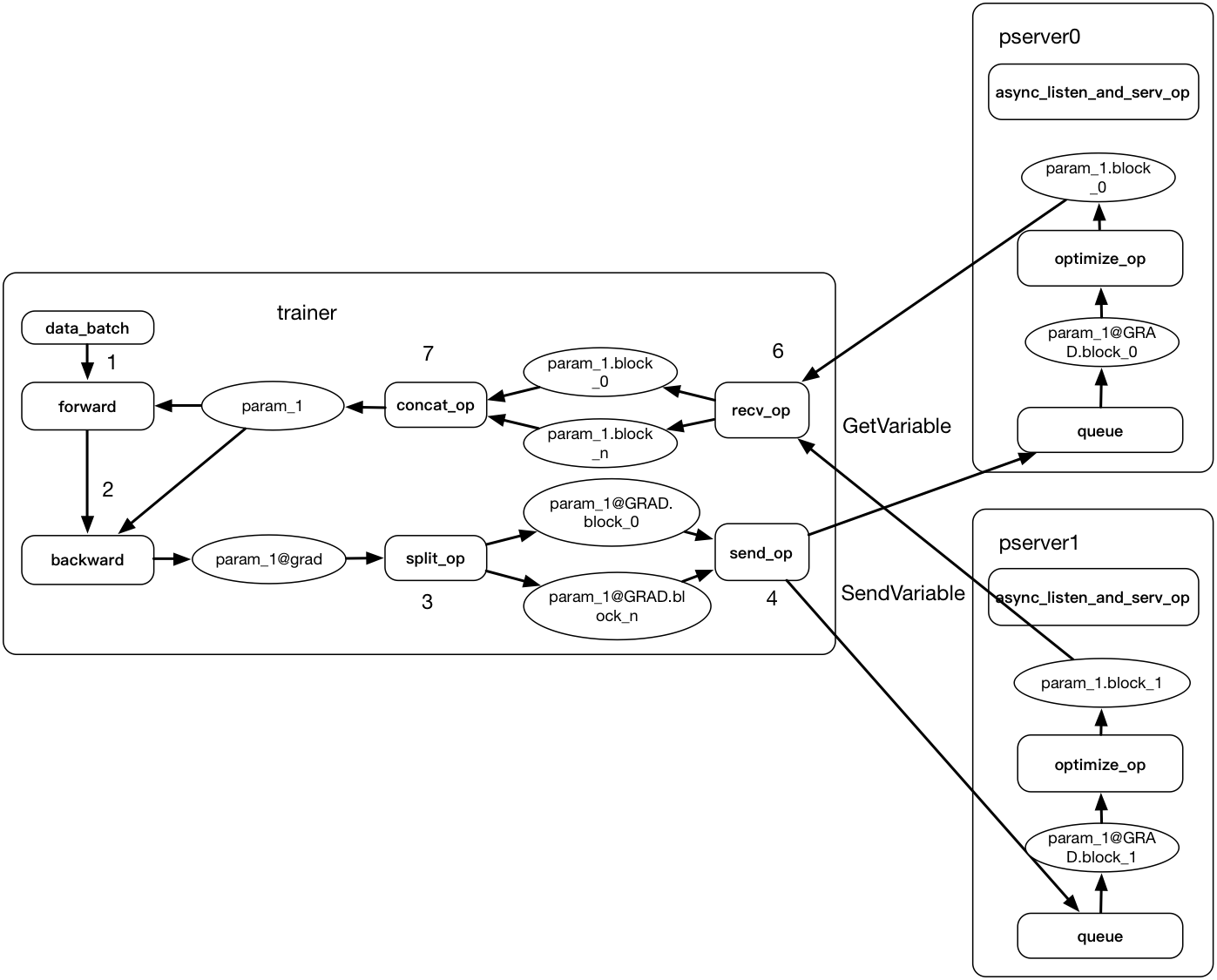
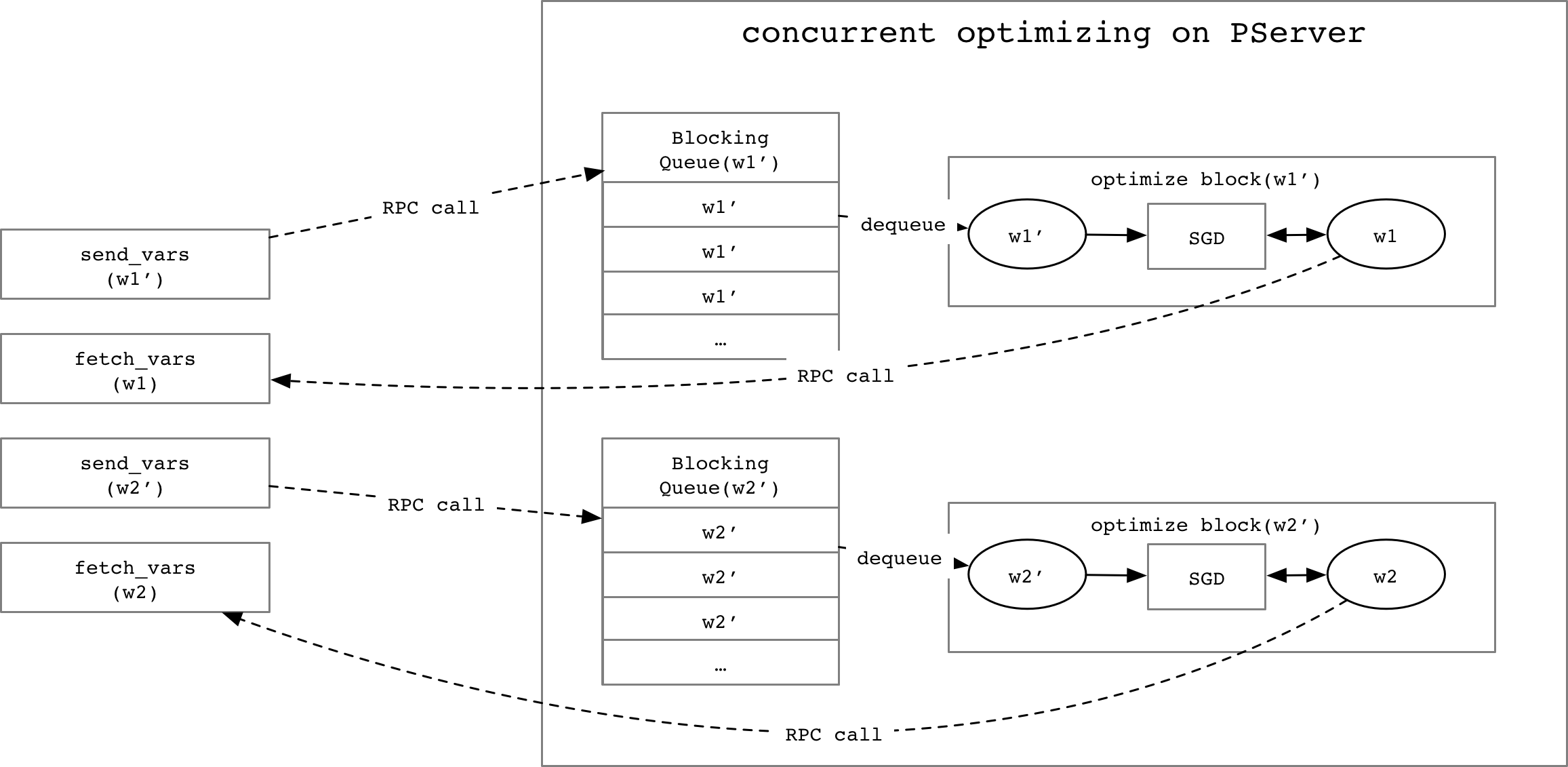
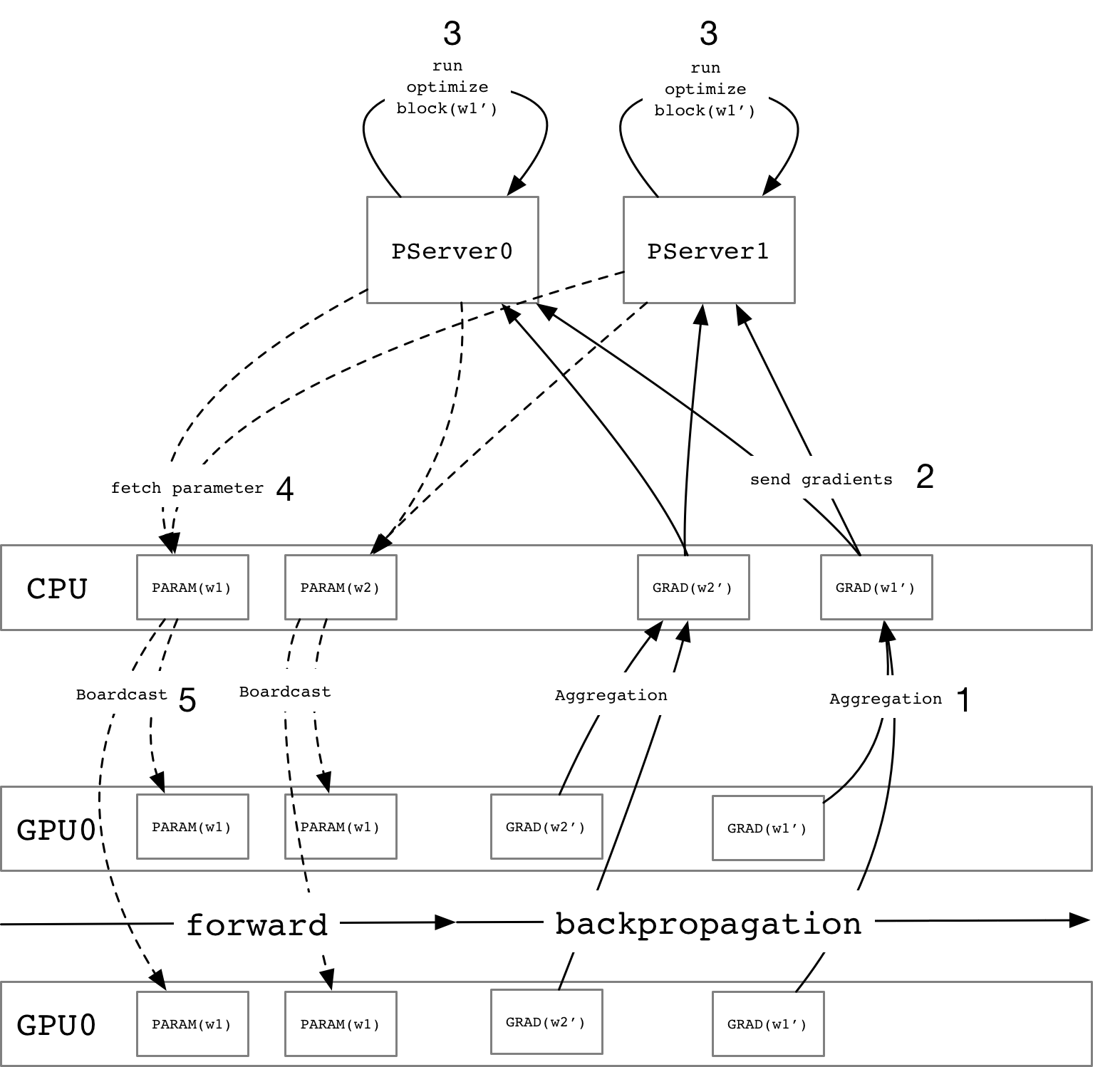
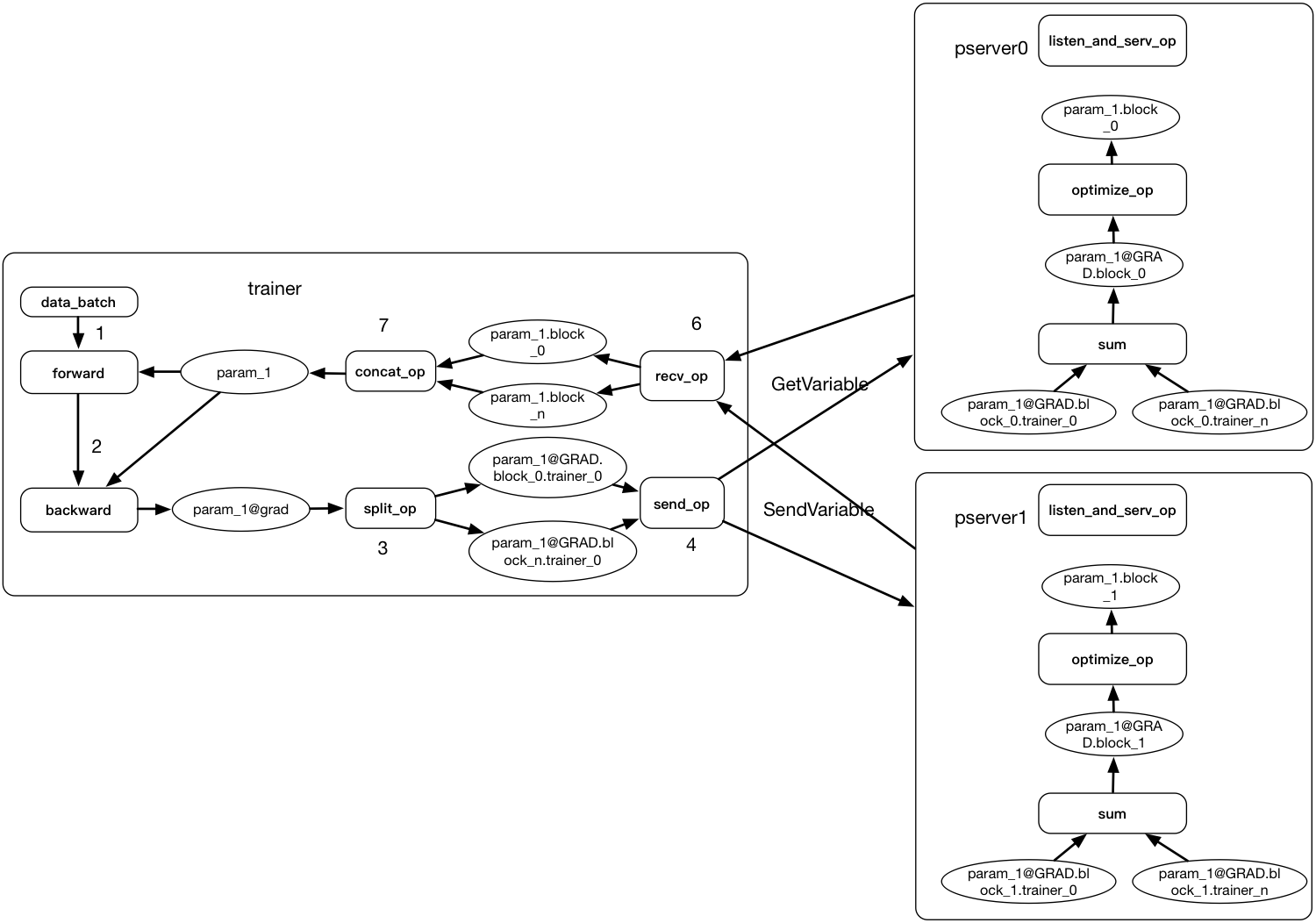
Merge branch 'develop' of https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle into add_parallel_executor_tests
Showing
180.2 KB
文件已添加
166.0 KB
文件已添加
179.6 KB
184.3 KB
doc/mobile/CMakeLists.txt
0 → 100644
doc/mobile/index_cn.rst
0 → 100644
doc/mobile/index_en.rst
0 → 100644
tools/aws_benchmarking/README.md
0 → 100644
39.8 KB
此差异已折叠。