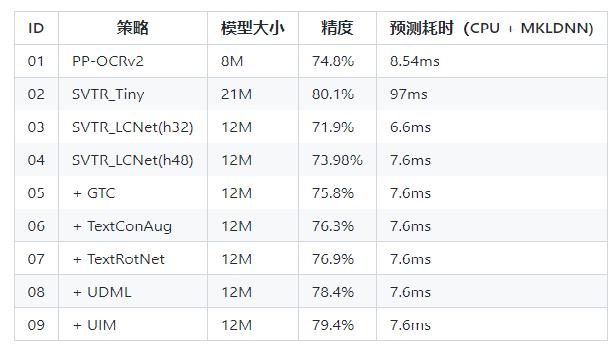
+* 检测:DBNet 识别:SVRT
+
+
+
+
+* PPOCRv3在文本检测、识别进行了一系列改进优化,在保证精度的同时提升预测效率
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+## 3. OCR技术拆解
+
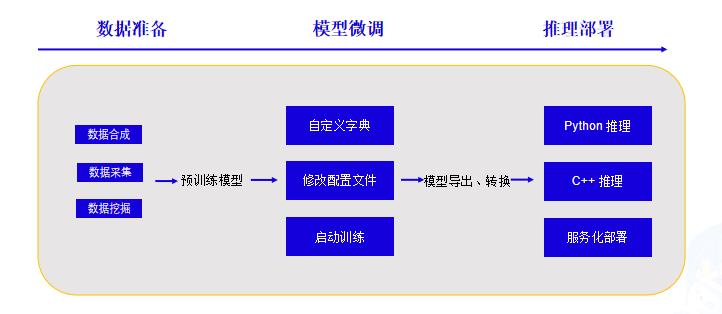
+### 3.1技术流程
+
+
+
+
+### 3.2 OCR技术拆解---卡证分类
+
+#### 卡证分类:数据、模型准备
+
+
+A 使用爬虫获取无标注数据,将相同类别的放在同一文件夹下,文件名从0开始命名。具体格式如下图所示。
+
+ 注:卡证类数据,建议每个类别数据量在500张以上
+
+
+
+B 一行命令生成标签文件
+
+```
+tree -r -i -f | grep -E "jpg|JPG|jpeg|JPEG|png|PNG|webp" | awk -F "/" '{print $0" "$2}' > train_list.txt
+```
+
+C [下载预训练模型 ](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleClas/blob/release/2.4/docs/zh_CN/models/PP-LCNet.md)
+
+
+
+#### 卡证分类---修改配置文件
+
+
+配置文件主要修改三个部分:
+
+ 全局参数:预训练模型路径/训练轮次/图像尺寸
+
+ 模型结构:分类数
+
+ 数据处理:训练/评估数据路径
+
+
+ 
+
+#### 卡证分类---训练
+
+
+指定配置文件启动训练:
+
+```
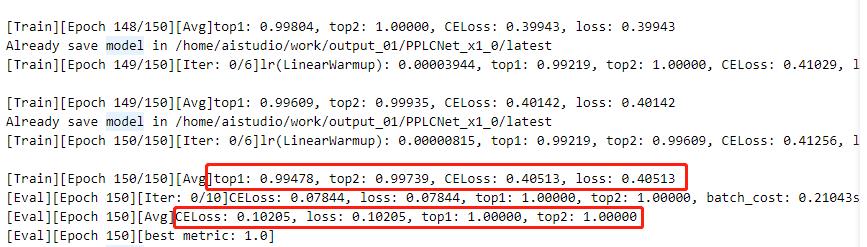
+!python /home/aistudio/work/PaddleClas/tools/train.py -c /home/aistudio/work/PaddleClas/ppcls/configs/PULC/text_image_orientation/PPLCNet_x1_0.yaml
+```
+
+
+ 注:日志中显示了训练结果和评估结果(训练时可以设置固定轮数评估一次)
+
+
+### 3.2 OCR技术拆解---卡证识别
+
+卡证识别(以身份证检测为例)
+存在的困难及问题:
+
+ * 在自然场景下,由于各种拍摄设备以及光线、角度不同等影响导致实际得到的证件影像千差万别。
+
+ * 如何快速提取需要的关键信息
+
+ * 多行的文本信息,检测结果如何正确拼接
+
+ 
+
+
+
+* OCR技术拆解---OCR工具库
+
+ PaddleOCR是一个丰富、领先且实用的OCR工具库,助力开发者训练出更好的模型并应用落地
+
+
+
+
+身份证识别:用现有的方法识别
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### 身份证识别:检测+分类
+
+> 方法:基于现有的dbnet检测模型,加入分类方法。检测同时进行分类,从一定程度上优化识别流程
+
+
+
+
+
+
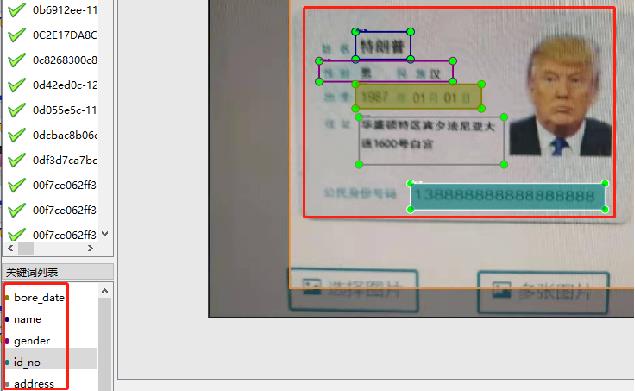
+#### 数据标注
+
+使用PaddleOCRLable进行快速标注
+
+
+
+
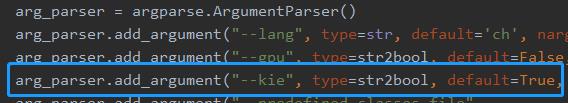
+* 修改PPOCRLabel.py,将下图中的kie参数设置为True
+
+
+
+
+
+* 数据标注踩坑分享
+
+
+
+ 注:两者只有标注有差别,训练参数数据集都相同
+
+## 4 . 项目实践
+
+AIStudio项目链接:[快速构建卡证类OCR](https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/projectdetail/4459116)
+
+### 4.1 环境准备
+
+1)拉取[paddleocr](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR)项目,如果从github上拉取速度慢可以选择从gitee上获取。
+```
+!git clone https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR.git -b release/2.6 /home/aistudio/work/
+```
+
+2)获取并解压预训练模型,如果要使用其他模型可以从模型库里自主选择合适模型。
+```
+!wget -P work/pre_trained/ https://paddleocr.bj.bcebos.com/PP-OCRv3/chinese/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train.tar
+!tar -vxf /home/aistudio/work/pre_trained/ch_PP-OCRv3_det_distill_train.tar -C /home/aistudio/work/pre_trained
+```
+3) 安装必要依赖
+```
+!pip install -r /home/aistudio/work/requirements.txt
+```
+
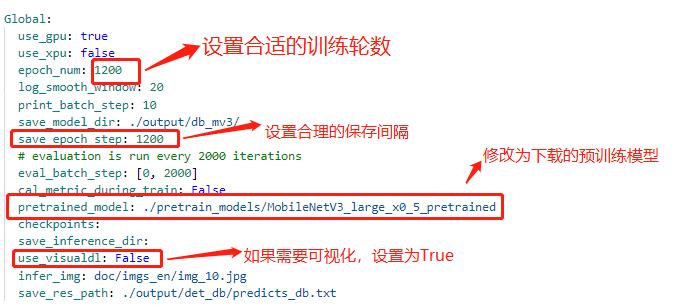
+### 4.2 配置文件修改
+
+修改配置文件 *work/configs/det/detmv3db.yml*
+
+具体修改说明如下:
+
+
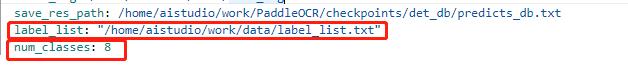
+
+ 注:在上述的配置文件的Global变量中需要添加以下两个参数:
+
+ label_list 为标签表
+ num_classes 为分类数
+ 上述两个参数根据实际的情况配置即可
+
+
+
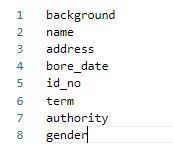
+
+其中lable_list内容如下例所示,***建议第一个参数设置为 background,不要设置为实际要提取的关键信息种类***:
+
+
+
+配置文件中的其他设置说明
+
+
+
+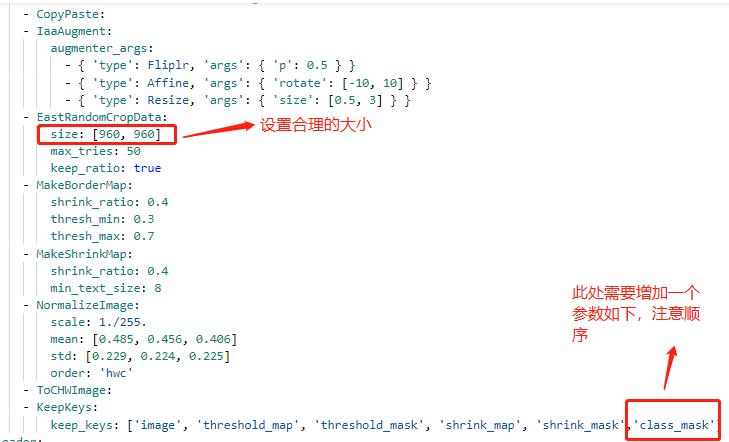
+
+
+
+
+
+
+### 4.3 代码修改
+
+
+#### 4.3.1 数据读取
+
+
+
+* 修改 PaddleOCR/ppocr/data/imaug/label_ops.py中的DetLabelEncode
+
+
+```python
+class DetLabelEncode(object):
+
+ # 修改检测标签的编码处,新增了参数分类数:num_classes,重写初始化方法,以及分类标签的读取
+
+ def __init__(self, label_list, num_classes=8, **kwargs):
+ self.num_classes = num_classes
+ self.label_list = []
+ if label_list:
+ if isinstance(label_list, str):
+ with open(label_list, 'r+', encoding='utf-8') as f:
+ for line in f.readlines():
+ self.label_list.append(line.replace("\n", ""))
+ else:
+ self.label_list = label_list
+ else:
+ assert ' please check label_list whether it is none or config is right'
+
+ if num_classes != len(self.label_list): # 校验分类数和标签的一致性
+ assert 'label_list length is not equal to the num_classes'
+
+ def __call__(self, data):
+ label = data['label']
+ label = json.loads(label)
+ nBox = len(label)
+ boxes, txts, txt_tags, classes = [], [], [], []
+ for bno in range(0, nBox):
+ box = label[bno]['points']
+ txt = label[bno]['key_cls'] # 此处将kie中的参数作为分类读取
+ boxes.append(box)
+ txts.append(txt)
+
+ if txt in ['*', '###']:
+ txt_tags.append(True)
+ if self.num_classes > 1:
+ classes.append(-2)
+ else:
+ txt_tags.append(False)
+ if self.num_classes > 1: # 将KIE内容的key标签作为分类标签使用
+ classes.append(int(self.label_list.index(txt)))
+
+ if len(boxes) == 0:
+
+ return None
+ boxes = self.expand_points_num(boxes)
+ boxes = np.array(boxes, dtype=np.float32)
+ txt_tags = np.array(txt_tags, dtype=np.bool)
+ classes = classes
+ data['polys'] = boxes
+ data['texts'] = txts
+ data['ignore_tags'] = txt_tags
+ if self.num_classes > 1:
+ data['classes'] = classes
+ return data
+```
+
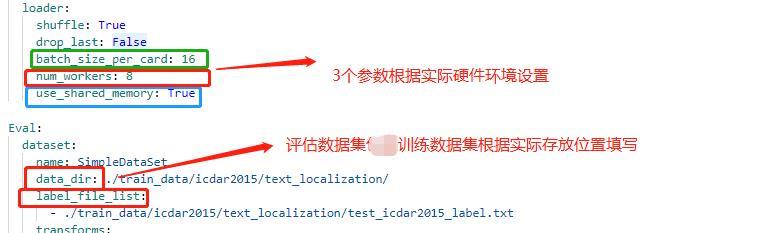
+* 修改 PaddleOCR/ppocr/data/imaug/make_shrink_map.py中的MakeShrinkMap类。这里需要注意的是,如果我们设置的label_list中的第一个参数为要检测的信息那么会得到如下的mask,
+
+举例说明:
+这是检测的mask图,图中有四个mask那么实际对应的分类应该是4类
+
+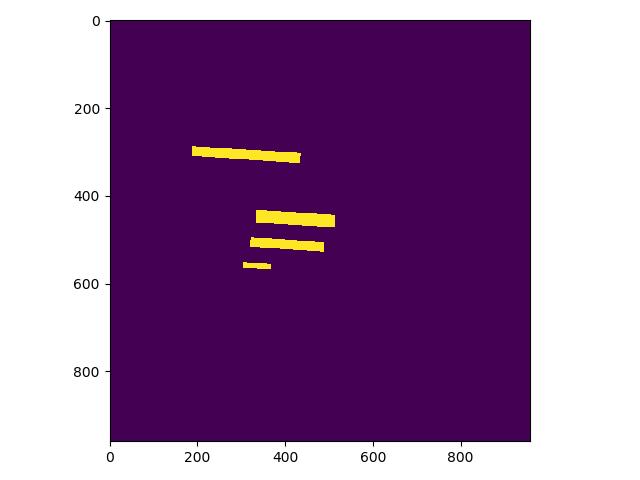
+
+
+
+label_list中第一个为关键分类,则得到的分类Mask实际如下,与上图相比,少了一个box:
+
+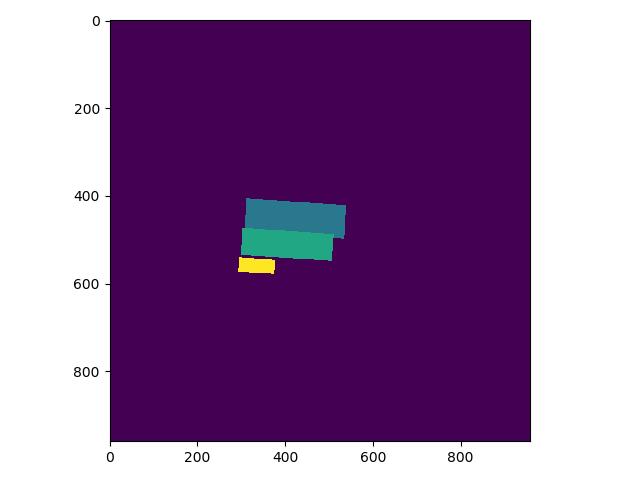
+
+
+
+```python
+class MakeShrinkMap(object):
+ r'''
+ Making binary mask from detection data with ICDAR format.
+ Typically following the process of class `MakeICDARData`.
+ '''
+
+ def __init__(self, min_text_size=8, shrink_ratio=0.4, num_classes=8, **kwargs):
+ self.min_text_size = min_text_size
+ self.shrink_ratio = shrink_ratio
+ self.num_classes = num_classes # 添加了分类
+
+ def __call__(self, data):
+ image = data['image']
+ text_polys = data['polys']
+ ignore_tags = data['ignore_tags']
+ if self.num_classes > 1:
+ classes = data['classes']
+
+ h, w = image.shape[:2]
+ text_polys, ignore_tags = self.validate_polygons(text_polys,
+ ignore_tags, h, w)
+ gt = np.zeros((h, w), dtype=np.float32)
+ mask = np.ones((h, w), dtype=np.float32)
+ gt_class = np.zeros((h, w), dtype=np.float32) # 新增分类
+ for i in range(len(text_polys)):
+ polygon = text_polys[i]
+ height = max(polygon[:, 1]) - min(polygon[:, 1])
+ width = max(polygon[:, 0]) - min(polygon[:, 0])
+ if ignore_tags[i] or min(height, width) < self.min_text_size:
+ cv2.fillPoly(mask,
+ polygon.astype(np.int32)[np.newaxis, :, :], 0)
+ ignore_tags[i] = True
+ else:
+ polygon_shape = Polygon(polygon)
+ subject = [tuple(l) for l in polygon]
+ padding = pyclipper.PyclipperOffset()
+ padding.AddPath(subject, pyclipper.JT_ROUND,
+ pyclipper.ET_CLOSEDPOLYGON)
+ shrinked = []
+
+ # Increase the shrink ratio every time we get multiple polygon returned back
+ possible_ratios = np.arange(self.shrink_ratio, 1,
+ self.shrink_ratio)
+ np.append(possible_ratios, 1)
+ for ratio in possible_ratios:
+ distance = polygon_shape.area * (
+ 1 - np.power(ratio, 2)) / polygon_shape.length
+ shrinked = padding.Execute(-distance)
+ if len(shrinked) == 1:
+ break
+
+ if shrinked == []:
+ cv2.fillPoly(mask,
+ polygon.astype(np.int32)[np.newaxis, :, :], 0)
+ ignore_tags[i] = True
+ continue
+
+ for each_shirnk in shrinked:
+ shirnk = np.array(each_shirnk).reshape(-1, 2)
+ cv2.fillPoly(gt, [shirnk.astype(np.int32)], 1)
+ if self.num_classes > 1: # 绘制分类的mask
+ cv2.fillPoly(gt_class, polygon.astype(np.int32)[np.newaxis, :, :], classes[i])
+
+
+ data['shrink_map'] = gt
+
+ if self.num_classes > 1:
+ data['class_mask'] = gt_class
+
+ data['shrink_mask'] = mask
+ return data
+```
+
+由于在训练数据中会对数据进行resize设置,yml中的操作为:EastRandomCropData,所以需要修改PaddleOCR/ppocr/data/imaug/random_crop_data.py中的EastRandomCropData
+
+
+```python
+class EastRandomCropData(object):
+ def __init__(self,
+ size=(640, 640),
+ max_tries=10,
+ min_crop_side_ratio=0.1,
+ keep_ratio=True,
+ num_classes=8,
+ **kwargs):
+ self.size = size
+ self.max_tries = max_tries
+ self.min_crop_side_ratio = min_crop_side_ratio
+ self.keep_ratio = keep_ratio
+ self.num_classes = num_classes
+
+ def __call__(self, data):
+ img = data['image']
+ text_polys = data['polys']
+ ignore_tags = data['ignore_tags']
+ texts = data['texts']
+ if self.num_classes > 1:
+ classes = data['classes']
+ all_care_polys = [
+ text_polys[i] for i, tag in enumerate(ignore_tags) if not tag
+ ]
+ # 计算crop区域
+ crop_x, crop_y, crop_w, crop_h = crop_area(
+ img, all_care_polys, self.min_crop_side_ratio, self.max_tries)
+ # crop 图片 保持比例填充
+ scale_w = self.size[0] / crop_w
+ scale_h = self.size[1] / crop_h
+ scale = min(scale_w, scale_h)
+ h = int(crop_h * scale)
+ w = int(crop_w * scale)
+ if self.keep_ratio:
+ padimg = np.zeros((self.size[1], self.size[0], img.shape[2]),
+ img.dtype)
+ padimg[:h, :w] = cv2.resize(
+ img[crop_y:crop_y + crop_h, crop_x:crop_x + crop_w], (w, h))
+ img = padimg
+ else:
+ img = cv2.resize(
+ img[crop_y:crop_y + crop_h, crop_x:crop_x + crop_w],
+ tuple(self.size))
+ # crop 文本框
+ text_polys_crop = []
+ ignore_tags_crop = []
+ texts_crop = []
+ classes_crop = []
+ for poly, text, tag,class_index in zip(text_polys, texts, ignore_tags,classes):
+ poly = ((poly - (crop_x, crop_y)) * scale).tolist()
+ if not is_poly_outside_rect(poly, 0, 0, w, h):
+ text_polys_crop.append(poly)
+ ignore_tags_crop.append(tag)
+ texts_crop.append(text)
+ if self.num_classes > 1:
+ classes_crop.append(class_index)
+ data['image'] = img
+ data['polys'] = np.array(text_polys_crop)
+ data['ignore_tags'] = ignore_tags_crop
+ data['texts'] = texts_crop
+ if self.num_classes > 1:
+ data['classes'] = classes_crop
+ return data
+```
+
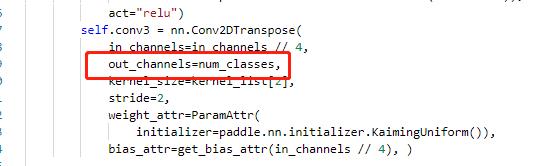
+#### 4.3.2 head修改
+
+
+
+主要修改 ppocr/modeling/heads/det_db_head.py,将Head类中的最后一层的输出修改为实际的分类数,同时在DBHead中新增分类的head。
+
+
+
+
+
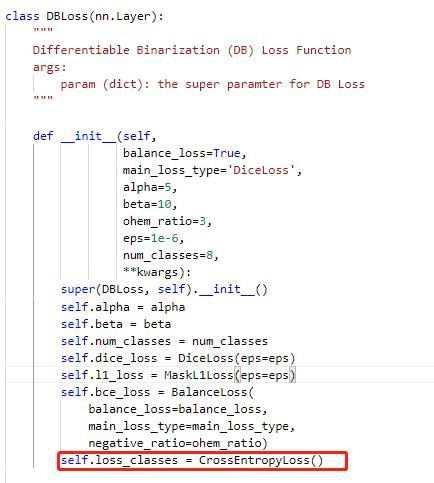
+#### 4.3.3 修改loss
+
+
+修改PaddleOCR/ppocr/losses/det_db_loss.py中的DBLoss类,分类采用交叉熵损失函数进行计算。
+
+
+
+
+#### 4.3.4 后处理
+
+
+
+由于涉及到eval以及后续推理能否正常使用,我们需要修改后处理的相关代码,修改位置 PaddleOCR/ppocr/postprocess/db_postprocess.py中的DBPostProcess类
+
+
+```python
+class DBPostProcess(object):
+ """
+ The post process for Differentiable Binarization (DB).
+ """
+
+ def __init__(self,
+ thresh=0.3,
+ box_thresh=0.7,
+ max_candidates=1000,
+ unclip_ratio=2.0,
+ use_dilation=False,
+ score_mode="fast",
+ **kwargs):
+ self.thresh = thresh
+ self.box_thresh = box_thresh
+ self.max_candidates = max_candidates
+ self.unclip_ratio = unclip_ratio
+ self.min_size = 3
+ self.score_mode = score_mode
+ assert score_mode in [
+ "slow", "fast"
+ ], "Score mode must be in [slow, fast] but got: {}".format(score_mode)
+
+ self.dilation_kernel = None if not use_dilation else np.array(
+ [[1, 1], [1, 1]])
+
+ def boxes_from_bitmap(self, pred, _bitmap, classes, dest_width, dest_height):
+ """
+ _bitmap: single map with shape (1, H, W),
+ whose values are binarized as {0, 1}
+ """
+
+ bitmap = _bitmap
+ height, width = bitmap.shape
+
+ outs = cv2.findContours((bitmap * 255).astype(np.uint8), cv2.RETR_LIST,
+ cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
+ if len(outs) == 3:
+ img, contours, _ = outs[0], outs[1], outs[2]
+ elif len(outs) == 2:
+ contours, _ = outs[0], outs[1]
+
+ num_contours = min(len(contours), self.max_candidates)
+
+ boxes = []
+ scores = []
+ class_indexes = []
+ class_scores = []
+ for index in range(num_contours):
+ contour = contours[index]
+ points, sside = self.get_mini_boxes(contour)
+ if sside < self.min_size:
+ continue
+ points = np.array(points)
+ if self.score_mode == "fast":
+ score, class_index, class_score = self.box_score_fast(pred, points.reshape(-1, 2), classes)
+ else:
+ score, class_index, class_score = self.box_score_slow(pred, contour, classes)
+ if self.box_thresh > score:
+ continue
+
+ box = self.unclip(points).reshape(-1, 1, 2)
+ box, sside = self.get_mini_boxes(box)
+ if sside < self.min_size + 2:
+ continue
+ box = np.array(box)
+
+ box[:, 0] = np.clip(
+ np.round(box[:, 0] / width * dest_width), 0, dest_width)
+ box[:, 1] = np.clip(
+ np.round(box[:, 1] / height * dest_height), 0, dest_height)
+
+ boxes.append(box.astype(np.int16))
+ scores.append(score)
+
+ class_indexes.append(class_index)
+ class_scores.append(class_score)
+
+ if classes is None:
+ return np.array(boxes, dtype=np.int16), scores
+ else:
+ return np.array(boxes, dtype=np.int16), scores, class_indexes, class_scores
+
+ def unclip(self, box):
+ unclip_ratio = self.unclip_ratio
+ poly = Polygon(box)
+ distance = poly.area * unclip_ratio / poly.length
+ offset = pyclipper.PyclipperOffset()
+ offset.AddPath(box, pyclipper.JT_ROUND, pyclipper.ET_CLOSEDPOLYGON)
+ expanded = np.array(offset.Execute(distance))
+ return expanded
+
+ def get_mini_boxes(self, contour):
+ bounding_box = cv2.minAreaRect(contour)
+ points = sorted(list(cv2.boxPoints(bounding_box)), key=lambda x: x[0])
+
+ index_1, index_2, index_3, index_4 = 0, 1, 2, 3
+ if points[1][1] > points[0][1]:
+ index_1 = 0
+ index_4 = 1
+ else:
+ index_1 = 1
+ index_4 = 0
+ if points[3][1] > points[2][1]:
+ index_2 = 2
+ index_3 = 3
+ else:
+ index_2 = 3
+ index_3 = 2
+
+ box = [
+ points[index_1], points[index_2], points[index_3], points[index_4]
+ ]
+ return box, min(bounding_box[1])
+
+ def box_score_fast(self, bitmap, _box, classes):
+ '''
+ box_score_fast: use bbox mean score as the mean score
+ '''
+ h, w = bitmap.shape[:2]
+ box = _box.copy()
+ xmin = np.clip(np.floor(box[:, 0].min()).astype(np.int), 0, w - 1)
+ xmax = np.clip(np.ceil(box[:, 0].max()).astype(np.int), 0, w - 1)
+ ymin = np.clip(np.floor(box[:, 1].min()).astype(np.int), 0, h - 1)
+ ymax = np.clip(np.ceil(box[:, 1].max()).astype(np.int), 0, h - 1)
+
+ mask = np.zeros((ymax - ymin + 1, xmax - xmin + 1), dtype=np.uint8)
+ box[:, 0] = box[:, 0] - xmin
+ box[:, 1] = box[:, 1] - ymin
+ cv2.fillPoly(mask, box.reshape(1, -1, 2).astype(np.int32), 1)
+
+ if classes is None:
+ return cv2.mean(bitmap[ymin:ymax + 1, xmin:xmax + 1], mask)[0], None, None
+ else:
+ k = 999
+ class_mask = np.full((ymax - ymin + 1, xmax - xmin + 1), k, dtype=np.int32)
+
+ cv2.fillPoly(class_mask, box.reshape(1, -1, 2).astype(np.int32), 0)
+ classes = classes[ymin:ymax + 1, xmin:xmax + 1]
+
+ new_classes = classes + class_mask
+ a = new_classes.reshape(-1)
+ b = np.where(a >= k)
+ classes = np.delete(a, b[0].tolist())
+
+ class_index = np.argmax(np.bincount(classes))
+ class_score = np.sum(classes == class_index) / len(classes)
+
+ return cv2.mean(bitmap[ymin:ymax + 1, xmin:xmax + 1], mask)[0], class_index, class_score
+
+ def box_score_slow(self, bitmap, contour, classes):
+ """
+ box_score_slow: use polyon mean score as the mean score
+ """
+ h, w = bitmap.shape[:2]
+ contour = contour.copy()
+ contour = np.reshape(contour, (-1, 2))
+
+ xmin = np.clip(np.min(contour[:, 0]), 0, w - 1)
+ xmax = np.clip(np.max(contour[:, 0]), 0, w - 1)
+ ymin = np.clip(np.min(contour[:, 1]), 0, h - 1)
+ ymax = np.clip(np.max(contour[:, 1]), 0, h - 1)
+
+ mask = np.zeros((ymax - ymin + 1, xmax - xmin + 1), dtype=np.uint8)
+
+ contour[:, 0] = contour[:, 0] - xmin
+ contour[:, 1] = contour[:, 1] - ymin
+
+ cv2.fillPoly(mask, contour.reshape(1, -1, 2).astype(np.int32), 1)
+
+ if classes is None:
+ return cv2.mean(bitmap[ymin:ymax + 1, xmin:xmax + 1], mask)[0], None, None
+ else:
+ k = 999
+ class_mask = np.full((ymax - ymin + 1, xmax - xmin + 1), k, dtype=np.int32)
+
+ cv2.fillPoly(class_mask, contour.reshape(1, -1, 2).astype(np.int32), 0)
+ classes = classes[ymin:ymax + 1, xmin:xmax + 1]
+
+ new_classes = classes + class_mask
+ a = new_classes.reshape(-1)
+ b = np.where(a >= k)
+ classes = np.delete(a, b[0].tolist())
+
+ class_index = np.argmax(np.bincount(classes))
+ class_score = np.sum(classes == class_index) / len(classes)
+
+ return cv2.mean(bitmap[ymin:ymax + 1, xmin:xmax + 1], mask)[0], class_index, class_score
+
+ def __call__(self, outs_dict, shape_list):
+ pred = outs_dict['maps']
+ if isinstance(pred, paddle.Tensor):
+ pred = pred.numpy()
+ pred = pred[:, 0, :, :]
+ segmentation = pred > self.thresh
+
+ if "classes" in outs_dict:
+ classes = outs_dict['classes']
+ if isinstance(classes, paddle.Tensor):
+ classes = classes.numpy()
+ classes = classes[:, 0, :, :]
+
+ else:
+ classes = None
+
+ boxes_batch = []
+ for batch_index in range(pred.shape[0]):
+ src_h, src_w, ratio_h, ratio_w = shape_list[batch_index]
+ if self.dilation_kernel is not None:
+ mask = cv2.dilate(
+ np.array(segmentation[batch_index]).astype(np.uint8),
+ self.dilation_kernel)
+ else:
+ mask = segmentation[batch_index]
+
+ if classes is None:
+ boxes, scores = self.boxes_from_bitmap(pred[batch_index], mask, None,
+ src_w, src_h)
+ boxes_batch.append({'points': boxes})
+ else:
+ boxes, scores, class_indexes, class_scores = self.boxes_from_bitmap(pred[batch_index], mask,
+ classes[batch_index],
+ src_w, src_h)
+ boxes_batch.append({'points': boxes, "classes": class_indexes, "class_scores": class_scores})
+
+ return boxes_batch
+```
+
+### 4.4. 模型启动
+
+在完成上述步骤后我们就可以正常启动训练
+
+```
+!python /home/aistudio/work/PaddleOCR/tools/train.py -c /home/aistudio/work/PaddleOCR/configs/det/det_mv3_db.yml
+```
+
+其他命令:
+```
+!python /home/aistudio/work/PaddleOCR/tools/eval.py -c /home/aistudio/work/PaddleOCR/configs/det/det_mv3_db.yml
+!python /home/aistudio/work/PaddleOCR/tools/infer_det.py -c /home/aistudio/work/PaddleOCR/configs/det/det_mv3_db.yml
+```
+模型推理
+```
+!python /home/aistudio/work/PaddleOCR/tools/infer/predict_det.py --image_dir="/home/aistudio/work/test_img/" --det_model_dir="/home/aistudio/work/PaddleOCR/output/infer"
+```
+
+## 5 总结
+
+1. 分类+检测在一定程度上能够缩短用时,具体的模型选取要根据业务场景恰当选择。
+2. 数据标注需要多次进行测试调整标注方法,一般进行检测模型微调,需要标注至少上百张。
+3. 设置合理的batch_size以及resize大小,同时注意lr设置。
+
+
+## References
+
+1 https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR
+
+2 https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleClas
+
+3 https://blog.csdn.net/YY007H/article/details/124491217
diff --git "a/applications/\346\211\253\346\217\217\345\220\210\345\220\214\345\205\263\351\224\256\344\277\241\346\201\257\346\217\220\345\217\226.md" "b/applications/\346\211\253\346\217\217\345\220\210\345\220\214\345\205\263\351\224\256\344\277\241\346\201\257\346\217\220\345\217\226.md"
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000..26c64a34c14e621b4bc15df67c66141024bf7cc4
--- /dev/null
+++ "b/applications/\346\211\253\346\217\217\345\220\210\345\220\214\345\205\263\351\224\256\344\277\241\346\201\257\346\217\220\345\217\226.md"
@@ -0,0 +1,284 @@
+# 金融智能核验:扫描合同关键信息抽取
+
+本案例将使用OCR技术和通用信息抽取技术,实现合同关键信息审核和比对。通过本章的学习,你可以快速掌握:
+
+1. 使用PaddleOCR提取扫描文本内容
+2. 使用PaddleNLP抽取自定义信息
+
+点击进入 [AI Studio 项目](https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/projectdetail/4545772)
+
+## 1. 项目背景
+合同审核广泛应用于大中型企业、上市公司、证券、基金公司中,是规避风险的重要任务。
+- 合同内容对比:合同审核场景中,快速找出不同版本合同修改区域、版本差异;如合同盖章归档场景中有效识别实际签署的纸质合同、电子版合同差异。
+
+- 合规性检查:法务人员进行合同审核,如合同完备性检查、大小写金额检查、签约主体一致性检查、双方权利和义务对等性分析等。
+
+- 风险点识别:通过合同审核可识别事实倾向型风险点和数值计算型风险点等,例如交付地点约定不明、合同总价款不一致、重要条款缺失等风险点。
+
+
+
+
+传统业务中大多使用人工进行纸质版合同审核,存在成本高,工作量大,效率低的问题,且一旦出错将造成巨额损失。
+
+
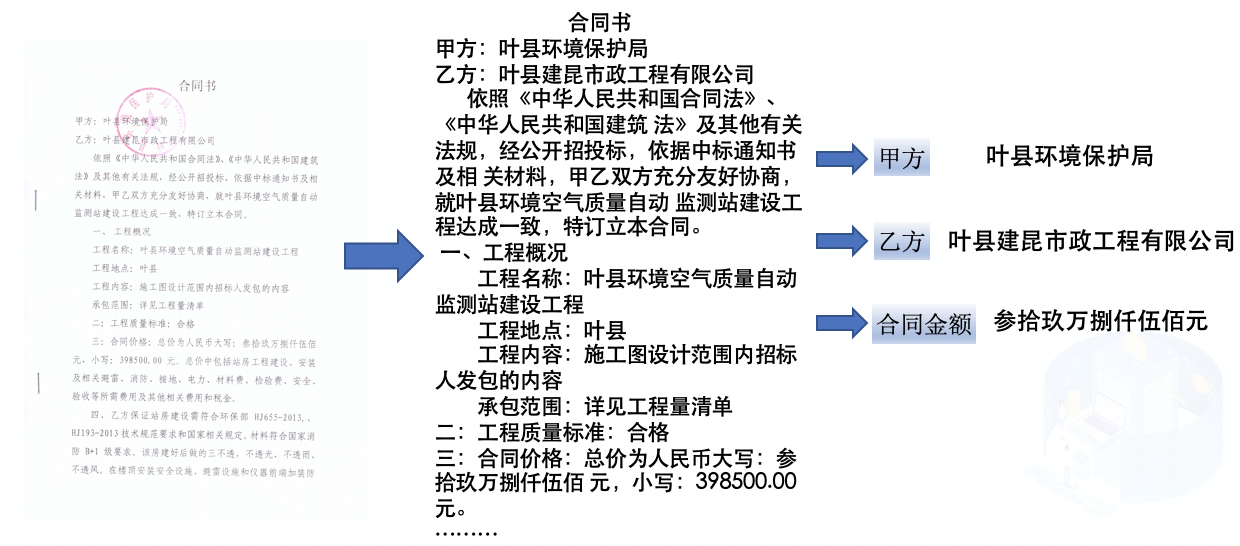
+本项目针对以上场景,使用PaddleOCR+PaddleNLP快速提取文本内容,经过少量数据微调即可准确抽取关键信息,**高效完成合同内容对比、合规性检查、风险点识别等任务,提高效率,降低风险**。
+
+
+
+
+## 2. 解决方案
+
+### 2.1 扫描合同文本内容提取
+
+使用PaddleOCR开源的模型可以快速完成扫描文档的文本内容提取,在清晰文档上识别准确率可达到95%+。下面来快速体验一下:
+
+#### 2.1.1 环境准备
+
+[PaddleOCR](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR)提供了适用于通用场景的高精轻量模型,提供数据预处理-模型推理-后处理全流程,支持pip安装:
+
+```
+python -m pip install paddleocr
+```
+
+#### 2.1.2 效果测试
+
+使用一张合同图片作为测试样本,感受ppocrv3模型效果:
+
+ +
+使用中文检测+识别模型提取文本,实例化PaddleOCR类:
+
+```
+from paddleocr import PaddleOCR, draw_ocr
+
+# paddleocr目前支持中英文、英文、法语、德语、韩语、日语等80个语种,可以通过修改lang参数进行切换
+ocr = PaddleOCR(use_angle_cls=False, lang="ch") # need to run only once to download and load model into memory
+```
+
+一行命令启动预测,预测结果包括`检测框`和`文本识别内容`:
+
+```
+img_path = "./test_img/hetong2.jpg"
+result = ocr.ocr(img_path, cls=False)
+for line in result:
+ print(line)
+
+# 可视化结果
+from PIL import Image
+
+image = Image.open(img_path).convert('RGB')
+boxes = [line[0] for line in result]
+txts = [line[1][0] for line in result]
+scores = [line[1][1] for line in result]
+im_show = draw_ocr(image, boxes, txts, scores, font_path='./simfang.ttf')
+im_show = Image.fromarray(im_show)
+im_show.show()
+```
+
+#### 2.1.3 图片预处理
+
+通过上图可视化结果可以看到,印章部分造成的文本遮盖,影响了文本识别结果,因此可以考虑通道提取,去除图片中的红色印章:
+
+```
+import cv2
+import numpy as np
+import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
+
+#读入图像,三通道
+image=cv2.imread("./test_img/hetong2.jpg",cv2.IMREAD_COLOR) #timg.jpeg
+
+#获得三个通道
+Bch,Gch,Rch=cv2.split(image)
+
+#保存三通道图片
+cv2.imwrite('blue_channel.jpg',Bch)
+cv2.imwrite('green_channel.jpg',Gch)
+cv2.imwrite('red_channel.jpg',Rch)
+```
+#### 2.1.4 合同文本信息提取
+
+经过2.1.3的预处理后,合同照片的红色通道被分离,获得了一张相对更干净的图片,此时可以再次使用ppocr模型提取文本内容:
+
+```
+import numpy as np
+import cv2
+
+
+img_path = './red_channel.jpg'
+result = ocr.ocr(img_path, cls=False)
+
+# 可视化结果
+from PIL import Image
+
+image = Image.open(img_path).convert('RGB')
+boxes = [line[0] for line in result]
+txts = [line[1][0] for line in result]
+scores = [line[1][1] for line in result]
+im_show = draw_ocr(image, boxes, txts, scores, font_path='./simfang.ttf')
+im_show = Image.fromarray(im_show)
+vis = np.array(im_show)
+im_show.show()
+```
+
+忽略检测框内容,提取完整的合同文本:
+
+```
+txts = [line[1][0] for line in result]
+all_context = "\n".join(txts)
+print(all_context)
+```
+
+通过以上环节就完成了扫描合同关键信息抽取的第一步:文本内容提取,接下来可以基于识别出的文本内容抽取关键信息
+
+### 2.2 合同关键信息抽取
+
+#### 2.2.1 环境准备
+
+安装PaddleNLP
+
+
+```
+pip install --upgrade pip
+pip install --upgrade paddlenlp
+```
+
+#### 2.2.2 合同关键信息抽取
+
+PaddleNLP 使用 Taskflow 统一管理多场景任务的预测功能,其中`information_extraction` 通过大量的有标签样本进行训练,在通用的场景中一般可以直接使用,只需更换关键字即可。例如在合同信息抽取中,我们重新定义抽取关键字:
+
+甲方、乙方、币种、金额、付款方式
+
+
+将使用OCR提取好的文本作为输入,使用三行命令可以对上文中提取到的合同文本进行关键信息抽取:
+
+```
+from paddlenlp import Taskflow
+schema = ["甲方","乙方","总价"]
+ie = Taskflow('information_extraction', schema=schema)
+ie.set_schema(schema)
+ie(all_context)
+```
+
+可以看到UIE模型可以准确的提取出关键信息,用于后续的信息比对或审核。
+
+## 3.效果优化
+
+### 3.1 文本识别后处理调优
+
+实际图片采集过程中,可能出现部分图片弯曲等问题,导致使用默认参数识别文本时存在漏检,影响关键信息获取。
+
+例如下图:
+
+
+
+使用中文检测+识别模型提取文本,实例化PaddleOCR类:
+
+```
+from paddleocr import PaddleOCR, draw_ocr
+
+# paddleocr目前支持中英文、英文、法语、德语、韩语、日语等80个语种,可以通过修改lang参数进行切换
+ocr = PaddleOCR(use_angle_cls=False, lang="ch") # need to run only once to download and load model into memory
+```
+
+一行命令启动预测,预测结果包括`检测框`和`文本识别内容`:
+
+```
+img_path = "./test_img/hetong2.jpg"
+result = ocr.ocr(img_path, cls=False)
+for line in result:
+ print(line)
+
+# 可视化结果
+from PIL import Image
+
+image = Image.open(img_path).convert('RGB')
+boxes = [line[0] for line in result]
+txts = [line[1][0] for line in result]
+scores = [line[1][1] for line in result]
+im_show = draw_ocr(image, boxes, txts, scores, font_path='./simfang.ttf')
+im_show = Image.fromarray(im_show)
+im_show.show()
+```
+
+#### 2.1.3 图片预处理
+
+通过上图可视化结果可以看到,印章部分造成的文本遮盖,影响了文本识别结果,因此可以考虑通道提取,去除图片中的红色印章:
+
+```
+import cv2
+import numpy as np
+import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
+
+#读入图像,三通道
+image=cv2.imread("./test_img/hetong2.jpg",cv2.IMREAD_COLOR) #timg.jpeg
+
+#获得三个通道
+Bch,Gch,Rch=cv2.split(image)
+
+#保存三通道图片
+cv2.imwrite('blue_channel.jpg',Bch)
+cv2.imwrite('green_channel.jpg',Gch)
+cv2.imwrite('red_channel.jpg',Rch)
+```
+#### 2.1.4 合同文本信息提取
+
+经过2.1.3的预处理后,合同照片的红色通道被分离,获得了一张相对更干净的图片,此时可以再次使用ppocr模型提取文本内容:
+
+```
+import numpy as np
+import cv2
+
+
+img_path = './red_channel.jpg'
+result = ocr.ocr(img_path, cls=False)
+
+# 可视化结果
+from PIL import Image
+
+image = Image.open(img_path).convert('RGB')
+boxes = [line[0] for line in result]
+txts = [line[1][0] for line in result]
+scores = [line[1][1] for line in result]
+im_show = draw_ocr(image, boxes, txts, scores, font_path='./simfang.ttf')
+im_show = Image.fromarray(im_show)
+vis = np.array(im_show)
+im_show.show()
+```
+
+忽略检测框内容,提取完整的合同文本:
+
+```
+txts = [line[1][0] for line in result]
+all_context = "\n".join(txts)
+print(all_context)
+```
+
+通过以上环节就完成了扫描合同关键信息抽取的第一步:文本内容提取,接下来可以基于识别出的文本内容抽取关键信息
+
+### 2.2 合同关键信息抽取
+
+#### 2.2.1 环境准备
+
+安装PaddleNLP
+
+
+```
+pip install --upgrade pip
+pip install --upgrade paddlenlp
+```
+
+#### 2.2.2 合同关键信息抽取
+
+PaddleNLP 使用 Taskflow 统一管理多场景任务的预测功能,其中`information_extraction` 通过大量的有标签样本进行训练,在通用的场景中一般可以直接使用,只需更换关键字即可。例如在合同信息抽取中,我们重新定义抽取关键字:
+
+甲方、乙方、币种、金额、付款方式
+
+
+将使用OCR提取好的文本作为输入,使用三行命令可以对上文中提取到的合同文本进行关键信息抽取:
+
+```
+from paddlenlp import Taskflow
+schema = ["甲方","乙方","总价"]
+ie = Taskflow('information_extraction', schema=schema)
+ie.set_schema(schema)
+ie(all_context)
+```
+
+可以看到UIE模型可以准确的提取出关键信息,用于后续的信息比对或审核。
+
+## 3.效果优化
+
+### 3.1 文本识别后处理调优
+
+实际图片采集过程中,可能出现部分图片弯曲等问题,导致使用默认参数识别文本时存在漏检,影响关键信息获取。
+
+例如下图:
+
+ +
+
+直接进行预测:
+
+```
+img_path = "./test_img/hetong3.jpg"
+# 预测结果
+result = ocr.ocr(img_path, cls=False)
+# 可视化结果
+from PIL import Image
+
+image = Image.open(img_path).convert('RGB')
+boxes = [line[0] for line in result]
+txts = [line[1][0] for line in result]
+scores = [line[1][1] for line in result]
+im_show = draw_ocr(image, boxes, txts, scores, font_path='./simfang.ttf')
+im_show = Image.fromarray(im_show)
+im_show.show()
+```
+
+可视化结果可以看到,弯曲图片存在漏检,一般来说可以通过调整后处理参数解决,无需重新训练模型。漏检问题往往是因为检测模型获得的分割图太小,生成框的得分过低被过滤掉了,通常有两种方式调整参数:
+- 开启`use_dilatiion=True` 膨胀分割区域
+- 调小`det_db_box_thresh`阈值
+
+```
+# 重新实例化 PaddleOCR
+ocr = PaddleOCR(use_angle_cls=False, lang="ch", det_db_box_thresh=0.3, use_dilation=True)
+
+# 预测并可视化
+img_path = "./test_img/hetong3.jpg"
+# 预测结果
+result = ocr.ocr(img_path, cls=False)
+# 可视化结果
+image = Image.open(img_path).convert('RGB')
+boxes = [line[0] for line in result]
+txts = [line[1][0] for line in result]
+scores = [line[1][1] for line in result]
+im_show = draw_ocr(image, boxes, txts, scores, font_path='./simfang.ttf')
+im_show = Image.fromarray(im_show)
+im_show.show()
+```
+
+可以看到漏检问题被很好的解决,提取完整的文本内容:
+
+```
+txts = [line[1][0] for line in result]
+context = "\n".join(txts)
+print(context)
+```
+
+### 3.2 关键信息提取调优
+
+UIE通过大量有标签样本进行训练,得到了一个开箱即用的高精模型。 然而针对不同场景,可能会出现部分实体无法被抽取的情况。通常来说有以下几个方法进行效果调优:
+
+
+- 修改 schema
+- 添加正则方法
+- 标注小样本微调模型
+
+**修改schema**
+
+Prompt和原文描述越像,抽取效果越好,例如
+```
+三:合同价格:总价为人民币大写:参拾玖万捌仟伍佰
+元,小写:398500.00元。总价中包括站房工程建设、安装
+及相关避雷、消防、接地、电力、材料费、检验费、安全、
+验收等所需费用及其他相关费用和税金。
+```
+schema = ["总金额"] 时无法准确抽取,与原文描述差异较大。 修改 schema = ["总价"] 再次尝试:
+
+```
+from paddlenlp import Taskflow
+# schema = ["总金额"]
+schema = ["总价"]
+ie = Taskflow('information_extraction', schema=schema)
+ie.set_schema(schema)
+ie(all_context)
+```
+
+
+**模型微调**
+
+UIE的建模方式主要是通过 `Prompt` 方式来建模, `Prompt` 在小样本上进行微调效果非常有效。详细的数据标注+模型微调步骤可以参考项目:
+
+[PaddleNLP信息抽取技术重磅升级!](https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/projectdetail/3914778?channelType=0&channel=0)
+
+[工单信息抽取](https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/projectdetail/3914778?contributionType=1)
+
+[快递单信息抽取](https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/projectdetail/4038499?contributionType=1)
+
+
+## 总结
+
+扫描合同的关键信息提取可以使用 PaddleOCR + PaddleNLP 组合实现,两个工具均有以下优势:
+
+* 使用简单:whl包一键安装,3行命令调用
+* 效果领先:优秀的模型效果可覆盖几乎全部的应用场景
+* 调优成本低:OCR模型可通过后处理参数的调整适配略有偏差的扫描文本, UIE模型可以通过极少的标注样本微调,成本很低。
+
+## 作业
+
+尝试自己解析出 `test_img/homework.png` 扫描合同中的 [甲方、乙方] 关键词:
+
+
+
+
+
+
+直接进行预测:
+
+```
+img_path = "./test_img/hetong3.jpg"
+# 预测结果
+result = ocr.ocr(img_path, cls=False)
+# 可视化结果
+from PIL import Image
+
+image = Image.open(img_path).convert('RGB')
+boxes = [line[0] for line in result]
+txts = [line[1][0] for line in result]
+scores = [line[1][1] for line in result]
+im_show = draw_ocr(image, boxes, txts, scores, font_path='./simfang.ttf')
+im_show = Image.fromarray(im_show)
+im_show.show()
+```
+
+可视化结果可以看到,弯曲图片存在漏检,一般来说可以通过调整后处理参数解决,无需重新训练模型。漏检问题往往是因为检测模型获得的分割图太小,生成框的得分过低被过滤掉了,通常有两种方式调整参数:
+- 开启`use_dilatiion=True` 膨胀分割区域
+- 调小`det_db_box_thresh`阈值
+
+```
+# 重新实例化 PaddleOCR
+ocr = PaddleOCR(use_angle_cls=False, lang="ch", det_db_box_thresh=0.3, use_dilation=True)
+
+# 预测并可视化
+img_path = "./test_img/hetong3.jpg"
+# 预测结果
+result = ocr.ocr(img_path, cls=False)
+# 可视化结果
+image = Image.open(img_path).convert('RGB')
+boxes = [line[0] for line in result]
+txts = [line[1][0] for line in result]
+scores = [line[1][1] for line in result]
+im_show = draw_ocr(image, boxes, txts, scores, font_path='./simfang.ttf')
+im_show = Image.fromarray(im_show)
+im_show.show()
+```
+
+可以看到漏检问题被很好的解决,提取完整的文本内容:
+
+```
+txts = [line[1][0] for line in result]
+context = "\n".join(txts)
+print(context)
+```
+
+### 3.2 关键信息提取调优
+
+UIE通过大量有标签样本进行训练,得到了一个开箱即用的高精模型。 然而针对不同场景,可能会出现部分实体无法被抽取的情况。通常来说有以下几个方法进行效果调优:
+
+
+- 修改 schema
+- 添加正则方法
+- 标注小样本微调模型
+
+**修改schema**
+
+Prompt和原文描述越像,抽取效果越好,例如
+```
+三:合同价格:总价为人民币大写:参拾玖万捌仟伍佰
+元,小写:398500.00元。总价中包括站房工程建设、安装
+及相关避雷、消防、接地、电力、材料费、检验费、安全、
+验收等所需费用及其他相关费用和税金。
+```
+schema = ["总金额"] 时无法准确抽取,与原文描述差异较大。 修改 schema = ["总价"] 再次尝试:
+
+```
+from paddlenlp import Taskflow
+# schema = ["总金额"]
+schema = ["总价"]
+ie = Taskflow('information_extraction', schema=schema)
+ie.set_schema(schema)
+ie(all_context)
+```
+
+
+**模型微调**
+
+UIE的建模方式主要是通过 `Prompt` 方式来建模, `Prompt` 在小样本上进行微调效果非常有效。详细的数据标注+模型微调步骤可以参考项目:
+
+[PaddleNLP信息抽取技术重磅升级!](https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/projectdetail/3914778?channelType=0&channel=0)
+
+[工单信息抽取](https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/projectdetail/3914778?contributionType=1)
+
+[快递单信息抽取](https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/projectdetail/4038499?contributionType=1)
+
+
+## 总结
+
+扫描合同的关键信息提取可以使用 PaddleOCR + PaddleNLP 组合实现,两个工具均有以下优势:
+
+* 使用简单:whl包一键安装,3行命令调用
+* 效果领先:优秀的模型效果可覆盖几乎全部的应用场景
+* 调优成本低:OCR模型可通过后处理参数的调整适配略有偏差的扫描文本, UIE模型可以通过极少的标注样本微调,成本很低。
+
+## 作业
+
+尝试自己解析出 `test_img/homework.png` 扫描合同中的 [甲方、乙方] 关键词:
+
+
+
+ +
+
+
+更多场景下的垂类模型获取,请扫下图二维码填写问卷,加入PaddleOCR官方交流群获取模型下载链接、《动手学OCR》电子书等全套OCR学习资料🎁
+
+
+
+
+
+更多场景下的垂类模型获取,请扫下图二维码填写问卷,加入PaddleOCR官方交流群获取模型下载链接、《动手学OCR》电子书等全套OCR学习资料🎁
+
+ diff --git a/ppstructure/table/README.md b/ppstructure/table/README.md
index 08635516ba8301e6f98f175e5eba8c0a97b1708e..1d082f3878c56e42d175d13c75e1fe17916e7781 100644
--- a/ppstructure/table/README.md
+++ b/ppstructure/table/README.md
@@ -114,7 +114,7 @@ python3 table/eval_table.py \
--det_model_dir=path/to/det_model_dir \
--rec_model_dir=path/to/rec_model_dir \
--table_model_dir=path/to/table_model_dir \
- --image_dir=../doc/table/1.png \
+ --image_dir=docs/table/table.jpg \
--rec_char_dict_path=../ppocr/utils/dict/table_dict.txt \
--table_char_dict_path=../ppocr/utils/dict/table_structure_dict.txt \
--det_limit_side_len=736 \
@@ -145,6 +145,7 @@ python3 table/eval_table.py \
--table_char_dict_path=../ppocr/utils/dict/table_structure_dict.txt \
--det_limit_side_len=736 \
--det_limit_type=min \
+ --rec_image_shape=3,32,320 \
--gt_path=path/to/gt.txt
```
diff --git a/ppstructure/table/README_ch.md b/ppstructure/table/README_ch.md
index 1ef126261d9ce832cd1919a1b3991f341add998c..feccb70adfe20fa8c1cd06f33a10ee6fa043e69e 100644
--- a/ppstructure/table/README_ch.md
+++ b/ppstructure/table/README_ch.md
@@ -118,7 +118,7 @@ python3 table/eval_table.py \
--det_model_dir=path/to/det_model_dir \
--rec_model_dir=path/to/rec_model_dir \
--table_model_dir=path/to/table_model_dir \
- --image_dir=../doc/table/1.png \
+ --image_dir=docs/table/table.jpg \
--rec_char_dict_path=../ppocr/utils/dict/table_dict.txt \
--table_char_dict_path=../ppocr/utils/dict/table_structure_dict.txt \
--det_limit_side_len=736 \
@@ -149,6 +149,7 @@ python3 table/eval_table.py \
--table_char_dict_path=../ppocr/utils/dict/table_structure_dict.txt \
--det_limit_side_len=736 \
--det_limit_type=min \
+ --rec_image_shape=3,32,320 \
--gt_path=path/to/gt.txt
```
diff --git a/ppstructure/table/README.md b/ppstructure/table/README.md
index 08635516ba8301e6f98f175e5eba8c0a97b1708e..1d082f3878c56e42d175d13c75e1fe17916e7781 100644
--- a/ppstructure/table/README.md
+++ b/ppstructure/table/README.md
@@ -114,7 +114,7 @@ python3 table/eval_table.py \
--det_model_dir=path/to/det_model_dir \
--rec_model_dir=path/to/rec_model_dir \
--table_model_dir=path/to/table_model_dir \
- --image_dir=../doc/table/1.png \
+ --image_dir=docs/table/table.jpg \
--rec_char_dict_path=../ppocr/utils/dict/table_dict.txt \
--table_char_dict_path=../ppocr/utils/dict/table_structure_dict.txt \
--det_limit_side_len=736 \
@@ -145,6 +145,7 @@ python3 table/eval_table.py \
--table_char_dict_path=../ppocr/utils/dict/table_structure_dict.txt \
--det_limit_side_len=736 \
--det_limit_type=min \
+ --rec_image_shape=3,32,320 \
--gt_path=path/to/gt.txt
```
diff --git a/ppstructure/table/README_ch.md b/ppstructure/table/README_ch.md
index 1ef126261d9ce832cd1919a1b3991f341add998c..feccb70adfe20fa8c1cd06f33a10ee6fa043e69e 100644
--- a/ppstructure/table/README_ch.md
+++ b/ppstructure/table/README_ch.md
@@ -118,7 +118,7 @@ python3 table/eval_table.py \
--det_model_dir=path/to/det_model_dir \
--rec_model_dir=path/to/rec_model_dir \
--table_model_dir=path/to/table_model_dir \
- --image_dir=../doc/table/1.png \
+ --image_dir=docs/table/table.jpg \
--rec_char_dict_path=../ppocr/utils/dict/table_dict.txt \
--table_char_dict_path=../ppocr/utils/dict/table_structure_dict.txt \
--det_limit_side_len=736 \
@@ -149,6 +149,7 @@ python3 table/eval_table.py \
--table_char_dict_path=../ppocr/utils/dict/table_structure_dict.txt \
--det_limit_side_len=736 \
--det_limit_type=min \
+ --rec_image_shape=3,32,320 \
--gt_path=path/to/gt.txt
```
|  +
+使用中文检测+识别模型提取文本,实例化PaddleOCR类:
+
+```
+from paddleocr import PaddleOCR, draw_ocr
+
+# paddleocr目前支持中英文、英文、法语、德语、韩语、日语等80个语种,可以通过修改lang参数进行切换
+ocr = PaddleOCR(use_angle_cls=False, lang="ch") # need to run only once to download and load model into memory
+```
+
+一行命令启动预测,预测结果包括`检测框`和`文本识别内容`:
+
+```
+img_path = "./test_img/hetong2.jpg"
+result = ocr.ocr(img_path, cls=False)
+for line in result:
+ print(line)
+
+# 可视化结果
+from PIL import Image
+
+image = Image.open(img_path).convert('RGB')
+boxes = [line[0] for line in result]
+txts = [line[1][0] for line in result]
+scores = [line[1][1] for line in result]
+im_show = draw_ocr(image, boxes, txts, scores, font_path='./simfang.ttf')
+im_show = Image.fromarray(im_show)
+im_show.show()
+```
+
+#### 2.1.3 图片预处理
+
+通过上图可视化结果可以看到,印章部分造成的文本遮盖,影响了文本识别结果,因此可以考虑通道提取,去除图片中的红色印章:
+
+```
+import cv2
+import numpy as np
+import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
+
+#读入图像,三通道
+image=cv2.imread("./test_img/hetong2.jpg",cv2.IMREAD_COLOR) #timg.jpeg
+
+#获得三个通道
+Bch,Gch,Rch=cv2.split(image)
+
+#保存三通道图片
+cv2.imwrite('blue_channel.jpg',Bch)
+cv2.imwrite('green_channel.jpg',Gch)
+cv2.imwrite('red_channel.jpg',Rch)
+```
+#### 2.1.4 合同文本信息提取
+
+经过2.1.3的预处理后,合同照片的红色通道被分离,获得了一张相对更干净的图片,此时可以再次使用ppocr模型提取文本内容:
+
+```
+import numpy as np
+import cv2
+
+
+img_path = './red_channel.jpg'
+result = ocr.ocr(img_path, cls=False)
+
+# 可视化结果
+from PIL import Image
+
+image = Image.open(img_path).convert('RGB')
+boxes = [line[0] for line in result]
+txts = [line[1][0] for line in result]
+scores = [line[1][1] for line in result]
+im_show = draw_ocr(image, boxes, txts, scores, font_path='./simfang.ttf')
+im_show = Image.fromarray(im_show)
+vis = np.array(im_show)
+im_show.show()
+```
+
+忽略检测框内容,提取完整的合同文本:
+
+```
+txts = [line[1][0] for line in result]
+all_context = "\n".join(txts)
+print(all_context)
+```
+
+通过以上环节就完成了扫描合同关键信息抽取的第一步:文本内容提取,接下来可以基于识别出的文本内容抽取关键信息
+
+### 2.2 合同关键信息抽取
+
+#### 2.2.1 环境准备
+
+安装PaddleNLP
+
+
+```
+pip install --upgrade pip
+pip install --upgrade paddlenlp
+```
+
+#### 2.2.2 合同关键信息抽取
+
+PaddleNLP 使用 Taskflow 统一管理多场景任务的预测功能,其中`information_extraction` 通过大量的有标签样本进行训练,在通用的场景中一般可以直接使用,只需更换关键字即可。例如在合同信息抽取中,我们重新定义抽取关键字:
+
+甲方、乙方、币种、金额、付款方式
+
+
+将使用OCR提取好的文本作为输入,使用三行命令可以对上文中提取到的合同文本进行关键信息抽取:
+
+```
+from paddlenlp import Taskflow
+schema = ["甲方","乙方","总价"]
+ie = Taskflow('information_extraction', schema=schema)
+ie.set_schema(schema)
+ie(all_context)
+```
+
+可以看到UIE模型可以准确的提取出关键信息,用于后续的信息比对或审核。
+
+## 3.效果优化
+
+### 3.1 文本识别后处理调优
+
+实际图片采集过程中,可能出现部分图片弯曲等问题,导致使用默认参数识别文本时存在漏检,影响关键信息获取。
+
+例如下图:
+
+
+
+使用中文检测+识别模型提取文本,实例化PaddleOCR类:
+
+```
+from paddleocr import PaddleOCR, draw_ocr
+
+# paddleocr目前支持中英文、英文、法语、德语、韩语、日语等80个语种,可以通过修改lang参数进行切换
+ocr = PaddleOCR(use_angle_cls=False, lang="ch") # need to run only once to download and load model into memory
+```
+
+一行命令启动预测,预测结果包括`检测框`和`文本识别内容`:
+
+```
+img_path = "./test_img/hetong2.jpg"
+result = ocr.ocr(img_path, cls=False)
+for line in result:
+ print(line)
+
+# 可视化结果
+from PIL import Image
+
+image = Image.open(img_path).convert('RGB')
+boxes = [line[0] for line in result]
+txts = [line[1][0] for line in result]
+scores = [line[1][1] for line in result]
+im_show = draw_ocr(image, boxes, txts, scores, font_path='./simfang.ttf')
+im_show = Image.fromarray(im_show)
+im_show.show()
+```
+
+#### 2.1.3 图片预处理
+
+通过上图可视化结果可以看到,印章部分造成的文本遮盖,影响了文本识别结果,因此可以考虑通道提取,去除图片中的红色印章:
+
+```
+import cv2
+import numpy as np
+import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
+
+#读入图像,三通道
+image=cv2.imread("./test_img/hetong2.jpg",cv2.IMREAD_COLOR) #timg.jpeg
+
+#获得三个通道
+Bch,Gch,Rch=cv2.split(image)
+
+#保存三通道图片
+cv2.imwrite('blue_channel.jpg',Bch)
+cv2.imwrite('green_channel.jpg',Gch)
+cv2.imwrite('red_channel.jpg',Rch)
+```
+#### 2.1.4 合同文本信息提取
+
+经过2.1.3的预处理后,合同照片的红色通道被分离,获得了一张相对更干净的图片,此时可以再次使用ppocr模型提取文本内容:
+
+```
+import numpy as np
+import cv2
+
+
+img_path = './red_channel.jpg'
+result = ocr.ocr(img_path, cls=False)
+
+# 可视化结果
+from PIL import Image
+
+image = Image.open(img_path).convert('RGB')
+boxes = [line[0] for line in result]
+txts = [line[1][0] for line in result]
+scores = [line[1][1] for line in result]
+im_show = draw_ocr(image, boxes, txts, scores, font_path='./simfang.ttf')
+im_show = Image.fromarray(im_show)
+vis = np.array(im_show)
+im_show.show()
+```
+
+忽略检测框内容,提取完整的合同文本:
+
+```
+txts = [line[1][0] for line in result]
+all_context = "\n".join(txts)
+print(all_context)
+```
+
+通过以上环节就完成了扫描合同关键信息抽取的第一步:文本内容提取,接下来可以基于识别出的文本内容抽取关键信息
+
+### 2.2 合同关键信息抽取
+
+#### 2.2.1 环境准备
+
+安装PaddleNLP
+
+
+```
+pip install --upgrade pip
+pip install --upgrade paddlenlp
+```
+
+#### 2.2.2 合同关键信息抽取
+
+PaddleNLP 使用 Taskflow 统一管理多场景任务的预测功能,其中`information_extraction` 通过大量的有标签样本进行训练,在通用的场景中一般可以直接使用,只需更换关键字即可。例如在合同信息抽取中,我们重新定义抽取关键字:
+
+甲方、乙方、币种、金额、付款方式
+
+
+将使用OCR提取好的文本作为输入,使用三行命令可以对上文中提取到的合同文本进行关键信息抽取:
+
+```
+from paddlenlp import Taskflow
+schema = ["甲方","乙方","总价"]
+ie = Taskflow('information_extraction', schema=schema)
+ie.set_schema(schema)
+ie(all_context)
+```
+
+可以看到UIE模型可以准确的提取出关键信息,用于后续的信息比对或审核。
+
+## 3.效果优化
+
+### 3.1 文本识别后处理调优
+
+实际图片采集过程中,可能出现部分图片弯曲等问题,导致使用默认参数识别文本时存在漏检,影响关键信息获取。
+
+例如下图:
+
+ +
+
+直接进行预测:
+
+```
+img_path = "./test_img/hetong3.jpg"
+# 预测结果
+result = ocr.ocr(img_path, cls=False)
+# 可视化结果
+from PIL import Image
+
+image = Image.open(img_path).convert('RGB')
+boxes = [line[0] for line in result]
+txts = [line[1][0] for line in result]
+scores = [line[1][1] for line in result]
+im_show = draw_ocr(image, boxes, txts, scores, font_path='./simfang.ttf')
+im_show = Image.fromarray(im_show)
+im_show.show()
+```
+
+可视化结果可以看到,弯曲图片存在漏检,一般来说可以通过调整后处理参数解决,无需重新训练模型。漏检问题往往是因为检测模型获得的分割图太小,生成框的得分过低被过滤掉了,通常有两种方式调整参数:
+- 开启`use_dilatiion=True` 膨胀分割区域
+- 调小`det_db_box_thresh`阈值
+
+```
+# 重新实例化 PaddleOCR
+ocr = PaddleOCR(use_angle_cls=False, lang="ch", det_db_box_thresh=0.3, use_dilation=True)
+
+# 预测并可视化
+img_path = "./test_img/hetong3.jpg"
+# 预测结果
+result = ocr.ocr(img_path, cls=False)
+# 可视化结果
+image = Image.open(img_path).convert('RGB')
+boxes = [line[0] for line in result]
+txts = [line[1][0] for line in result]
+scores = [line[1][1] for line in result]
+im_show = draw_ocr(image, boxes, txts, scores, font_path='./simfang.ttf')
+im_show = Image.fromarray(im_show)
+im_show.show()
+```
+
+可以看到漏检问题被很好的解决,提取完整的文本内容:
+
+```
+txts = [line[1][0] for line in result]
+context = "\n".join(txts)
+print(context)
+```
+
+### 3.2 关键信息提取调优
+
+UIE通过大量有标签样本进行训练,得到了一个开箱即用的高精模型。 然而针对不同场景,可能会出现部分实体无法被抽取的情况。通常来说有以下几个方法进行效果调优:
+
+
+- 修改 schema
+- 添加正则方法
+- 标注小样本微调模型
+
+**修改schema**
+
+Prompt和原文描述越像,抽取效果越好,例如
+```
+三:合同价格:总价为人民币大写:参拾玖万捌仟伍佰
+元,小写:398500.00元。总价中包括站房工程建设、安装
+及相关避雷、消防、接地、电力、材料费、检验费、安全、
+验收等所需费用及其他相关费用和税金。
+```
+schema = ["总金额"] 时无法准确抽取,与原文描述差异较大。 修改 schema = ["总价"] 再次尝试:
+
+```
+from paddlenlp import Taskflow
+# schema = ["总金额"]
+schema = ["总价"]
+ie = Taskflow('information_extraction', schema=schema)
+ie.set_schema(schema)
+ie(all_context)
+```
+
+
+**模型微调**
+
+UIE的建模方式主要是通过 `Prompt` 方式来建模, `Prompt` 在小样本上进行微调效果非常有效。详细的数据标注+模型微调步骤可以参考项目:
+
+[PaddleNLP信息抽取技术重磅升级!](https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/projectdetail/3914778?channelType=0&channel=0)
+
+[工单信息抽取](https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/projectdetail/3914778?contributionType=1)
+
+[快递单信息抽取](https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/projectdetail/4038499?contributionType=1)
+
+
+## 总结
+
+扫描合同的关键信息提取可以使用 PaddleOCR + PaddleNLP 组合实现,两个工具均有以下优势:
+
+* 使用简单:whl包一键安装,3行命令调用
+* 效果领先:优秀的模型效果可覆盖几乎全部的应用场景
+* 调优成本低:OCR模型可通过后处理参数的调整适配略有偏差的扫描文本, UIE模型可以通过极少的标注样本微调,成本很低。
+
+## 作业
+
+尝试自己解析出 `test_img/homework.png` 扫描合同中的 [甲方、乙方] 关键词:
+
+
+
+
+
+
+直接进行预测:
+
+```
+img_path = "./test_img/hetong3.jpg"
+# 预测结果
+result = ocr.ocr(img_path, cls=False)
+# 可视化结果
+from PIL import Image
+
+image = Image.open(img_path).convert('RGB')
+boxes = [line[0] for line in result]
+txts = [line[1][0] for line in result]
+scores = [line[1][1] for line in result]
+im_show = draw_ocr(image, boxes, txts, scores, font_path='./simfang.ttf')
+im_show = Image.fromarray(im_show)
+im_show.show()
+```
+
+可视化结果可以看到,弯曲图片存在漏检,一般来说可以通过调整后处理参数解决,无需重新训练模型。漏检问题往往是因为检测模型获得的分割图太小,生成框的得分过低被过滤掉了,通常有两种方式调整参数:
+- 开启`use_dilatiion=True` 膨胀分割区域
+- 调小`det_db_box_thresh`阈值
+
+```
+# 重新实例化 PaddleOCR
+ocr = PaddleOCR(use_angle_cls=False, lang="ch", det_db_box_thresh=0.3, use_dilation=True)
+
+# 预测并可视化
+img_path = "./test_img/hetong3.jpg"
+# 预测结果
+result = ocr.ocr(img_path, cls=False)
+# 可视化结果
+image = Image.open(img_path).convert('RGB')
+boxes = [line[0] for line in result]
+txts = [line[1][0] for line in result]
+scores = [line[1][1] for line in result]
+im_show = draw_ocr(image, boxes, txts, scores, font_path='./simfang.ttf')
+im_show = Image.fromarray(im_show)
+im_show.show()
+```
+
+可以看到漏检问题被很好的解决,提取完整的文本内容:
+
+```
+txts = [line[1][0] for line in result]
+context = "\n".join(txts)
+print(context)
+```
+
+### 3.2 关键信息提取调优
+
+UIE通过大量有标签样本进行训练,得到了一个开箱即用的高精模型。 然而针对不同场景,可能会出现部分实体无法被抽取的情况。通常来说有以下几个方法进行效果调优:
+
+
+- 修改 schema
+- 添加正则方法
+- 标注小样本微调模型
+
+**修改schema**
+
+Prompt和原文描述越像,抽取效果越好,例如
+```
+三:合同价格:总价为人民币大写:参拾玖万捌仟伍佰
+元,小写:398500.00元。总价中包括站房工程建设、安装
+及相关避雷、消防、接地、电力、材料费、检验费、安全、
+验收等所需费用及其他相关费用和税金。
+```
+schema = ["总金额"] 时无法准确抽取,与原文描述差异较大。 修改 schema = ["总价"] 再次尝试:
+
+```
+from paddlenlp import Taskflow
+# schema = ["总金额"]
+schema = ["总价"]
+ie = Taskflow('information_extraction', schema=schema)
+ie.set_schema(schema)
+ie(all_context)
+```
+
+
+**模型微调**
+
+UIE的建模方式主要是通过 `Prompt` 方式来建模, `Prompt` 在小样本上进行微调效果非常有效。详细的数据标注+模型微调步骤可以参考项目:
+
+[PaddleNLP信息抽取技术重磅升级!](https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/projectdetail/3914778?channelType=0&channel=0)
+
+[工单信息抽取](https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/projectdetail/3914778?contributionType=1)
+
+[快递单信息抽取](https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/projectdetail/4038499?contributionType=1)
+
+
+## 总结
+
+扫描合同的关键信息提取可以使用 PaddleOCR + PaddleNLP 组合实现,两个工具均有以下优势:
+
+* 使用简单:whl包一键安装,3行命令调用
+* 效果领先:优秀的模型效果可覆盖几乎全部的应用场景
+* 调优成本低:OCR模型可通过后处理参数的调整适配略有偏差的扫描文本, UIE模型可以通过极少的标注样本微调,成本很低。
+
+## 作业
+
+尝试自己解析出 `test_img/homework.png` 扫描合同中的 [甲方、乙方] 关键词:
+
+
+
+ +
+
+
+更多场景下的垂类模型获取,请扫下图二维码填写问卷,加入PaddleOCR官方交流群获取模型下载链接、《动手学OCR》电子书等全套OCR学习资料🎁
+
+
+
+
+
+更多场景下的垂类模型获取,请扫下图二维码填写问卷,加入PaddleOCR官方交流群获取模型下载链接、《动手学OCR》电子书等全套OCR学习资料🎁
+
+ diff --git a/ppstructure/table/README.md b/ppstructure/table/README.md
index 08635516ba8301e6f98f175e5eba8c0a97b1708e..1d082f3878c56e42d175d13c75e1fe17916e7781 100644
--- a/ppstructure/table/README.md
+++ b/ppstructure/table/README.md
@@ -114,7 +114,7 @@ python3 table/eval_table.py \
--det_model_dir=path/to/det_model_dir \
--rec_model_dir=path/to/rec_model_dir \
--table_model_dir=path/to/table_model_dir \
- --image_dir=../doc/table/1.png \
+ --image_dir=docs/table/table.jpg \
--rec_char_dict_path=../ppocr/utils/dict/table_dict.txt \
--table_char_dict_path=../ppocr/utils/dict/table_structure_dict.txt \
--det_limit_side_len=736 \
@@ -145,6 +145,7 @@ python3 table/eval_table.py \
--table_char_dict_path=../ppocr/utils/dict/table_structure_dict.txt \
--det_limit_side_len=736 \
--det_limit_type=min \
+ --rec_image_shape=3,32,320 \
--gt_path=path/to/gt.txt
```
diff --git a/ppstructure/table/README_ch.md b/ppstructure/table/README_ch.md
index 1ef126261d9ce832cd1919a1b3991f341add998c..feccb70adfe20fa8c1cd06f33a10ee6fa043e69e 100644
--- a/ppstructure/table/README_ch.md
+++ b/ppstructure/table/README_ch.md
@@ -118,7 +118,7 @@ python3 table/eval_table.py \
--det_model_dir=path/to/det_model_dir \
--rec_model_dir=path/to/rec_model_dir \
--table_model_dir=path/to/table_model_dir \
- --image_dir=../doc/table/1.png \
+ --image_dir=docs/table/table.jpg \
--rec_char_dict_path=../ppocr/utils/dict/table_dict.txt \
--table_char_dict_path=../ppocr/utils/dict/table_structure_dict.txt \
--det_limit_side_len=736 \
@@ -149,6 +149,7 @@ python3 table/eval_table.py \
--table_char_dict_path=../ppocr/utils/dict/table_structure_dict.txt \
--det_limit_side_len=736 \
--det_limit_type=min \
+ --rec_image_shape=3,32,320 \
--gt_path=path/to/gt.txt
```
diff --git a/ppstructure/table/README.md b/ppstructure/table/README.md
index 08635516ba8301e6f98f175e5eba8c0a97b1708e..1d082f3878c56e42d175d13c75e1fe17916e7781 100644
--- a/ppstructure/table/README.md
+++ b/ppstructure/table/README.md
@@ -114,7 +114,7 @@ python3 table/eval_table.py \
--det_model_dir=path/to/det_model_dir \
--rec_model_dir=path/to/rec_model_dir \
--table_model_dir=path/to/table_model_dir \
- --image_dir=../doc/table/1.png \
+ --image_dir=docs/table/table.jpg \
--rec_char_dict_path=../ppocr/utils/dict/table_dict.txt \
--table_char_dict_path=../ppocr/utils/dict/table_structure_dict.txt \
--det_limit_side_len=736 \
@@ -145,6 +145,7 @@ python3 table/eval_table.py \
--table_char_dict_path=../ppocr/utils/dict/table_structure_dict.txt \
--det_limit_side_len=736 \
--det_limit_type=min \
+ --rec_image_shape=3,32,320 \
--gt_path=path/to/gt.txt
```
diff --git a/ppstructure/table/README_ch.md b/ppstructure/table/README_ch.md
index 1ef126261d9ce832cd1919a1b3991f341add998c..feccb70adfe20fa8c1cd06f33a10ee6fa043e69e 100644
--- a/ppstructure/table/README_ch.md
+++ b/ppstructure/table/README_ch.md
@@ -118,7 +118,7 @@ python3 table/eval_table.py \
--det_model_dir=path/to/det_model_dir \
--rec_model_dir=path/to/rec_model_dir \
--table_model_dir=path/to/table_model_dir \
- --image_dir=../doc/table/1.png \
+ --image_dir=docs/table/table.jpg \
--rec_char_dict_path=../ppocr/utils/dict/table_dict.txt \
--table_char_dict_path=../ppocr/utils/dict/table_structure_dict.txt \
--det_limit_side_len=736 \
@@ -149,6 +149,7 @@ python3 table/eval_table.py \
--table_char_dict_path=../ppocr/utils/dict/table_structure_dict.txt \
--det_limit_side_len=736 \
--det_limit_type=min \
+ --rec_image_shape=3,32,320 \
--gt_path=path/to/gt.txt
```