# ace2p
|Module Name|ace2p|
| :--- | :---: |
|Category|image segmentation|
|Network|ACE2P|
|Dataset|LIP|
|Fine-tuning supported or not|No|
|Module Size|259MB|
|Data indicators|-|
|Latest update date |2021-02-26|
## I. Basic Information
- ### Application Effect Display
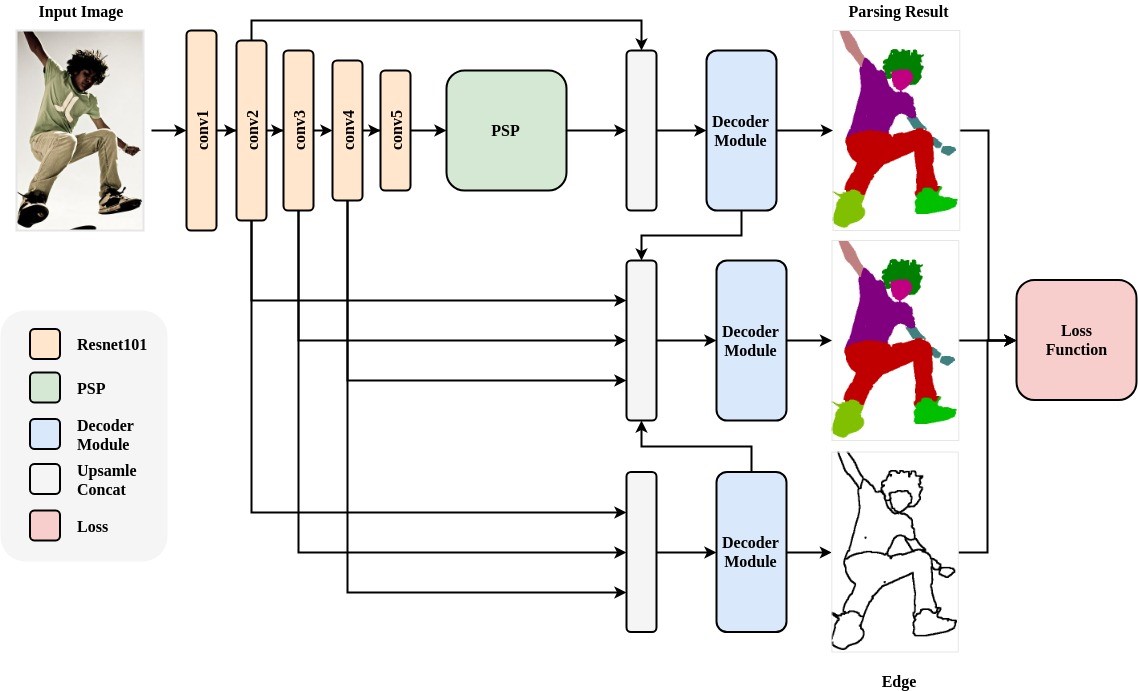
- Network architecture:
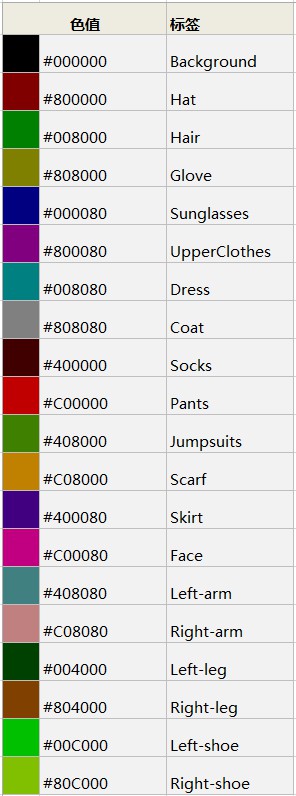
- Color palette
- Sample results:


- ### Module Introduction
- Human Parsing is a fine-grained semantic segmentation task that aims to identify the components (for example, body parts and clothing) of a human image at the pixel level. The PaddleHub Module uses ResNet101 as the backbone network, and accepts input image sizes of 473x473x3.
## II. Installation
- ### 1、Environmental Dependence
- paddlepaddle >= 2.0.0
- paddlehub >= 2.0.0
- ### 2、Installation
- ```shell
$ hub install ace2p
```
- In case of any problems during installation, please refer to:[Windows_Quickstart](../../../../docs/docs_ch/get_start/windows_quickstart.md)
| [Linux_Quickstart](../../../../docs/docs_ch/get_start/linux_quickstart.md) | [Mac_Quickstart](../../../../docs/docs_ch/get_start/mac_quickstart.md)
## III. Module API Prediction
- ### 1、Command line Prediction
```shell
$ hub run ace2p --input_path "/PATH/TO/IMAGE"
```
- ### 2、Prediction Code Example
```python
import paddlehub as hub
import cv2
human_parser = hub.Module(name="ace2p")
result = human_parser.segmentation(images=[cv2.imread('/PATH/TO/IMAGE')])
```
- ### 3、API
```python
def segmentation(images=None,
paths=None,
batch_size=1,
use_gpu=False,
output_dir='ace2p_output',
visualization=False):
```
- Prediction API, used for human parsing.
- **Parameter**
* images (list\[numpy.ndarray\]): image data, ndarray.shape is in the format [H, W, C], BGR;
* paths (list\[str\]): image path;
* batch\_size (int): batch size;
* use\_gpu (bool): use GPU or not; **set the CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES environment variable first if you are using GPU**
* output\_dir (str): save path of output, default is 'ace2p_output';
* visualization (bool): Whether to save the recognition results as picture files.
- **Return**
* res (list\[dict\]): The list of recognition results, where each element is dict and each field is:
* save\_path (str, optional): Save path of the result;
* data (numpy.ndarray): The result of portrait segmentation.
```python
def save_inference_model(dirname,
model_filename=None,
params_filename=None,
combined=True)
```
- Save the model to the specified path.
- **Parameters**
* dirname: Save path.
* model\_filename: model file name,defalt is \_\_model\_\_
* params\_filename: parameter file name,defalt is \_\_params\_\_(Only takes effect when `combined` is True)
* combined: Whether to save the parameters to a unified file.
## IV. Server Deployment
- PaddleHub Serving can deploy an online service of human parsing
- ### Step 1: Start PaddleHub Serving
- Run the startup command:
```shell
$ hub serving start -m ace2p
```
- The servitization API is now deployed and the default port number is 8866.
- **NOTE:** If GPU is used for prediction, set CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES environment variable before the service, otherwise it need not be set.
- ### Step 2: Send a predictive request
- With a configured server, use the following lines of code to send the prediction request and obtain the result
```python
import requests
import json
import cv2
import base64
import numpy as np
def cv2_to_base64(image):
data = cv2.imencode('.jpg', image)[1]
return base64.b64encode(data.tostring()).decode('utf8')
def base64_to_cv2(b64str):
data = base64.b64decode(b64str.encode('utf8'))
data = np.fromstring(data, np.uint8)
data = cv2.imdecode(data, cv2.IMREAD_COLOR)
return data
# Send an HTTP request
data = {'images':[cv2_to_base64(cv2.imread("/PATH/TO/IMAGE"))]}
headers = {"Content-type": "application/json"}
url = "http://127.0.0.1:8866/predict/ace2p"
r = requests.post(url=url, headers=headers, data=json.dumps(data))
# print prediction results
print(base64_to_cv2(r.json()["results"][0]['data']))
```
## 五、更新历史
- 1.0.0
First release
* 1.1.0
Adapt to paddlehub2.0




